HEENT - Ears
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
The otoscopic diagram can be divided into what quadrants
posterosuperior, posteroinferior, anterosuperior, anteroinferior
In hearing conduction, sound waves enter via the ______ and are then transmitted through the ___
base of the cochlea into the cochlear duct; basilar membrane towards the apex
High-frequency sound waves are received by the _____, which is why high frequency hearing loss is ____
base of the cochlea; the first type of hearing we tend to lose
Otoscopic examination requires us to look at (COMPLETES)
C = color
O = other conditions
M = mobility
P = position
L = lighting
E = entire surface
T = translucency
E = external auditory canal and auditory
S = seal
The posterosuperior quadrant allows us to visualize ___
incudostapedial joint and pars flaccida
The anterosuperior quadrant allows us to visualize
lateral process and manubrium of malleus
The anterioinferior quadrant allows us to visualize the
light reflex
The posteroinferior quadrant allows us to visualize the
pars tensa and umbo
AOM epi
preschool age, declines with age
AOM risk factors
previous infections, pacifier, cigarettes
AOM etio
S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, M. catarrhalis, viruses
AOM pathophys
inflammation obstructs the eustacian tube
AOM clinical presentation
children = crying, pulling on ear
otalgia
± fever
AOM PE findings
TM bulging (is MC), erythema or otalgia
middle ear effusion
AOM diagnoses
MEE (middle ear effusion) and inflammation
AOM tx
pain management, antibiotics? (if fever, inflammation, or purulence = give abx)
AOM complications
perforation, hearing loss, labyrinthitis, mastoiditis
AOM with Effusion epi
MC in children
AOM with Effusion risk factors
previous infections, pacifier, cigarettes
AOM with Effusion etiology
usually aseptic
AOM with Effusion clinical presentation
hearing loss (conductive), speech deficit
AOM with Effusion PE findings
TM - color; air fluid levels
mobility - pneumatic otoscopy (air puffer attachment for otoscope)
AOM with Effusion dx
MEE (middle ear effusion), no signs of infection
AOM with Effusion tx
3+ months or speech delay = audiology/speech eval
structural abnormalities = refer to ENT
generally abx are NOT a good option, maybe anithistamines
tympanostomy tubes = hearing loss/structural damage
AOM antibiotic guidance
< 6 months = give abx
6mo-2yr = unilat or bilat = give abx
> 2 yrs = maybe wait and see, look at duration, risk factors, etc
AOM with Effusion complications
conductive hearing loss, tympanosclerosis
Chronic AOM epi
MC in children
Chronic AOM risk factors
frequent AOM, socioeconomics
Chronic AOM etio/pathophys
P. aeruginosa, S. aureus
Eustachian tube
Chronic AOM clinical presentation
otorrhea >/= 2 weeks
hearing loss
usually painless
Chronic AOM PE findings
perforation with otorrhea
Chronic AOM dx
clinical; maybe get a culture
Chronic AOM tx
aural toilet/irrigation
antibiotics
surgery
Chronic AOM complications
mastoiditis, cholesteatoma
Cholesteatoma etio/patho
accumulation of squamous epithelium in middle ear/mastoid
Cholesteatoma epi
MC in children
not every perforation is
chronic otitis media
Cholesteatoma risk factors
recurrent AOM/MEE, frequent tubes, cleft palate, genetics
Cholesteatoma clinical presentation
MC is otorrhea > 2 weeks
new onset hearing loss
Cholesteatoma OE findings, otoscopy
white mass, retraction pocket, pocket of keratinized cells
Cholesteatoma dx
clinical suspicion, CT
Cholesteatoma tx
± tubes, excision
Cholesteatoma complications
hearing loss, CN palsies, venous thrombosis, meningitis
Mastoiditis clinical presentation
recent AOM, otalgia, fever
Mastoiditis patho
involves mastoid air cells
Mastoiditis epi
school aged children
Mastoiditis risk factors
prolonged AOM
Mastoiditis PE findings
postauricular findings, tenderness on the mastoid, more systemic
Mastoiditis dx
hx and PE (looking straight on, one ear can look asymmetric); CT
Mastoiditis tx
abx; refer to ENT
Perforated tympanic membrane cause
change of pressure, AOM, trauma (barotrauma = diving, flying, blast injuries, foreign bodies)
Perforated tympanic membrane hx
head injury, other
Perforated tympanic membrane PE findings
secondary survey (might see blood or other)
otoscopy
Perforated tympanic membrane management
infection = abx
trauma = maybe abx, not always depending on MOA
keep ears dry
ENT evaluation
otitis externa clinical presentation
pruritis, pain
otitis externa etio/patho
swimming, p. aeruginosa, s. aureus
otitis externa epi
older children
otitis externa risk factors
trauma to EAC (external auditory canal); Q-tips
otitis externa PE findings
EAC pain on movement, swelling
otitis externa dx
clinical (push/touch external ear/tragus = likely)
otitis externa tx
topical abx, wick
otitis externa complications
malignant OE, osteomyelitis
types of auditory disorders
bruits
endogenous, maskable tinnitus
exogenous tinnitus
slow brainstem tinnitus
bruits
objective sounds; hear rushing of blood
endogenous, maskable tinnitus
better when other stimuli masks ringing (think, noise bothering you is internally sourced, it gets better when it’s masked with external stimuli)
exogenous tinnitus
better when in silence (think exo is external, cut out all external noise)
slow brainstem tinnitus
among older patients, associated with vertigo, dizziness
auditory disorder treatments
instrumentation = ambient noise, hearing aids
pharmacotherapy = lidocaine, benzos, neurontin
other therapies = retraining, hypnosis, OMM
when irrigating an ear, always use….
warm (NOT hot) water, check for nystagmus afterwards
dizziness etio
heart, brain, or ear related issues
dizziness etio - more history
ROS = cardiovascular, neuro, ENT
medications
time and provoking/aggravating factors
dizziness PE findings/things to look for
orthostatic issues, neuro findings
lab studies should include EKG; ± labs and imaging, check for nystagmus
acute vestibular syndrome is ______; can be related to ____
acute onset of dizziness, persistent and continuous
posterior circulation ischemic stroke, vestibular neuritis/labyrinthitis, posterior fossa hemorrhage, Wernicke syndrome
vestibular neuritis patho
viral or postviral to CNVIII (vestibulocochlear n)
vestibular neuritis clinical presentation
vertigo, N/V, gait instability
vestibular neuritis PE findings
nystagmus - suppressed with visual fixation
gait instability, no neuro deficits
head thrust, rapidly turn head to one side to see if you can induce/stimulate nystagmus
vestibular neuritis dx
clinical; rule out other neuro bad things, can get CT/MRI if highly sus
vestibular neuritis tx
usually self-limited; can give steroids if needed to treat symptoms
Meniere’s disease definition
Idiopathic, distention of endolymph in inner ear
Meniere’s disease epi (syndrome vs disease)
Typically, middle age (20-40 y/o)
Meniere syndrome = identifiable cause
Meniere disease= idiopathic
Meniere’s disease pathophys
fluid build up, abnormal ion homeostasis
Meniere’s disease clinical presentation
episodic vertigo, tinnitus, hearing loss
Meniere’s disease dx
takes time, vertigo x2 episodes
SN hearing loss
tinnitus
Meniere’s disease tx
treat symptoms, ENT eval
watch triggers
meclizine, benzos, HCTZ
types of triggered episodic vestibular syndromes
benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BBPV)
orthostatic hypotension
central paroxysmal positional vertigo
benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BBPV) pathophys
canalithiasasis (little stone is semicircular canals)
benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BBPV) clinical presentation
episodic vertigo provoked by head movements; no neuro complaints
benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BBPV) exam
Dix-Hallpile manuever
benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BBPV) dx
history and exam
benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BBPV) tx
“particle repositioning”, Epley manuever
acoustic neuroma epi
not common, incidental
acoustic neuroma patho
Schwann cell tumor to CNVIII (vestibulocochlear)
acoustic neuroma risk factors
neurofibromatosis type II, occupational noise, radiation acoustic neuroma
acoustic neuroma clinical presentation
hearing loss, tinnitus
acoustic neuroma PE findings
SN loss, CN exam
acoustic neuroma dx
audiometry, CT/MRI if other CN deficits present
acoustic neuroma tx
surgery, radiation
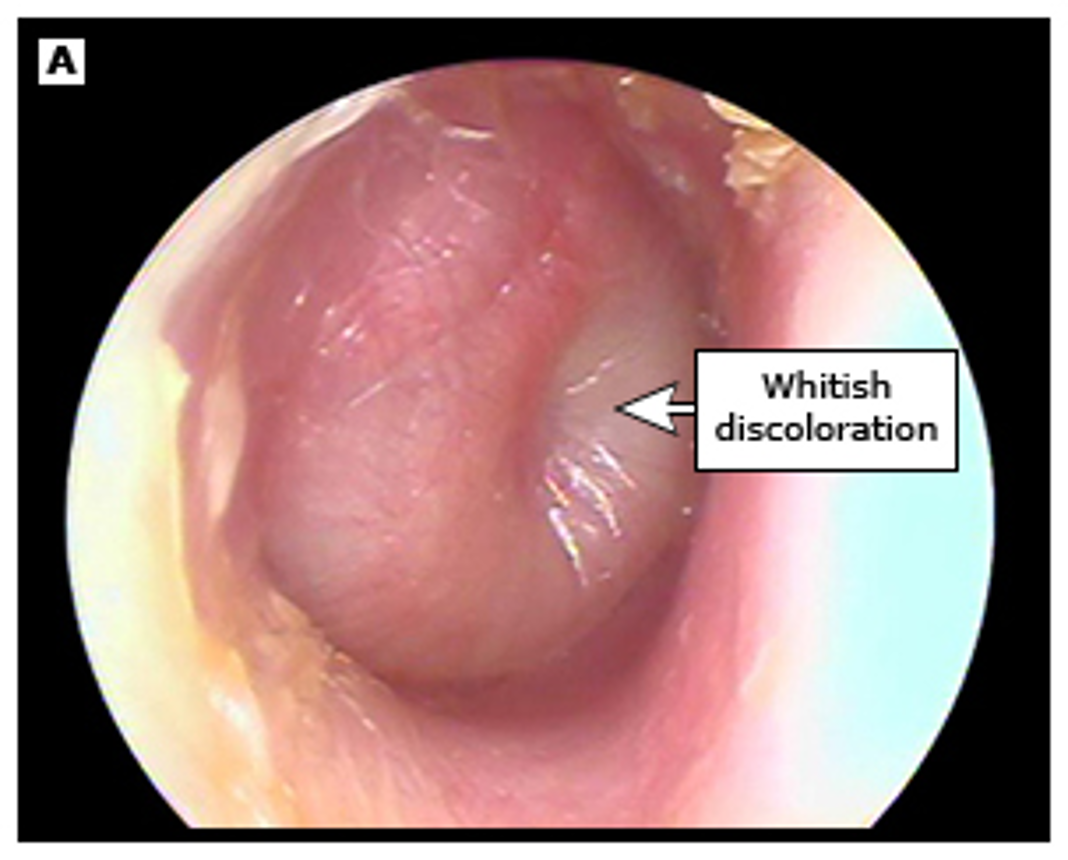
AOM, bulging TM over malleus
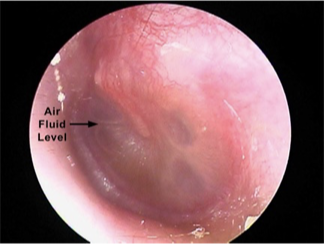
AOM with effusion, can see bubble outlines, still has TM bulging over malleus
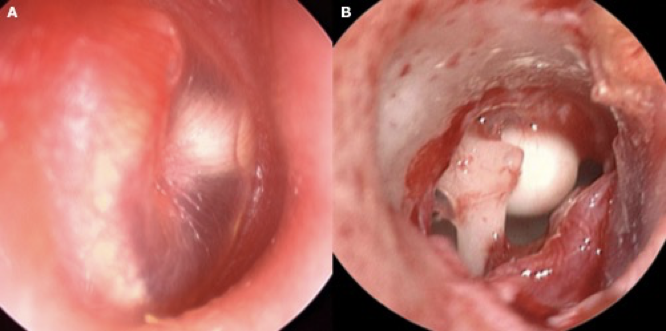
Cholesteatoma = white mass, retraction pocket