gezondheidspsych H6: placebo
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
1ste gebruik term placebo
W. Cullen (18de eeuw): “to offer comfort and reassurance” (latin: “i will please”)
placebo intervention
all factors capable of activating a placebo effect or response
→ inert treatments that lack any active ingredient that directly affects a disease
→ can result in a placebo effect/response OR a nocebo effect/response OR both
Placebo as RCT
= Randomized control trials where placebos are used to test/compare the true effectiveness of the active treatment
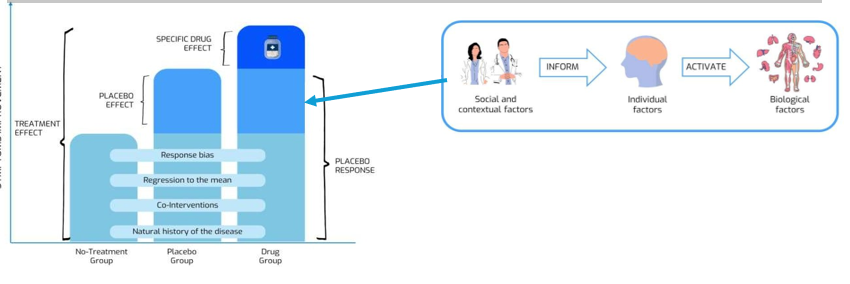
specific drug effects
directly related to its specific pharmacological action (E.g. morphine binding to opioid receptors)
non-specific drug effects
are not directly related to its mechanism of action but are caused by other factors related to its administration (E.g. Placebo responses)
placebo effect
positive health changes that occur because of placebo mechanisms
placebo mechanisms
The psychological and neurobiological processes by which the psychological context evokes the placebo effect
placebo response
broader term including any positive health changes occurring after the administration of an inert treatment (dus ook dingen die niet per se door placebo, zoals de natuurlijke fluctuatie v symptomen)
Concepts of placebo (image)
(image)
ontstaan van nocebo
‘60: patients experienced negative symptoms not be explained by the properties of the treatments they were receiving
Latin “nocebo” = “I will harm”
nocebo intervention?
doesn’t exists, niet ethisch → ethical concerns of wilfully producing negative symptoms
nocebo effect
Negative health changes that occur specifically due to nocebo mechanisms
nocebo mechanisms
The psychological and neurobiological processes by which the psychosocial context evokes the nocebo effect
nocebo response
broader term including any negative health changes occurring after the administration of an inert treatment
how are placebo/nocebo responses measured
includes placebo/nocebo effects + non specific-factors
Using randomized controlled trials (RCTs)
active ingredient treatment
inert treatment: attention from doctors + expectation (relief/worsening) + natural fluctuation
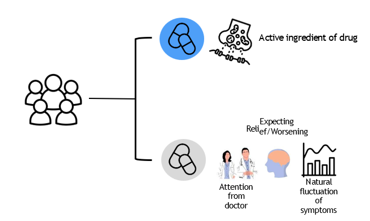
non-specific factors in placebo/nocebo response?
any health changes after the administration of an inert treatment
Natural fluctuation of symptoms (i.e. natural history of disease)
Co-interventions (e.g. changes in patient lifestyle, other medications)
Response bias (i.e. a conscious or unconscious preference for one response over others)
Statistical phenomena (e.g. regression to the mean)
Regression to the mean
non-specific factor in placebo/nocebo respons
= Extreme waarden gaan altijd richting gemiddelde als je ze opnieuw meet
omdat extreme waarden meer kans hebben op invloed van random variatie of error
makkelijk te verwarren met effect v drug of placebo
the size of placebo response
= The difference in symptoms within placebo group before and after a placebo intervention
How to measure placebo/nocebo effects (algemeen)
Only the pos/neg health changes specifically due to placebo mechanisms
RCTs → interest in the effect of the active treatment (no control group)
mechanism studies → interest in the effect of placebo intervention
the size of placebo effect
The difference in symptoms between a placebo group and a no-treatment group
are drug and placebo effects additive or interactive
the effects are interactive
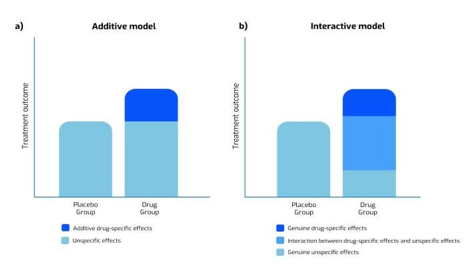
Common outcome measures of placebo/nocebo effects
Effecten kunnen voorkomen in verschillende klinische condities
De interventies kunnen voor verandering zorgen op verschillende vlakken gelijkend met active treatment
subjectieve ervaring
klinische uitkomsten
fysiologische responsen
3 types metingen
1) self-report
2) clinical assessment
3) physiological measures
self report measurement
toont grootse placebo/nocebo effect
omdat symptomen deze symptomen vaker bewust zijn (consciously accessible) en dus gevoelig zijn voor placebo mechanismen
physiological measures
toont he tminst effect
want vaak niet bewust van fysiologische gebeurtenissen (bv hormonen)
veranderen niet zomaar door dingen zoals verwachtingen/interpretaties/…
Uitzondering v resultaten bij metingen in mood disorders
Hier is clinical assessment beter dan self-report
groter placebo effecten door
minder accurate perceptie van mood changes bij mensen met depressie of angst
clinicians overschatten mogleijks verbetering
=> toont belang van meerdere methodes te gebruiken
3 types studies placebo/nocebo and pain
- Algesia = sensitivity to pain
- Analgesia = reduction of pain ( ~placebo)
- Hyperalgesia = increased sensitivity to pain (~nocebo)
Verwachtingen (expectations)
= BEWUSTE evaluaties over de kans van toekomstige gebeurtenissen
→ centrale rol in de effecten
Rol van verwachtingen studie
Experiment met RCTs: participanten kregen te horen wat de verhouding was van wie wel/niet placebo kreeg (maar wisten niet welke conditie zij hadden)
=> hoe groter de kans op effectieve ‘active drug’ te krijgen → hoe groter de verwachting → groter effect zowel drug als placebo
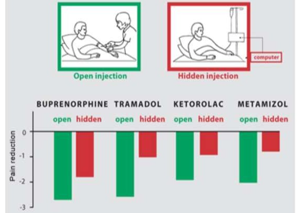
Open-hidden experiment
Onderzoeken van de impact of iemand ‘weet’ dat hij behandeling krijgt
=> Een behandeling verwachten maakt het meer effectief
theorie over hoe verwachtingen leiden tot minder symptomen
predictive processing theory
Predicitve processing theory
Perception = sensory data + predictions (past experience)
perceptie = “the brains best guess of …” → brein doet predicties obv sensorische info, wordt constant aangepast
MAAR perceptie is dus niet altijd fully in line met ervaringen v lichaam
=> perception that relief is coming → prediction → placebo effect
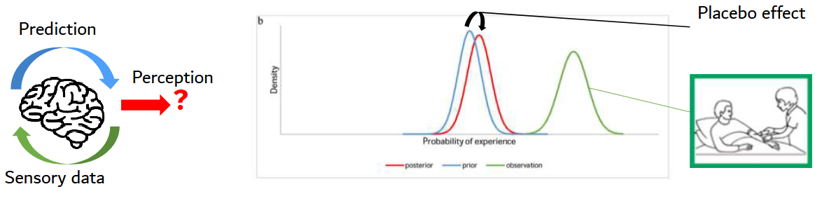
3 manieren hoe verwachtingen worden gevormd
1) verbale suggestie
2) direct experience/ervaring
3) observatie van anderen
verbale suggestie (en studies)
manier om verwachting te vormen
studie: placebo/drug krijgen maar versch informatie wordt meegegeven => Enhancing positive expectations about treatment can reduce the need for strong analgesics
studie: verwachting van de professionals hebben directe invloed op uitkomsten: uitleg + confidence + twijfel
invloed van verwachting van de professional/dokter?
hebben een directe invloed op uitkomsten
studie:
EXPLAINING de behandeling → minder angst, minder pijnstillers
CONFIDENCE in de behandeling → minder angst/pijn/distress
DOUBT in behandeling of side-effects → meer gerapporteerde symptomen
directe ervaring
manier om verwachting te vormen
rol van verwachting
EN rol van klassieke conditionering: cues = mediatie effect van klassieke conditionering bij onbewuste fysiologische functies
rol van klassieke conditionering
Door verwachtingen via ervaring: Cues associeren met het nemen v medicatie: hoe het eruitziet/proeft/voelt
→ cues die samenhangen met de behandeling medieert placebo effect op onbewuste, fysiologische functies
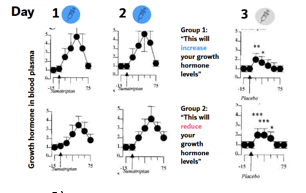
studie over rol van klassieke conditionering
participanten kregen groeihormonen behandeling 3 dagen lang, maar 3de dag is een placebo + verschillende verwachting!
dag 1 & 2: beide groepen stijging groeihormonen
dag 3
groep 1: “het zorgt voor stijging” → kleine piek in gh blijft (ookal is het placebo)
groep 2: “dit zorgt voor vermindering” → OOK nog een kleine piek
=> DUS NAAST VERWACHTING speelt ook de klassie conditionering en CUES hier een grote rol in onbewuste fysiologische functies
Observatie van anderen (studie)
manier om verwachtingen te vormen
studie: filmpje zien waar iemand pijn stim kreeg → zalfje → meer pijn
bij patient hetzelfde doen maar zalfje was puur placebo → rapporteerde mee pijn met zalf dan zonder
=> Observing someone else's experience can lead people to expect similar outcomes for themselves → nocebo effects
rol van emoties
is een sociale en contextuele cue die invloed heeft op hoe we informatie verwerken en hoe we verwachting vormen van een behandeling
pos. emoties → activeert/versterkt placebo effecten
neg. emoties → activeert/versterkt nocebo effecten
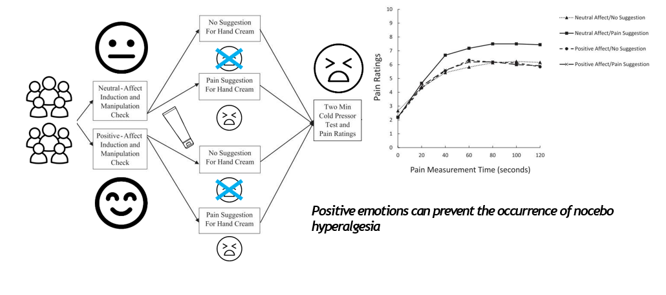
studie positieve emoties & nocebo
(zie foto) => positive emotions can prevent nocebo (hyperalgesia)
treatment context
the various environmental and psychological factors surrounding the administration of a treatment
2 componenten doctor-patient relatie
1) cognitive → information transmission
2) emotional → warmth, caring and understanding
Belang van warmte of competentie? (studie)
groep indeling:
placebo of nocebo (pos/neg expectation)
4 interactie manieren: hoge / lage competentie + hoge / lage warmte
=> Warmth and competence are equally important in the relationship
=> Provider warmth and competence, together with positive treatment expectations, can influence physiological health outcomes
Role of endogenous opiods in placebo pain relief
studie → endogene pijnstillers spelen effectief een rol in placebo pain relief
Active brain areas during placebo pain relief
placebo can diminisch activation in some regions that respond to pain
placebo may activate higher-orderbrain regions involved in emotional and cognitive processing to modulate pain perception
Brain areas active during nocebo pain relief
ACC, Insula, … = regio’s geassocieerd met ‘increased pain due to anxiety’
Negative treatment expectations influence pain through similar brain pathways as positive expectations but in opposite way
…possibly through increased anxiety
placebo/nocebo immunomodulation
doordat er bi-directionele communicatie tussen lichaam en brein is
→ Placebos can support immunosuppression
Lower drug dosage
Improve drug efficacy