Astro Physics
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Disadvantages of refracting telescopes
Requires large-diameter glass lens free from defects which is difficult to make
Large glass lenses are very heavy and tend to distort under their own weight
Lenses can only be supported around their edges which is the weakest part of the lens
Suffer from both chromatic and spherical aberration
Can only observe wavelengths of visible light
Disadvantages of reflecting telescopes
The secondary mirror blocks some of the light from entering the primary mirror and will cause some diffraction and affect clarity
mirrors in a reflecting telescope are exposed to air so they require regular maintenance
Some chromatic aberration may be introduced when the light is refracted in the eyepiece lens
Chromatic aberration
Due to the different focal length of red and blue light (as blue light is more refracted) meaning they focus at different points
Causes coloured fringing in the image
Can be minimised by using an achromatic doublet which is a convex lens and a concave lens cemented together to bring the light rays to focus in the same position
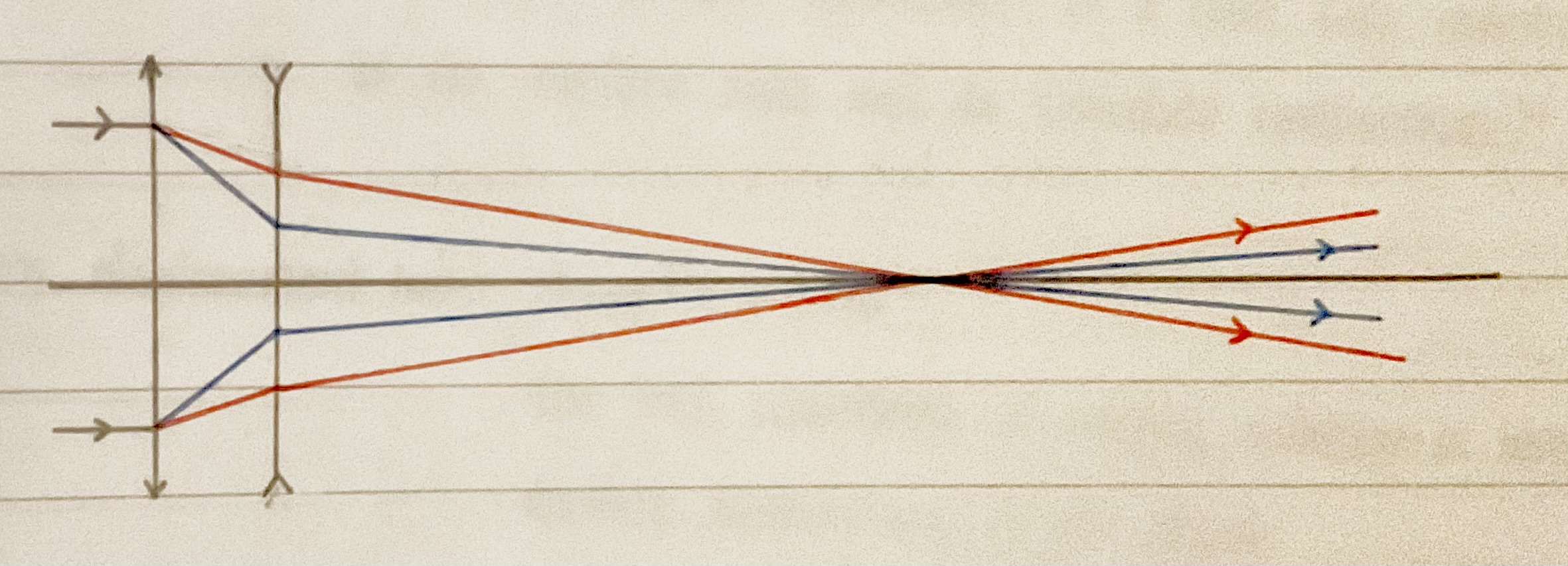
Spherical aberration
Due to the rays of light at the edge to be focused in a different position to those near the centre because of the curvature of the lens/mirror
Causes image blurring and distortion
Can be avoided completely by using parabolic objective mirrors in reflecting telescopes
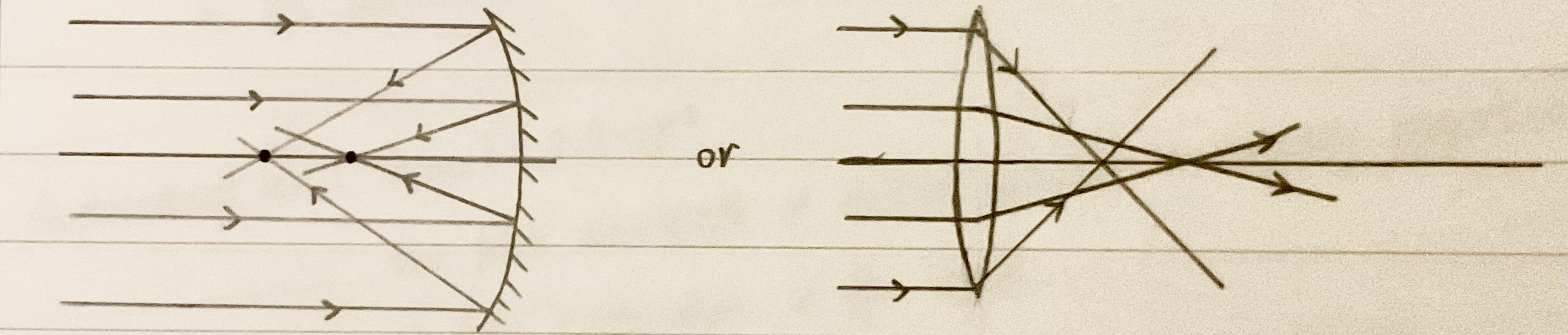
Collecting power
The measure of the ability of a lens/mirror to collect incident EM radiation
Directly proportional to the area of the objective lens/mirror (also to the square diameter of the lens/mirror)
The greater the collecting power the brighter the images produced
Resolving power
The ability of a telescope to produce separate images of close-together objects
The angle between the straight lines from Earth to each object must be at least the minimum angular resolution for them to be resolved [ θ~λ/D ]
Rayleigh criterion
It is the minimum angle subtended between two objects who’s images can be resolved
Identified at the point where the central maximum of the diffraction pattern from one objects coincides with the first minimum of the diffraction pattern from the second object
Advantages of charged-coupled devices (CCDs)
Has around 80% of quantum efficiency
Can observe infrared, UV and visible light
Can observe for long periods and produce digital images
Radio telescopes
ground base (atmosphere doesn’t absorb rodia waves
Observe 1mm to 10m wavelengths (detect H2 emission lines)
10^-3 rad resolution (low because of large wavelength)
Radio waves won’t be absorbed by dust and are used to map the Milky Way
Only uses a primary dish and it doesn’t need to be as smooth as optical mirrors
UV telescopes
Located in space so it is inconvenient to maintain
Observe 10 to 400nm wavelengths
10^-7 rad resolution (due to short wavelength)
Can detect supernovae and quasars, and used to determine the temperature/ chemical composition of objects
Similar structure + collecting power to optical telescopes
UV mirrors need to be smoother than optical mirrors
IR telescopes
Predominantly located out of space (IR is absorbed by H2O gas so the area must be dry)
Observe 1mm to 700nm wavelength
10^-7 resolution (space), 10^-6 resolution (ground)
Detect warm objects eg. Dust in nebulae and brown dwarfs
Mirrors must be kept very cold to avoid interference
X-Ray & Gamma Rays telescopes
located in space so it is inconvenient to maintain
Observe <10nm wavelength (very high resolving power)
10^-6 rad resolution
Images tent to be extremely bright despite low collective power
Used to observe energetic events eg. Black holes, neutron stars, pulsars, GRBs
Quantum efficiency
(no. of electrons produced per second/no. of photons absorbed per second)*100
Apparent magnitude
Is how bright an object appears in the sky
Absolute magnitude
The apparent magnitude of an object if if is 10 parsecs away from Earth
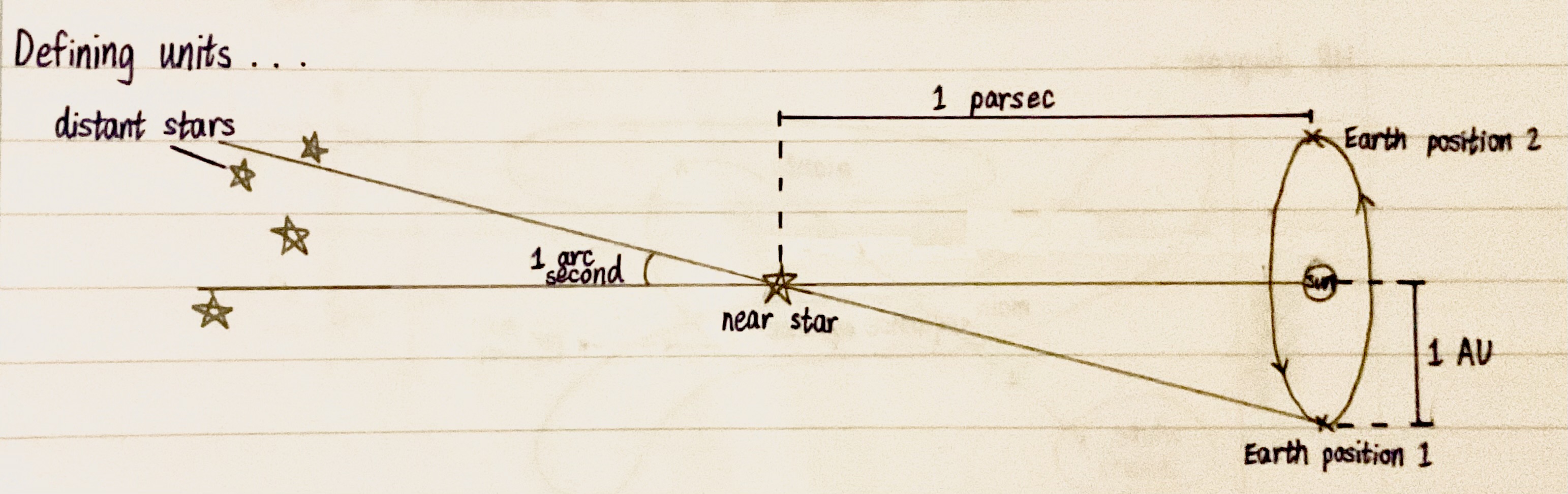
Definition of 1 parsec
Classification of stars
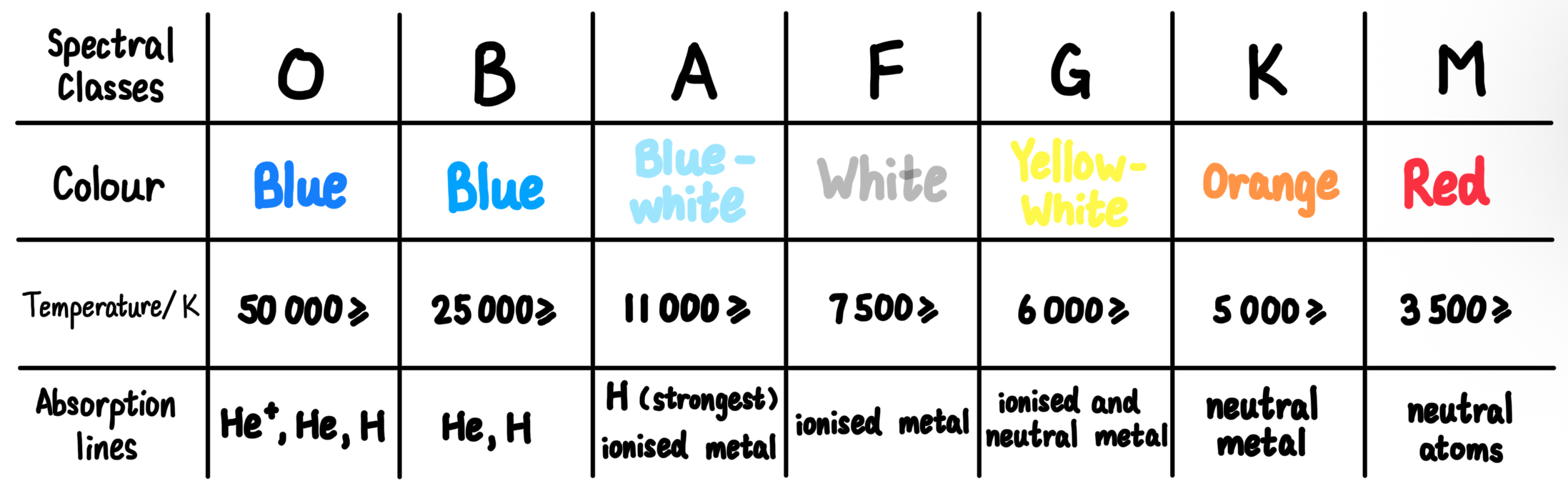
Hydrogen Balmer Lines
Absorption lines found in the spectra of O, B and A class stars
Caused by the excitation of H atoms from the n=2 state to higher/lower states and re-emit light in all directions which reduces light intensity in Earth’s direction
Inverse square law for light intensity
𝐼=𝑃/(4𝜋𝑟²)
HR diagram
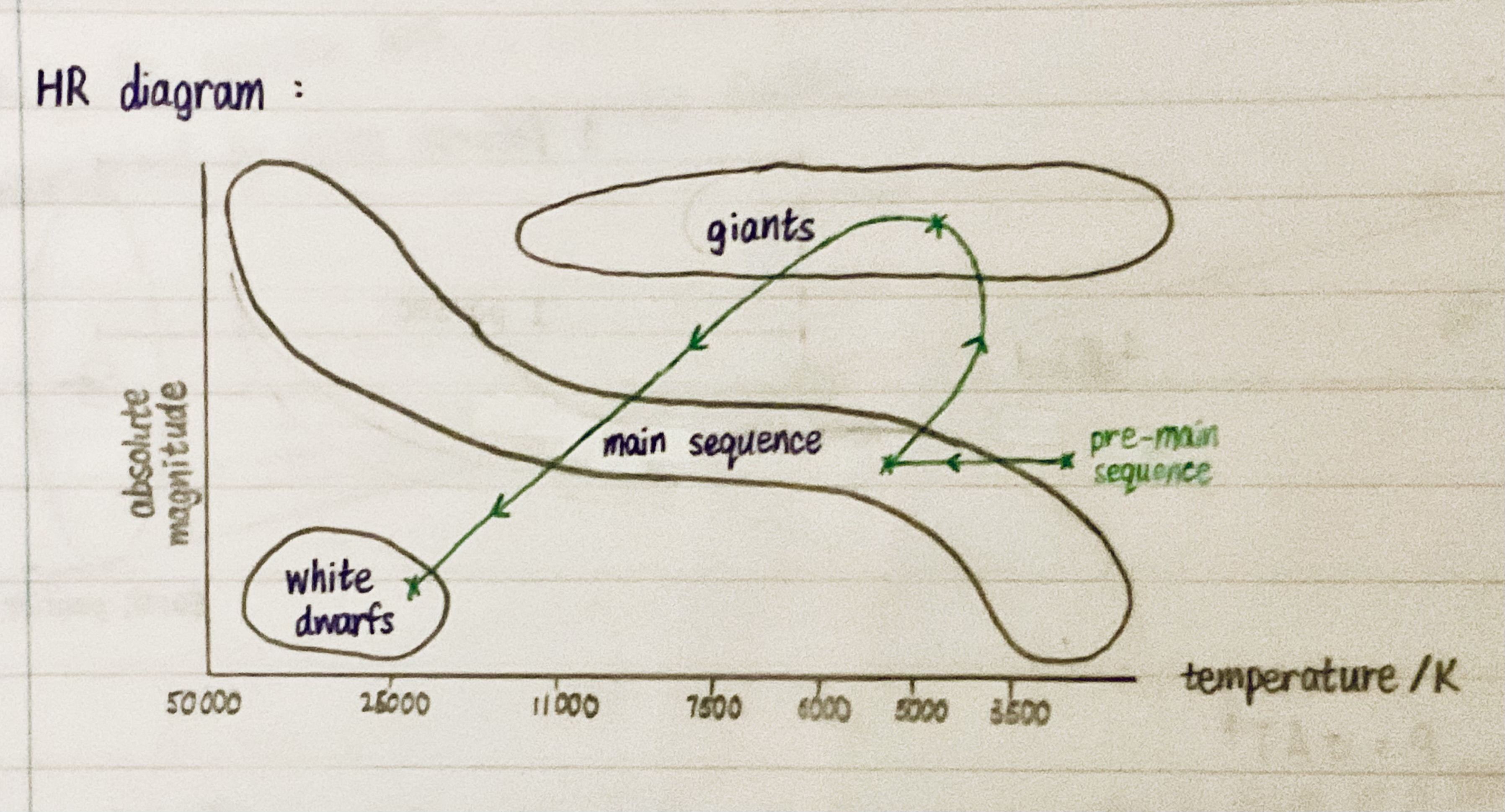
Stages of stellar evolution
Protostar
Main Sequence
Red Giant (for star <3 solar masses)
White Dwarf (for a star <1.4 solar masses)
Red Supergiant (for star>3 solar masses)
Supernova (for star >1.4 solar masses)
Neutron Star (for star between 1.4 and 3 solar masses)
Black Hole (for star >3 solar masses)
Protostar
Clouds of gas and dust of varying masses clump together under gravity
Irregular clumps rotate and gravity spins them inwards to form a dense center (Protostar)
When the protostar gets hot enough, it begins to fuse elements producing strong stellar wind
Main Sequence
Inward force (gravity) and outward force (due to fusion) are in equilibrium
The star is stable
Hydrogen nuclei are fused into helium
The bigger the mass the shorter this period is as fuel is used more quickly
Red Giant
Hydrogen in the center runs out
Outer layers expand and cool
Gravity causes the core to shrink and contract
Temperature of core increases and begins to fuse helium to heavier elements
Surface temperature is less than 4000–5000K but are very bright as they have a very large surface area
White Dwarf
When Red Giant used up its fuel, fusion stops and core contracts as gravity is now greater then the outward force
A planetary nebula is formed around the core as outer layers are thrown off
Core becomes very dense and stabilizes as white dwarf
Very high surface temperature but are very faint due to a small radius
Will eventually cool to a black dwarf
Red Supergiant
When Red Supergiant used up its fuel, fusion stops and core contracts as gravity is now greater then the outward force
It collapse in a supernova causing gamma ray bursts
Can fuse elements up to iron as iron nuclei are more stable than other nuclei
Has low surface temperatures (>4000K) but are really bright due to large surface area
Supernova