[PCOL and TOXICOLOGY] PPT Solvents and Pesticides (Part 3 of intro)
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Hydrocarbons
once found wide use as industrial solvents, degreasing agents and cleaning agents
• A few examples are: • Carbon tetrachloride • Trichloroethylene • Chloroform • Tetrachloroethylene • 1,1,1-trichloroethane
Halogenated Aliphatic HC
classified as known or probable human carcinogen
Fluorinated Aliphatic
freon and closely related compounds can cause severe damage to the ozone layer
Trichloroethylene and tetrachloroethylenes
listed as reasonably anticipated to be human carcinogens
Depressants of the CNS in humans
Hydrocarbons
• Chronic workplace exposure can cause
> neurotoxicity
> impaired memory
> peripheral neuropathy
• All can cause cardiac arrythmias, hepatotoxicity in acute and chronic exposures
Neurotoxic
memory impairment
Peripheral Neuropathy
Chronic exposure to Trichloroethylene and tetrachloroethylenes can cause what
Arrhythmia
Hepatotoxicity
2 common adverse effects of exposure to
Trichloroethylene and tetrachloroethylenes HC
Dichrolomethane
a potent neurotoxin a generator of CO in humans and a probable human carcinogen
• No specific treatment
• Management depended on the organ system involved
Treatment of hydrocarbon (Dichloromethane) exposure
Aromatic Hydrocarbons
Benzene is what type of HC
Benzene
Used for solvent properties and as an intermediate in the synthesis of other chemicals
May be found in premium gasolines
Acute exposure to Benzene
The following are adverse effect of what:
CNS Depression, Nausea, Euphoria, Locomotor Problems and Coma; Vertigo, Drowsiness and Headache
Chronic exposure to benzene
The following are adverse effect of what:
Bone Marrow Injury
lymphomas
myelodysplastic syndrome
Benzene
a potent clastogen
A mutagen that act by causing chromosomal breakage
Suggests to have specific chromosome reorganization and genomic patterns
• Supportive treatment
• Nonspecific
two treatments of benzene exposure
Toluene and Xylene
• Does not possess the myelotoxic properties of benzene
Toluene
• Not been associated with leukemia
• Not carcinogenic but it is a CNS depressant and a skin and eye irritant
• neurotoxic and fetotoxic
• Can lead to severe over fatigue and ataxia
Toluene
Chronic effects of long term exposure has behavioral effects
Xylene
Dimethylbenzene
Has been substituted for benzene in many solvent degreasing operations
Does not possess myelotoxic properties of benzene
Not associated with leukemia
Is also a CNS depressant and skin irritant
• Chlorophenothane (DDT)
• Benzene hexachlorides
• Cyclodienes
• Toxaphenes
4 classifications of Organochlorine pesticides
Organochlorine Pesticides
• Aryl, carbocyclic or heterocyclic compounds containing chlorine substituents
• Can be absorbed through the skin, it could be inhalational or orally ingested
• Have largely abandoned because of severe environmental damage
true
t/f:
• Acute toxic properties of all the organochlorine pesticides in humans are similar
Organochlorine
• Interfere with the activation of sodium channel in excitable membranes and cause rapid repetitive firing in most neurons
• Chlorophenothane (DDT)
> Can manifest as tremors initially
Organochlorine
• Major effect is CNS stimulation
> Continuing convulsions – as the first sign of intoxication
Chlorophenothane (DDT)
Can manifest as tremors initially
Organochlorine
• Calcium transport is inhibited
> This events affect repolarization and enhance the excitability of neurons
Organochlorine Pesticides
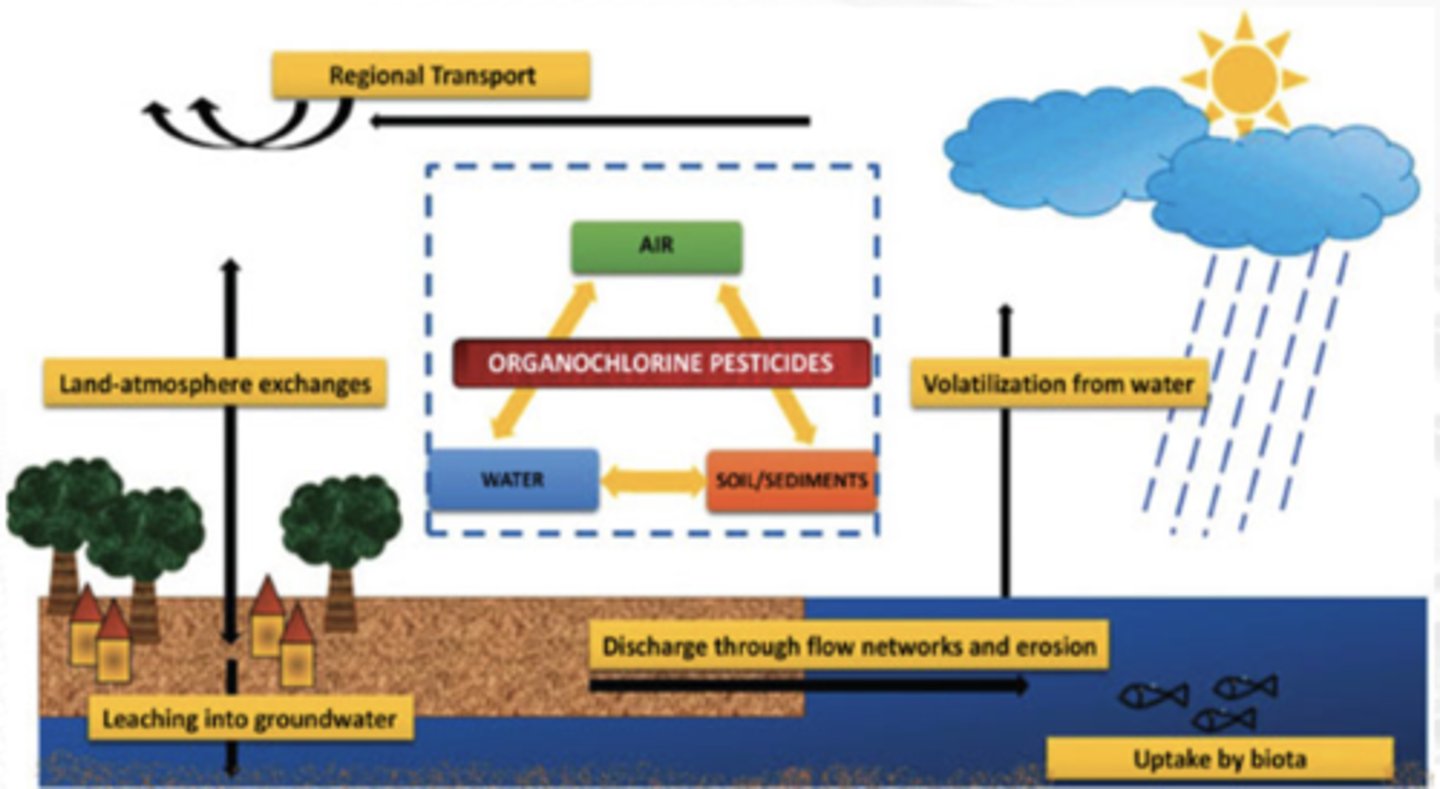
• Considered persistent chemicals
• Slow degradation as compared with other pesticides
• Bioaccumulation in aquatic ecosystems
• Mobility depends on soil composition
• Presence of organic matter favors absorption
• Induces significant abnormalities in the endocrine balance of sensitive animal and bird species
organic matter
In organochlorine, Presence of ___ matters favors absorption
Organochlorine
Organochlorine
Organophosphorous
Useful in direct contact with insects or when used as plant systemics
Based on compounds soman, sarin and tabun (G compounds)
Developed in Germany and later weaponized for use as war gas
VX compound developed by the British which is 20x more potent than G compounds
Parathion, Malathion, Azinphos
______________ and other OP pesticides are less toxic than the military grade compounds
Organophosphates
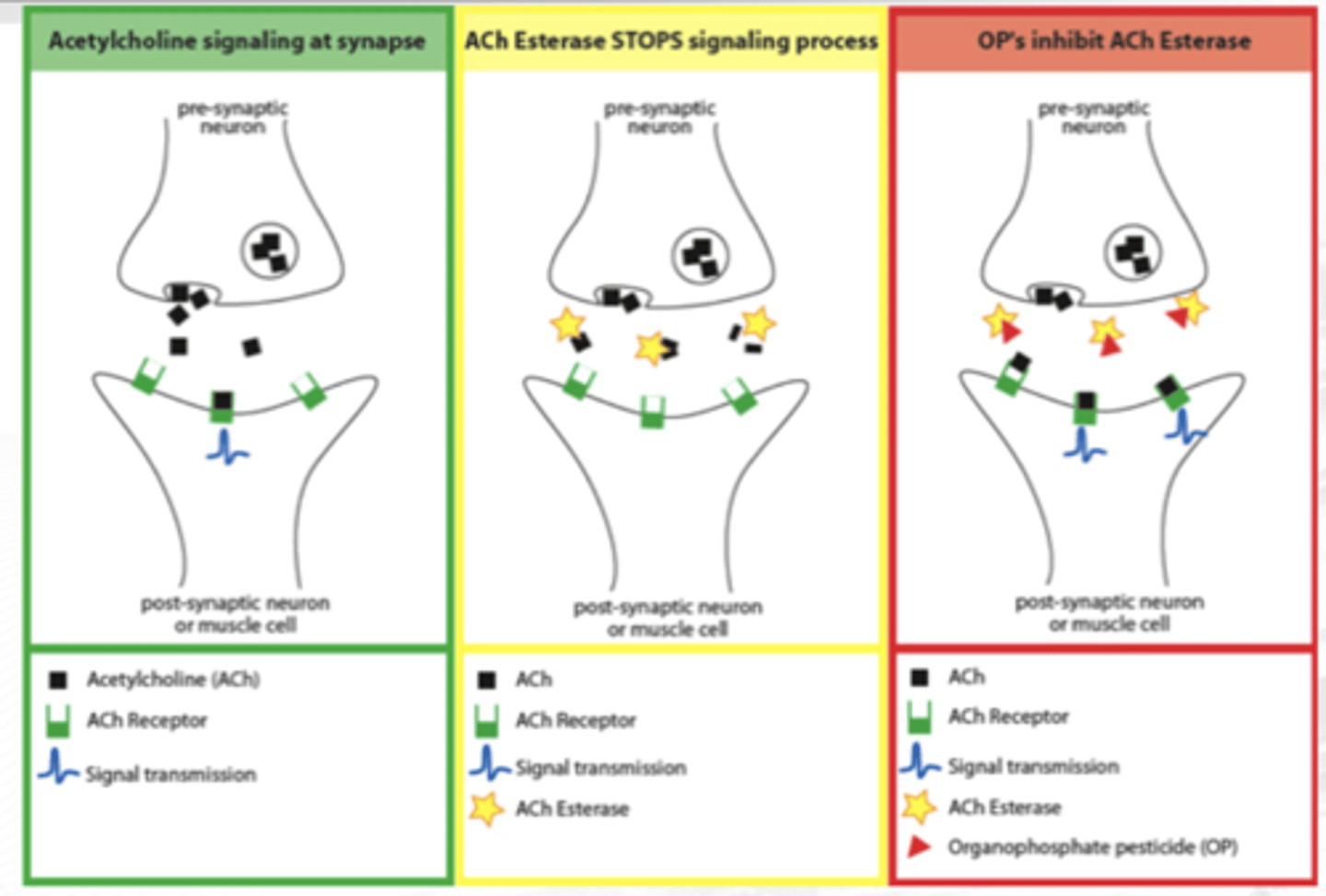
Major effect is inhibition of acetylcholinesterase through phosphorylation of the esteratic site
Direct cholinergic activity
Physostigmine
pretreatment and other short acting antagonist compounds
may provide protection against these pesticides or war gas
Organophosphates
Can cause Altered neurologic and cognitive functions as well as psychological symptoms of variable duration
Organophosphates
Also capable of phosphorylating Neuropathy target esterase (NTE)
> Present in neural tissue
> This result in progressive demyelination of the longest nerves
> Associated with paralysis and axonal degeneration lesion (organophosphorus ester-induced delayed polyneuropathy (OPIDP)
> Delayed central and autonomic neuropathy
triorthocresyl phosphate (TOCP)
In Humans, progressive chronic axonal neurotoxicity was observed with ___________
Organophosphates
Signs and Symptoms:
• Polyneuropathy: starts with burning and tingling sensations in the feet
• Sensory and motor difficulties may extend to legs and hands
• Gait affected and ataxia may be present
> balance in walking
Organophosphates
Neuromuscular transmission failure and cardiac failure more typical on nicotinic than muscarinic poisoning
Progressive neuromuscular failure leads to weakness of the respiratory muscles then eventually death
Organophosphates