CIE IGCSE Biology Unit 20: Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
How bacteria is useful in biotechnology and genetic engineering?
they reproduction rapidly and make complex molecules
Why bacteria are useful in biotechnology and genetic engineering?
- lack of ethical concerns over their
manipulation and growth
- genetic code shared with all other
organisms
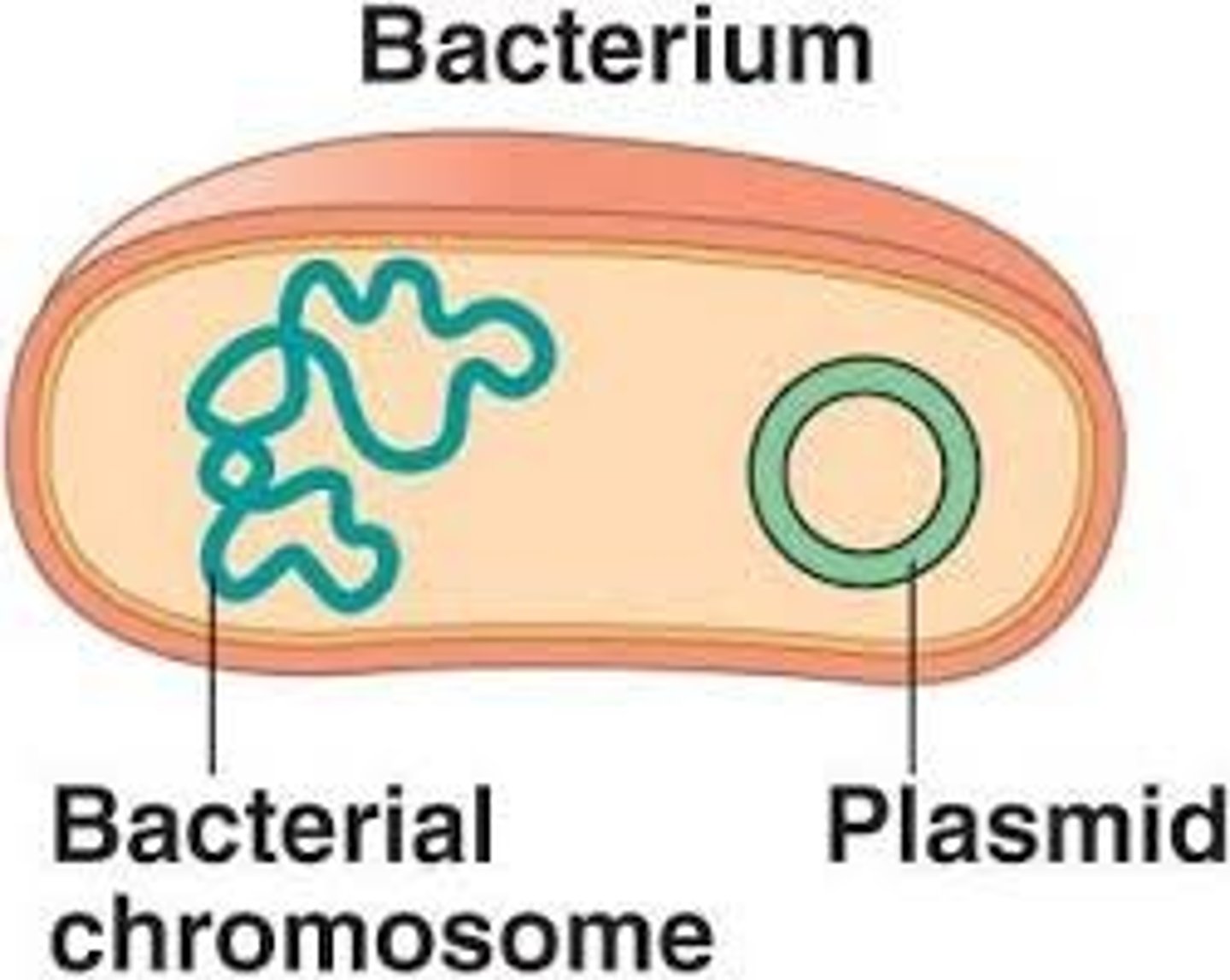
- presence of plasmids
plasmids
Circular DNA molecules that can replicate independently of the main chromosomes of bacteria
role of anaerobic respiration in yeast during production of ethanol for biofuels
Anaerobic respiration causes yeast to use glucose to produce ethanol

role of anaerobic respiration in yeast during bread-making
Causes yeast to produce alcohol and carbon dioxide causing bread to rise

use of pectinase in fruit juice production
Pectinase is an enzyme that dissolves cell wall of the plant cell extracting the juice

pectinase in fruit juice experiment
1.cut apple into 1cm cubes
2.place apple cubes into test tube filled with pectinase solution
3.cover test tube and place into water bath of 40c for 30 minutes
4.pour solution through a piece of filter paper
Results:juice is extracted
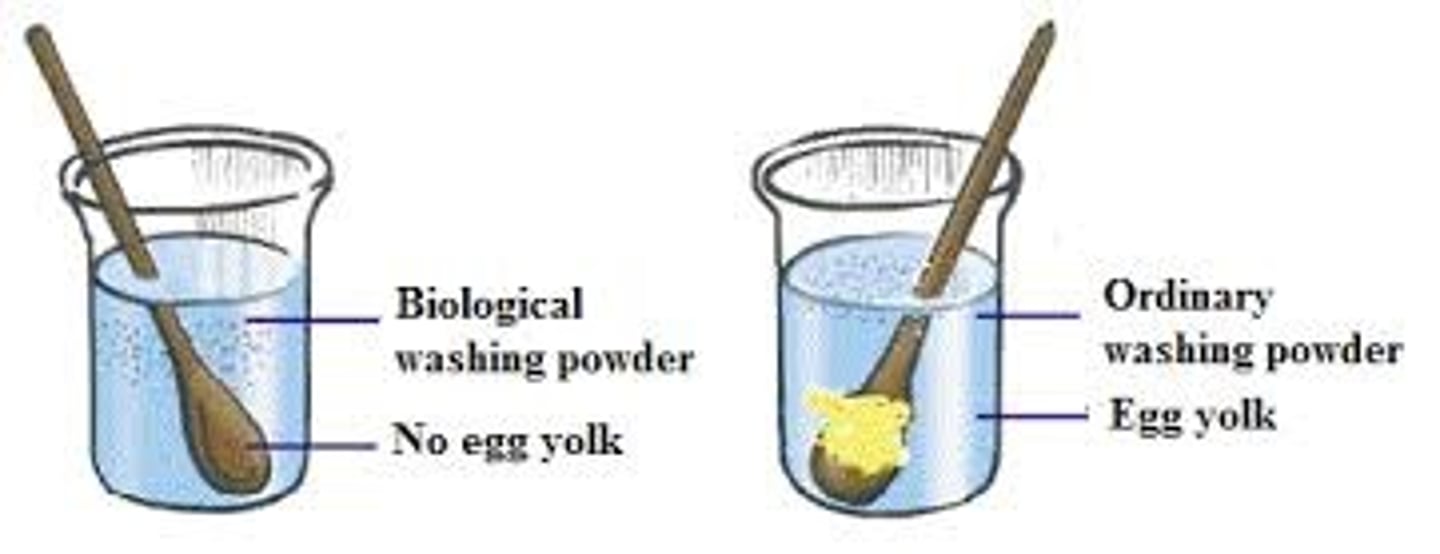
use of biological washing powders that contain enzymes
Breaks down protein and starches

biological washing powders experiment
1.Add biological washing powder into beaker filled with 300 ml of water
2.Stain cloth with (oil and egg) eg.
3.Place stained cloth into beaker and stir until bubbles produced
4.Remove cloth and wash with distilled water
Results:Stains on cloth removed
use of lactase to produce lactose-free milk
lactase is first added into the milk during production to remove lactose

role of the fungus Penicillium in the production of the antibiotic penicillin
undergo respiration to produce penicillin
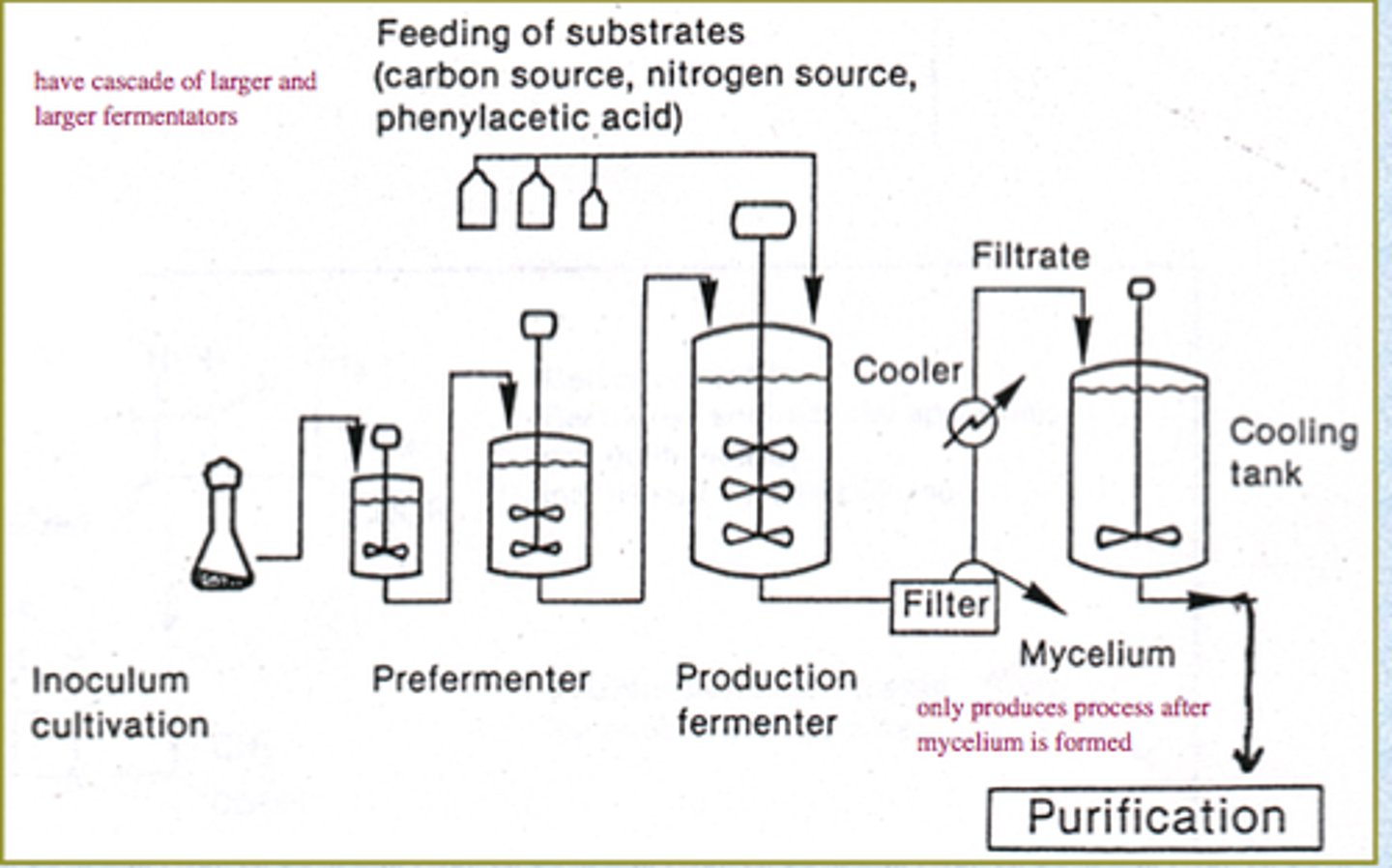
how fermenters are used in the production of penicillin
Contains:
-stirrer to allow fungi to have access to oxygen and nutrients
-air supply to provide oxygen for respiration
-water jacket to maintain constant temperature as respiration creates heat
-probes to monitor pH and temperature levels
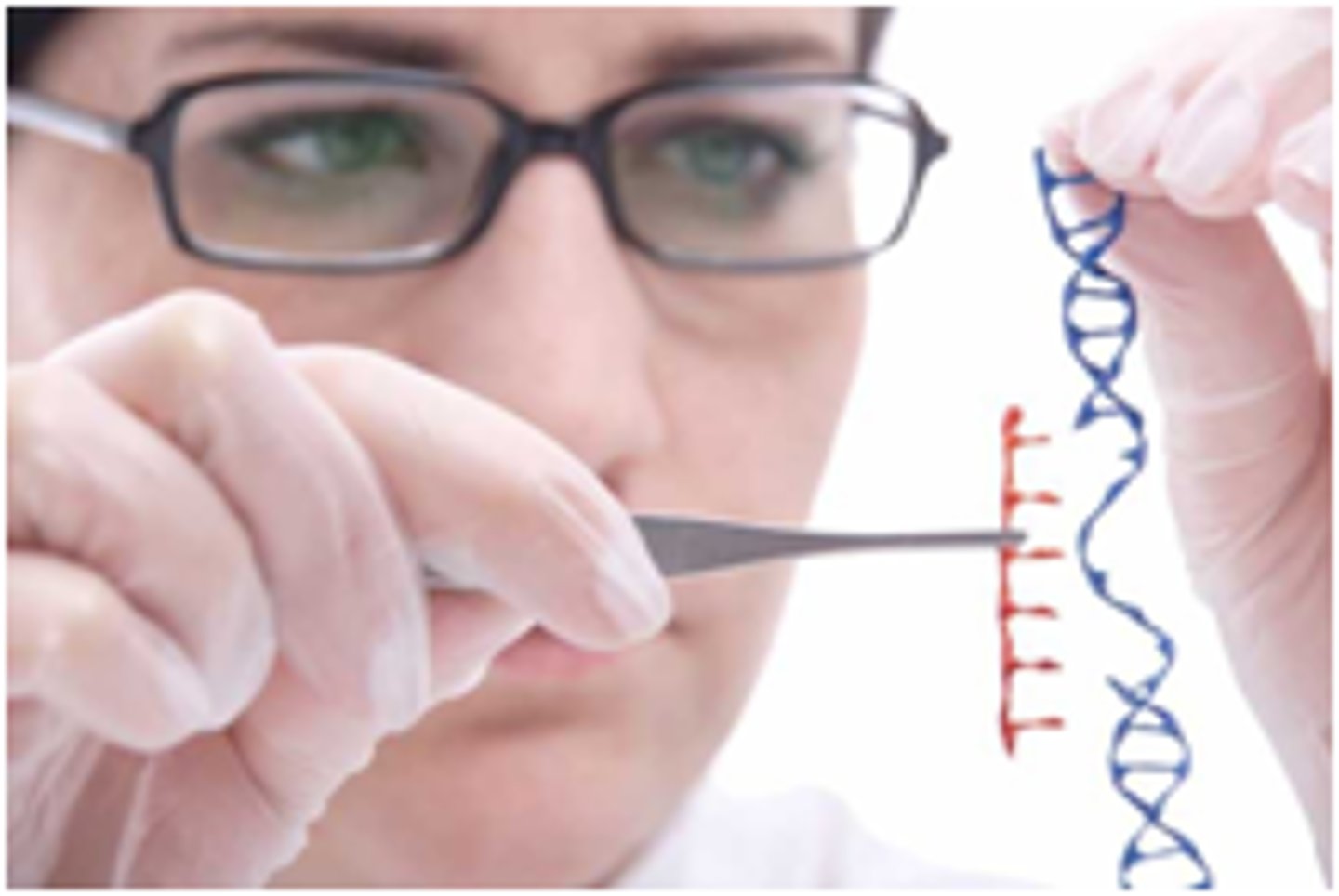
genetic engineering
changing the genetic material of an organism by removing, changing or inserting individual genes

examples of genetic engineering
- the insertion of human genes into bacteria
to produce human insulin
- the insertion of genes into crop plants to
confer resistance to herbicides
- the insertion of genes into crop plants to
confer resistance to insect pests
- the insertion of genes into crop plants to
provide additional vitamins
genetic engineering using bacterial production of a human protein
- isolation of the DNA making up a human
gene using restriction enzymes, forming
sticky ends
- cutting of bacterial plasmid DNA with
the same restriction enzymes, forming
complementary sticky ends
- insertion of human DNA into bacterial
plasmid DNA using DNA ligase to form a
recombinant plasmid
- insertion of plasmid into bacteria
- replication of bacteria containing
recombinant plasmids which make human
protein as they express the gene
advantages of genetically modifying crops
- solving global hunger
- environment friendly
- consumer benefits

disadvantages of genetically modifying crops
- environmental safety
- food safety concerns
- reduce bioderversity
