Electrostatic Forces
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
There are two kinds of electric charge.
like charges repel ; unlike charges attract
Electric charge is quantized.
That is, when an object is charged, its charge is always a multiple of a fundamental unit of charge.
Charge measurement
C ; Coulumb
F
Electrostatic force
Q or q1
First particle
q or q2
Second particle
K - constant
9×10^9
electrical conductor
material in which charges can move freely.
electrical insulator
material in which charges cannot move freely.
Insulators and conductors
can be charged by contact
induction
process of charging a conductor by bringing it near another charged object and grounding the conductor.
A surface charge can be induced on insulators by polarization.
With polarization, the charges within individual molecules are realigned such that the molecule has a slight charge separation.
Inverse Squared Law
For every distance (r) from the source (S), intensity decreases by r2
Universal Law of Gravitation:
any two bodies in the universe attract each other with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
1C
charge of 6.25 x 10^18 protons
Conductors in Electrostatic Equilibrium
The electric field is zero everywhere
inside the conductor.
Any excess charge on an isolated conductor
resides entirely on the conductor’s outer
surface.
The electric field just outside a charged
conductor is perpendicular to the conductor’s
surface.
On an irregularly shaped conductor, charge tends
to accumulate where the radius of curvature of
the surface is smallest, that is, at sharp points.
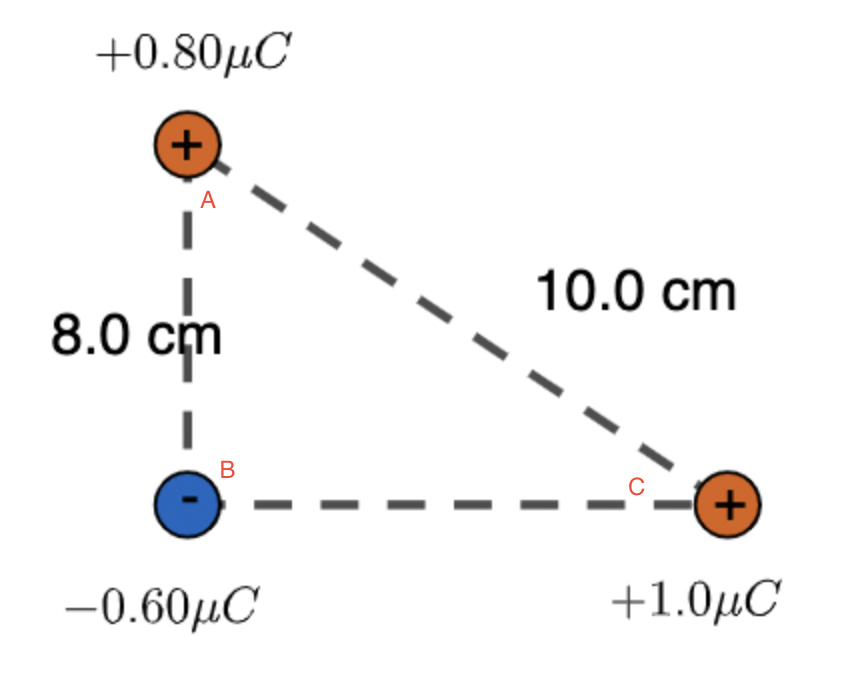
When solving for triangle electrostatic force problems
Step 1: Find A-b, A-C, B-C ising coulumb’s law and state whether it’s repulsive or attractive
Step 2: find the net force by using the direction each force is going in so it would be √(force 1)²+(force 2)²
Step 3: Find the angle by using tan-1 |y force/x force| = wtv degree and state whether it is below or above (-)x
capacitor
is a device that is used to
store electrical potential energy.
Capacitance
is the ability of a conductor to store energy in the form of electrically separated charges
Farad (F)
SI unit for capacitance which equal a coloumb per volt