W2- PREPARING TO DESIGN
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Design in the context of architecture
the activity of generating proposals that change something that already exists into something that is better
Design Process
Initiation > Preparations > Proposal Making > Evaluation > Iteration
Design Process
for us to achieve design and propose a changes to something into a better state
Initiation
Problem seeking and Identification
Preparations
Collection or analysis of data
Proposal Making
synthesis or bringing together the variety of considerations
Evaluation
Based on goals
Iteration
cycles and feedback phase
Initiation, Preparation, Proposal Making, Evaluation and Iteration
All these process are Architectural Programming
Architectural Programming
is the process of managing information so that the right kind of information is available at the right stage of the design process and the best possible decisions can be made in shaping the outcome of the building designs
Architectural Programming
the process that creates the structure for fulfilling the dreams, hopes, wishes and desires of the building’s future inhabitants.
Architectural Programming
Problem seeking phase of the design process
Architectural Programming
The orderly definition of the architectural problem and the articulation of the project requirements in a manner that promotes the creation of a responsible solution for the design of the building
Architectural Programming
the gathering, organizing, analyzing, interpreting and presenting of the information relevant to a design project
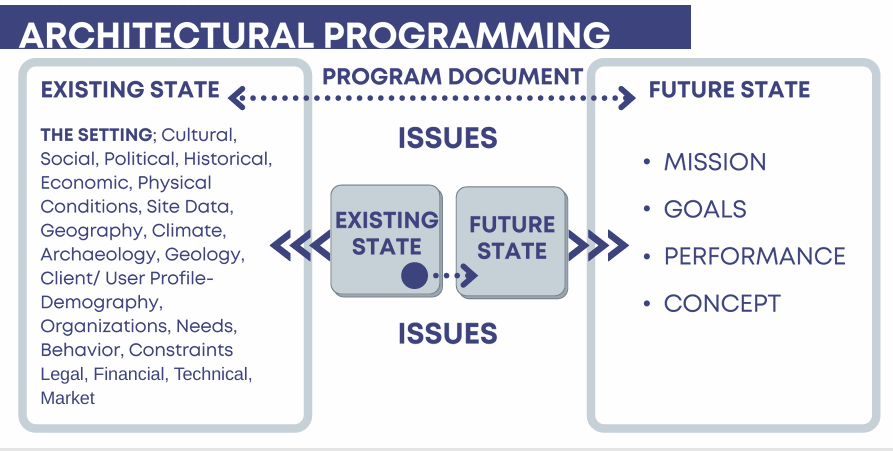
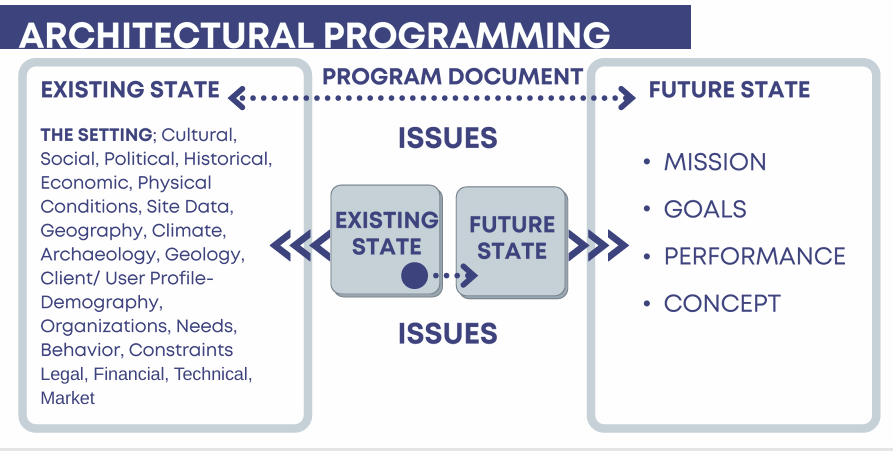
Analysis of the existing state or condition
the current or the existing situations where problems, issues arises where action and/or solution is necessary (something that you want to change)
Projection of what the future state should be
the changes that the designer wants to happen once the issues or problems from existing state addressed (something that t you want to happen)
Issues of Existing State

Issues of Future State
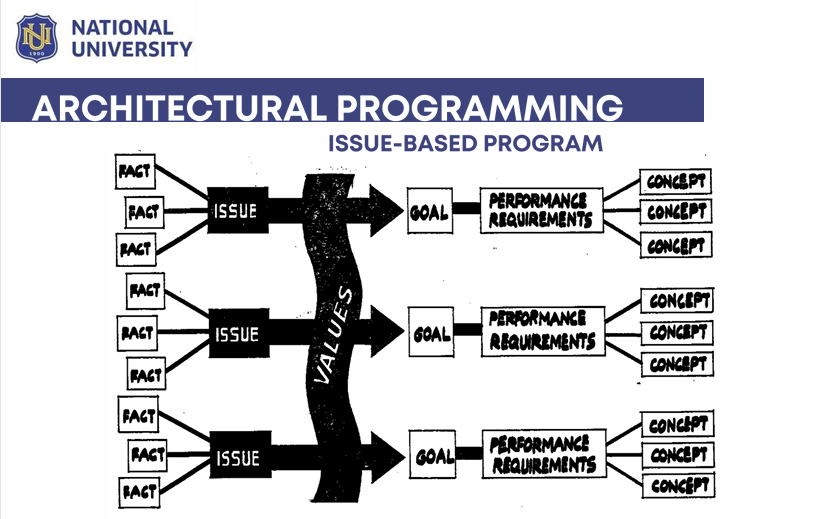
Architectural Programming (Issue- Based Program)
Fact, Issue, Values, Goals, Performance Requirements & Concept
Fact
are objective, specific and verifiable by some measurement or observation.
Fact
Their existence is not subject to judgment but their use and interpretation is based on values
Issue
any matter, concern question topic, proportion or situation that demands a design in order for a building project to be successful for its clients and users
Values
different building types require different design responses for the same issues based upon the values of different users and the needs of different activities
Values
design issues, when processed through the filter of values of the client, user and designer yield goal statements about qualities the design must have.
Goals /Project Goal
goals that relate only to the outcome of the project; these are based upon the underlying values of the designer, clients and users
Goals/Mission Statements
the overall purpose; a statement that concisely explains the need to undertake a project in the first place.
Performance Requirement
a statement about the measurable level of function that a designed object, building of place must provide for a good to be met; performance specification standard or criterion
Performance Requirement
This statement is more specific than a goal since it relates to function (a doing) instead of a quality (a being); must be general enough to allow for multiple, alternative physical solutions or concepts
Concept
a statement of an ideal set of relationships among several of the elements under an architect’s control such as form (dimension and direction) material, texture, color (value, intensity) and adjacency.
Concept
A concept statement is made of a single diagram and a few words
Architectural Programming (Issue Based Program)
6 Checklist of issues
Audibility, Behavioral Settings, Circulation, Comfort, Convenience & Durability
Audibility
ability to hear what needs to be heard and to mask unwanted sounds
Behavioral Settings
interdependencies of activity and physical settings
Circulation
movement of people, objects, information or substances
Comfort
providing ease and enjoyment
Convenience
ease of access to places, materials and information
Durability
ability to endure the designed use over time
4 Required State Program
Design Philosophy and Overall Concepts, concept breakdown, translation guidelines and Synthesis
Philosophy
a statement of the beliefs, values or viewpoints from which the development of design solutions take off.
Philosophy
They are often formed out of universally held principles, and thus become bases for socially desirable design objectives
Concept
an initial generalized idea, a perception about form or relationships among variables resulting from an analysis of the problem
Concept
a mental image deriving from the project situation and the first ideas in the building morphology
Concept breakdown
consists of sub concepts that correspond to a particular areas of architectural concerns. An overall concept can be broken down into a sub-concepts under one or more categories
Concept breakdown
The mix varies depending on the research problem
Translation Guidelines
These are specific design guidelines formulated out of sub-concepts.
Translation Guidelines
They may be refined versions of the chosen sub-concept or could also be the product of the consolidation of two or more sub-concepts
Translation Guidelines
The guidelines prescribe performance and quality standards that are based on the design parameters derived out of the performance requirements.