AQA A Level Business - Unit 2
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Functions of Management
Planning
Organising
Directing
Controlling
Planning
Involves looking into the future. Foundation upon which the other 3 functions of management should be based.
Setting Objectives- management responsibility.
Analysis- gather forecasts of key data (costs, revenue).
Drawing up plans- for functional areas.
Estimating- likely resources needed for proposed plans.
Organising
Management must gather the resources that they need to carry out the actions set as part of planning. Will determine:
Internal organisational structure.
Establish and maintain relationships.
Allocate the necessary resources.
Directing
Influence and oversee behaviour.
Motivation: willingness to achieve target. Highly motivated = perform better so objectives are achieved.
Communication: exchange of info.
Controlling
Involves setting standards and reporting performance.
Financial reports- many publish, Plc legally required to.
Employee performance- reports provide info on productivity. Vital to measure performance.
Social performance- measure ethically, minimise pollution and creating jobs.
Leadership
Deciding on direction for a business, setting objectives and motivating staff.
Management
Getting things done by planning, organising, directing and controlling.
Good Leadership
Getting tasks done differently.
Change rules for the better.
Getting others to do jobs in a new way.
Motivating others to do new things.
Good Management
Getting tasks done well.
Work with existing rules and doing this well.
Getting other to do job in expected way.
Motivating other people to do what is expected.
Autocratic
One way communication (down).
Minimal delegation (one person with authority).
Close supervision of employees.
Democratic
Leader delegates a great deal and encourages decentralisation.
Leader and subordinates discuss issues and employee participation is actively encouraged.
Subordinates are empowered.
Laissez Faire
Manager/leader is one among a number of equals in terms of experience and qualifications.
Workforce self motivated and understands management.
Workforce understands and agrees with organisation objectives.
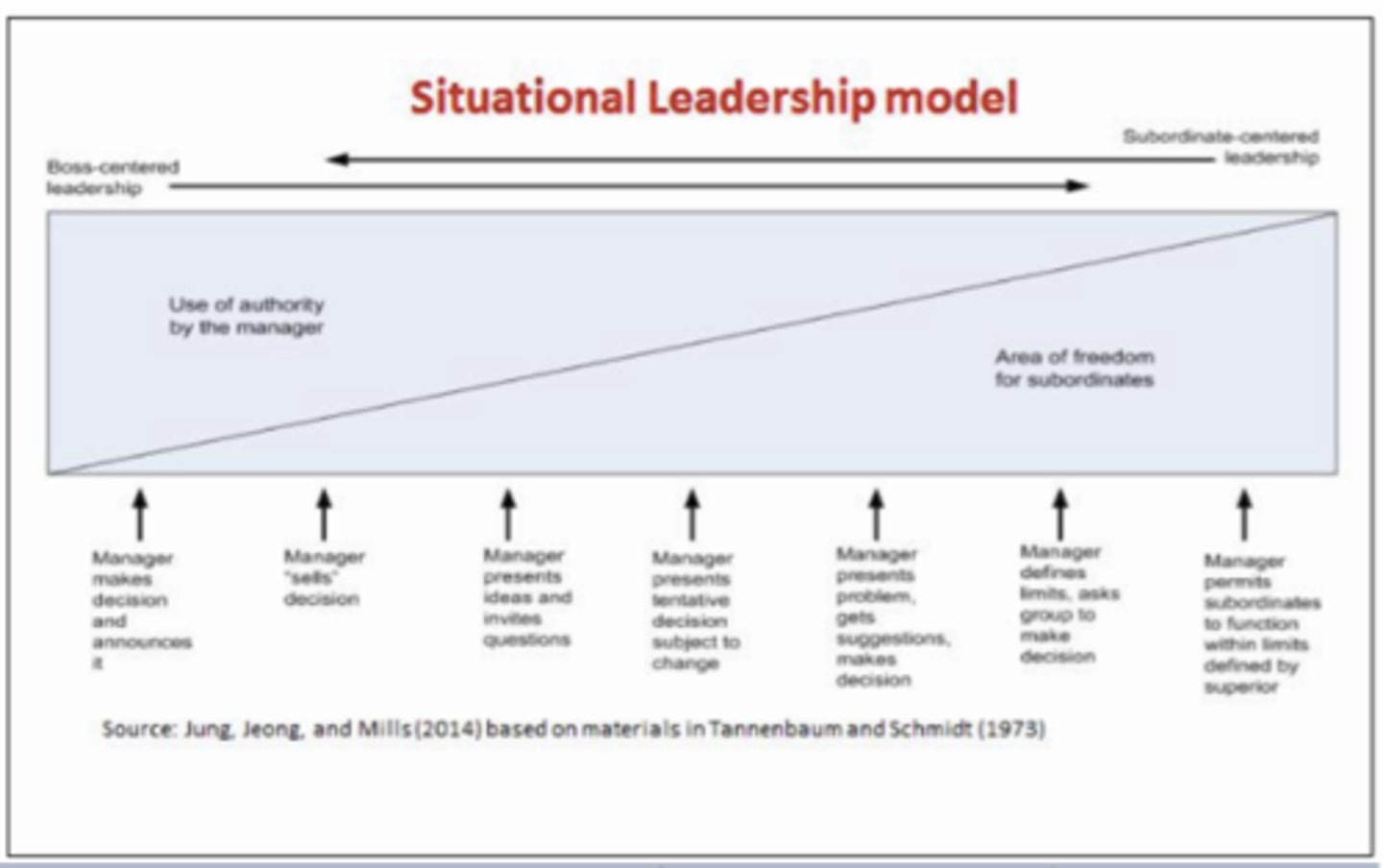
Tannenbaum-Schmidt Continuum
Range of potential leadership and management styles. From autocratic to democratic.
Tells- Sells- Consults- Joins
Tells- leader finds problems and expects subordinate to implement it.
Sells- overcomes resistance with discussion and persuasion.
Consults- listens to advice and suggestions before decision.
Joins- passes problem to group for all to decide.
Influences on Management and Leadership Style
Size, Task, Experience, Culture, Company Structure, Personality, Employee Skills and Time Frame.
Effective
Meet objectives in set time frame.
Programmed Decisions
Deal with familiar problems. Info easy to get. Routine procedures.
Non-Programmed Decisions
Unstructured. Need unique decisions. Risky.
Tactical Decisions
Short term and regular. Need fewer resources. Junior management. For example, re order stock.
Strategic Decisions
Long term. Hard to make. Senior. For example, investment.
Factors Affecting Decision Making
Risk.
Expect a reward.
Uncertainty.
Opportunity Cost
The next best alternative foregone.
Scientific Decision Making Model
Gather data- Analyse- Select- Implement- Review- Set objectives- Repeat
Benefits of Scientific Decision Making
Clear sense of direction.
Rational and logical.
More than one person so less bias.
Comparisons between alternatives.
Flexible.
Defend policy as its scientific.
Drawbacks of Scientific Decision Making
Slow process to gather and analyse info.
Opportunities missed in fast moving markets.
Have to judge benefits against costs.
Data may not be reliable.
Intuition
Making decisions on a felling/hunch. For smaller business that can't afford to do the Scientific Model.
Factors Between Scientific and Intuition
Speed of decision- sci needs time.
Info available.
Size- lacks time and resources.
Predictability of situation- likely is gut.
Character.
Decision Trees
Mathematical model or tool used to help managers make decisions.
Guide to Decision Trees
Square- represents the decision.
Add options to tree. Circles represent outcomes.
Add the costs under each option and financial results. Probabilities must add to 1.
Expected Value (EV)- probability x expected outcome.
Net Gain- EV1 + EV2 - Costs.
Decide best option.
Advantages of Decision Trees
Sets out problem and encourages a logical approach.
Makes manager consider all options.
Quantifies impact (costs, benefits).
Used for similar scenarios.
Tactical or routine rather than strategic.
Disadvantages of Decision Trees
Ignores constant change of business.
Difficult to get accurate and realistic data for estimates.
Management bias influence probabilities.
Less useful for new or one off decisions.
Influences of Decision Making
Mission.
Objectives.
Ethics (values).
External enviro: market conditions, incomes, competition, interest rates, environment.
Resource constraints: finance, time, people.
Relative Power of Stakeholders
Depends on nature of business.
Small family business- shareholders may be major influence.
Competitive- customers are stakeholders- their needs influence decisions.
Culture
Way to do things. Each business is unique. Values of leader influence it.
Stakeholder
Individuals or groups who have an interest in a business or are affected by its activities. Can be internal or external.
Internal Stakeholders
Inside a business. Owner, shareholder, manager, director.
External Stakeholders
Outside a business. Customers, bank, suppliers, gov, media.
Primary Stakeholders
Directly affected by business. Customers and employees.
Secondary Stakeholders
Indirectly affected by organisations actions, affect/ influence actions. Local community and pressure groups.
Key Stakeholders
Stakeholders with a significant influence or importance within a business. Primary or secondary.
Social Responsibility
The idea that businesses should balance profit making and activities that benefit society. Develop businesses with positive relationships to society they operate in.
High Stakeholder Interest
As managers they have significant personal, financial or career investment in what the business does.
There are few alternatives.
Local councils or gov, they may be called to account for failing to monitor the business activity.
Extent Stakeholders Have the Power to Impose Their Needs
Their status in the organisational hierarchy., their pay, their rep and social standing.
Claim on resources in terms of size of budgets and the number and levels of employees.
Their level of engagement in decision making.
Employees VS Managers
Job security and high wages (increases costs) VS high bonuses paid as a result of improved cost efficiency.
Customers VS Shareholders
Good quality products and low prices (reduce profits) VS high profits and dividends.
Local Community VS Shareholders
Reduction of impact on enviro (high costs) VS low costs leading to high profits and dividends.
Win-Lose Approach
Fixed pot of benefits to share among stakeholder groups. If one group gains more, another gains less.
Win-Win Approach
A firm can, by its actions, cause the pot of benefits to grow so all groups gain more.
Stakeholder Engagement
Reduce likelihood of opposition from stakeholders to a business's actions and decisions through communication and involving them in the process to some extent.
Partnership
Involve stakeholder group most closely to decision- taken jointly by management and stakeholders. Responsibility shared and great deal of 2 way communication. Stakeholders with high power and interest.
Participation
Lesser partnership. Stakeholders still relevant and involved. Responsible for part of decision. 2 way. High power, low interest.
Consultation
Finding out views from relevant stakeholder groups. Respond to questions. 2 way. Stakeholders have limited power to influence decision. High interest, low power.
Push Communication
1 way communication from business to stakeholders. Email, podcast or letters used. Low interest and power.
Pull Communication
Communication with stakeholders but only if they choose to engage. Little interest and power. Advise minor suppliers. Unlikely to have much impact because of little interest.