L94a: GDV in dogs
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
what is gastric dilation volvulus?
life-threatening disorder in which abnormal twisting of the stomach on its mesenteric axis, with subsequent gastric gas accumulation and distention
what is GDV commonly referred to as?
bloat or gastric torsion
what are the characteristics of simple gastric dilation in dogs (simple bloat)?
distentsion of the stomach alone
can resolve on its own
what is an intrinsic factor?
an internal characteristic of an animal (anatomy or physiology) that increases its likelihood of a disease or condition developing
extrinsic factor
an external or environmental factor that increase the likelihood of a disease or condition developing
what intrinsic factors predispose dogs to GDV?
large deep chested dogs
dogs with a deep and narrow thoracic cavity
genetics
middle to older aged dogs
what breeds are predisposed to GDV?
irish setters
standard poodles
german sheperds
great danes
doberman pinschers
what extrinsic factors predispose dogs to GDV?
eating one large meal rather than small meals
rapidly eating food
stress or anxiety
vigorous exercise immediately after eating
list the overview of GDV.
gas accumulation in the stomach
stomach rotation
obstruction of blood flow
splenic displacement and vascular damage
gastric wall ischemia and necrosis
systemic circulatory collapse
multi-organ failure and acidosis
re-perfusion injury and sepsis risk
what local effects can occur from GDV?
displacement of duodenum and pylorus
avulsion of gastrosplenic ligament
splenic infarction
ischemia in the gastric wall
what organ systems are affected by GDV?
cardiovascular
respiratory
gastrointestinal
lymphatic system
coagulation dysfunction
what leads to a hypovolemic state in the heart due to GDV?
significant decrease in venous return to the heart
what does hypovolemic shock from GDV result in?
organ hypoxia, tissue damage, and death from decreased cardiac output to organs
what leads to cardiac arrhythmias due to GDV?
decreased myocardial perfusion and increased inflammatory mediators
how is the respiratory system affected from GDV?
gastric dilatation and increased intra-abdominal pressure severely reduces the total thoracic volume leading to decreased lung volume and poor ventilation
what is the most commonly affected area by gastric necrosis from GDV?
fundus
what part of the lymphatic system is affected by GDV?
spleen
what are the intestinal effects from GDV?
loss of movement of intestinal contents
causes dysbiosis
sequestration of fluids and protein loss
what coagulation dysfunction can occur from GDV?
disseminated intravascular coagulation
what effects can happen when cardiac output decreases from GDV?
reduced perfusion to tissues
acidosis and metabolic imbalances
hyperlactemia
oliguria to anuria
what happens when the stomach is surgically repositioned after GDV?
reactive oxygen species are released and inflammation occurs, potentially leading to further tissue injury
what re-perfusion injuries are caused by reactive oxygen species?
endothelial damage of blood vessels
disseminated intravascular coagulation
systemic inflammatory response syndrome
what are the early signs of GDV?
restlessness or pacing
panting
retching/vomiting (non-productive)
hypersalivation
distension of abdomen
abdominal pain
what are the progressive signs of GDV?
tachycardia
rapid shallow breathing
weak pulse
dark red mucous membranes
severe abdominal distension
depression
cardiac arrhythmias
what are the severe/late signs of GDV?
hypothermia
coma
collapse
evidence of metabolic disturbances
white or blue mucous membranes
why is GDV considered an emergency?
stomach can perforate and spleen can die
compromised blood flow can risk death of other organs
poor ventilation
what is used to help diagnose GDV?
signalment and physical exams
blood analysis
radiography (not often necessary)
ECG
when is a radiography performed in a patient with GDV?
only when patient is stable
what is a radiograph used to determine in patients with GDV?
location of pylorus to determine gastric dilation from gastric voluvulus
what does volvulus result in?
displacement of the pylorus dorsally to the left
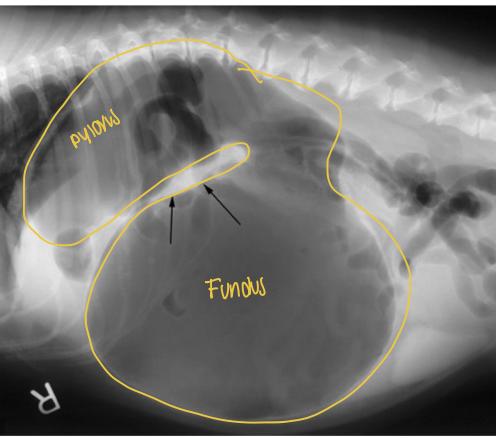
what does the radiograph show?
gastric volvulus displacing pylorus to dorsal left
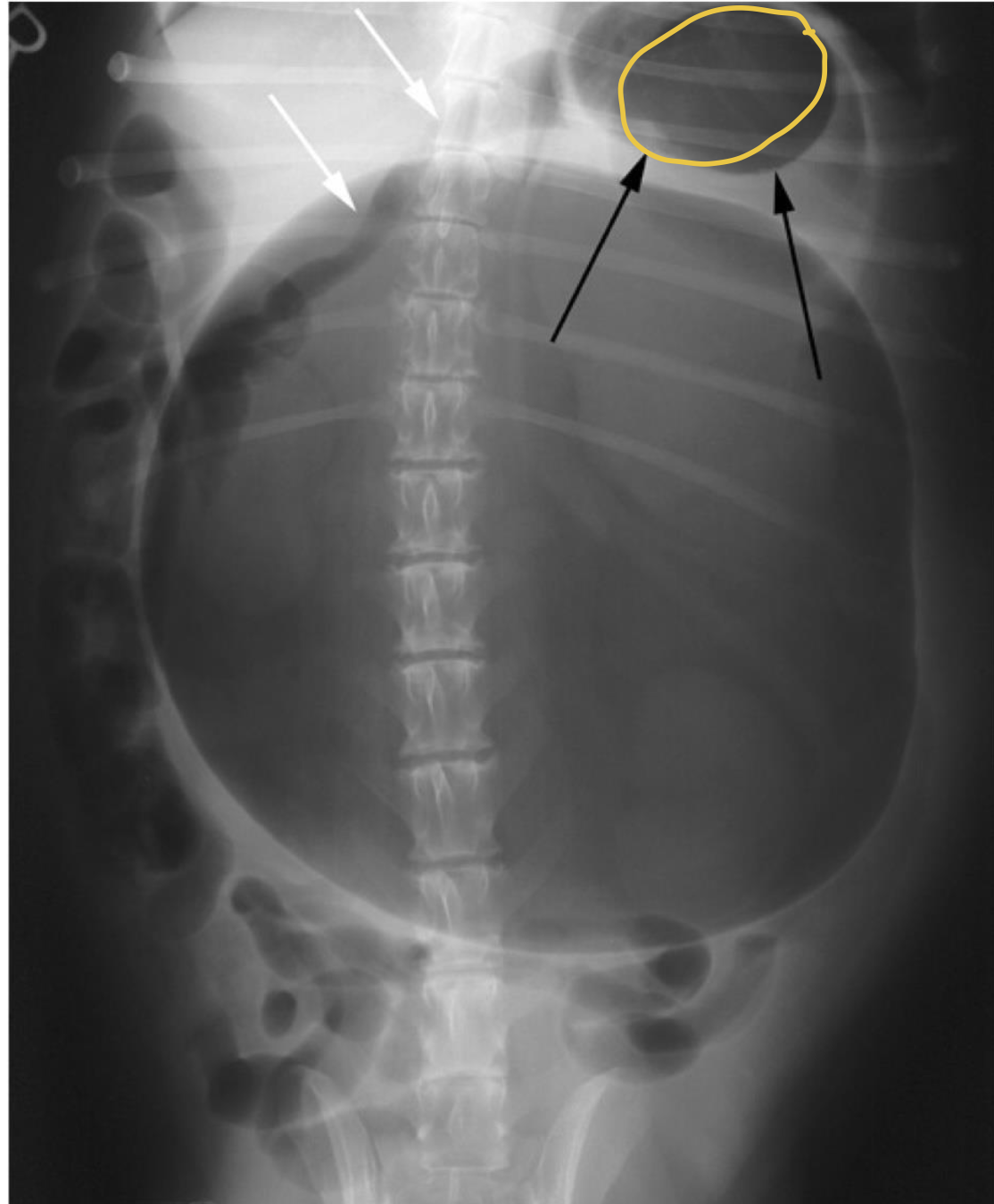
what does the radiograph show?
displacement of pylorus from gastric voluvulus
what are the therapeutic goals of GDV?
restore and support circulation
decompress the stomach
establish if volvulus or simple dilation is present
provide prophylaxis
what are the treatment options for gastric decompression?
stomach tube
percutaneous trocarisation
what surgical techinque are we going to do to fix GDV?
gastropexy
what is the survival rate if dog is diagnosed and treated quickly from GDV?
98%
what type of diagnosis do we give for a dog that has gastric necrosis from GDV?
guarded prognosis 66% survival rate
what signs of GDV will give a poor prognosis of the dog?
evidence of DIC
sepsis
heart arrhythmias
severe damage or perforation of stomach
what test is essential to confirm the diagnosis of GDV?
radiograph