aggregate demand and aggregate supply (chap 19-21)
1/72
Earn XP
Description and Tags
circular flow of income, aggregate demand, aggregate supply, multiplier and accelerator affect
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
demand
willingness to buy and sell goods and services at a given price point
aggregate
mass/ as a whole
wealth effect/ income effect
when the general price level rises/ falls allowing households to have less/ more wealth as they have more or less purchasing power
aggregate demand
measure for the total level of goods and services demanded in an economy, based on general price level and demand
what is the equation for aggregate demand and what does each component stand for
C+I+G+(X-M) consumption + investment/ inventories + government spending + (exports - imports)
capital labour
machinery making things
recession
two consecutive quaters of negative economic (GDP) growth
recovery
return from negative gdp growth to positive gdp growth
boom
significantly high gdp growth in a given time
slump
sudden fall of rapid economic growth
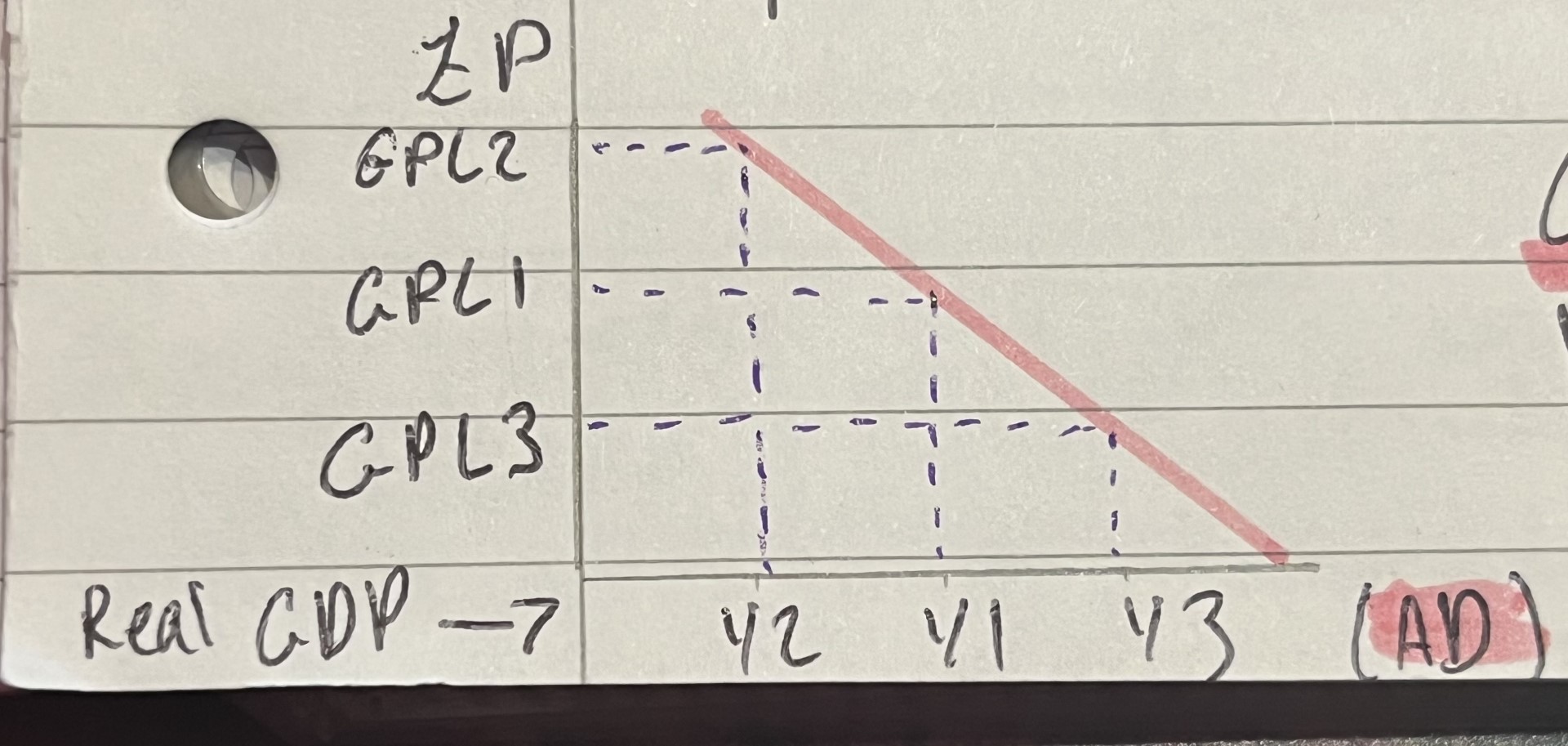
explain the ad graph / curve
when prices levels are too high ad contracts and when general price level decreases ad expands
what does gpl stand for
general price level, shows at what price goods and services are currently at, GPL3 is the highest and GPL1 is the lowest
what does y stand for
income, y1 is the lowest and y3 is the highest
recovery
return from negative gdp growth to positive gdp growth
explain the circular flow model including how each element interacts with each other
the interaction of economic agents exchanging money, households give governments taxes and governments give households welfare benefits
governments give firms money through purchasing, firms give governments taxes
households purchase goods and services from firms, firms provide rent wages dividends and labour to households
the external sector brings in and takes out goods and services
gdp
gross domestic product, shows actual value of expenditure over a given period
examples of injections
exports, capital spending such as investing in machinery, government investment such as hs2
leakages/ withdrawls
money leaving the domestic economy
examples of leakages
savings, imports, payments to the government such as taxation
commodity
product that is bought and sold globally e.g diamonds, flour
dynamic prices
prices that continuously fluctuate such as oil
factors affecting consumption
income, taxes, inflation, wealth, trends, interest rates, consumer confidence, unemployment
balance of trade effect
fall of prices in an economy could cause foreign imports to be more expensive increasing exports and decreasing imports
interest rate effect
if inflation is low, interest rates may reduce which encourages people to spend rather than save which increases exports as other countries can afford our goods and services
shift
a new line on a curve
what does SPICED stand for
strong pound means imports cheaper exports dearer
factors causing shifts in the aggregate demand curve
changed in income and employment, government spending, monetary policy, countries exchange rates, economic partner nations growth (slower, faster), consumer and business confidence
simply, changes in C+I+G+(X-M)
what are the four elements to the circular flow model
households, businesses/firms, government, external sector
domestic circular flow
circular flow diagram only with households, governments and firms
external shock
external events to the domestic economy that impact the local aggregate demand e.g covid
when we study supply, who do we refer to
businesses and firms rather than consumers
aggregate supply
total amount of goods and services available to buy
sras
short run aggregate supply, how supply is in the short run and how much the economy can generate in a short term at each price level
what does the sras curve represent
the relationship between planned national output and the general price level
what two things are always assumed to be consistent when drawing the sras curve
state of technology is the same, production costs are the same
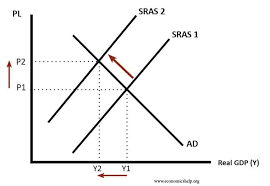
when will the sras curve shift
when there is change in finance/ costs to a business
what factors cause the sras shift
unit wage cost e.g higher minimum wage, labour productivity (economies of scale), raw material or component prices, business taxes such as VAT, exchange rate on imports, supply shocks such as war
basically always think of costs to the firm
injection
money coming into the domestic economy
lras
long run aggregate supply, the ability of an economy to produce goods and services based on the state of production, technology and quality of factor inputs
what four factors affect lras
capital land labour enterprise
rise / expansion of ad causes
rise in house prices, depreciation of exchange rates, tax cuts, higher interest rates
what causes a shift in long run aggregate supply
quantity of factor inputs and the effectiveness of the inputs
what does an outward shift of lras show
economic growth
give some examples of what causes a shift in lras
higher productivity of labour, increased efficiency of technology, growing population for a larger workforce, higher competitiveness in international markets due to more entrepreneurship, capital investment such as fdi
stock of natural environmental resources
the ability of an economy to find and harness their natural resources in a sustainable way
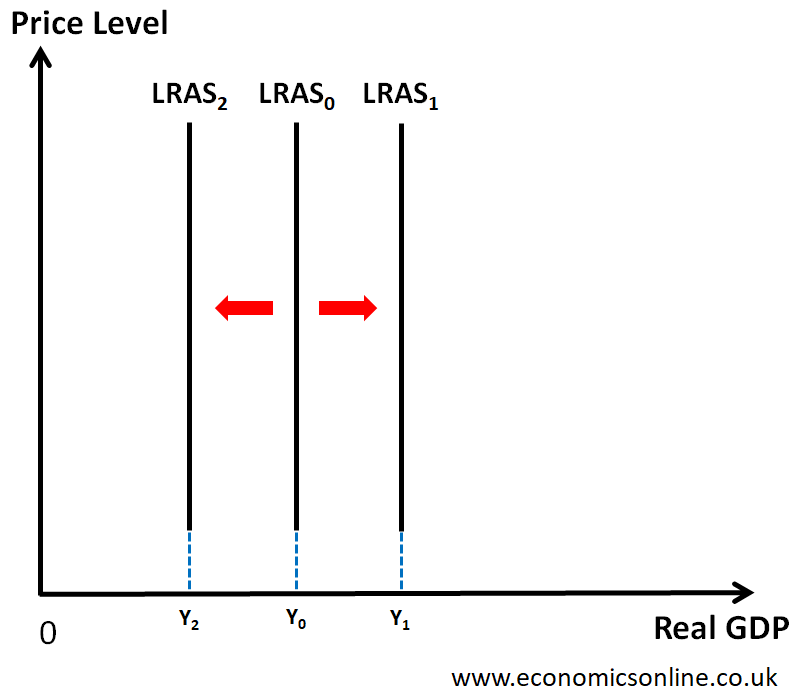
explain the classical lras curve including reasons for shifts
vertical line that assumes the economy is always operating at full employment, change in price level does not affect the curves position, shifts outwards when quantity or quality of goods increases or when costs decrease, shifts inwards when decrease in amount of resources or quality or when costs increase
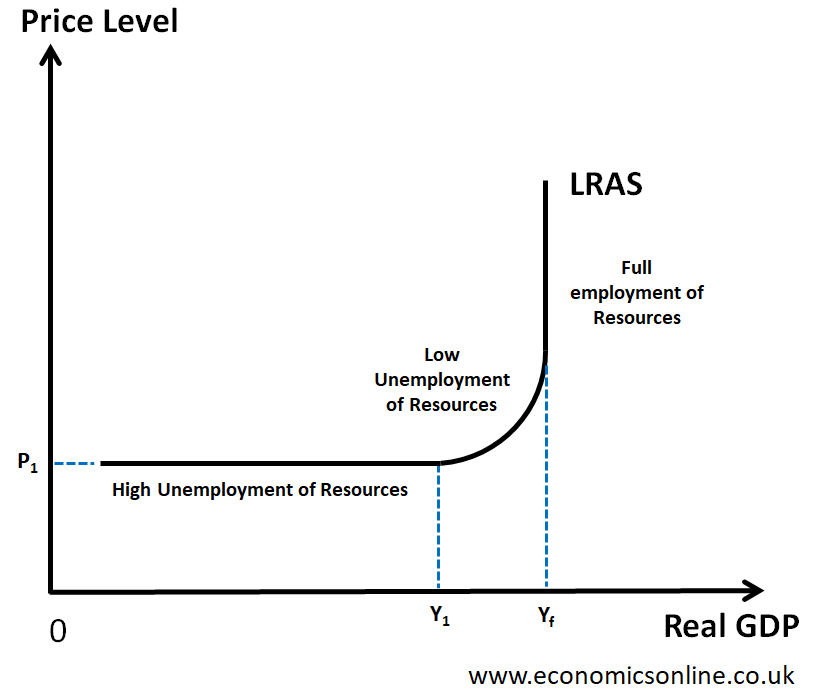
explain the keynesian lras curve
a non linear supply curve that shows how firms are able to supply based on levels of employment, demand can change with or without changes in the general price level
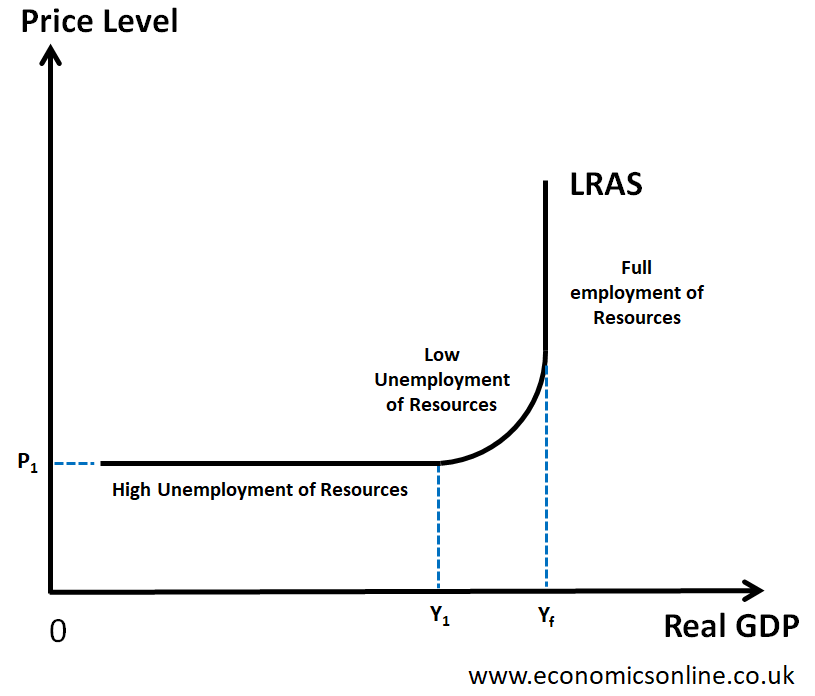
spare productive capacity in relation to keynesian lras
when businesses are able to produce more as they are not operating at full capacity, shown at any point on the curve before it moves vertically (full capacity)
what is price elasticity of demand, when are prices elastic during keynesian lras and why
where the change in gpl of a good or service causes the supplyor demand to change such as in food or luxury goods, shown in the horizontal portion of the keynesian lras curve, price elasticity reduces when the curve slopes upwards
where on a curve would non inflationary economic growth occur
ad lines movement along the horizontal portion of the curve
demand pull inflation
demand rises higher than supply causing the rise in prices as supply is scarce
when can and cant businesses react on a keynesian lras curve
during price elasticity they can react, during price inelasticity they cannot react
negative output gap
when the economy is operating below full employment so their maximum output is not fulfilled
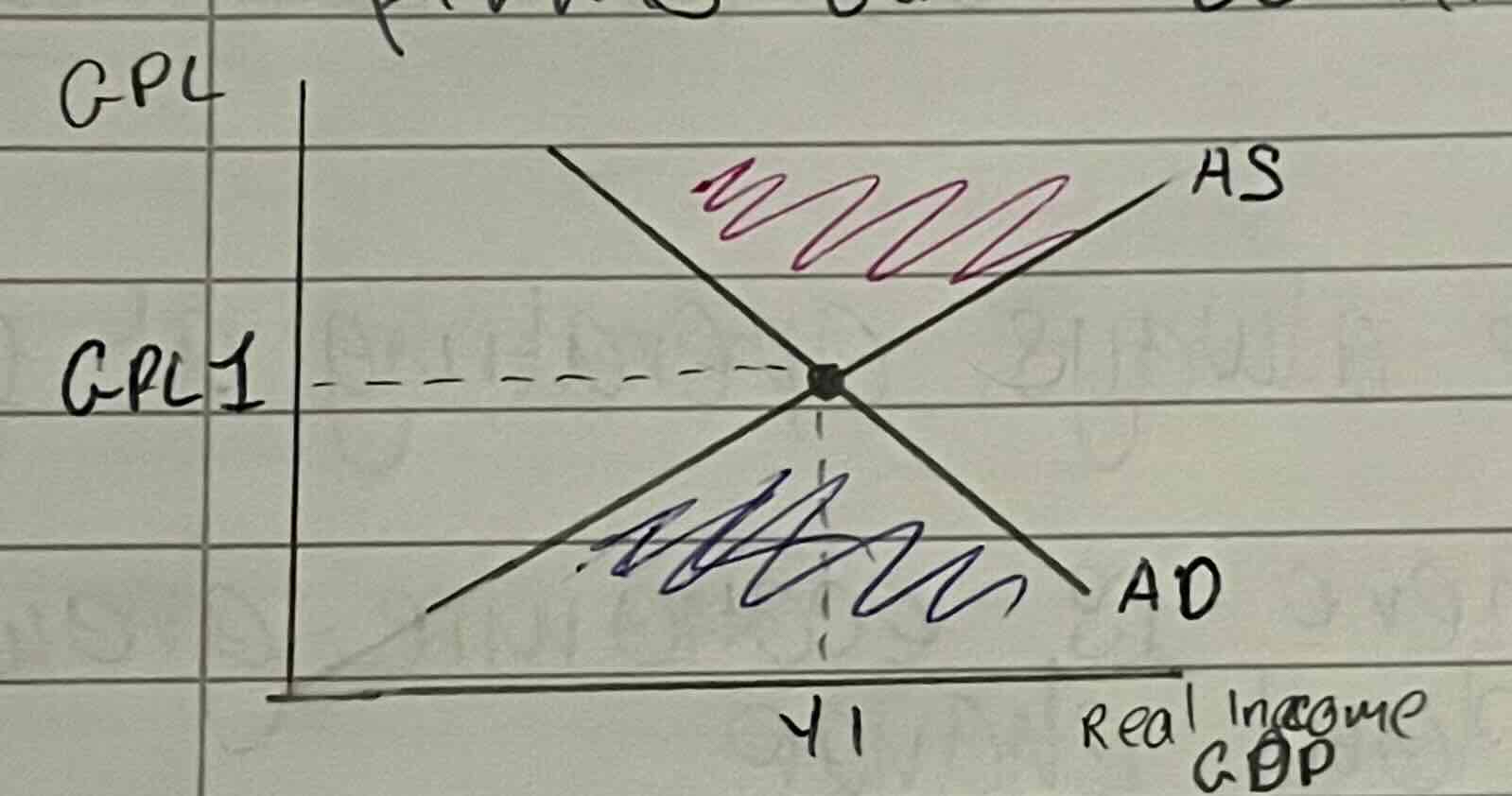

macroeconomic equilibrium
where aggregate demand = aggregate supply as consumers are willing to pay the price firms are willing to charge
real gdp
gross domestic product adjusted for inflation
diminishing marginal returns
as each new unit of production is increased, returns begin to reduce and the ratio of returns to factor inputs decreases
what is the multiplier
ratio of change of equilibrium income to the actual change that is brought about
who thought of the multiplier
keynes
what is the formula for the multiplier
1/ MPW which includes mps mpt and mpm
what is an example of the positive multiplier effect
a gigafactory being builts as the revenue generates jobs which generates incomes which get used in the local and wider economy
MPW
marginal propensity to withdraw, consists of MPS MPT and MPM, measure of tendency to take money out of the circular flow of income
MPS
marginal propensity to save, measure of how much additional income that is earned is saved
MPT
marginal propensity to tax, measure of how much additional income that is earned is spent on taxes
MPM
marginal propensity to import, measure of how much additional income that is earned is spent on imports
MPC
marginal propensity to consume, measure of how much additional income that is earned is spent
what/who should the government focus on to increase ad
those with a high marginal propensity to consume as they will spend a larger proportion of their income, usually those on low incomes as they have minimal marginal propensity to save
multiplier affect
the ratio of change in national income following a change in government spending
what are some variables impacted by the multiplier
unemployment, economic growth, spare capacity in the economy (AD increase may not be able to be met by firms), exchange rates, inflation
spare capacity
where a business doesnt make full use of its supplies such as capital and labour which means they are producing below full capacity
negative multiplier effect
initial withdraw or leakage in CFI results in a bigger final drop in GDP
accelerator
effect where firms see increased demand so will turn to more investment to expand their output
what does the accelerator do to supply
shifts it outwards
how do the accelerator and multiplier interact
multiplier results in more income being spent and going round the economy which increases demand which tells firms to expound their output and invest resulting in the accelerator