Isomers
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What is an isomer?
It is a group of compounds which :-
Have the same Molecular formulae but different arrangement of atoms in bond line and 3d too
They have the same degree of unsaturation
What is tautomerism
The intermolecular transfer of a Hydrogen ion (H+)
What is the full form of Z and E in Geometric isomers?
Z → Zusammen
E → Entgegon
If 2 substituents are on the same side (Show Cis) of the restricted atoms, then what are they called? What is their opposite (Showing Trans) called?
They are called syn; Anti - syn
What is the formula that we will use to find out the possible number of combinations of GI in an unsymmetrical non-cyclic compound
Total number of GI = 2^n
Where,
n = number of double bonds present in the compound
What is the formula that we will use to find out the possible number of combinations of GI in a symmetrical non-cyclic compound

What is a chiral carbon?; What is its opposite called?
It is a type of carbon where all 4 bonds have different groups attached to it; achiral carbon
What are the three possibilities in a PPL, what are they called?
If PPL does not rotate → Compound is optically inactive.
If PPL does Clockwise rotation → Dextrorotatory compound.
If PPL does Anticlockwise rotation → Levorotatory compound.,
What is the formula for specific rotation? What is its formula?
It is the observed rotation when the conc of the organic compound is 1 gram/ml and the length of the polar tube is 1 decimeter

What are enantiomers?
They are different compounds that are non-superimposable on each other but are mirror images of one another
What are diastereomers?
They are different compounds that are non-superimposable on each other but are not mirror images of one another
What is achiral compounds?
Compounds that have more than 1 carbon, but these carbons don’t necessarily have different groups attached to them for all their bonds
What is the process that separates the racemic mixture called?
Resolution is the name of the process
What was the standard compound used to compare other compounds in D/L configuration? What is its structure??
Glyceraldehyde
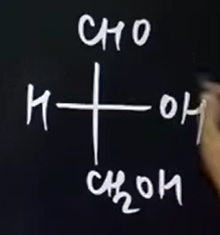
How would you name the copmounds in D/L configuration?

What are erythro and threo?
erythro → Same groups are on the same side
threo → Similar groups are on the opposite side
What is the formula that we will use to calculate the number of optical isomers if the compound is unsymmetrical?
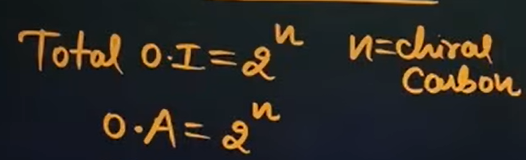
What is the formula that we will use to calculate the number of optical isomers if the compound is symmetrical, where n = even?
n → Number of chiral carbons
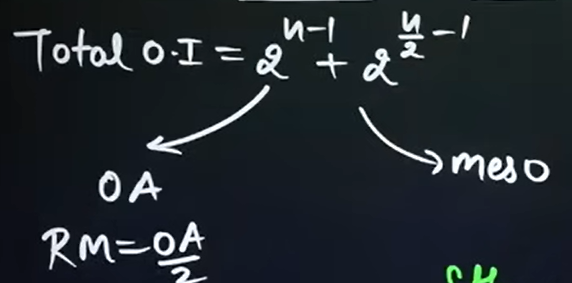
What is the formula that we will use to calculate the number of optical isomers if the compound is symmetrical, where n = odd?
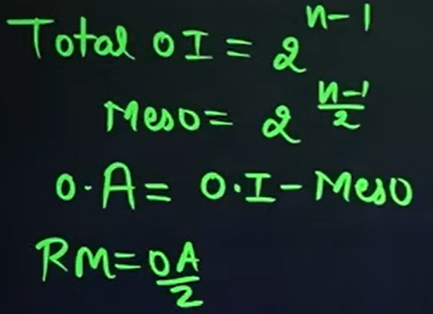
What is the formula for calculating the number of stereoisomers?
Where,
Geometrical area → The number of double bonds due to which Geometrical isomerism is showing
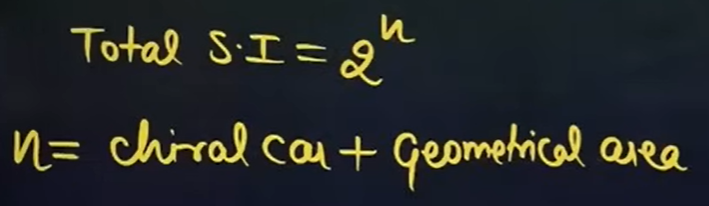
What is the formula for calculating the number of Stereocenters?
Where,
Geometrical centres → The number of restricted sites

What is a diheadral angle?
It is the angle between two bonds on opposite carbons, measured in the plane perpendicular to the central bond.
What is anti in Newman’s projection?
It is a type of projection where the largest groups are 60 degrees apart from each other (Dihedral angle)
What is gauche in Newman’s projection?
It is a type of projection where the largest groups are 180 degrees apart from each other (Dihedral angle)
What is partially eclipsed in Newman’s projection?
It is a type of projection where the largest groups are 120 degrees apart from each other (Dihedral angle)
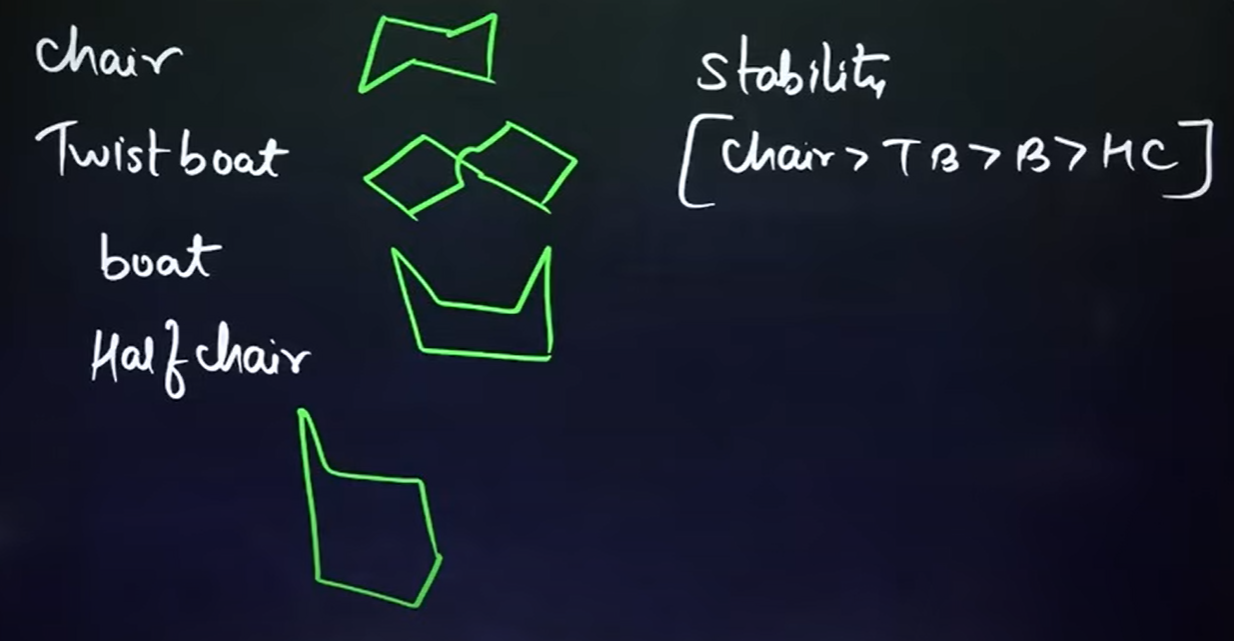
What are the different types of isomers seen in cyclohexanes? What is their order of stability?