Psych Exam 2 Drug Design: CNS Depressants (Vino)
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
subtypes of subunits of GABA
· 6 types of alpha subunits
· 3 beta subunits
· Three gamma subunits
· Single sigma, epsilon, pi, and theta subunits
subunit combo of most GABA receptors
a1-B2-y2
bidning site of benzodiazepines on GABA
· extracellular N-terminus of alpha 1,2, 3, and 5 subunits for benzos
GABA alpha 1 subunit fuction
required for sedative + hypnotic effects
GABA alpha 2 subunit function
anxiolytic effects
GABA alpha 4 + 6 subunit function
insensitive to classical 1.4 BZDs
GABA gamma-2 subunit function
needed for best positive allosteric effect
what happens when a BZD binds to GABA-AR
this increases the affinity of GABA for the receptor which increases the frequency of ion channel opening
net result in hyperpolarization of the membrane
factors of efficiency of a hypnotic drug
o development of acute tolerance to BZD before it's eliminated from CNS
o redistribution from CNS to other tissues
o drug elimination
SAR of first-generation BZDs
· : 1-N and 2-carbonyl function are optimal for activity
which BZDs are 2nd gen and how do they differ?
o Triazolam and estazolam
o High receptor binding affinity and rapid elimination (eliminates drowsiness)
general properties of BZDs
lipophilic so rapidly absorbed
where do barbiturates bind on GABA-AR
bind to an allosteoc recognition site
effect of barbiturates when they bind to GABA-AR
· GABA mimetic effect: can increase Cl ion influx without GABA attaching to the receptor
SAR of barbiturates
· 5,5 disubstitution
o Both protons at 5 position must be replaced for activity and duration of action
ramelteon, where does it bind and what does it do?
binds to MT1 only and helps initiate sleep
which BZDs are class A?
§ Clonazepam
§ Clorazepam
§ Diazepam
§ Flurazepam
§ Halazepam
§ Lorazepam
§ Oxazepam
§ temazepam
which BZDs are class B?
§ Alprazolam
§ Estazolam
§ Midazolam
which drugs are serotonin receptor-active agents
busprione (partial agonist, SSRIs, SNRIs)
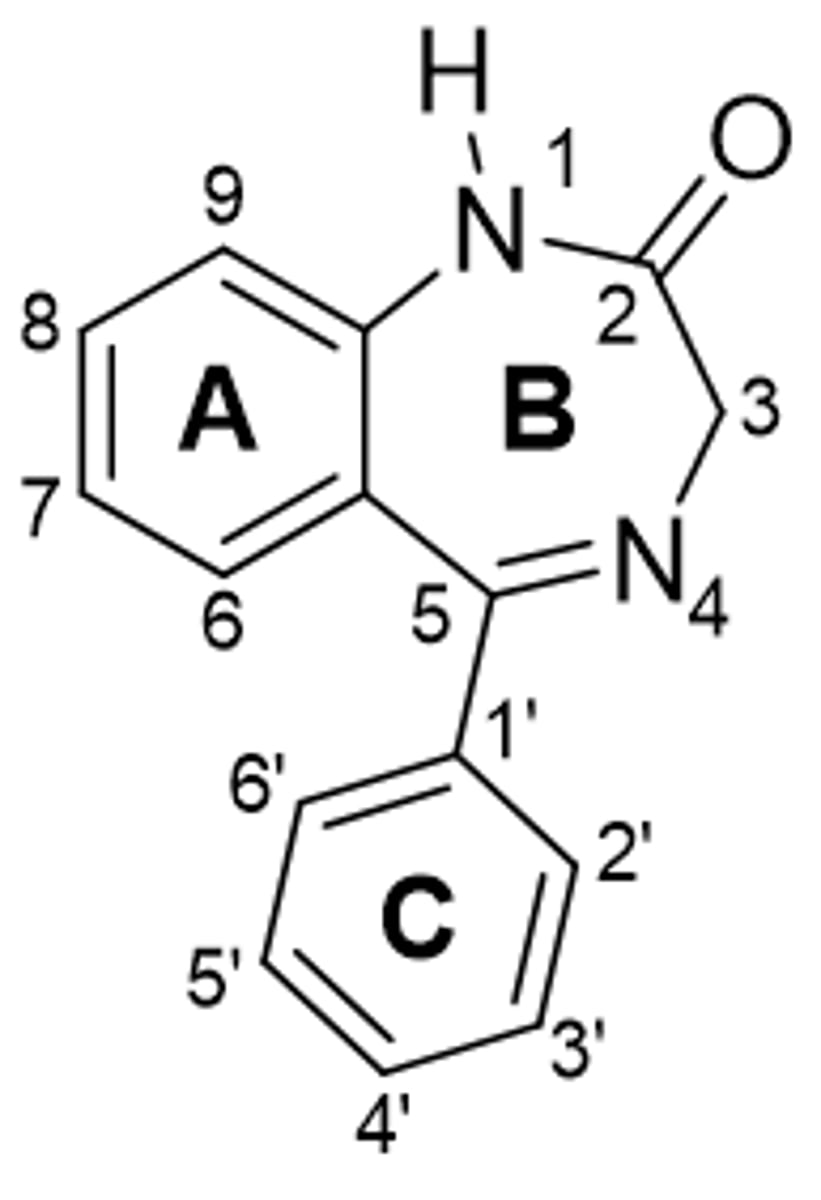
BZD ring A SAR
· replacing ring A with a heterocycle reduces activity
o Electronegative group (halogen or nitro) at C7 increases anxiolytic activity
o C6, C8, C9 substituents decrease anxiolytic anxiety
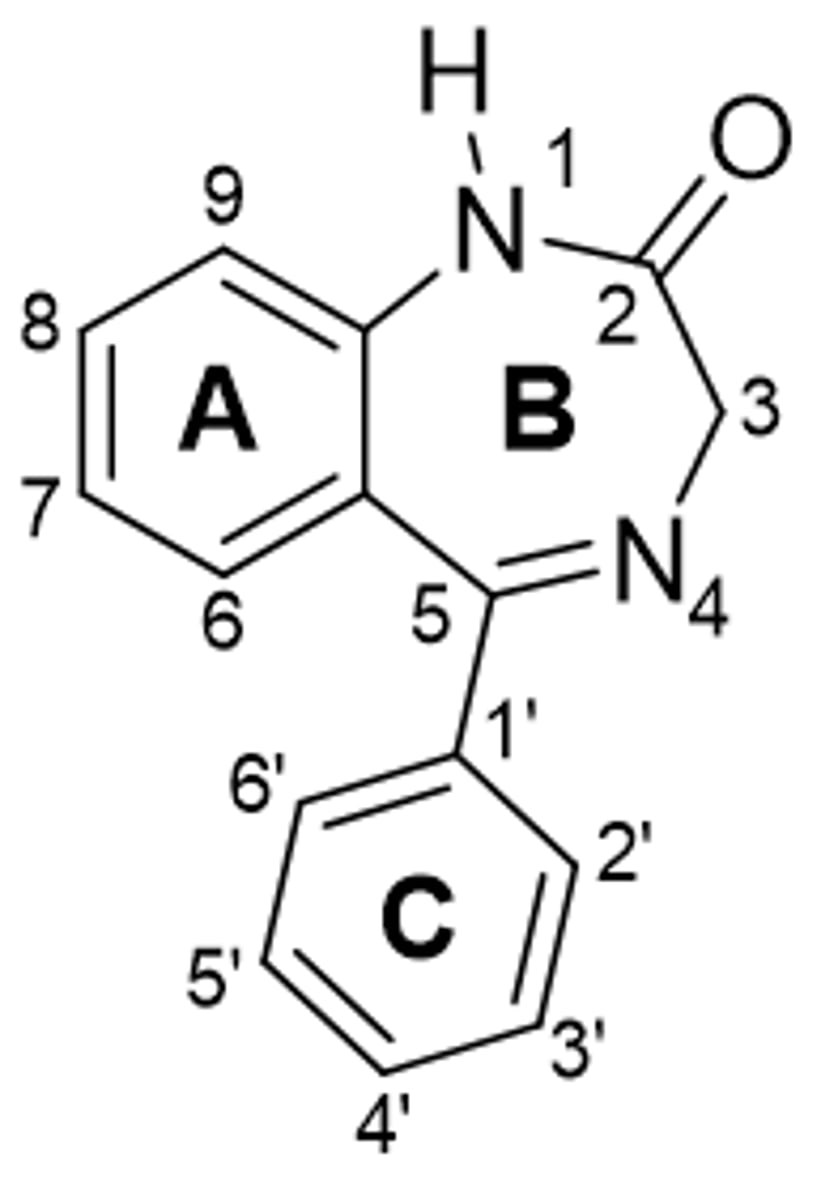
BZD ring B SAR
o Presence of proton-accepting grouop is needed
o For optimal affinity should be in coplanar spatial orientation with ring A
o Substitution of sulfur for oxygen at C2 may affect the selectivity of binding to receptor but the anxiolytic activity is maintained
o Sub at C3 or imine nitrogen is unfavorable for antagonist activity but doesn’t have affect on anxiolytic activity
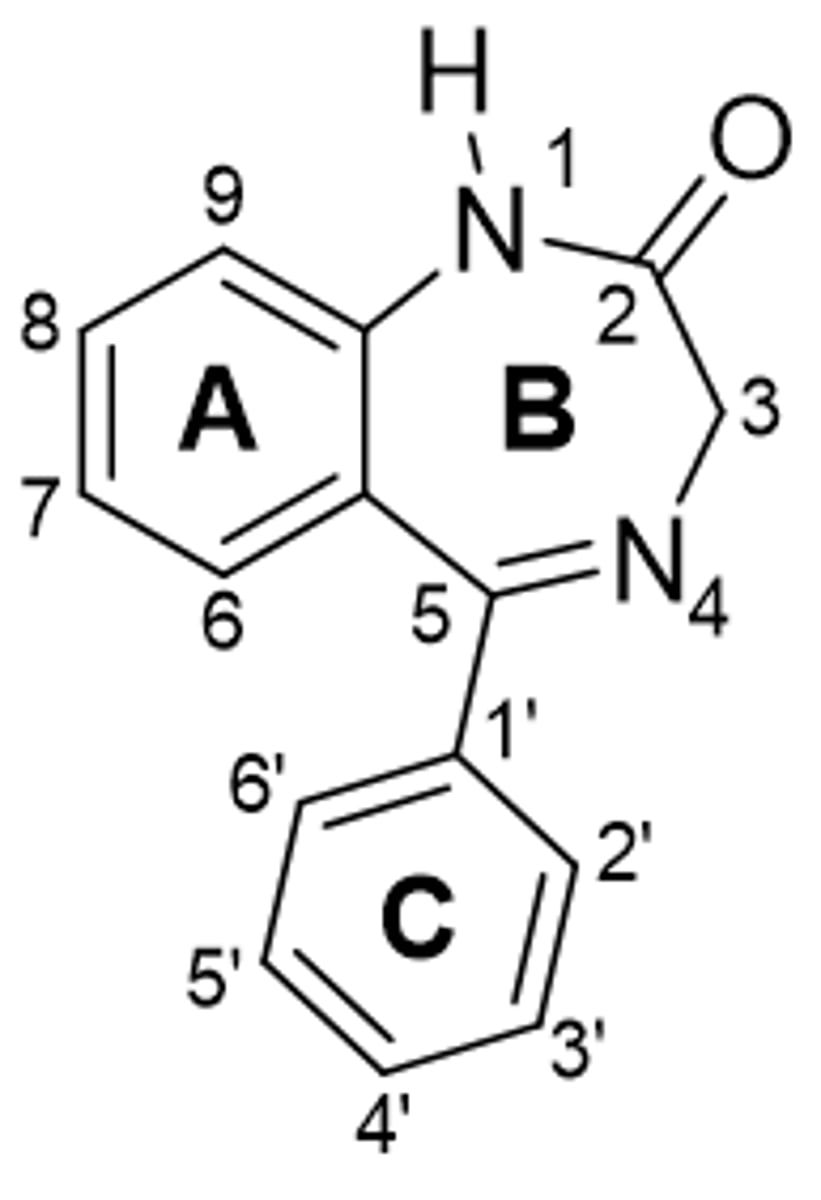
BZD ring C SAR
o not required for binding but may increase affinity to receptor due to favorable hydrophobic interactions
o sub at 4' (para) decreases activity
which drugs are inhaled general anesthetics?
o ether
o halothane
o desflurane
o enflurane
o isoflurane
o methoxyflurane
o sevoflurane
o nitrous oxide
usually halogenated
which drugs are IV general anestehtics?
o etomidate
o ketamine
o propofol
o fospropofol
o thiopental
general anesthetic defintion
drugs that bring reversible loss of consciousness
MAC (minimum alveolar concentration)
o 1 MAC is the concentration necessary to produce immobility in 50% of adult population
o 1.3 MAC causes immobility in 99% population
o Measure of potency
o When used together, MACs of inhaled anesthetics are additive