Chemistry-Redox
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
titration
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Acidified potassium permanganate (KMnO4)
Oxidising agent
Acidified potassium dichromate (k2cr2o7)
Oxidising agent
Acidified hydrogen peroxide (h2o2)
oxidising agent
Oxalic acid dihydrate (H2C2O4.2H2o)
reducing agent
Ammonium iron (II) sulfate hexahydrate
(NH4)2SO4.FeSO4.6H2o
reducing agent
Hydrogen peroxide h2o2
reducing agent
Sodium oxalate Na2C2O4
reducing agent
Iodine
oxidising agent
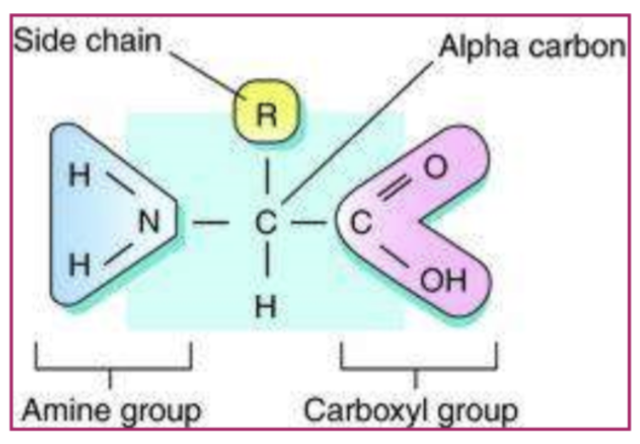
a amino acids
amine
carboxylic acid functional group (carboxyl)
Attached to the same carbon (alpha carbon)
Peptide bond
A peptide bond is the amide linkage formed between the carbonyl carbon of one amino acid and the nitrogen of another amino group
Peptide link
an amide/peptide link forms between COOH group of one molecule and NH2 group of another molecule
Primary structure of protein
Unique sequence of a-amino acids that make up a polypeptide chain
held together by covalent bonds (peptide bonds)
The sequence determines the proteins 3D shape which leads to the protein function
Peptide bonds are created by enzyme catalysed condensation reactions and broken down by enzyme catalysed hydrolysis reactions
Secondary structure of protein
The result from hydrogen bonding between the polar -NH group (amide) of a peptide link and the polar -C=O group (carbonyl) in another peptide link at regular intervals
alpha helix structure
the hydrogen bond between the carbonyl O group of one
beta pleated sheets
tertiary structure of protein
determines the 3D shape of the protein influenced by the predominant forces of the side