CASE STUDY - Amazon Rainforest
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Where are tropical rainforests typically located in relation to the equator?
5’ North and South of the equator
What are the key climatic characteristics of tropical rainforests?
humid climate - hot and wet all year round
annual rainfall of > 2000 mm
Annual temperature of 26’C (so, no distinct seasons)
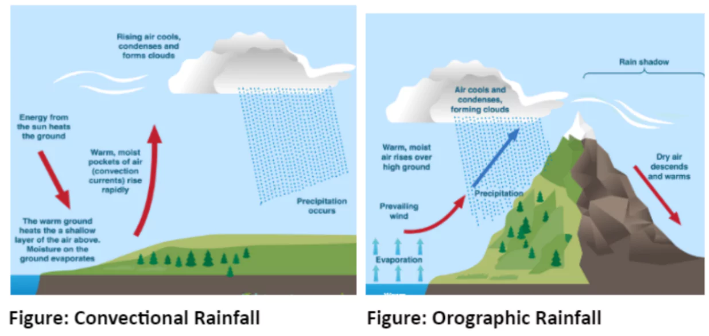
Describe the difference between convectional and orographic rainfall.
Convectional
It occurs in tropical rainforests regions when the ground is heated up by the sun, causing evaporation of moisture
This then condenses in the air, creating clouds, which then rain.
Orographic - also known as ‘relief rainfall’
It occurs in tropical rainforests regions regions when air carrying moisture is forced to rise over mountains
This causes the air to condense, forming clouds which then rain over the highland areas
Describe the location and size of the Amazon Rainforest.
It is located in South America, covering an area of over 6 million km² .
70% of the Amazon is in Brazil, but it extends to Peru, Ecuador, Venezuela, Colombia, Bolivia and Guyana.
How many trees are found in the Amazon Rainforest, and what types are the most common?
There is a dense vegetation of approximately 400 billion trees, mostly hardwood evergreen trees like mahogany and rubber trees.
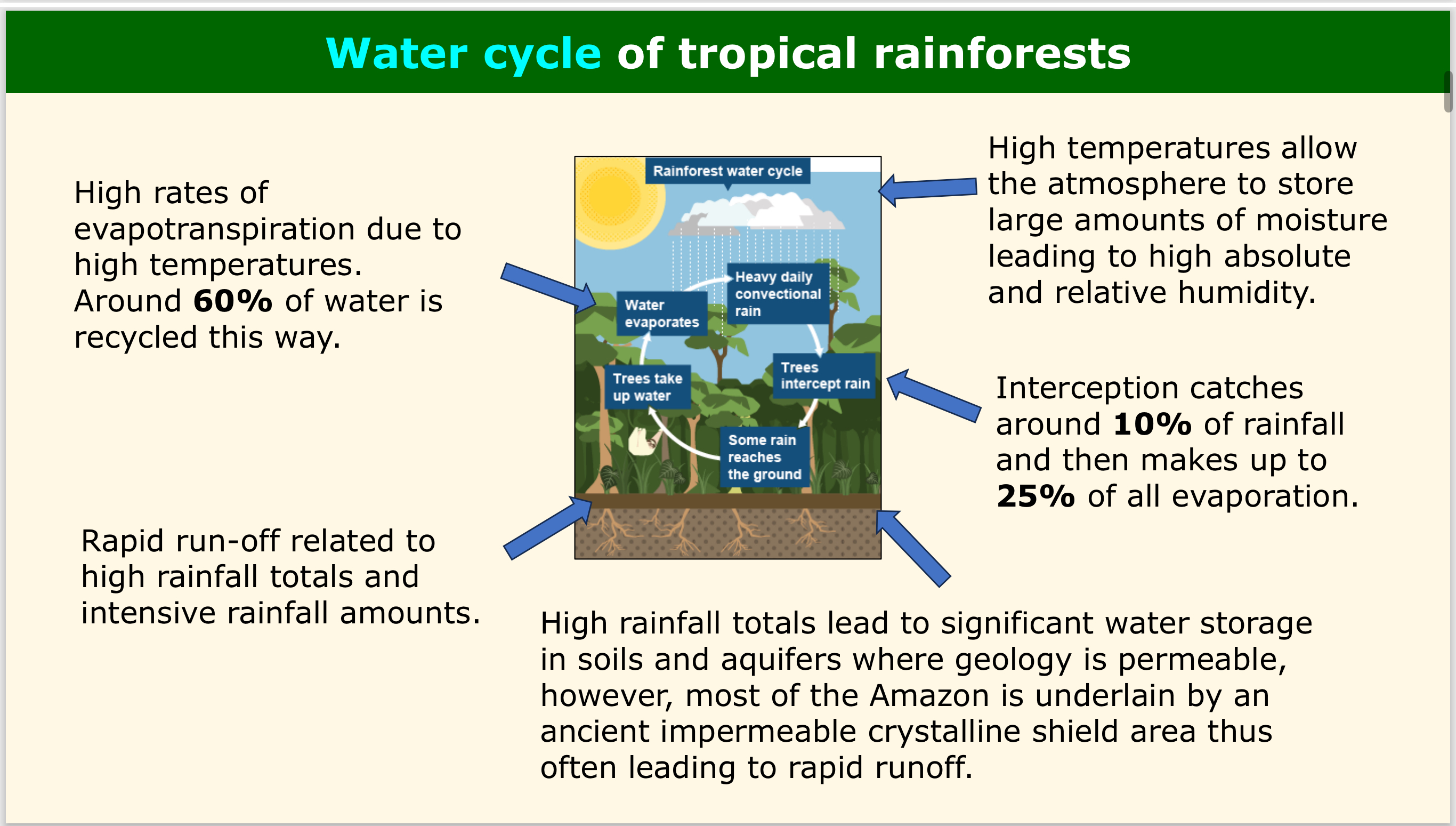
WATER - What % of water in the rainforest is recycled by evapotranspiration?
Around 60%, high rates of evapotranspiration are due to high temperatures.
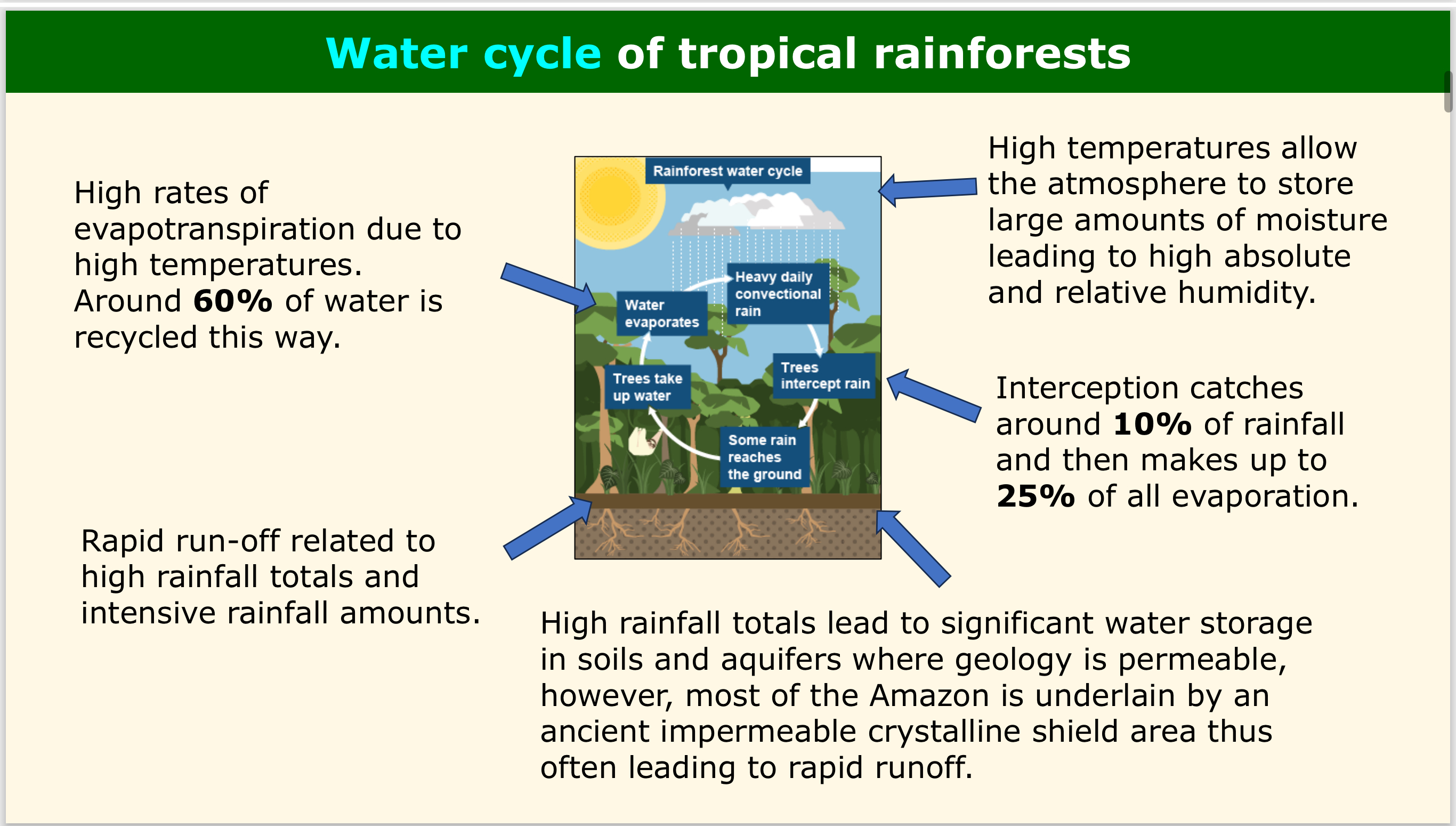
WATER - How does the impermeable crystalline shield in the Amazon affect water storage and runoff?
The Amazon geology is impermeable, leading to rapid runoff and decreased water storage.
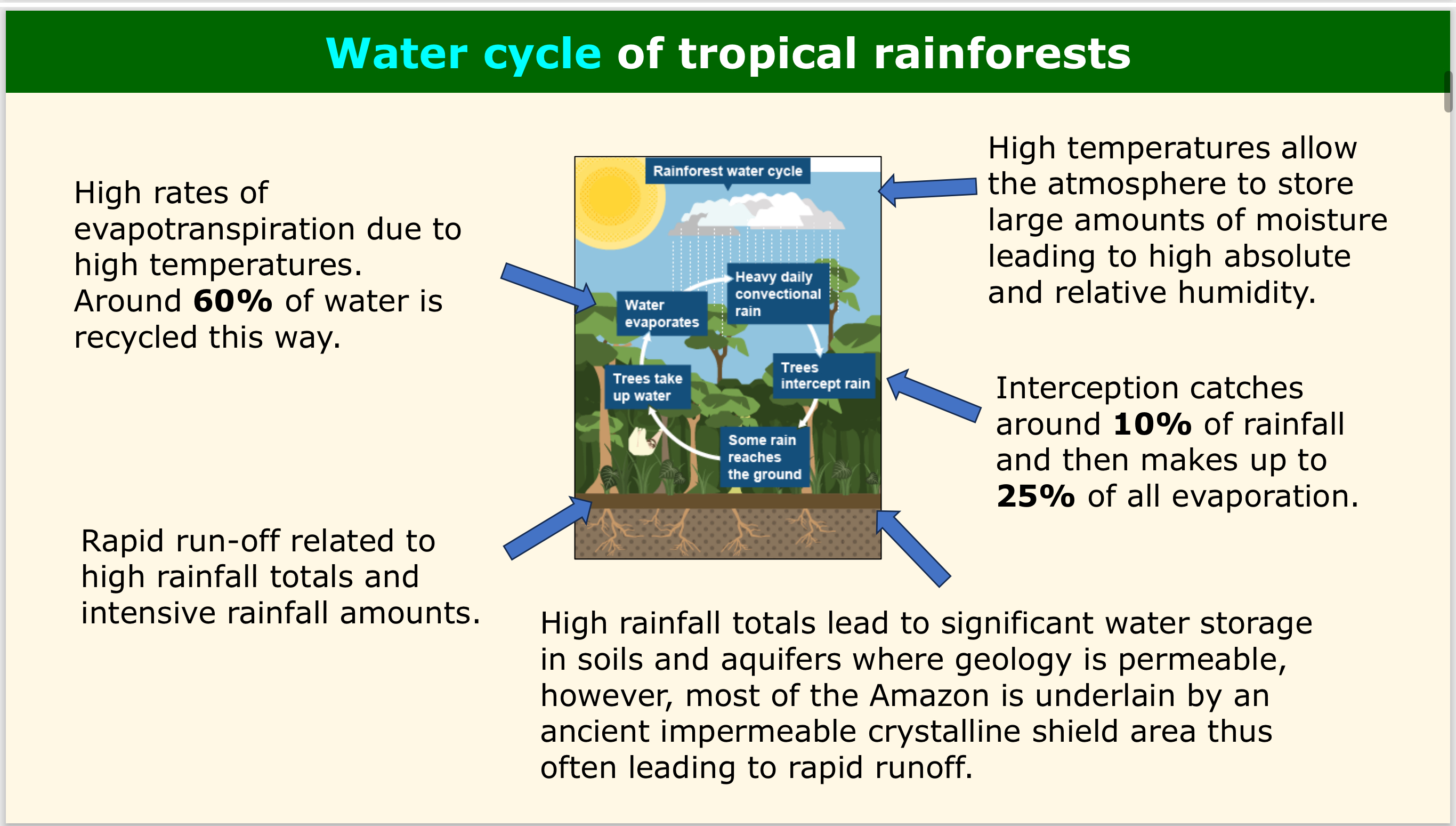
WATER - What role does high temperature play in the water cycle?
High temps allow the atmosphere to store large amounts of moisture, leading to high absolute and relative humidity.
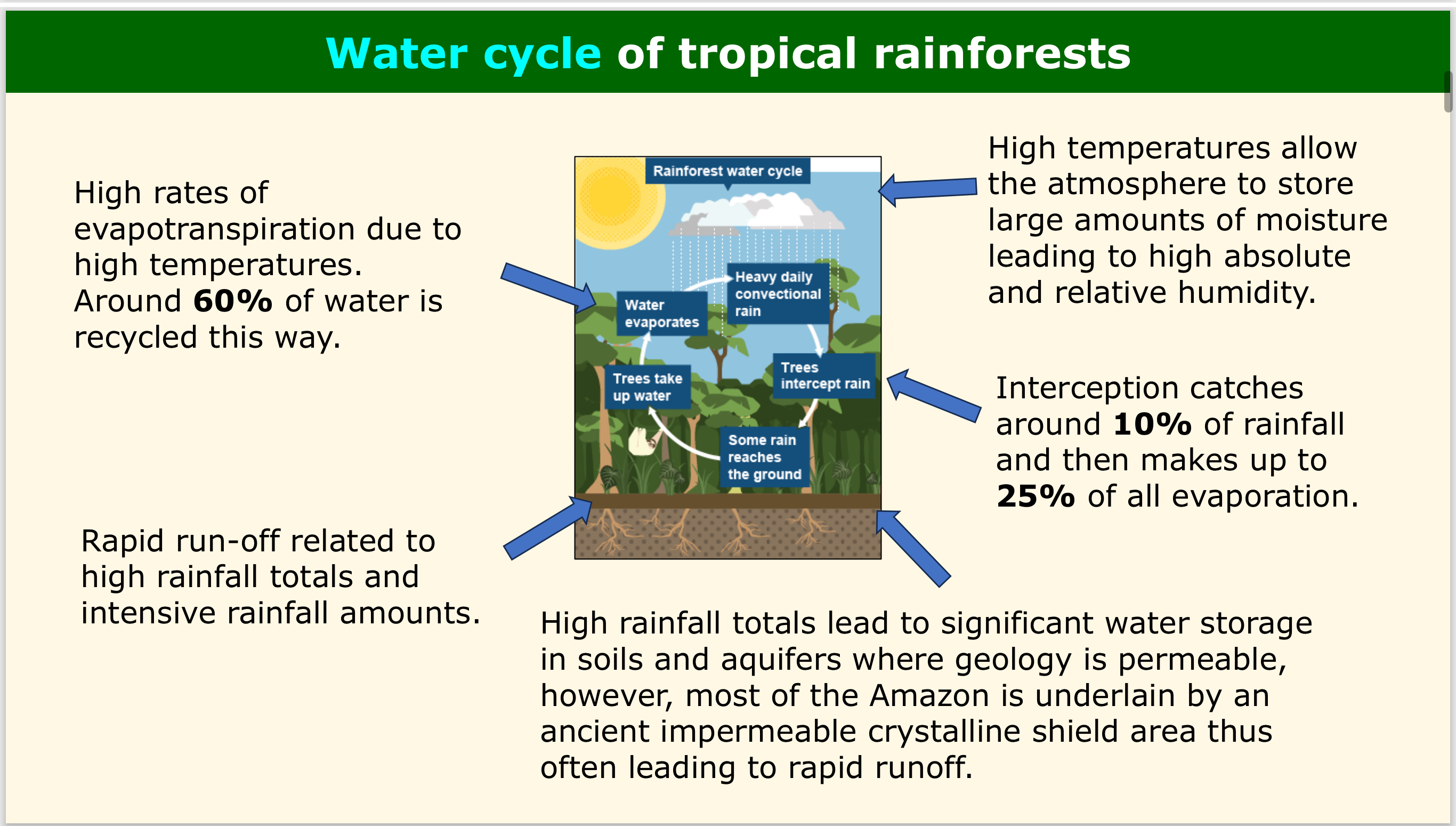
WATER - How much rainfall is intercepted by the rainforest canopy?
Around 10%
CARBON - How much carbon does the Amazon absorb each year?
2.4 billion tonnes
CARBON - What is NPP?
Net primary productivity - which is the amount of energy produced by plant biomass, minus the losses by respiration.
It is measured in grams of organic matter produced per m² per year. (g/m²/year)
CARBON - What is the average NPP of a tropical rainforest?
2,500 g/m²/year
CARBON - How much carbon is stored in trees above ground compared to in their roots, per hectare?
180 tonnes/ha is stored in trees above ground
40 tonnes/ha is stored in trees in their roots
over 4x
CARBON - Why do soils contain limited carbon?
This is because the warm, humid conditions causes rapid decomposition, so leaching and rapid removal of carbon via the vast biomass causes the soil to contain less carbon.
How high can emergent trees reach?
They can reach >40m.
Some examples are kapok and mahogany.
WATER - How can a single emergent tree influence the water cycle locally?
The extensive canopy of an emergent will have the potential to intercept over a relatively large area at a local scale.
Their tall heights make them more exposed to winds, increasing the rate of evapotranspiration.
WATER - How much water can an emergent tree intercept per year?
10,000 litres/ year
(can recycle around 900 litres)
CARBON - How might the carbon content vary depending on their size?
Large trees : 180 tonnes
Small trees : 10 tonnes
CARBON - How much carbon does the average rainforest tree sequester annually?
25 kg
How much leaf litter will an average rainforest tree produce in a year?
15 kg of leaf litter = 8kg of carbon
Why is the Madeira Basin a particularly significant tributary basin in the Amazon?
The Madeira basin encompasses 1.3 million km², covering approximately 19% of the Amazon.
It is also the most complex tributary basin in the Amazon, source found in the Bolivian Andes.
Compare the rates of deforestation in Brazil and Bolivia in 2024.
Brazil : 6500 km²
Bolivia : 15,000 km²
How much forest lost has occurred in the Madeira basin?
2,800 km²/ year from 2001 to 2020
with roughly 78% being anthropogenic land use conversion into pasture (farmland for cattle)
WATER - Outline the impacts of deforestation on the water cycle in the Madeira basin.
Reduction in evapotranspiration and interception will lead to more surface runoff and increased channel flow, therefore possible flooding.
Removing biomass increases ground surface temperature and reduced soil moisture. This also has potential to increase surface runoff as heavy rainfall will find infiltration more difficult through a thick surface of crust as the soil dries out.
WATER - Outline the impacts of farming on the water cycle in the Madeira basin.
Grassland produces significantly less leaf litter than rainforest, therefore altering the amount of water storage in the soil as decaying matter is effective at holding water.
Farming may lead to ground compaction as machinery or cattle trampling reduces soil pores and reduces rates of infiltration, therefore reduces water storage potential.
CARBON - How does deforestation impact carbon biomass store?
It exhausts the carbon biomass store.
CARBON - How does the biomass of grasslands compare to soya cultivation?
Grassland : 16 tonnes/ha
Soya cultivation : 3 tonnes/ha
CARBON - What impacts does carbon depletion in soils have on decomposers?
Soils that are depleted on carbon and are exposed to strong sunlight, support fewer decomposer organisms, therefore, reducing the flow of carbon from soil to the atmosphere.
CARBON - How does deforestation change the Amazon from a carbon sink to a carbon source?
Deforest forest sequesters 12 tonnes of carbon/ha/year via photosynthesis.
However, it respires 25 tonnes/ha/year back into the atmosphere.
This significantly changes when biomass is removed and the forest becomes a source of carbon instead.
What impacts does monoculture farming have on the soil nutrient stores?
The same nutrients are taken up by the same species of plants, so the land may become infertile in the future.
STRATEGIES - Outline how afforestation can have positive effects on the water and carbon cycles.
Establishing forest conservation areas which is comprised of wildlife reserves and indigenous reserves where farming is banned.
STRATEGIES - Give details of an example of an afforestation scheme.
The Parica project in Rondonia in western Amazon
Sustainable forestry scheme aims to develop a 1000 km² commercial timber plantation on government owned, deforested land.
20 million tropical hardwood seedlings are planted on 4000 small holdings, allowing them the mature over 25 years.
Although it is mono-cultured, it will still sequester carbon and help regulate the water cycle whilst also providing an income to help reduce illegal loggers.
STRATEGIES - Outline how improved agriculture techniques can have positive effects on the water and carbon cycles.
It will improve diversification. - Soil fertility can be maintained by rotational cropping and combining livestock and arable operations.
Integrating crops and livestock allow a five-fold increase in ranching productivity and help slow rates of of deforestation.
STRATEGIES - Give details of an example of a scheme to improve agricultural techniques.
The RECA project in Acre, Brazil helps farmers move towards agroforestry.
There has been more than 6000 hectares of forest being restored, improving soil fertility.