LEC.165 Lecture 7
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/19
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
1
New cards
Chondrichthyes
\
\
Cartilaginous fish
2
New cards
Examples of Chondrichthyes
Sharks, Rays
3
New cards
Benefits of cartilage
Enables tighter turning, flexibility, and aids in buoyancy
4
New cards
Negatives of cartilage
Less structural differentiation and adaptability between species.
5
New cards
What is the oldest scale types, what properties does it have.
Placoid. In cartilaginous fish, heavy, inflexible, rough.
6
New cards
Properties of cycloid scales
Teleost fishes. Round, contains rings which can be used for aging fish and finding growth rates. Lighter
7
New cards
What is the most modern scale type
Ctenoid scales
8
New cards
What type of fin allows increased speed
Symmetrical, homocercal caudal fin.
9
New cards
What type of fins do shark, lungfish, and perch have (respectively)
Heterocercal, diphycercal, homocercal.
10
New cards
How has the pectoral fin changed over time
Moved from almost horizontal, to a vertical angle
11
New cards
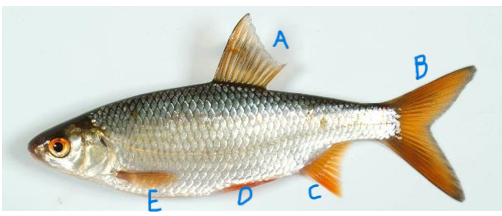
Name these fins
A. Dorsal
B. Caudal
C. Anal
D. Pelvic
E. Pectoral
B. Caudal
C. Anal
D. Pelvic
E. Pectoral
12
New cards
Why might teleost fins diversify? Give 5 reasons
•Camouflage
•Communication
•Lures
•Complex movements
•Hydrodynamics
•Predator evasion
•Attachment to habitat (ramora)
13
New cards
What is fusiform. Why is it used?
Typical elongated teardrop fish shape. More efficient for hydrodynamics and reducing drag.
14
New cards
How is drag reduced?
Fusiform shape, overlapping scales, mucus coating.
15
New cards
How do sharks maintain buoyancy?
Pectoral fin has a positive attack angle, constantly moving forwards means this provides uplift.
16
New cards
Myomeres
Muscle blocks attatched to collegenous septa, binds them to bone.
17
New cards
What can the caudal fin tell us?
The deeper the fork, the more frequent sustained swimming is for that species.
18
New cards
What does less caudal fin wake indicate?
More efficient fin design.
19
New cards
Where is the pelvic fin
Varies between species, more recent the fish, the closer to the head.
20
New cards
What is the pelvic fin for
Steering, by operating antagonistically. Breaking by flaring out.