quiz 2 math 112
[3.1]Exponents are used to…

Denote repeated multiplication
[3.1]Example of exponents

1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
[3.1]Exponents are used to…
Denote repeated multiplication

[3.1]Example of exponents

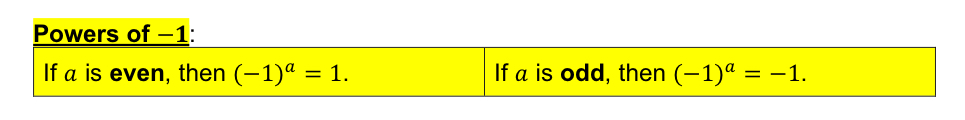
[3.1]Powers of -1
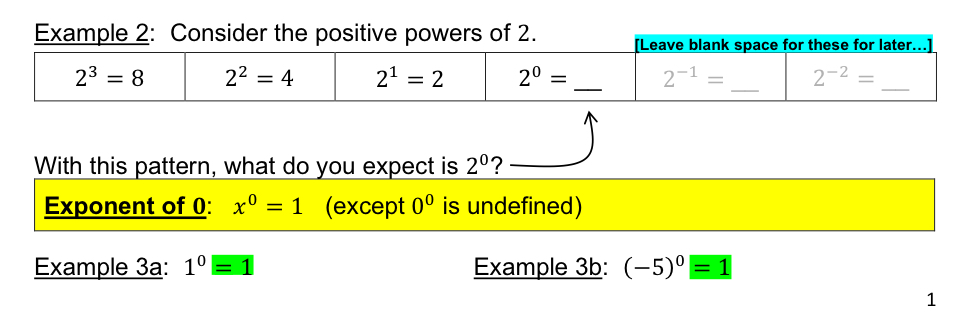
Exponent of 1

Consider positive powers of 2…
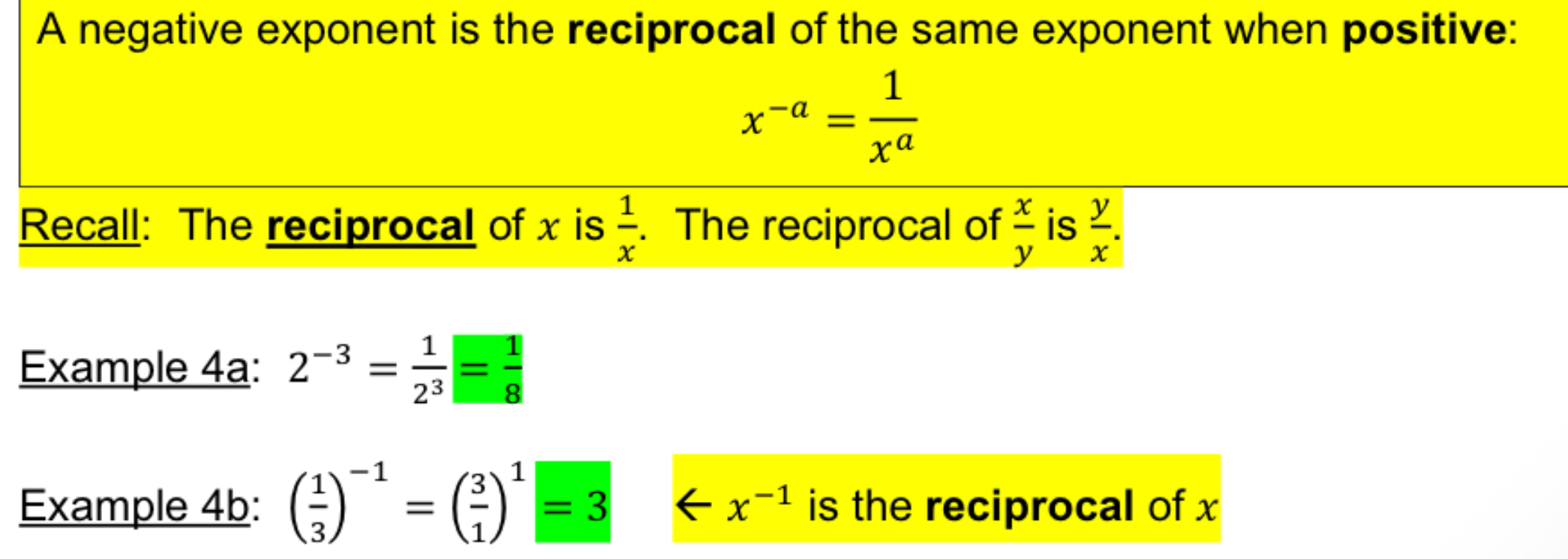
Negative Exponents
Power of Product Rule

Product rule
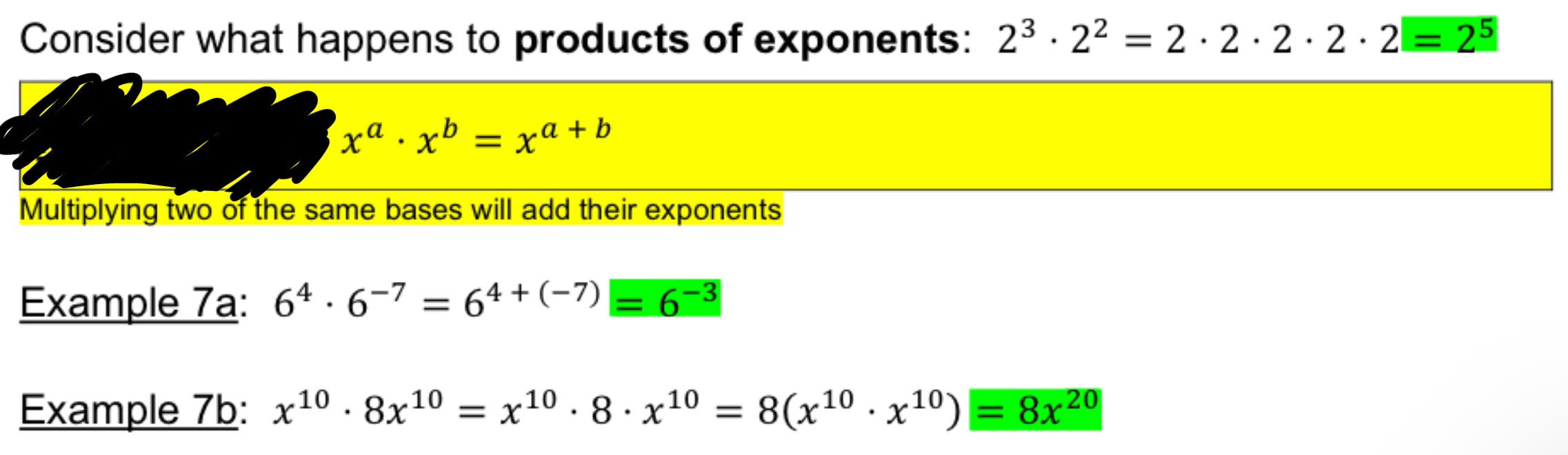
Quotient Rule
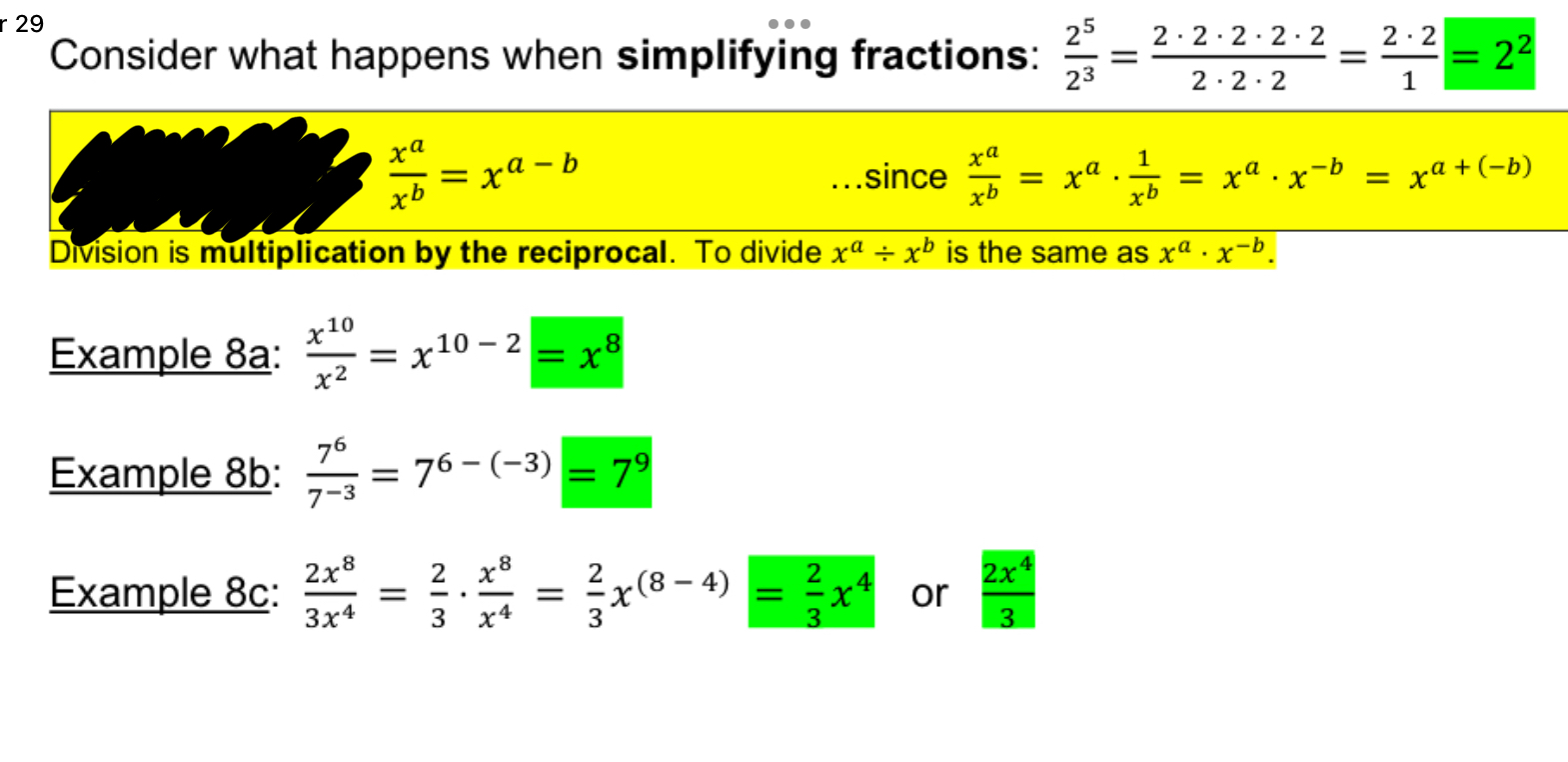
Power rule

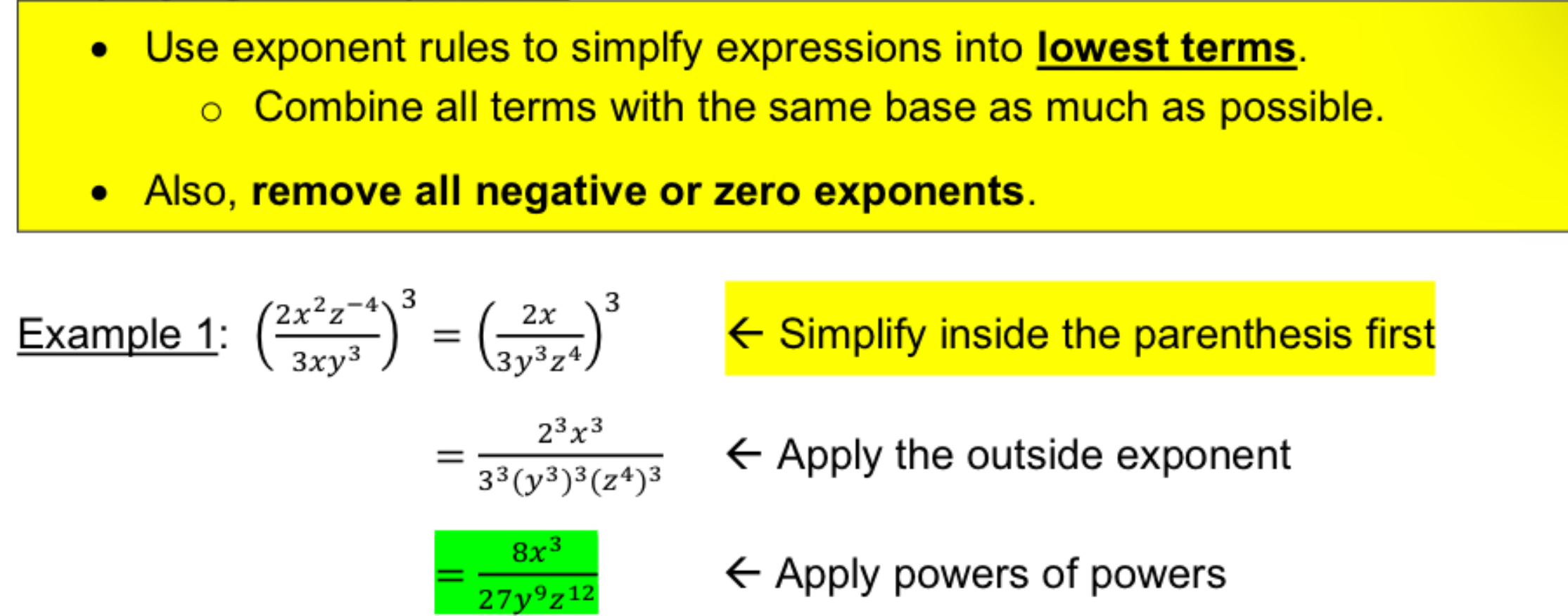
Simplifying with exponents
[3.2] Factors
Real numbers, variables, or expressions multipled ( or divided ) together

[3.2] Terms
Real numbers, variables or expressions added/subtracted Together
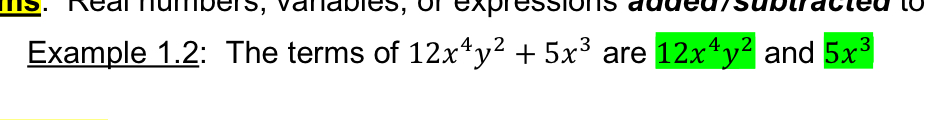
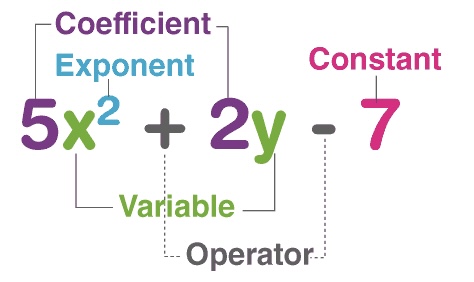
[3.2] Coefficient
The value multipled to a variable

[3.2] Degree
The exponent of the variable
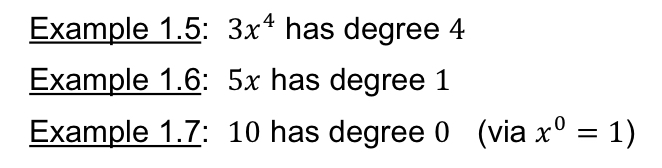
Like Term
Terms that share the same variables and variable exponents
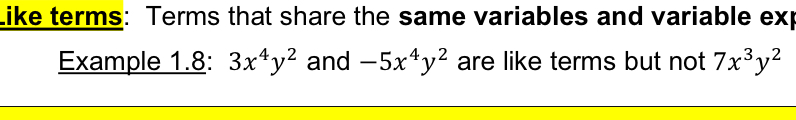
Add/subtract like Terms by adding /subtracting their…
Coefficients
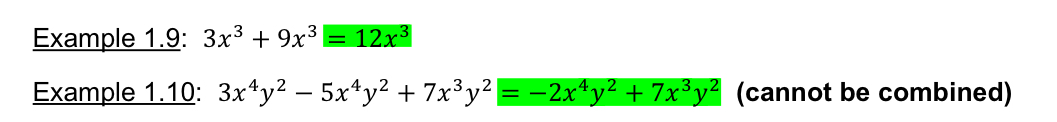
Polynomials
expression of more than two algebraic terms, especially the sum of several terms that contain different powers of the same variable(s)
Poly = Many
Nomials = Terms
Polynomials Standard Forms

Degree of a Polynomial
The largest degree of the variables (aka :n)
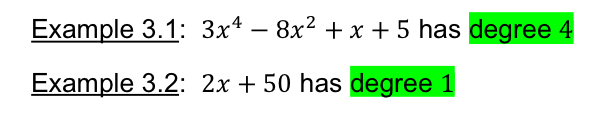
Distributive Property
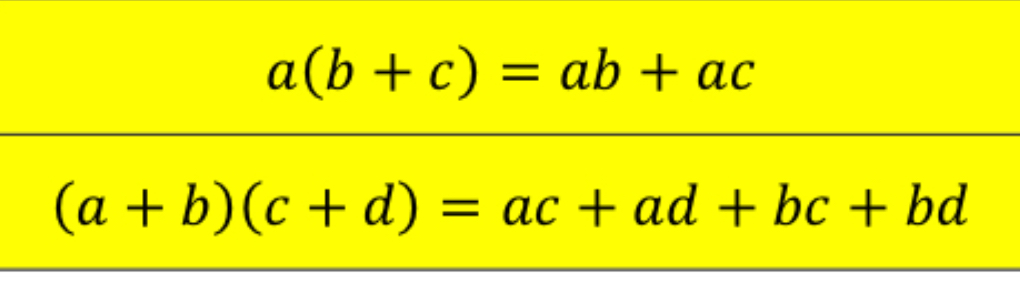
[3.2] Special cases of distributive property
Perfect Square Trinomial
Negative
Positive
Difference if Squares

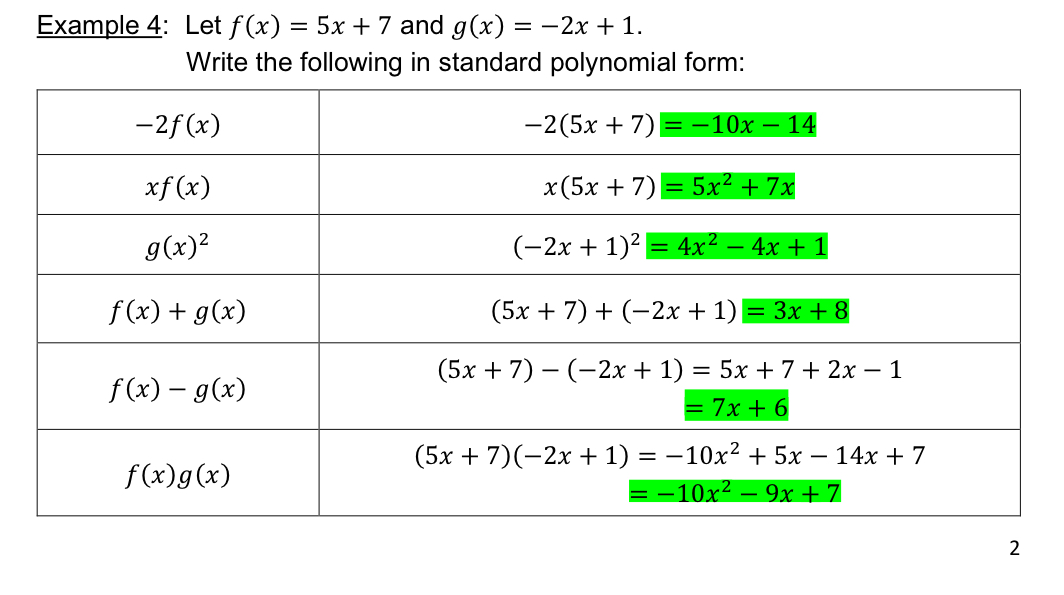
[3.2] Polynomial operations
Replace the function notation with the function definition.
[3.2] Factoring
Is the process of undoing distribution ( turning sums into products of sums )
There are two types!
Expanded forms
Factored forms
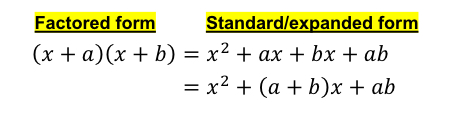
[3.2] Process of Factoring
We need to find A and B we will use “restricted guess and check”
Guessing and checking values within certain parameter

[3.2]What if the coefficient of 𝒙𝟐 is not 1?

[3.2] GCD !
Greatest common Divisor of two terms is the largest factor shared between both terms
Only do this is possible
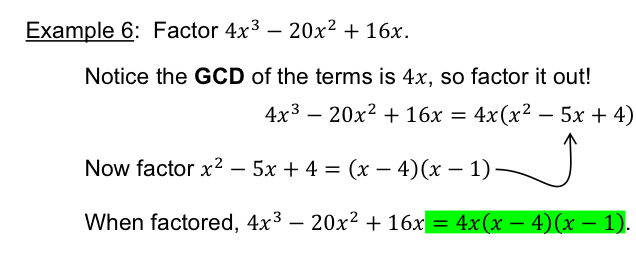
[3.2] What If factorization is possible?
If a polynomial cannot be factored it is considered to be prime

[3.2] Factoring by grouping!
If you rewrite the polynomial, you may be able to factor out the GCD.
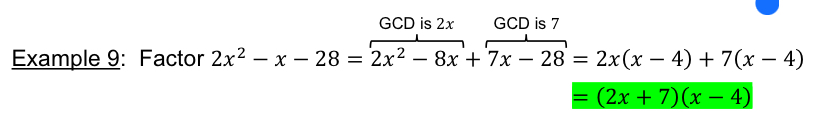
[3.2] ABC method!

[3.2] Example of ABC method

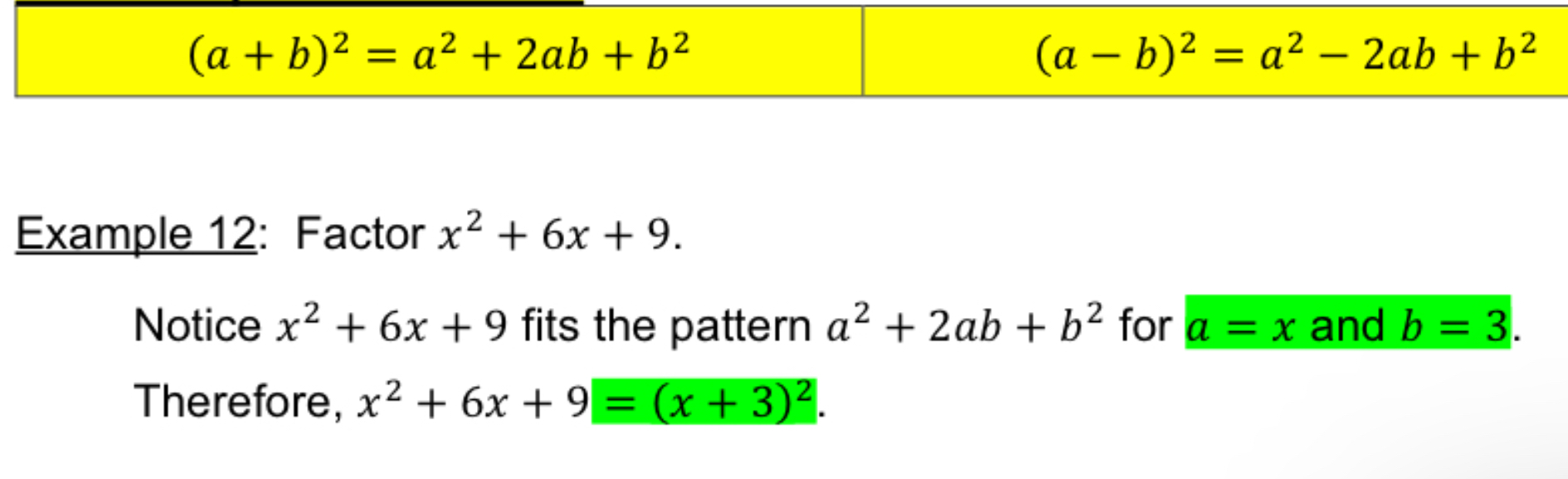
[3.2] Special factoring techniques: Perfect Square Trinonial
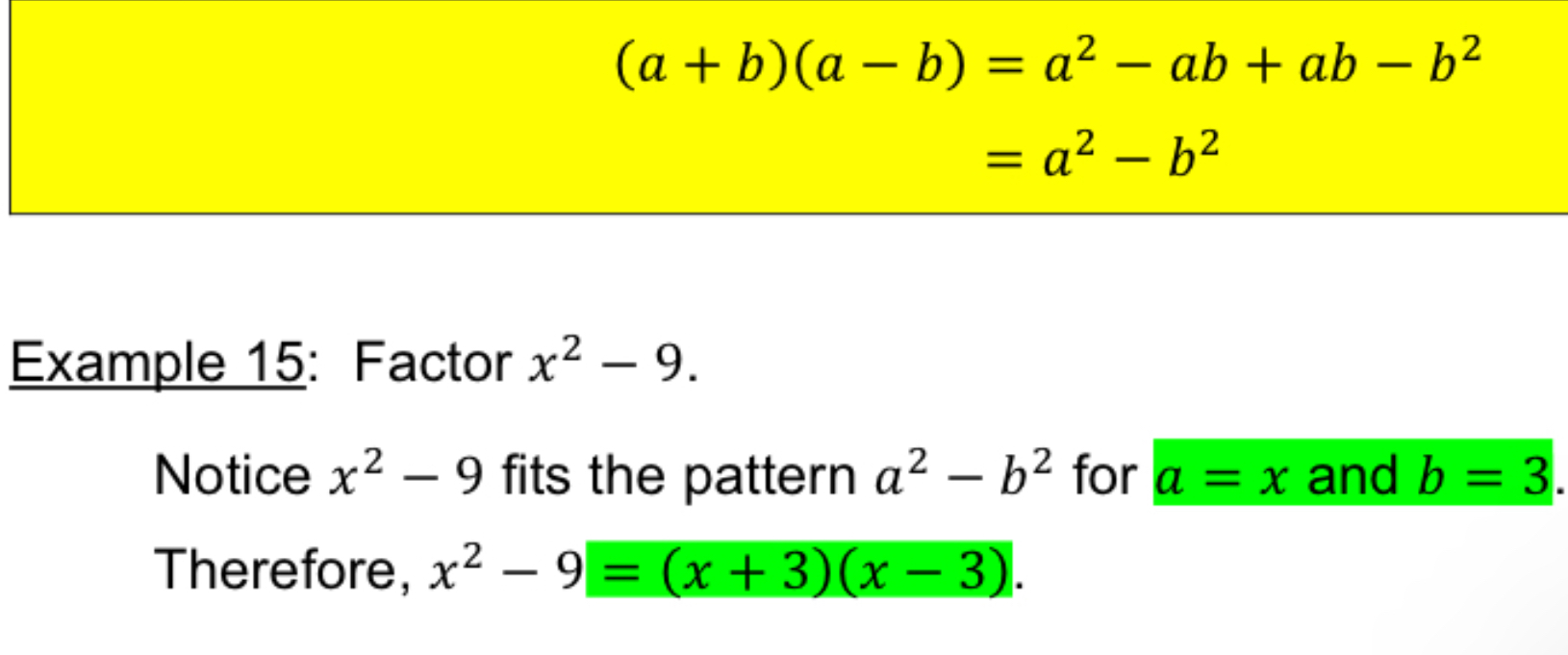
[3.2] Special Factoring :Different of squares
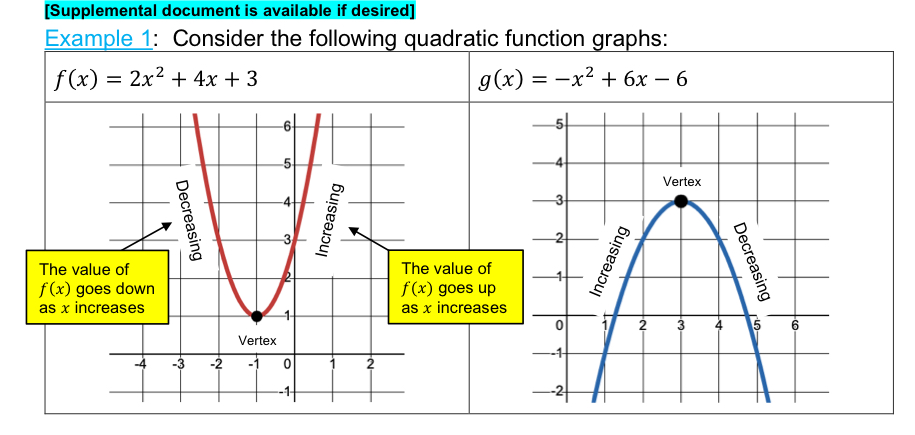
[4.1] a quadratic function has the general form…

[4.1]The graph of quadratic function are called..
Parabolas
[4.1] quadratic function graphs look like
[4.1] Quad-Ratic
Largest term is Square. Square has 4 sides ( reminder )
[4.1] properties of Parabolas
Vertex, vertical and horizontal intercept and Concavity.
[4.1] Vertex
Its the point whose y-value is either less than or greater than the y - values of all the other points
The lowest or the highest
![<p>[4.1] if the parabola opens UP ( U shape ) then it is…(concavity)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/5f6f2e30-05d2-4763-bcbc-2c4eec877262.jpg)
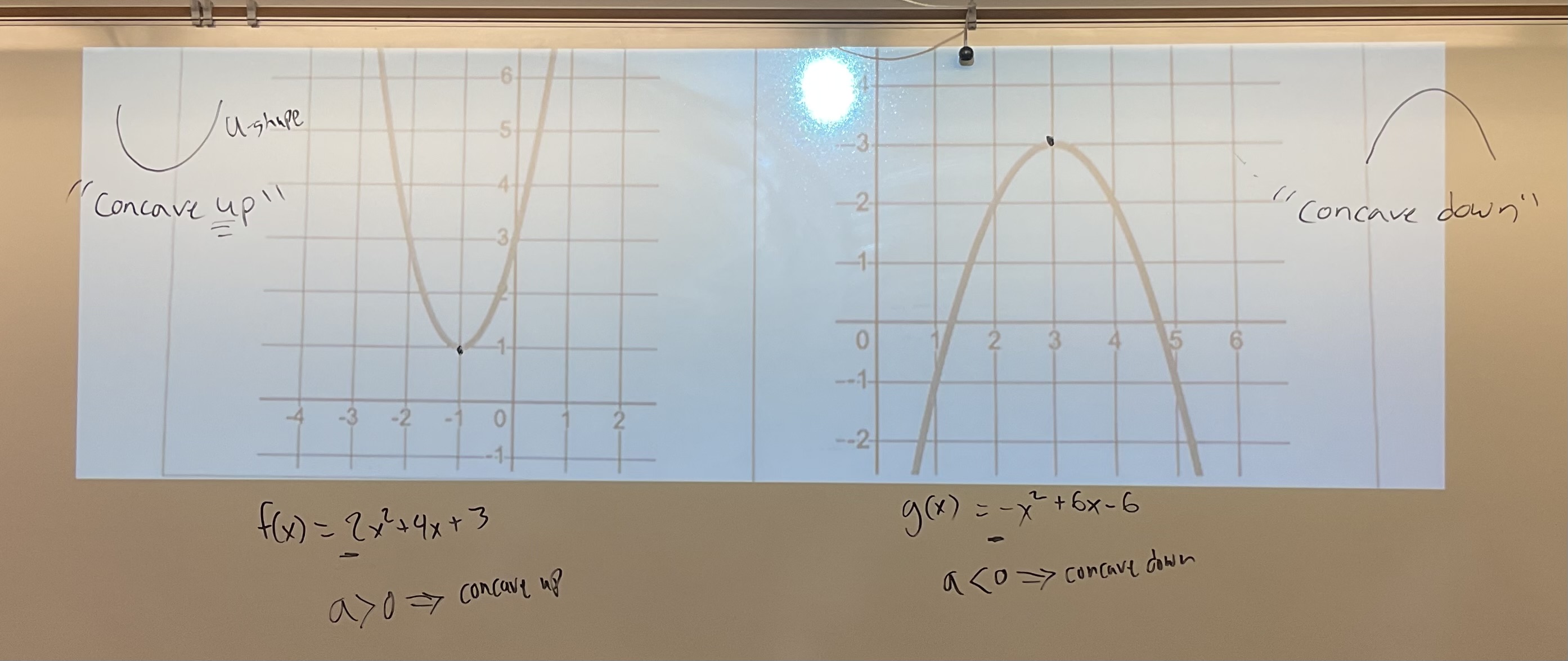
[4.1] if the parabola opens UP ( U shape ) then it is…(concavity)
Concave Up

![<p>[4.1] ( Concavity ) if the parabola opens down then it is is..…</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c2ebe0be-0346-46bb-af3b-fda3f445fcee.jpg)
[4.1] ( Concavity ) if the parabola opens down then it is is..…
Concave down

[4.1] Vertical intercept…
Parabolas will always have just 1 vertical intercept

[4.1] horizontal intercept ….
Parabola may have… 0 1 or 2 horizontal intercepts
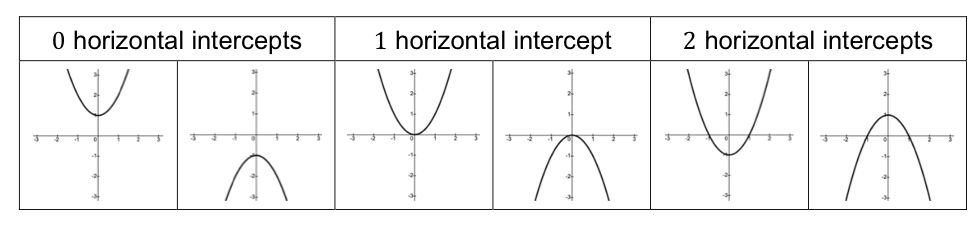
[4.1] how to know if something is a quadratic function…
Knowing if the quadratic function is up or down but If it isn't either then it isn't one

[4.1]Another example of quadratic functions

[4.1] Zero Factors
If a product equals zero then at least the factor must be Zero
If ab=0 then A= 0 and/or b= 0

[4.1] the horizontal interception(s) of a quadratic fiction occurs when…
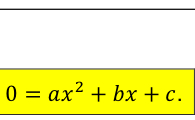
[4.1] the horizontal interceptions for solving quadratic equations are also called..…
“Zeroes” and “roots” of the polynomial
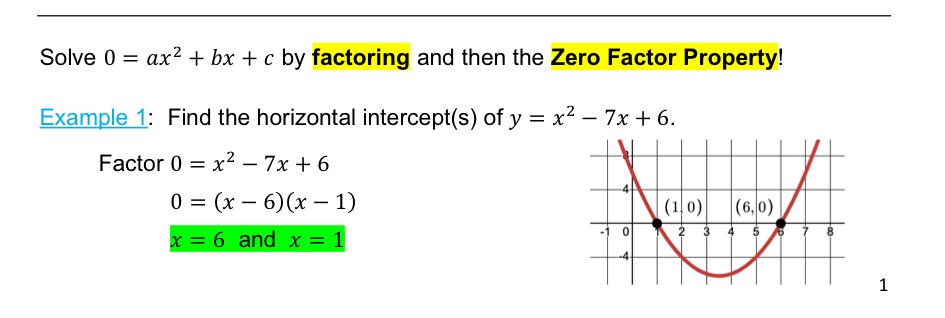
[4.1] Word problem for solving quadratic equations
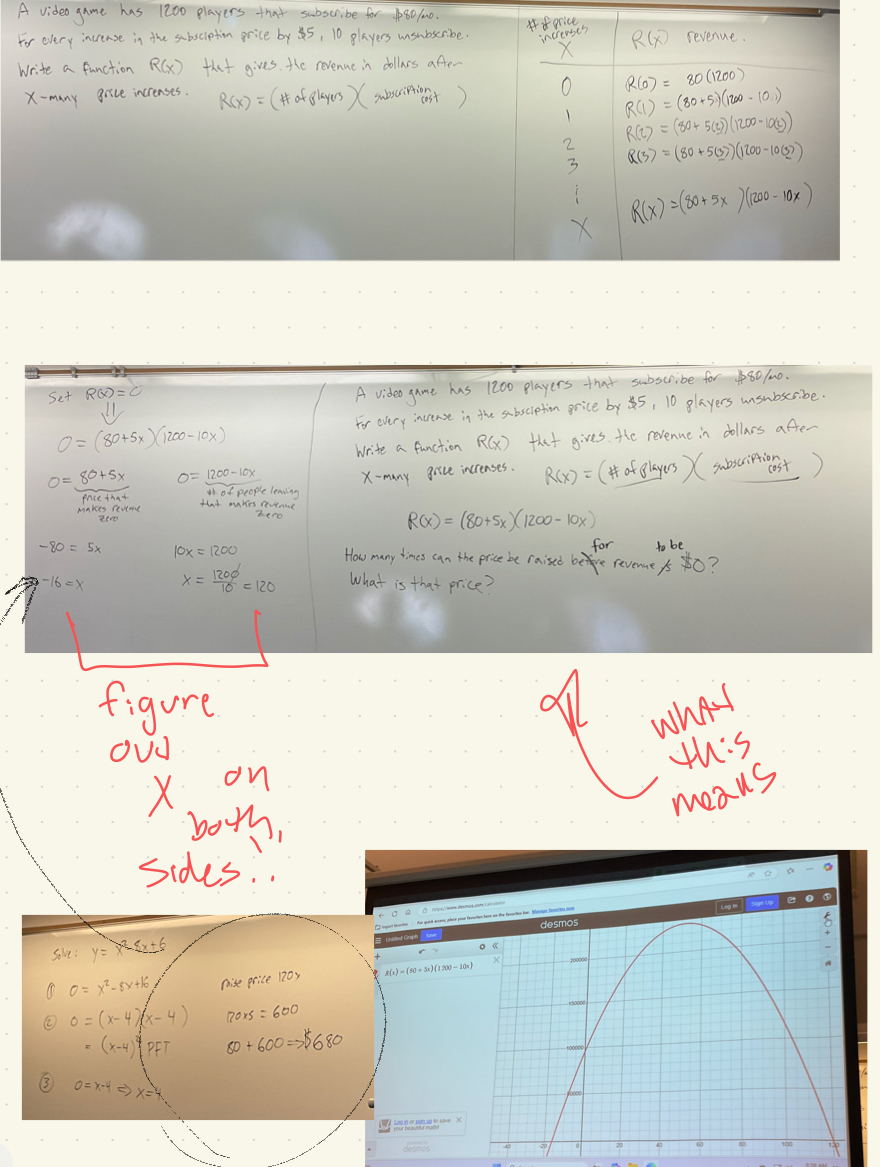
[4.1]Square Root

[4.1] getting two values from the same operations is not ideal so….

[4.1] Square Root Property
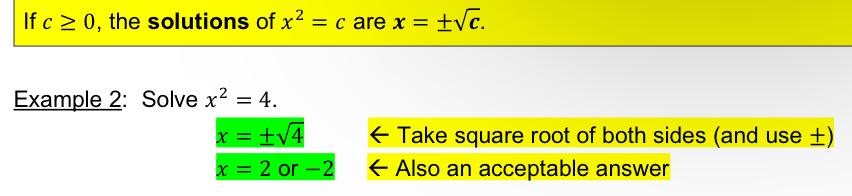
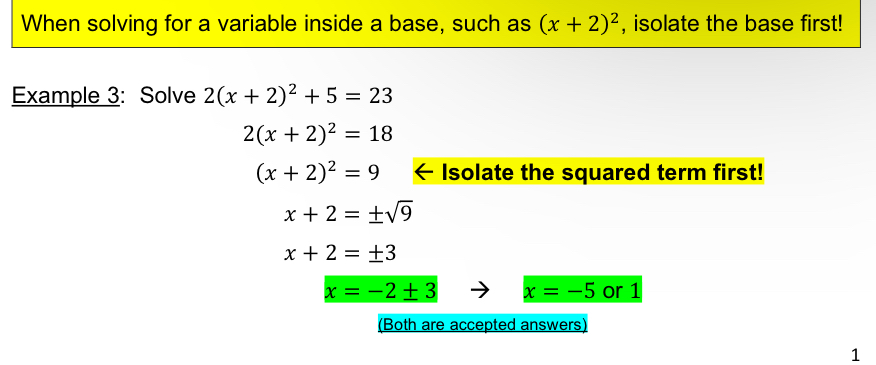
[4.1] Solving for variable inside bases
[4.1] Perfect Square Trinomials
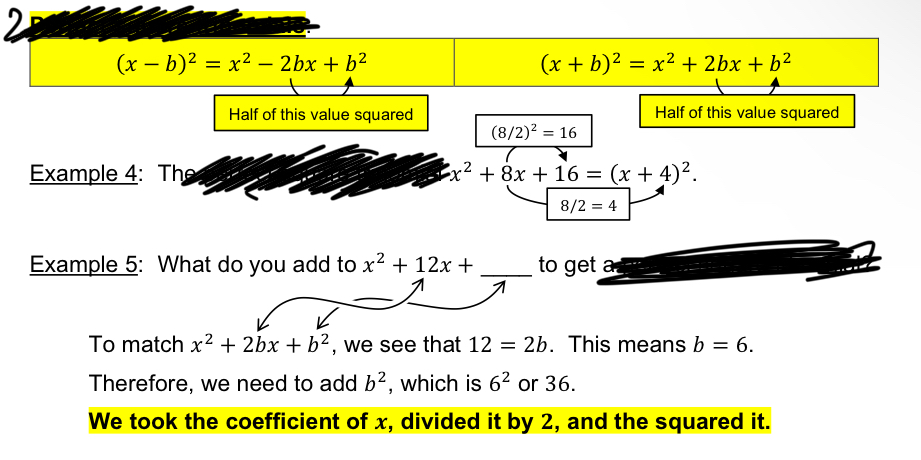
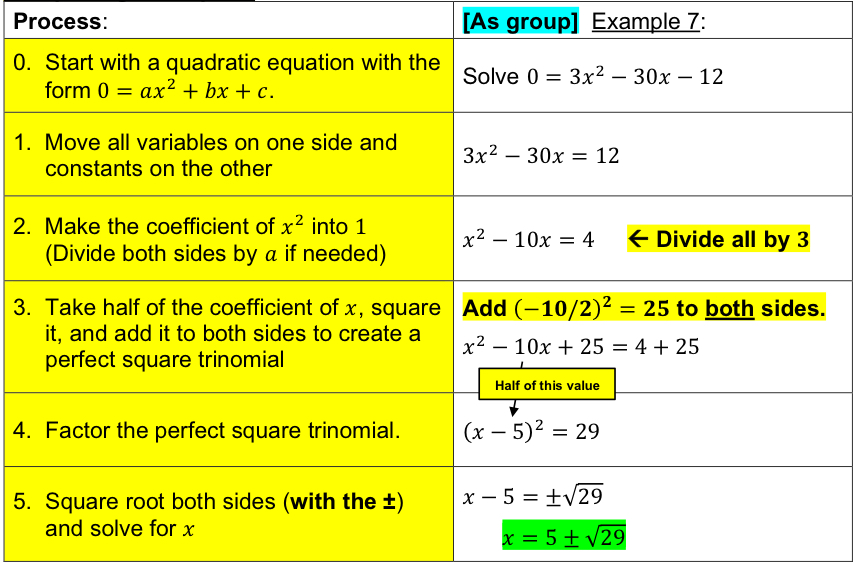
[4.1] Completing the Square