Control and Coordination
1/175
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
176 Terms
function of the nervous system
oversees communication among the organ systems
sensory input
recieves stimuli via sensory receptors
integration
processes the input stimuli, decides what to do
motor output
activates the effector organs to cause a response
neurons (nerve cells)
excitable cells that respond to stimluli by conducting impulses to transmit signals
neuroglia (glial cells)
supportive cells that provide nutrition, insulation, and help with signal transmission
astrocyte
subtype of glial cells
oligodenrocyte
creates the myelin sheath that insulates axonsregul
microglia
regulate brain development, maintenance, and repair
schwann cells
glial cells that form the myelin sheath on axons outside the brain
they engulf a segment of the axon
soma
contains nucelus and most organelles
processes
extensions from the cell body
dendrites
main receptor of signals (input region)
axon
generates and transmits nerve impulses
conducting region
also known as nerve fiber
ganglion
collection of nerve cell bodies located in the body
nerves
bundles of axons that extend from the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body
axon terminal
the end of the axon that releases neurotransmitters at a synapse when a nerve impusle is recieved
the secretory region
myelin sheath
covers long axons (nerve fibers) to protect and electrically insulte them to increase the speed of nerve impulse transmission
nodes of ranvier
unmyelinated gaps in the myelin sheath that aid in increasing the velocity of a nerve signal transduction
multipolar
meaning >3 processes
bipolar
2 processes, 1 axon and 1 dendrite
unipolar
1 process dividing from the cell body like a T
senosry neurons (afferent)
transmit info from sensory receptors (CNS)
most are unipolar
motor neurons (efferent neurons)
transmit info from the CNS to the rest of the body
most are multipolar to send impulses to many different places
interneurons
housed in the CNS and transport info between the sensory and motor neurons
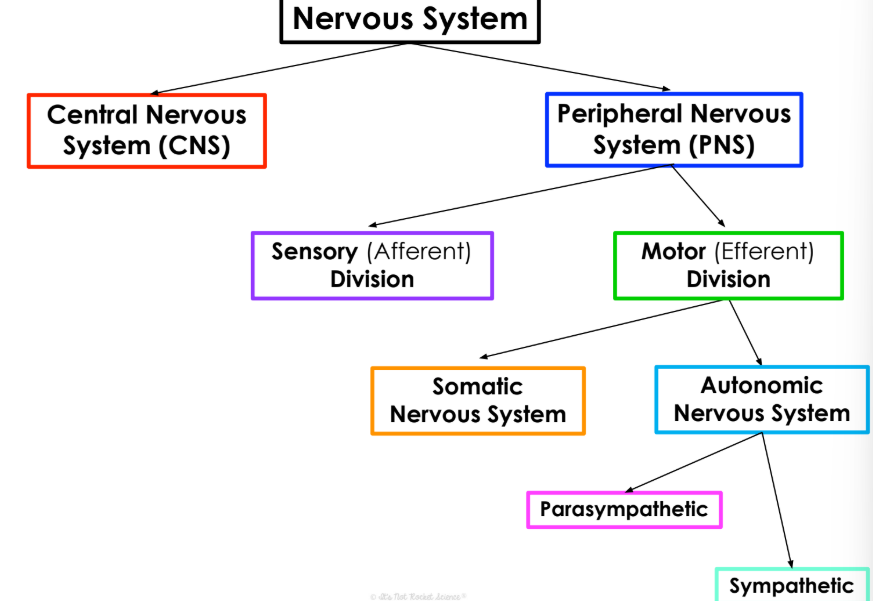
organization of the nervous system
nervous sytem → PNS and CNS
PNS → sensory (afferent division) and motor (efferent division)
motor division → somatic and autonomic
autonomic → parasympathetic and sympathetic
central nervous system
brain and spinal cord
integration and control center
peripheral nervous sytem
spinal and cranial nerves
communication system between the cns and the rest of the body
ventricles
hollow fluid filled cavities within the brain that contain the chroid plexus
choroid plexus
makes cerebrospinal fluid
meminges
layer of tissue that protects the brain
cerebrospinal fluid
cushions the brain from injury
cerebrum
largest part of the brain
made of left and right hemispheres
dividied into 4 lobes
functions in learning, speech, emotion, reasoning, vision, hearing, and fine movements
cerebral cortex is the surface and is arragned in folds to increase surface area
cerebellum
maintains posture and blance
coordinates patterns for smooth and agile subconcious movements
brainstem
base of the cerebrumand anterior to the cerebellum
includes the medulla obolongata, midbrain, and pons
relays info between rest of brain and the spinal chord
coordinates functions like respiration, circulation, body temperature, sleep, digestion, and swallowing
pareital lobe
helps integrate sensory input and processes language
frontal lobe
needed for memory, motivation, and porblem solving
temporal lobe
essential to language and speech
behind the ears
occipital lobe
visual processing center
limbic system
emotional center of the brain, controls things like moods and instincts
Na/K pump
moves 3 Na out of cell and 2 K into cell to maintain resting membrane potential of - 70 mv
voltage gated channels
open and close in response to changes in membrane potential
ligand gated channels
only open when a specific chemical lieka neurotransmitter binds to channel
mechanically gated channels
open if the membrane is stretched or physically deformed
threshold
the cell membrane reaches a specific threshold activating the action potential
depolarization
the sodium protein channel opens up and the sodium ions rush into the cell returning to 0 mv
overshoot
membrane potential becomes more positive and the sodium ion channel becomes inactivated
repolarization
the potassium channel opens up and potassium ions leave the cell
hyperpolorization
the potassiu chanel causes teh cell to be hyperpolarized and potassium ions close
excitatory neurotransmitters
open ion channels in the cell membrane and depolarize the postsynaptic neuron, causing an action potential to be passed along
inhibitory neurotransmitters
can hyperpolarize the postsynaptic neuron so it can’t send on teh action potential and thus the message isn’t passed on
sensory (afferent) division
sensory nerve fibers
recieves sensory stimuli to send back to CNS/brain
motor division
sends out information from teh brain to effector organs like muscles and glands
somatic nervous system
somatic motor nerve fibers
conduct impulses from cns to skeletal muscles
controls voluntary movements
autonomic nervous system
visceral motor nerve fibers
conduct impulses from CNS to smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and glands
controls involunatry movements
acetycholine
neurotransmitter released to muscles to stimulate contractions
released in parasympathetic
norepinehrine
released in symphathetic nervous system
parasympathetic
craniosacral nerves (start at base of brain or just above tailbone)
ganglia are far from spinal cord or right next to/inside effector organs
calms you down, does the opposite of everything the sympathetic does
sympathetic
thoracolumbar nerves (start between thoracic and lumbar vertebrae)
ganglia are in the spinal cord and send signals far distances
excites you/amps you up
mechanoreceptors
mechanical force like vibration, pressure, stretch, and touch
thermoreceptors
change in temperature
photoreceptors
light
chemoreceptors
chemicals
nociceptors
pain
reflex
automatic reaction to stimuli
innate (intrinsic) reflex
a rapid, predictable motor resposne to a startling stimulus
learned (acquired) reflex
a response resulting from practice repetition or experience
5 components of a reflex arc
receptor
sensory neuron
integration center
motor neuron
effector
olfactory nerve
sensory
sends scent info from nose to brain
optic nerve
sensory
sends visual info from eyes to brain
oculomotor nerve
motor
controls the movement of 4 out of the 6 eye muscles as well as pupils reaction to light
trochlear nerve
motor
controls movement for an eye muscle
trigeminal nerve
both
largest nerve that has 3 main branches that innervate the face and jaw muscles
abducens nerve
motor
controls movement for an eye muscle
facial nerve
both
operates muscles for most facial expressions, taste buds, salivating
sends info from outer ear to brain
vestibulocochlear nerve
sensory
sends auditory info from cochlea to brain, key for hearing and balance
glossopharyngeal nerve
both
sensation, tase, swallowing
sends sensory info from sinuses to brain
vagus nerve
both
longest nerve
controls heart and digestive tract
accesory nerve
motor
controls muscles in the neck
hypoglossal nerve
controls most muscles in tongue so we can swallow and talk
sensing
sensory cells that translate stimuli into action potentials that our nervous system can integrate
general sensory receptors
modified nerve ending
touch
special senses
vision, smell, taste, hearing, and equilibrium
light
electromagnetic waves
photoreceptors
convert light energy into electircal energy that travel to the brain
eyebrows
keep sweat and sunlight out of the eyes
eyelids and eyelashes
trigger reflexive blinking to keep eyes moist
lacrimal apparatus
consists of the lacrimal gland that produces and secretes tears and the ducts that drain the secretions
extrinsic eye muscles
control the eye movements
superior oblique
depresses and turns eye laterally
superior rectus
elevates and turns eye medially
lateral rectus
lateral movement
medial rectus
medial movement
inferior rectus
depresses and turns it medially
inferior oblique
elevates and turns it laterally
fibrous layer
outermost layer of the eye
sclera
anchoring site for extrinsic eye muscles
cornea
window that lets light into the eye
vascular layer
middle layer of eye
choroid
supplies all the layers with blood