Biology topic 1 part 1- Lifestyle, health and risk
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
How is an aqueous solution formed
When solutes are dissolved in a solvent
Why is water a powerful solvent
Water is a polar molecule, which allows it to easily dissolve ionic and polar molecules
What is meant by a polar molecule
A molecule that has regions of negativity and regions of positivity.
How do ions dissolve in water
Water molecules are attracted to the ions in contact with the water, as they are polar molecules and have negative regions and positive regions that are attracted to the positive and negative ions. This causes the water molecules to cluster around each ion, separating them from its ionic lattice (The slightly positive hydrogens are attracted to the negative ions, while the slightly negative oxygens are attracted to the positive ions). They are attracted by electrostatic forces of attraction.
Why is water a good transport medium
It can carry a range of solutes
What are some uses of water as a transport medium in animals
Can carry important substances in the blood:
Gases- Carbon dioxide and oxygen
Polar biological molecules- Amino acids, glucose, nucleotides
Inorganic ions- Sodium, chloride, potassium
What are some uses of water as a transport medium in plants
Plants use water in sap in the phloem to carry important substances like amino acids, sugars and ions
Why is water a good reaction medium
Solutes can dissolve in water, allowing them to move freely and collide and interact with each other. e.g. enzymes react with substrates to catalyse reactions
Why does water have an unusually high boiling point
It contains hydrogen bonds, which require much more energy to be broken than other inter molecular forces
Why is waters high boiling point essential for life
- It provides habitat for aquatic organisms, as it is liquid at room temperature
- It provides a medium for chemical reactions, as it allows substances to move freely and interact
- It provides a medium for transport, as ionic substances and polar molecules can easily be dissolved in it
What is specific heat capacity
The amount of energy required to increase the temperature of 1kg of a substance by 1oC
Why is it important for water to have a high SHC
- Lakes and seas are able to maintain a stable temperature for organisms to live in
- The water inside of cells can provide a stable environment necessary for enzymes to function effectively
What is latent heat of vapourisation
energy needed for a substance to change from liquid to gas
Why does evaporation have a cooling effect
When water molecules are heated, they gain kinetic energy, allowing them to break the hydrogen bonds present between them and form a gas. When these gas molecules break off, it decreases the total average energy of the remaining molecules, as it has been taken away in the form of kinetic energy
What do humans use evaporation for in the body
The evaporation of sweat. When temperatures become too high, this can cause our enzymes to denature. The body produces sweat in order to decrease body temperature. This is because the thermal energy from our surroundings is absorbed by the hydrogen bonds between the water molecules, causing them to break and evaporate.
How do plants use evaporation
Plants use evaporation to cool themselves as water evaporates from the mesophyll cells in the leaves and diffuses into the air (transpiration)
What is cohesion
Attraction between molecules of the same substance
Why is water cohesion important in plants
The water molecules are attracted to one another, so when water is taken from one end of the tube, water molecules follow behind. This is important in plants to be able to draw water up the xylem vessels in a continuous stream against the pull of gravity during transpiration
How is tension created at the surface of water and why is it important
Cohesion of water causes tension at the surface of water. At the interface between water and air, the water molecules at the waters surface is more attracted to the other water molecules than to the molecules in the air. This uneven attraction pulls the water molecules inwards toward the water below, placing the surface of the water under tension. This results in a thin "skin" at the surface of the water that is difficult to break through. This can act as a habitat for insects, such as pond-skaters.
What is adhesion
An attraction between molecules of different substances
When does water display adhesive properties
when it is attracted to other polar or charged surfaces
Why is water able to move up glass straws when they are placed in water
Glass straws are made up of materials that contain polar properties. Due to adhesion, the water molecules are attracted to the straw, and are able to move up it. This is known as capillary action. The narrower the glass straw is, the higher up the water can travel, as there is more surface in contact with the water.
What is a monomer
a molecule that can be bonded to other identical molecules to form a polymer.
What is a polymer
long chain of monomers
How is water formed in condensation reactions between monosaccharides
The grouping of a hydroxyl group of one monomer and the hydrogen of another
What is the general formula for monosaccharides
(CH2O)n
What is the general formula of glucose
C6H12O6
Draw glucose
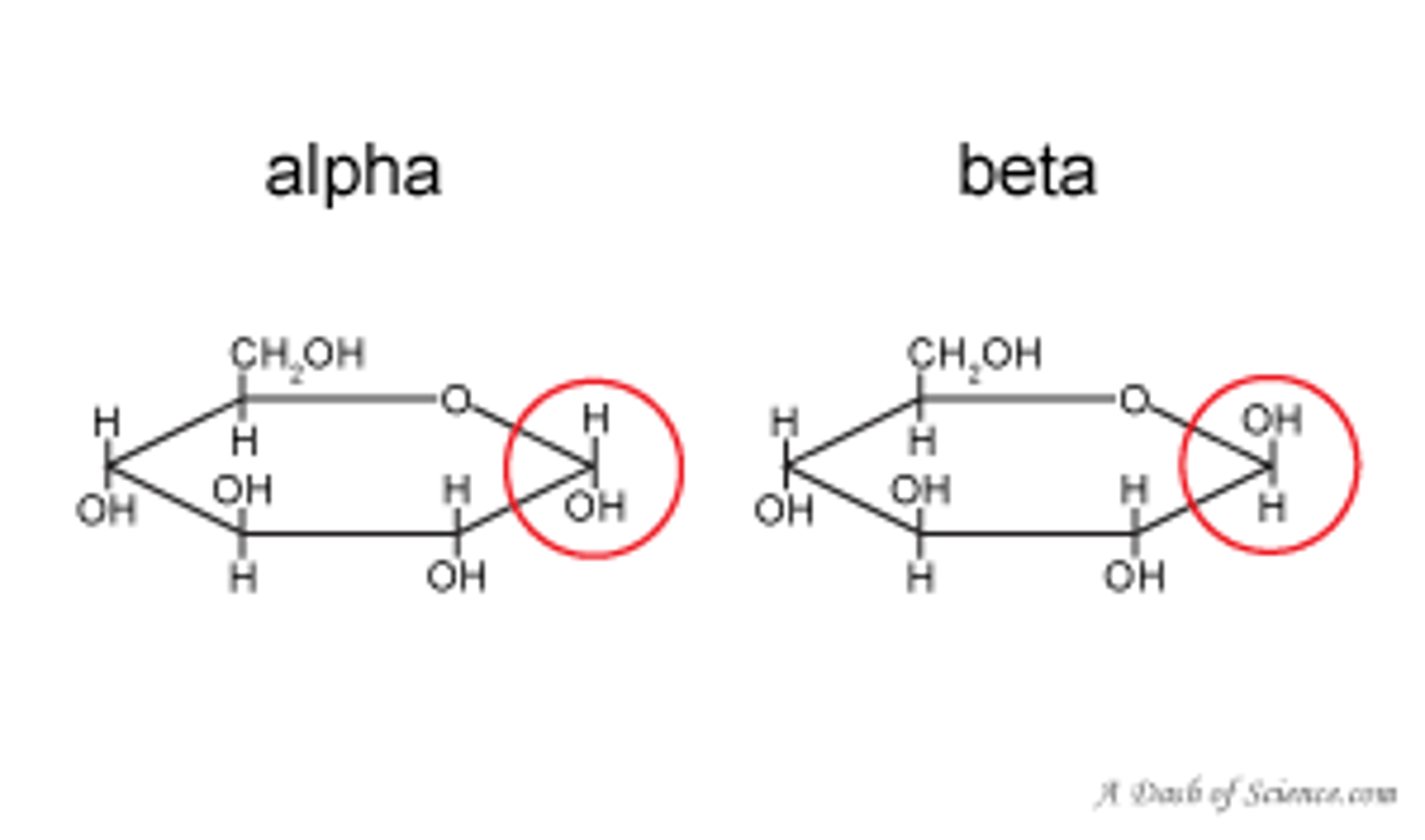
Give some useful properties of glucose
- Small so can be easily transported in and out of cells through carrier proteins
- Soluble so can be easily transported
- Less reactive than other monosaccharides so breakdown must be catalysed and therefore controlled by enzymes
What is an isomer
Compound with same atoms, but arranged differently
What are the isomers of glucose
alpha glucose and beta glucose
Draw ribose
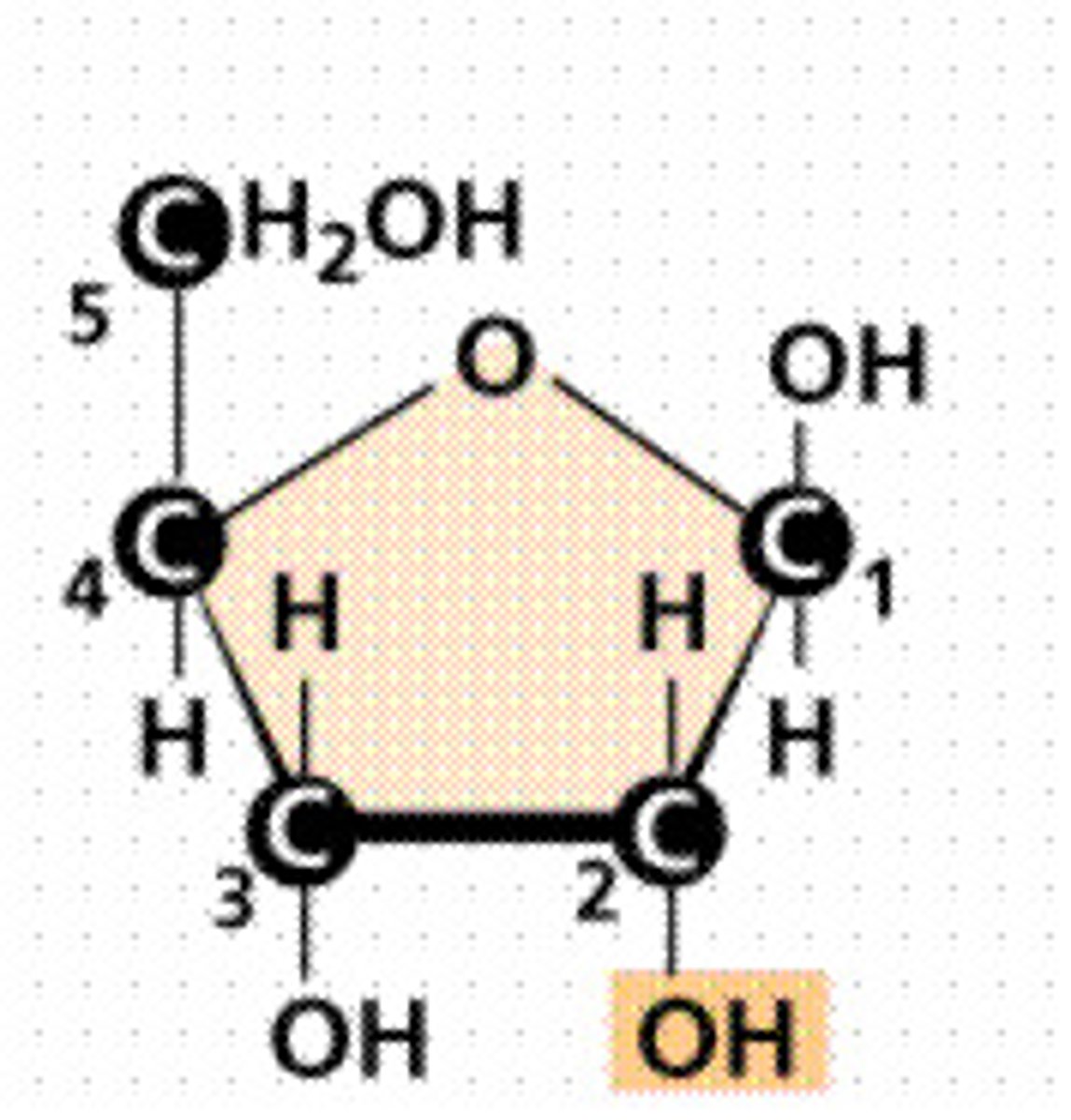
What is the general formula of ribose
C5H10O5
How is ice less dense than water
As liquid water cools, more hydrogen bonds are formed and water becomes more dense, until its maximum density at 4 degrees. As water freezes to ice, the water molecules begin to spread out in a regular geometrical structure, in order to allow each molecule to form the maximum 4 hydrogen bonds. This means that there are less molecules in a given volume, making it less dense than water
What temperature is water at its most dense state
4 degrees
Why is floating ice essential to life
- Provides habitat for creatures that live in a cold climate
- Provides an insulating layer on lakes and rivers, which prevents it from freezing solid, allowing aquatic organisms to survive in cold external temperatures
What is maltose made out of
glucose and glucose
What is sucrose made out of
glucose and fructose
What is lactose made out of
glucose and galactose
Where is glycogen found
animals- cells with a high metabolic rate
Starch structure
amylose and amylopectin
Amylose structure
Linear polysaccharide
alpha 1-4 glycosidic bonds
What shape is amylose
helix
Amylopectin structure
1. Branched Chains of alpha glucose
2. 1-4 and 1-6 glycosidic bonds
3. With Branches
Why is amylopectin more easily broken down than amylose
It has branches, making it more accessible to enzymes to break it down into individual alpha glucose molecules.
Glycogen structure
Long, branched chain of alpha-glucose.
Similar structure to amylopectin, but has much more side branches.
Properties of starch
Amylose- coiling makes it compact and stores much more in a smaller space
Amylopectin- Branching increases surface area for enzymes to hydrolyse glycosidic allowing glucose to be released quickly
Uses of starch
Plants use starch as a way of storing excess glucose as it is too large cells and insoluble. Starch can be hydrolysed to release glucose for respiration
Cellulose structure
1. Long, unbranched chain of beta-glucose.
2. Bonds between the sugars are straight, so cellulose chains are straight.
3. Cellulose chains are linked together by hydrogen bonds to form strong fibres called microfibrils.
Cellulose properties
Hydrogen bonds between the cellulose chains make the microfibrils very strong but still flexible allowing them to provide support
Cellulose uses
Major component of cell walls for rigidity and prevents call bursting, allows the cell to become turgid
How do you test for reducing sugars
1) Add the sample to a clean test tube and add an equal volume of Benedict's reagent
2) Heat the solution in a water bath for 3-5 minutes
3) If reducing sugars are present, copper (II) ions will be reduced to form copper oxide, which will change the colour from blue to orange-red
How to test for non-reducing sugars
1) Following a negative reducing sugars test, add dilute HCl to the solution and heat it in a water bath to break bonds
2) Add an alkali (sodium hydrocarbonate) to neutralise it
3) Add excess Benedict's reagent and heat to above 80 degrees
How to test for starch
1) Place the sample in a clean test tube
2) Add iodide solution and gently shake
3) A positive result will go from orange to blue/black
How to test for proteins
1) add the sample to a clean test tube and add biuret solution
2) Shake and leave at room temperature
3) If amino acids are present, it will go from blue to purple
How to test for lipids
1) add sample to ethanol
2) Add water and shake
3) if lipids are present a milky white emulsion will form
How can a colorimeter be used to do a quantative Benedict's test
Filter the solution and weigh the precipitate and use the colorimeter to measure the absorbance of the remaining solution
Triglycerides structure
glycerol + 3 fatty acids
How are ester bonds formed in triglycerides
Condensation reactions between each of the 3 OH groups on the glycerol and OH group on each fatty acid chain
Triglycerides properties
Fatty acid chains are hydrophobic, so are insoluble in water
Triglycerides uses
Used as an energy store as a lot of energy is released when the fatty acid chains are broken down
Phospholipids structure
glycerol, 2 fatty acids, and a phosphate group
How are ester bonds formed in a phospholipid
Condensation reaction between 2 OH groups on the glycerol and the OH group on each fatty acid chain
Phospholipids properties
Phosphate group is hydrophillic, while fatty acid chains are hydrophobic, which allows them to form bilayers which make up membranes
Uses of phospholipids
Membranes and hormones
What is a saturated fatty acid
One without double bonds.
What is an unsaturated fatty acid
a fatty acid with at least one double bond between carbon atoms
4 main roles of lipids in the body
insulation, energy, waterproofing, form membranes and hormones
What is a phospholipid bilayer
a two-layered arrangement of phosphate and lipid molecules that form a cell membrane, the hydrophobic lipid ends facing inward and the hydrophilic phosphate ends facing outward.
Why is it important for starch and glycogen to be insoluble
They do not affect the concentration of water in the cytoplasm, so do not affect the movement of substances in and out of the cell by osmosis