Volcanoes ( Earth Science )
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
From Filipi Know
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Volcanism
geological process where hot molten rock from underneath the earth reaches the surface through an opening in the ground.
volcano
most recognizable form of an opening, where molten material flows out onto the surface during a volcanic eruption.
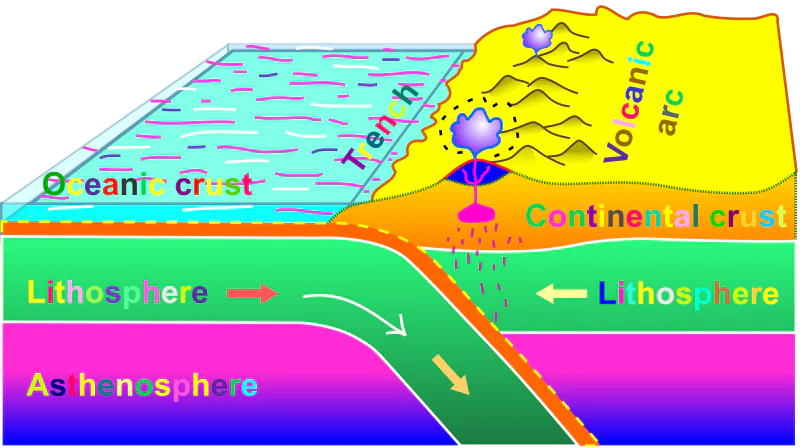
Convergent Boundaries
partial melting occurs in subduction zones, which are responsible for the heating and partially melting of the rocks in the overlying plate
volatiles
(seawater, water from minerals, and other fluids) from the oceanic lithosphere, lowering the surrounding rocks’ melting temperature. The molten rock then starts to ascend to the surface in the form of volcanic activity.
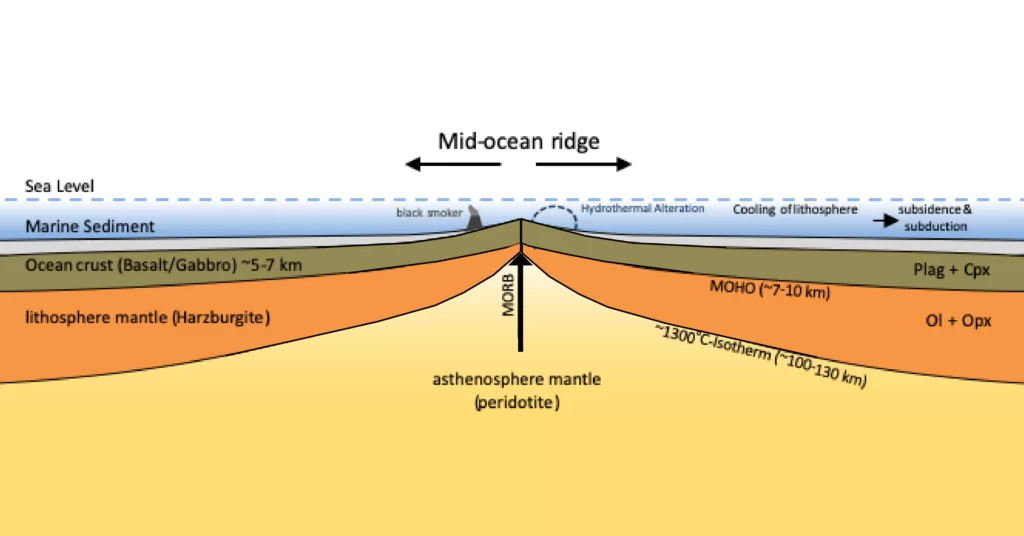
Divergent Boundaries
When plates move apart, pressure in the lithosphere reduces
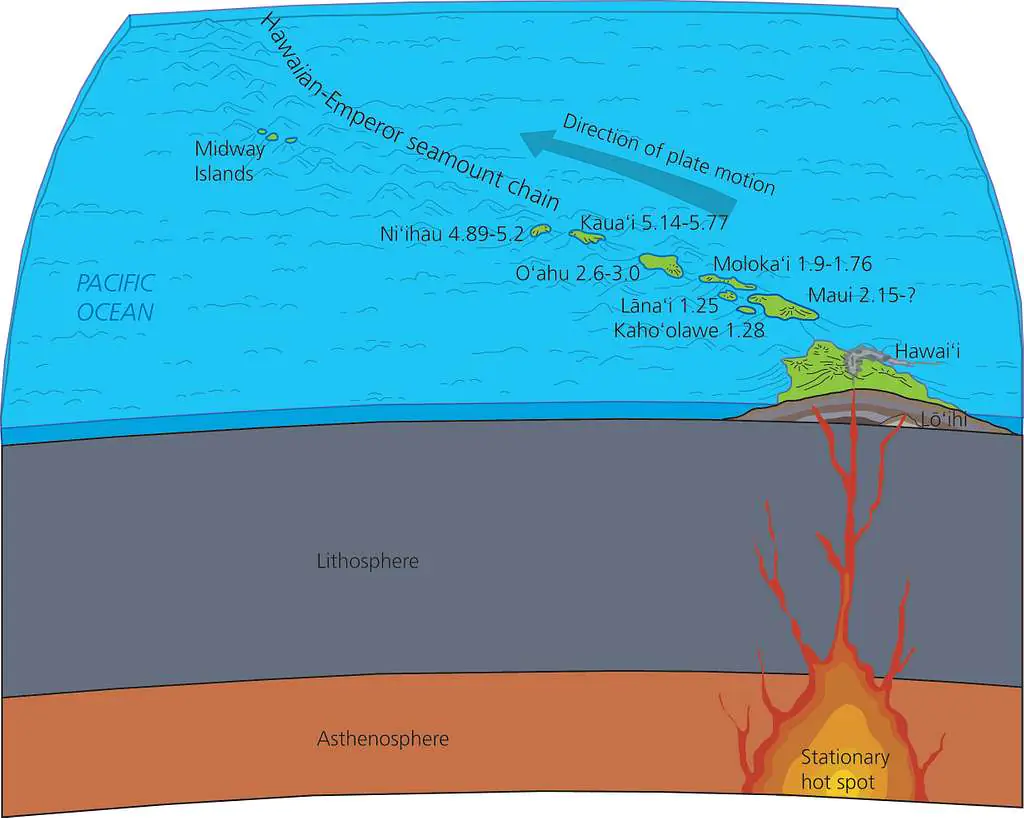
Hotspots and Mantle Plumes
As volcanoes move away from the hotspot, they become inactive, subside, erode, and drop below sea level. This image shows the ages of the Hawaiian Islands in millions of years.
Mantle Plumes
Areas where the mantle rises towards the surface
Hotspot
Surface manifestation of a mantle plume
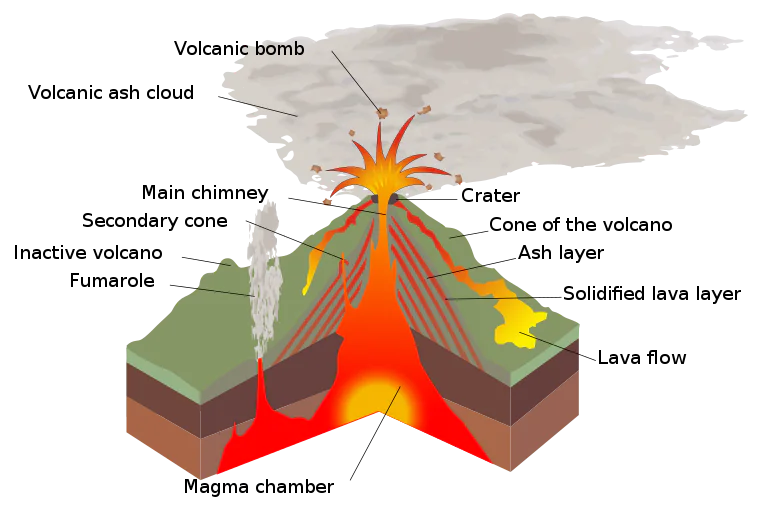
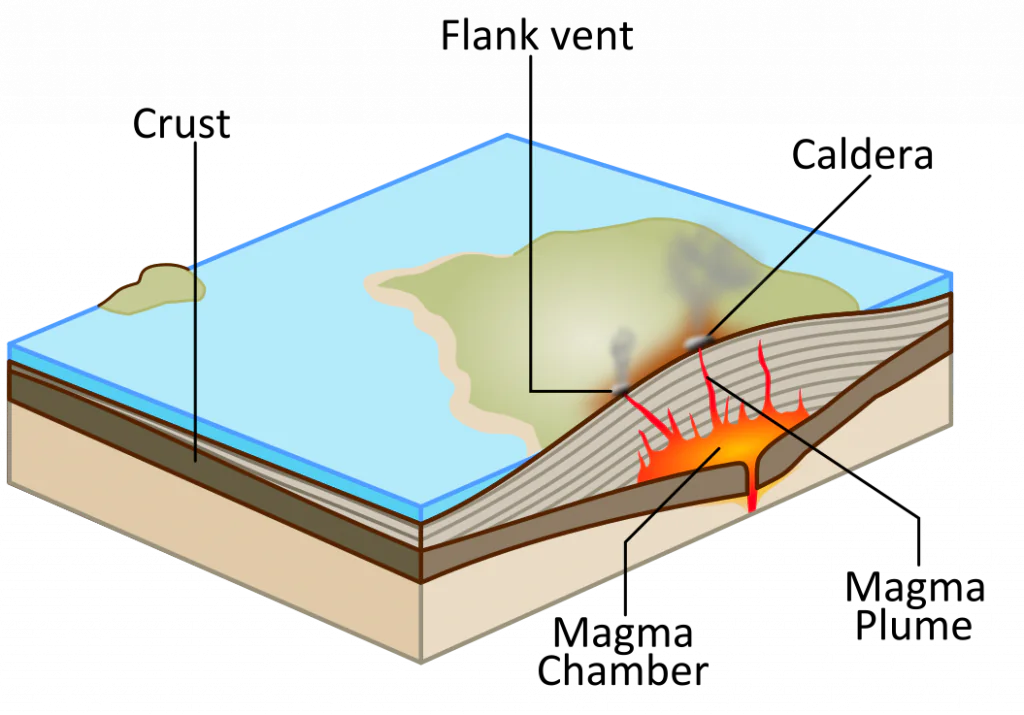
Volcano Morphology
Different types of volcanoes have different shapes and sizes. However, most volcanoes share certain characteristics. Here is the anatomy of a generalized volcano
Magma Chamber
the reservoir of molten material in the Earth’s crust, replenished with magma from a deeper reservoir in the mantle
Main vent
pathway for magma to come
Crater
Bowl-shaped located at the summit of the volcano serves as opening of volcano
Second cone
smaller parasitic volcanoes
usually emit volcanic gas called fumaroles (openings in the earth's surface that emit steam and volcanic gases, such as sulfur dioxide and carbon dioxide)
Pyroclastic materials
any volcanic material
such as bombs, blocks, ashes, and others
Shield Volcano
- Large dome- shaped volcanoes with broad gentle slopes and large craters.
- fast-moving basaltic lava flows.
- non-explosive
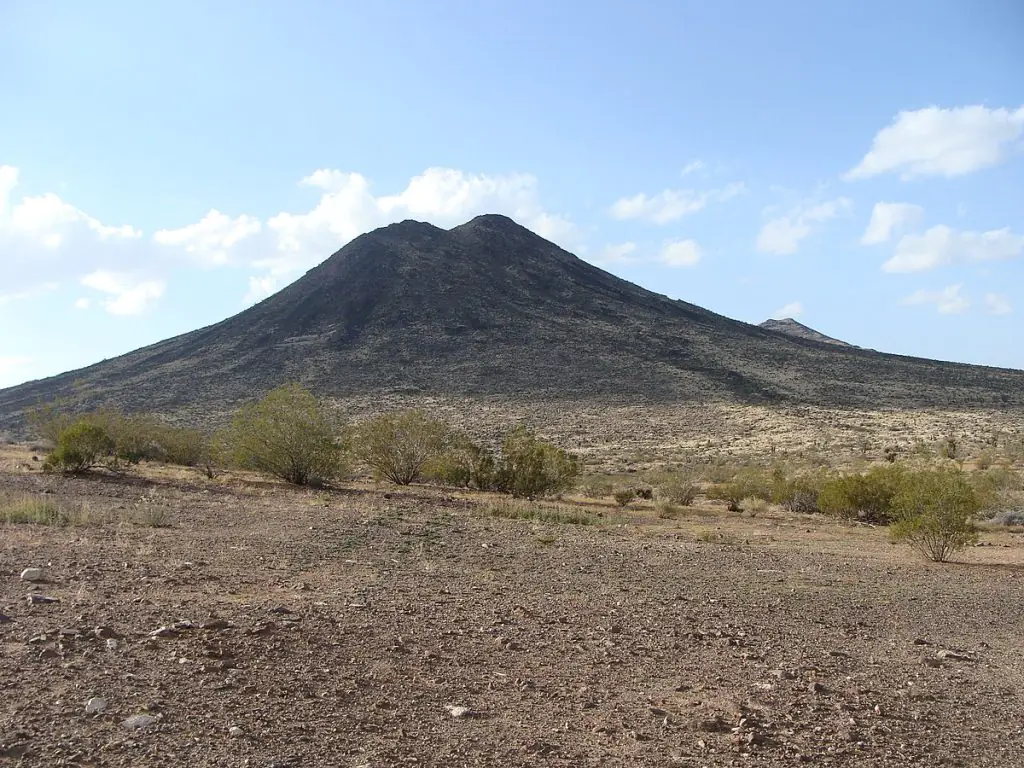

Cinder Cones
are steeper and have smaller crater
- Moderately explosive
- short lifespan (common type of volcano)
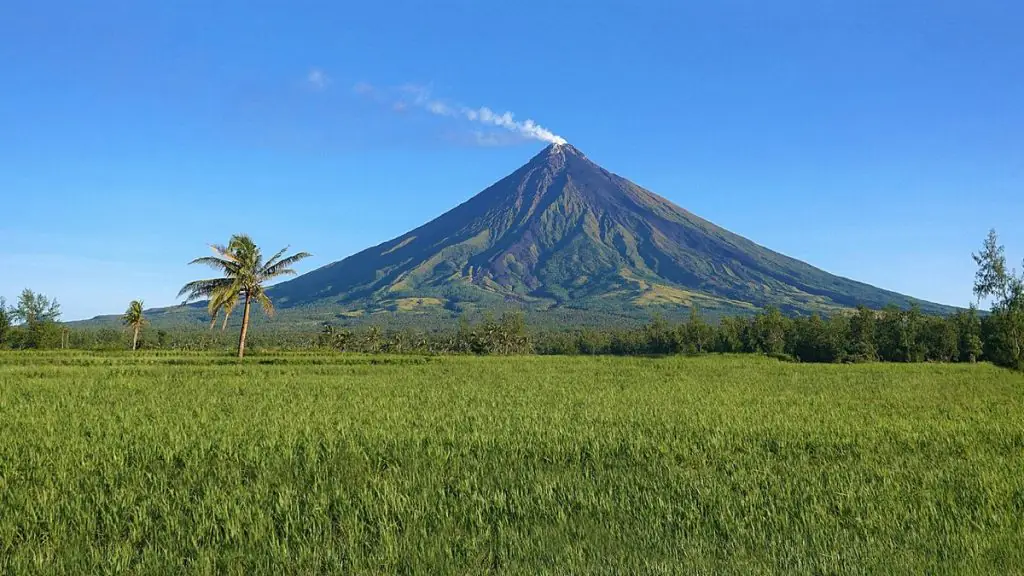

Composite Volcanoes or Stratovolcanoes
Symmetrical steep-sided cone-shaped morphology
- andesitic lava flows (an extrusive usually dark grayish rock)
- Eruptions tend to be violent explosive
caldera
forming large depression called a caldera
pyroclastic flow
rapidly-moving current of hot gasses and tephra (all pieces of all fragments of rock ejected into the air by an erupting volcano)
explosive eruptions
Lahars
volcanic material becomes saturated with water
Lava flows
spread out over large distances
aa flows (ah-ah
spiky and rough
pahoehoe flows (pa-hoy-hoy)
ropey appearance with smooth surfaces
pillow lavas
smooth rounded shapes
When hot molten materials reach the surface, we call these materials as _________.
Lava
Lava refers to the hot molten materials that reach the surface
_____________ have symmetrical cone-shaped morphology. Famous examples are the Mt.
Stratovolcanoes
Stratovolcanoes, also known as Composite Volcanoes, have symmetrical steep-sided cone-shaped morphology. Examples of Stratovolcanoes are Mt. Fuji and Mt. Mayon.
Which of the following describes what a caldera is?
a large depression formed when a stratovolcano collapsed from an explosive eruption
Caldera refers to a large depression that was formed when a stratovolcano collapsed from an explosive eruption
How many active volcanoes are there in the Philippines?
24
Out of 407 volcanoes in the Philippines, 24 are active volcanoes
How do shield volcanoes get their broad form?
accumulation of basaltic lava flows
Shield volcanoes obtained its broad form due to the accumulation of layers of runny, fast-moving basaltic lava flows.