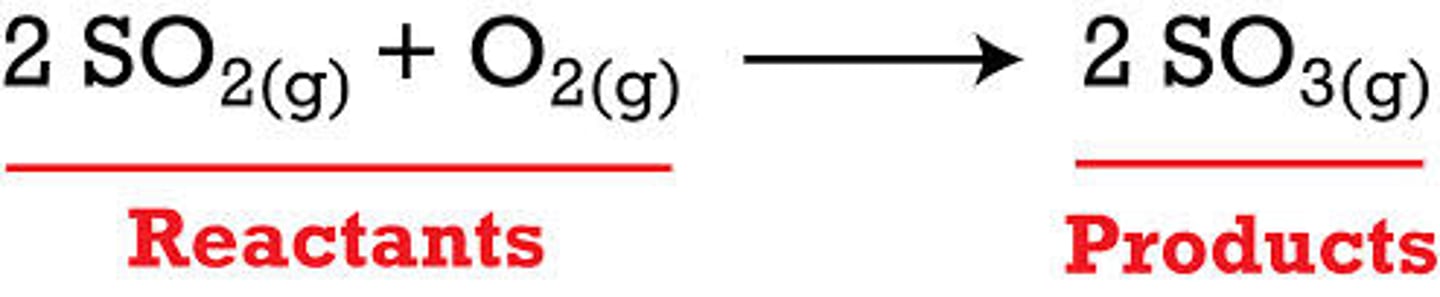Unit 2 Chemical Basis of Life Test Prep!
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
How Many Bonds Does Carbon Form
4 bonds
How Many Bonds does Hydrogen Form
1 bond
How Many Bonds does Oxygen Form
2 bonds
How Many Bonds Does Nitrogen Form
3 bonds
How Many Bonds Does Phosphorous Form
5 bonds
Covalent Bond
A chemical bond that involves sharing a pair of electrons between atoms in a molecule
ionic bond
Formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another
Organic Compound
Contains carbon
Hydrogen Bond
Attraction between a slightly positive hydrogen atom and a slightly negative atom.
Isomer
Compounds with the same formula but different structures.
Monomer
A simple compound whose molecules can join together to form polymers
Polymer
A long molecule consisting of many similar or identical monomers linked together.
Carbohydrate Monomer
Monosaccharide
Carbohydrate Polymer
polysaccharide
Protein Monomer
amino acids
Protein Polymer
Protein (Polypeptide)
Lipid Monomer
glycerol and fatty acids
Lipid Polymer
lipid
Nucleic Acid Monomer
nucleotide
Nucleic Acid Polymer
Nucleic Acid
dehydration synthesis
A chemical reaction in which two molecules are bonded together with the removal of a water molecule.
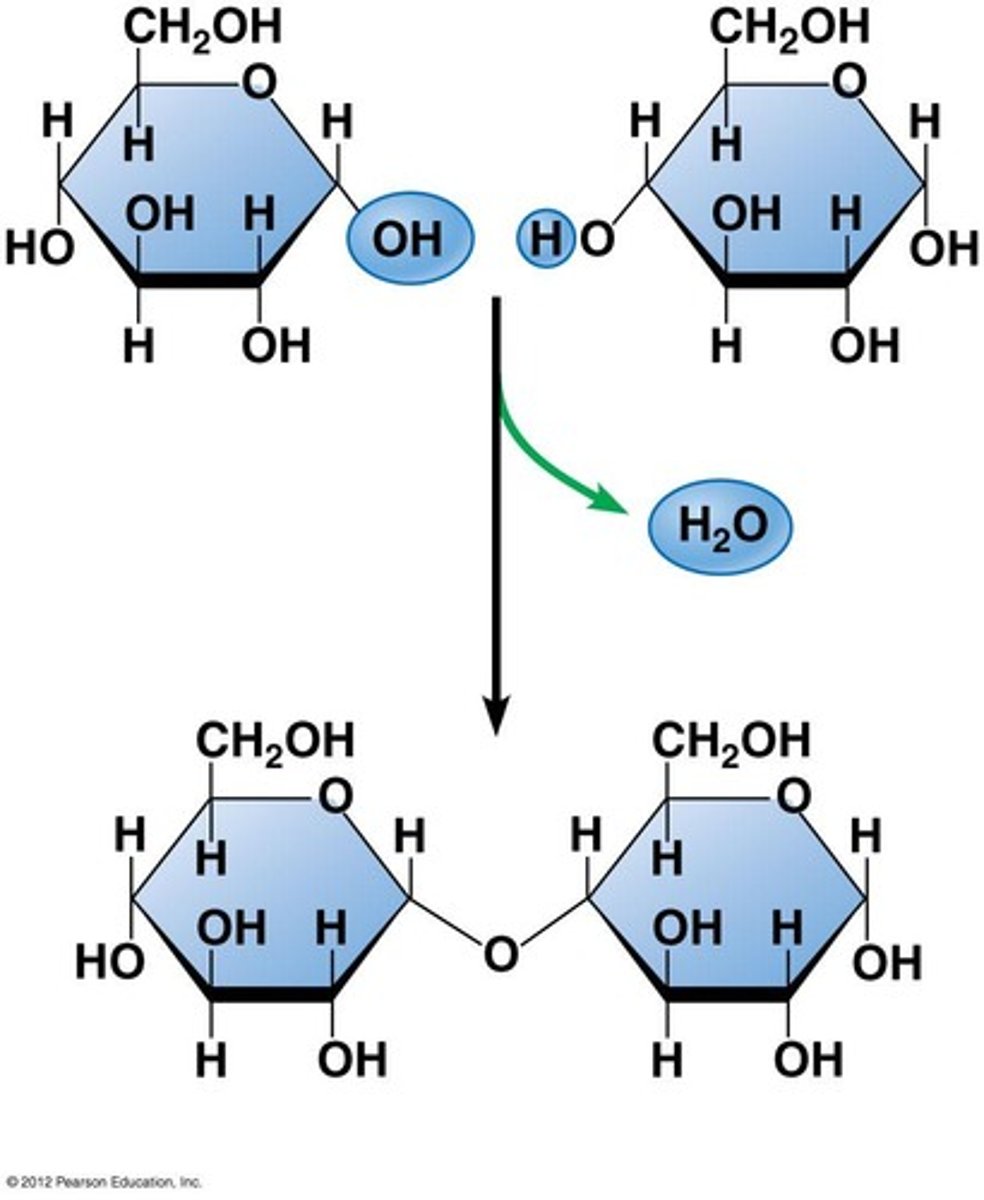
Hydrolysis
A chemical process that splits a molecule by adding water.
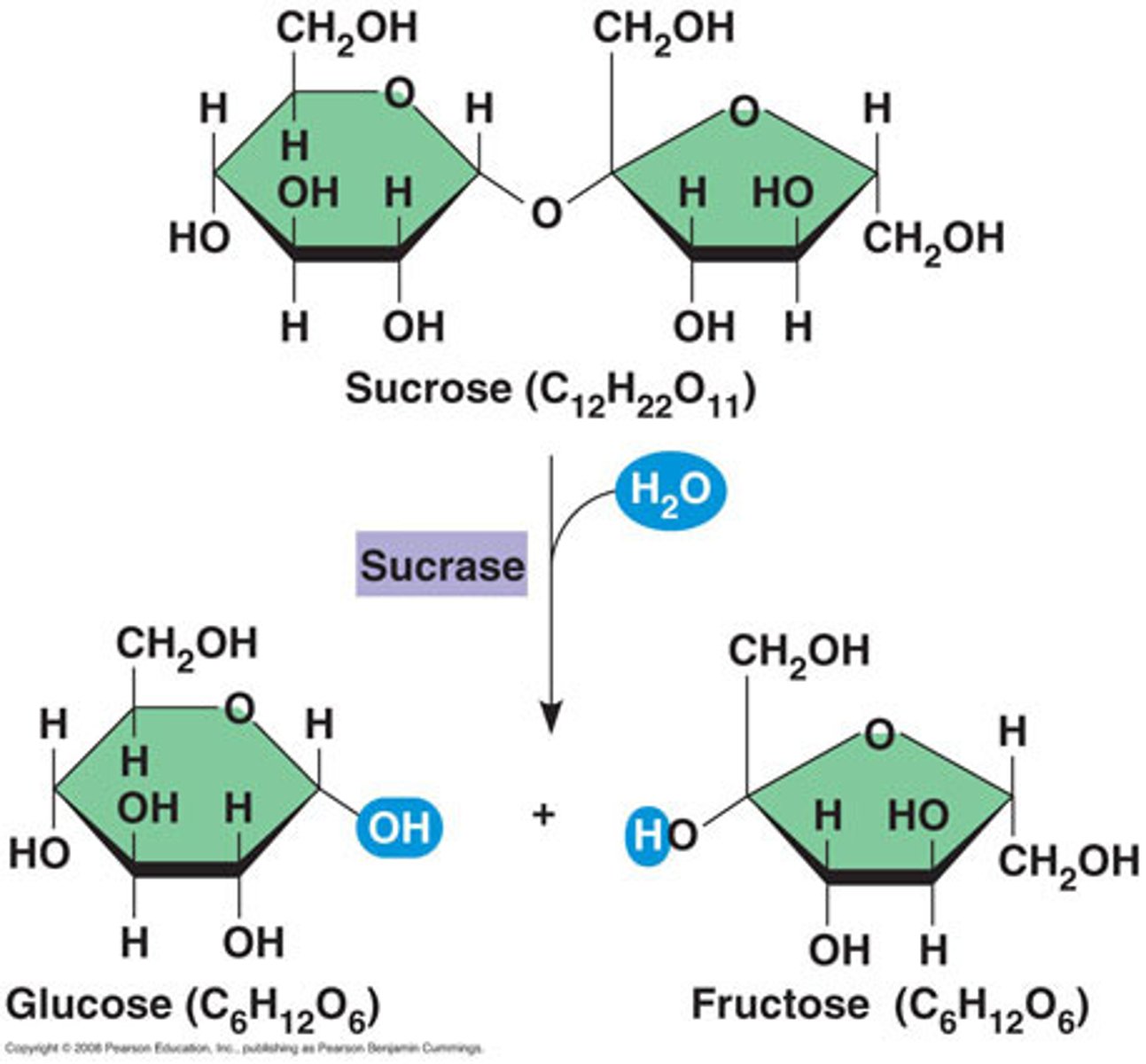
Carbohydrate Elements
C,H,O in 1:2:1 ratio
Lipid Elements
C, H, O (little Oxygen)
Protein Elements
C,H,O,N
nucleic acid elements
C, H, O, N, P
Function of Carbohydrates
Quick (short term) energy, structure for cells, builds cells walls of plants, exoskeleton of insects.
Functions of Lipids
Long term energy storage, insulation, protects organs, waterproof covering, forms cells membrane.
Functions of Proteins
catalyst, transport, defense, movement, regulation, forms bone, skin, tissue, hair, nails.
Function of Nucleic Acids
store and transmit genetic information
Examples of Carbohydrates
Glucose, Fructose, Cellulose, Lactose, Starch
Examples of Lipids
fats, oils, waxes
Examples of Proteins
enzymes, antibodies, hemoglobin
examples of nucleic acids
DNA and RNA
Carbohydrate Picture
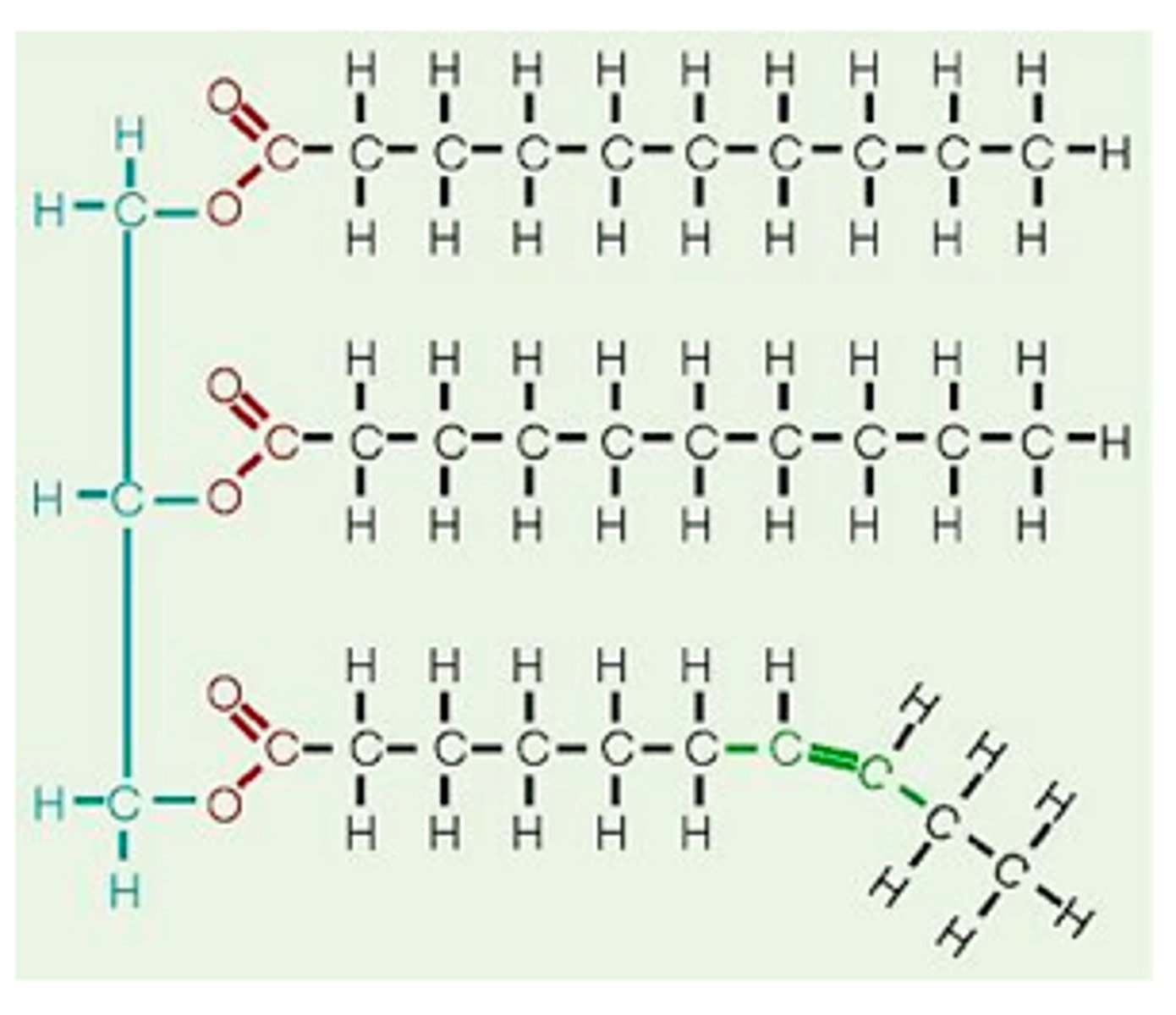
Lipid Picture
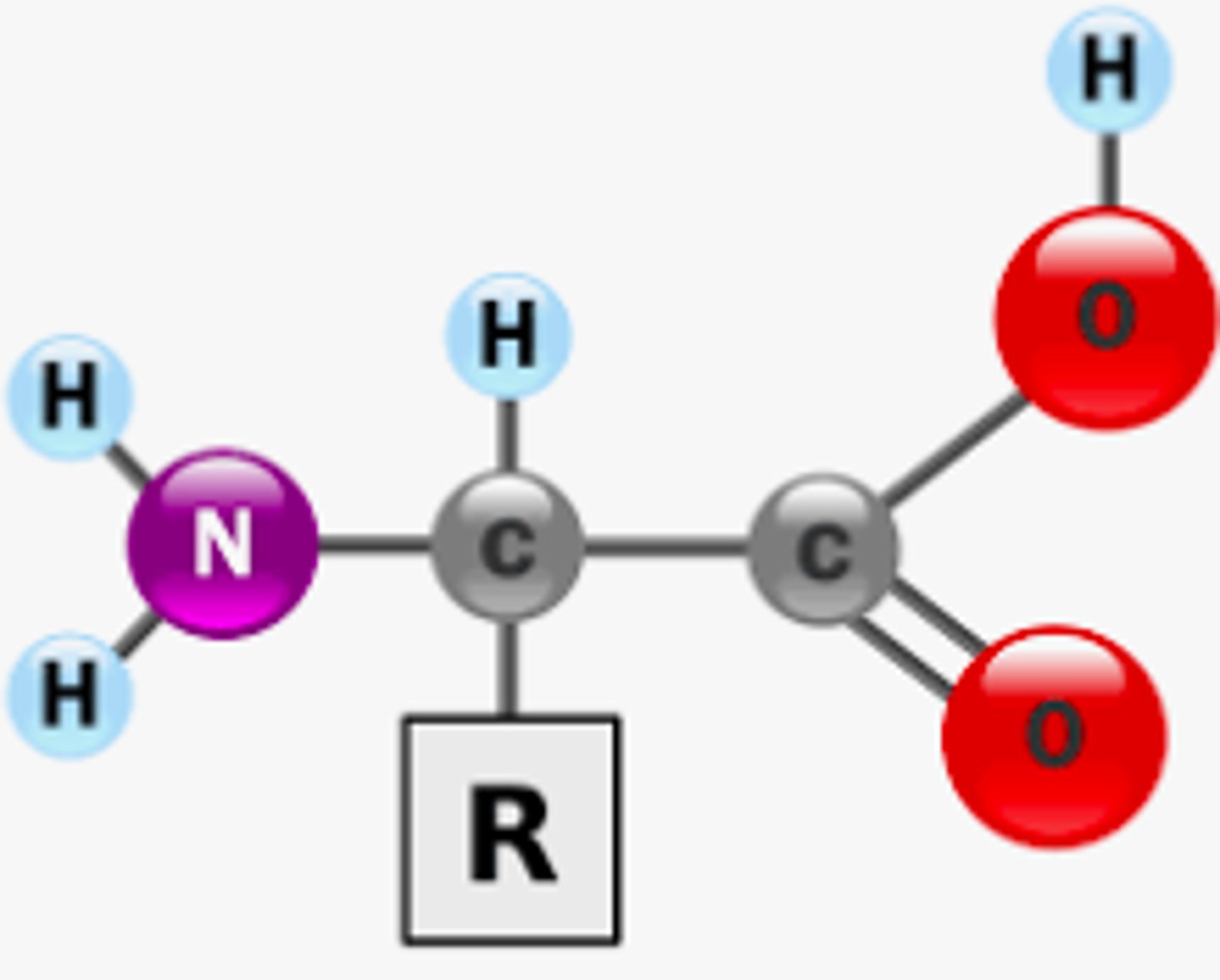
Protein Picture
Nucleic Acid Picture
Enzyme
A type of protein that speeds up a chemical reactions by lowering activation energy.
Catalyst
substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction
Substrate
reactant of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction
Active Site
a region on an enzyme that binds to a substrate during a reaction.
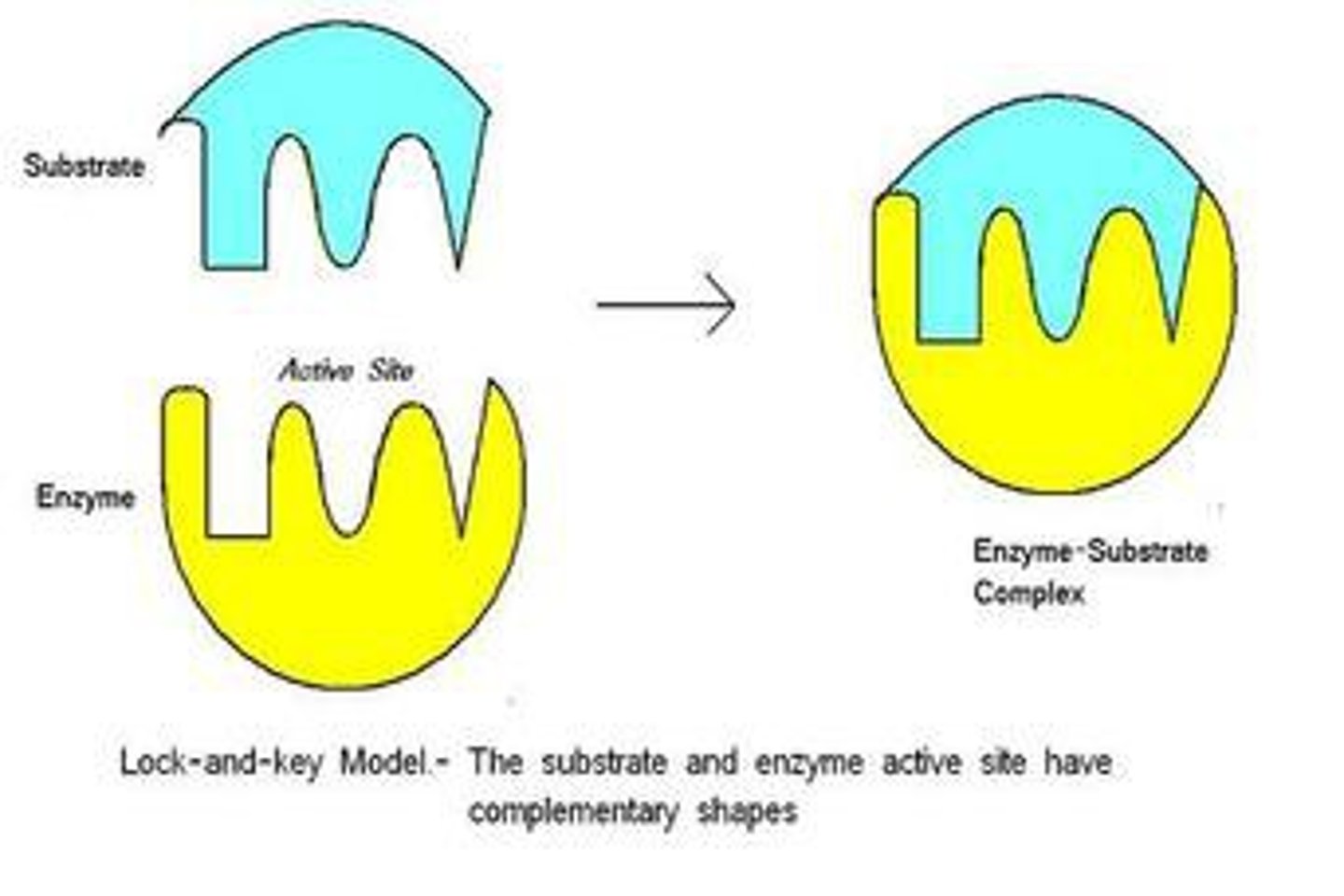
Enzyme Substrate Complex
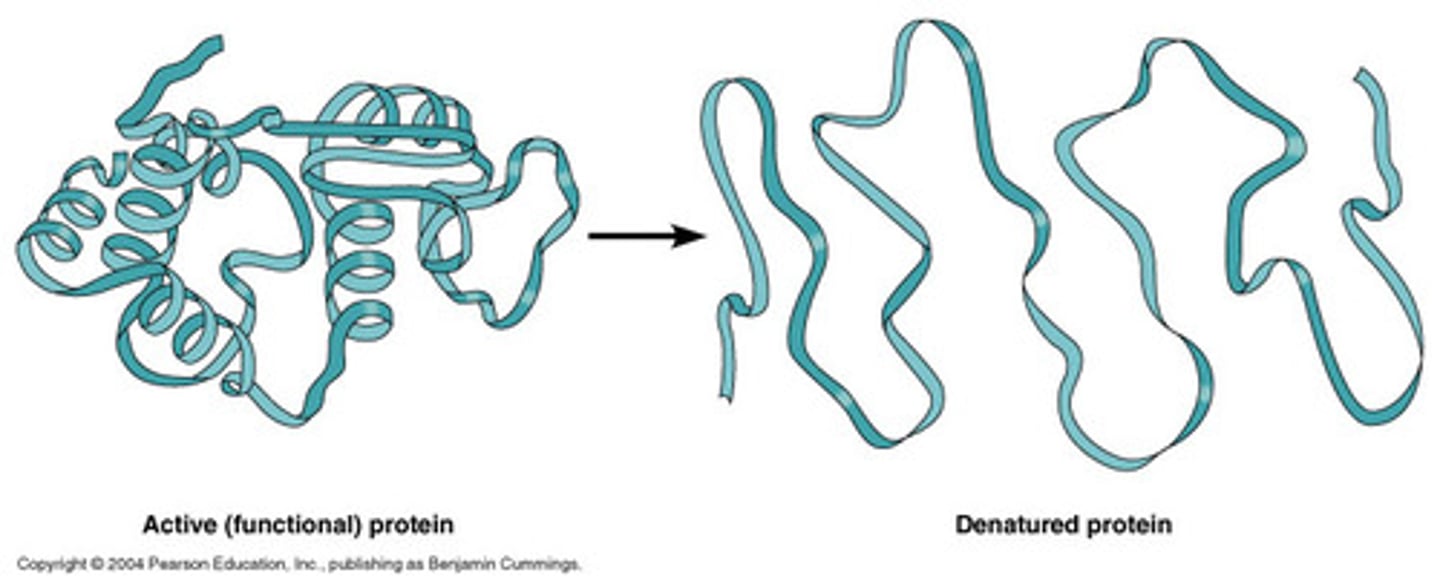
Denature
When an enzyme loses its shape and it can no longer function.
Factors that Affect Enzyme Activity
pH, temperature, and concentration of enzyme or substrate
The Bond that Forms Between Two Amino Acids to create a protein
Peptide Bond
Reactants
A starting material in a chemical reaction
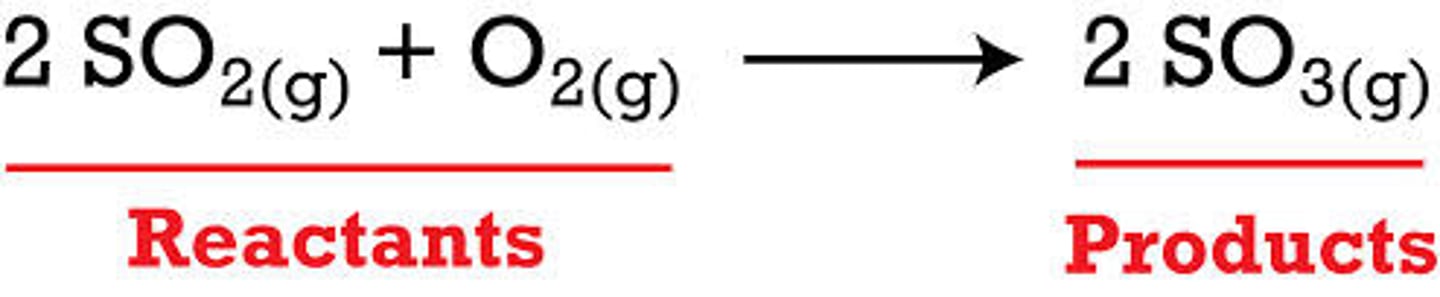
Products
What is made (produced) in a chemical reaction