TOGAF Foundations
1/127
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flash cards for studying for the TOGAF Foundations Exam
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
128 Terms
Define Enterprise Architecture?
Architecture is a formal description of a system, or a detailed plan of the system at the component level, to guide its implementation.
What is the purpose of Enterprise Architecture?
Provides a framework for change, linked to both strategic direction and business value and a sufficient view of the Organization to manage complexity, support continuous change, and manage the risk of unanticipated consequences.
Guides effective change and to govern change.
It can facilitate effective governance, management, risk management, and exploitative opportunities.
During implementation, EA is used by Stakeholders to govern Change.
Why is Enterprise Architecture Important?
EA is developed to guild effective change. Guidance on effective change will take place during the activity to realize the approved EA.
During implementation, EA is used by stakeholders to govern change.
What are some Benefits of Enterprise Architecture?
More effective strategic decision-making by C-level exec's and business leaders, enabling quick responses to change and support for enterprise agility.
More effective and efficient business operations leading to lower operational costs due to the sharing of capabilities across the Enterprise
More effective and efficient Digital Transformation and operations by bringing components into a harmonized environment.
Maximizing ROI by reducing complexity and risk.
Faster, simpler, and cheap procurement efficiency
Enables sponsors and the enterprise to achieve the right balance between conflicting demands and trade-offs.
Address concerns and requirements.
What are the 4 main types (or Domains) of Archiecture
Business Architecture, Data Architecture, Application Architecture, Technology Architecture
What is Business Architecture?
Defines the business strategy, governance, organization, and key business processes
What is Data Architecture?
Describes the structure of an org's logical and physical data assets and data mgmt resources.
What is Application Architecture?
Provides a blueprint for the individual app's to be deployed, interactions and relationships to the core business processes of the org
What is Technology Architecture?
Describes the digital architecture and the logical software and hardware infrastructure capabilities and standards required to support the deployment of business, data, and app services.
Architecture Abstraction level: Contextual
This is the “why”. Understanding the env in which the enterprise operates and the context in which architecture work is planned and executed. It answers why an enterprise undertakes architecture work, the scope of that work, it motivation in terms of goals and drivers.
Architecture Abstraction level: Conceptual
This is the “what”. The focus is on what functionality and requirements need to be met by the architecture. It typically involves modeling desired behavior using service models (e.g., business services, application services, technology services) without detailing how they will be implemented
Architecture Abstraction level: Logical
This is the “How”. Identifying the kinds of business, data, application, and tech components needed to achieve the services identified in the conceptual level. It is about identifying how the arch will be organized and structured, independent of it's implementation
Architecture Abstraction level: Physical (with what)
The allocation and implementation of physical components to meet the identified logical components. Determining what physical components will satisfy the logical abstraction.
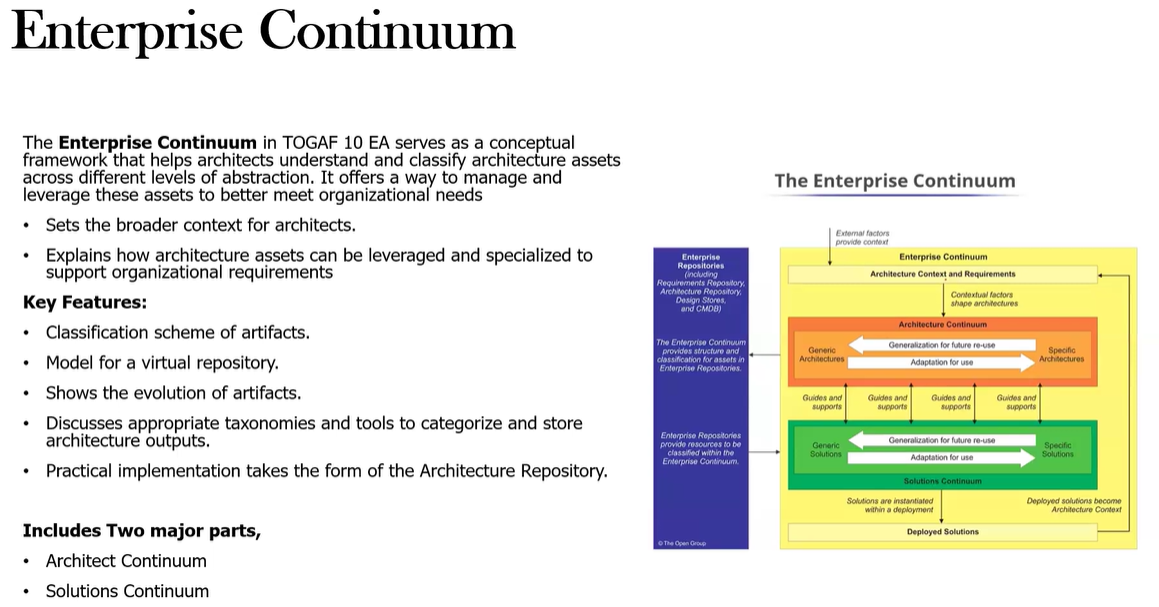
Define the Enterprise Continuum?
The Enterprise Continuum is a conceptual framework designed to help architects organize and evolve architectures and solutions within an enterprise. It provides a structured approach to managing the development of architectures from generic, abstract models to specific, concrete implementations tailored to an organization's unique needs.
It is a roadmap for evolving architectures and solutions from generic to specific, ensuring alignment with the org’s goals and requirements.
What is the Architecture Continuum?
Focuses on the classification and evolution of Architecture artifacts. Progression from generic Foundation architectures to Org-specific architectures.
It helps understanding the different levels of abstraction and specificity in architecture artifacts.
What is the Solutions Continuum?
Complements the Architecture Continuum by providing a view of how solutions evolve.
Demonstrates the progress from generic solutions to org-specific solutions.
Focuses on evolving the architecture into concrete implementations.
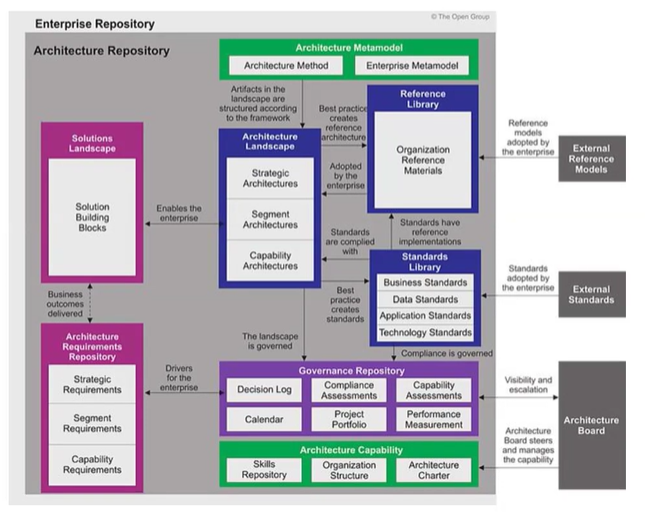
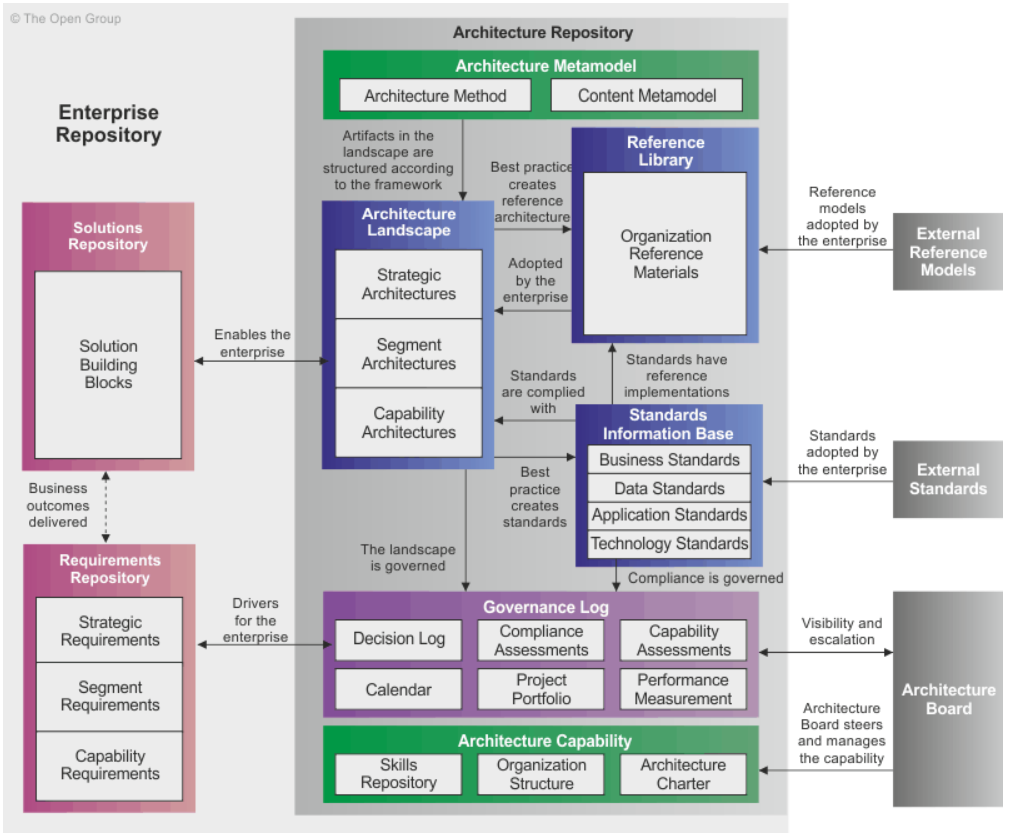
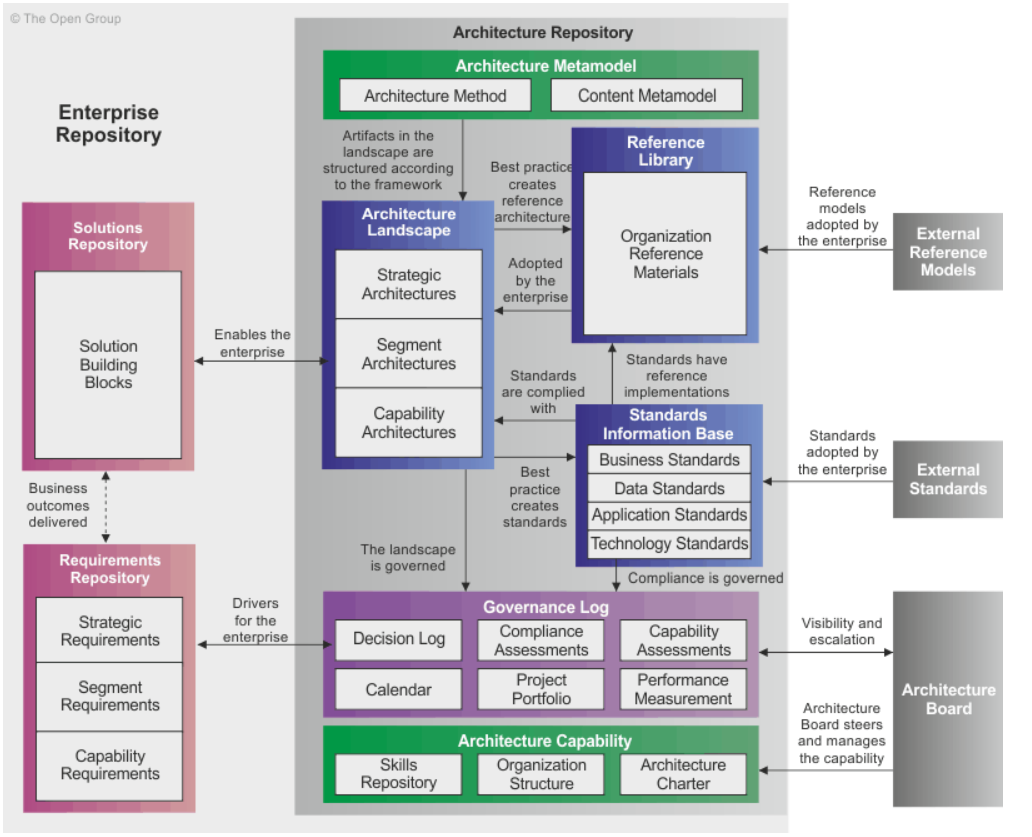
*What is the “Architecture Repository”?
The Architecture Repository serves as a structured collection of architectural information used in enterprise architecture. It acts as a centralized storage system for various architecture-related assets, models, and documentation that support an organization's architecture development efforts.
What are the 9 key components of the Architecture Repository?
Architecture Models - Conceptual frameworks and diagrams representing EA encompassing business, data, apps, and tech architectures.
Architecture Metamodel - describes how the architecture framework is applied within the org.
Architecture Patterns - Reusable solutions and best practices applied to specific design problems during architecture development
Standards and Guidelines - Documentation outlining principles, standards, and guidelines for architecture development and governance
Architecture Views/Viewpoints - Different perspectives on the architecture addressing various stakeholders' concerns
Architecture Landscape - Presents an architecture representation of assets in use or planned at any point in time.
Standards Information Base (SIB) - Captures the standards with which new architectures must comply, including industry standards and selected products and services.
Reference Library - Provides guidelines, templates, patterns, and other forms of reference material to accelerate the creation of new architectures.
Governance Log - Records governance activities across the enterprise, including architecture decisions and their rationales.
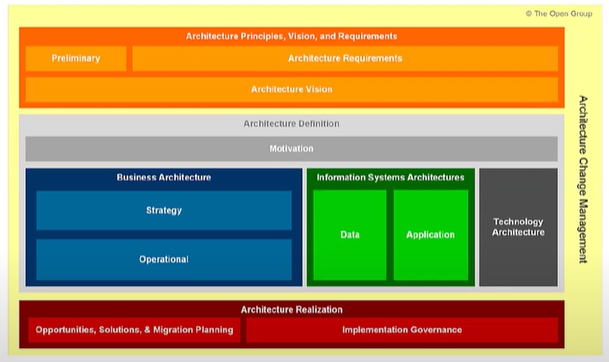
What is the Content Framework?
The Content Framework is a categorization and organization framework to be used for organizing and categorizing architectural work products. It includes deliverables, artifacts within those deliverables, and the architectural building blocks (ABBs) that these deliverables represent. The framework is designed to ensure consistency in the outputs produced during the Architecture Development Method (ADM) process.
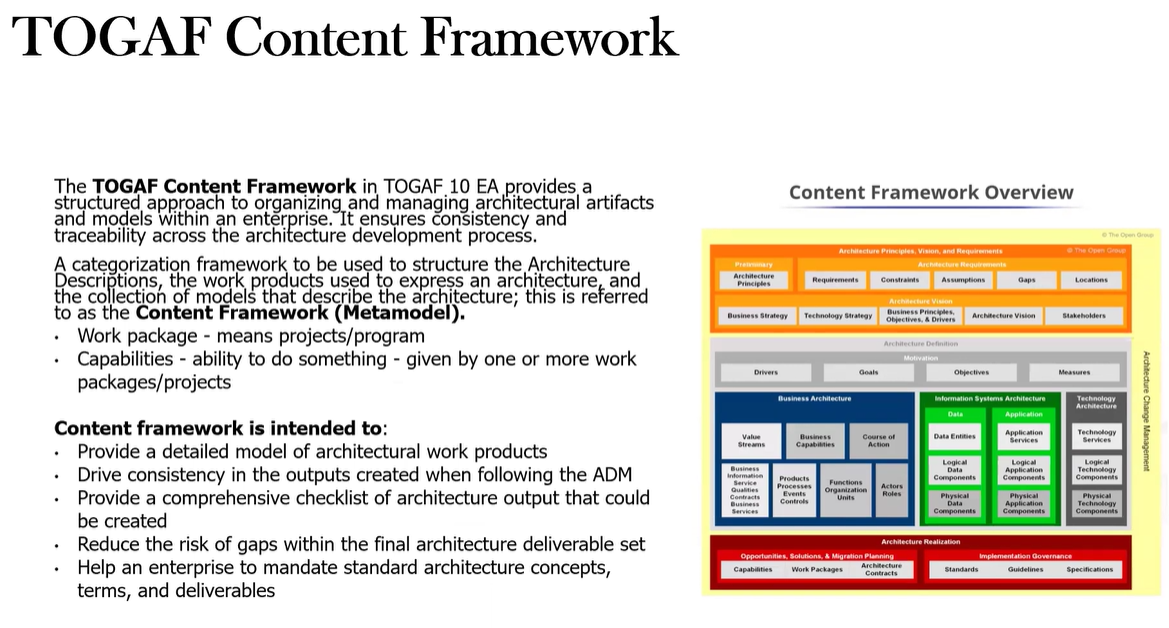
What Parts / Components are part of the Content Framework?
Deliverables: These are formal products that are contractually specified and are outputs from a project. Deliverables can contain many artifacts.
Artifacts: These are fine-grained products that describe an architecture from a specific viewpoint. Examples include use-case diagrams and business interaction matrices.
Architecture Building Blocks (ABBs): These are components that can be combined with other building blocks to deliver architectures and solutions. ABBs are represented by the artifacts within deliverables.
What is the purpose and benefits of the Content Framework?
Drive greater consistency in the outputs created when following the ADM.
Improve communication and collaboration with Stakeholders by providing a shared repository of architectural artifacts.
Ensure all aspects of EA are captured and organized effectively.
Provide a common language for communicating differences between architectures.
Define the Enterprise Metamodel
The enterprise metamodel:
The enterprise metamodel defines the types of entities to appear in the models that describe the enterprise together with the relationship between those entities. It allows architectural concepts to be captured stored filtered queried and represented in a way that supports consistency completeness and traceability.
It provides a formal structure for architectural content, e.g. deliverables, artifacts, and architectural building blocks
Supports traceability across artifacts and ensures consistency in outputs created when following the ADM.
What are the core components (or layers) of the Enterprise Metamodel?
It consists for the following inter-connected layers:
Business Layer: Defines business capabilities, processes, organizational structures, and roles
Data Layer: Addresses data entities, their relationships, and data governance principles
Application Layer: Describes applications, their interactions, and how they support business functions
Technology Layer: Covers IT infrastructure, including hardware, software, networks, and technology standards
What are some of the Key Entities included in the Enterprise Metamodel?
The enterprise metamodel includes the following entities:
Actor
Application Component
Business Service
Function
Organization Unit
Platform Service
Technology Component
What are the benefits attributed to the Enterprise Metamodel?
Benefits include:
Improve communication and collaboration among stakeholders
Enhance consistency in architectural outputs
Facilitate reuse of architectural assets
Support effective decision-making and governance in enterprise architecture initiatives
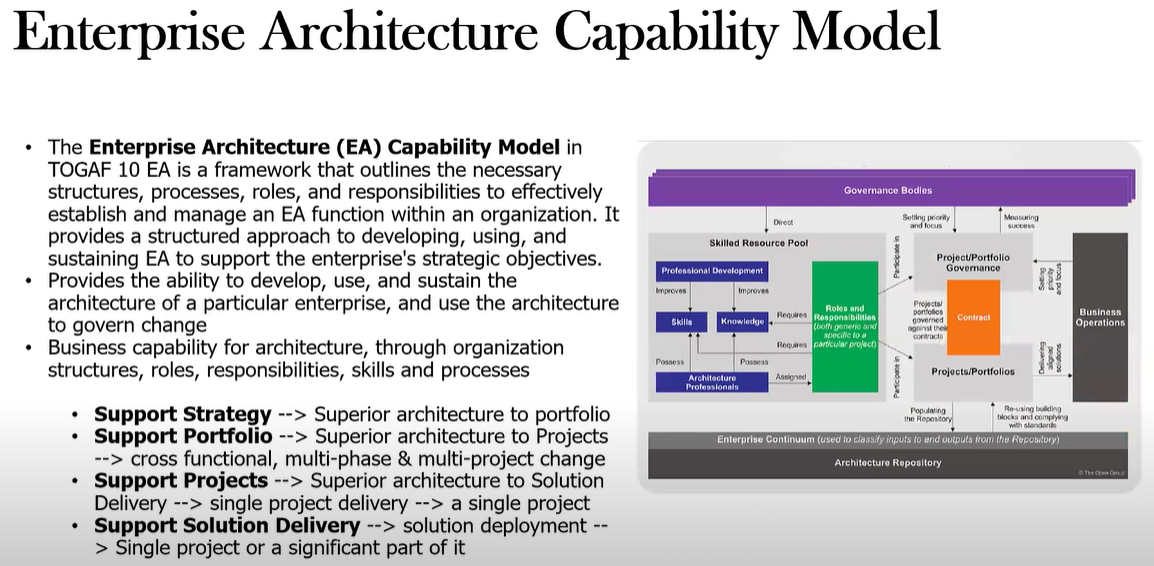
What is the Enterprise Architecture Capability Model?
It’s a framework that outlines the necessary structures, processes, roles, and responsibilities to effectively establish and manage an EA function within an organization.
Provides the ability to develop, use, and sustain the architecture of a particular enterprise, and use the Arch to govern change.
It’s the business capability for architecture, through organization structures, roles, responsibilities, skills and processes.
Define “Architecture Capability”
it is the ability to develop, use, and sustain the architecture for the enterprise and use architecture to govern change
What are the main components of the “Architecture Capability Framework”
Establishing an Architecture Capability
Architecture (Review) Board
Architecture Compliance
Architecture Contracts
Architecture Governance
Architecture Maturity Models
Architecture Skills Framework
Define “Risk” (not “Risk Management)
The effect of uncertainty on objectives
Define Risk Management
Coordinated activities to direct and control a risk. It involves risk classification, identification, assessment, and mitigation planning.
Define Risk appetite
Risk appetite describes the enterprise's attitude towards risk and guides decision-making to balance risk and expected outcomes
What is the purpose of a Gap Analysis?
A gap analysis identified components that need to be added, changed, left-alone, or deleted in order to move from the current state to the future state. So, it documents the differences between the current and future state architectures.
What other purposes does a Gap Analysis serve?
Identify omissions: Highlight items that have been deliberately omitted, accidentally left out, or not yet defined in the Target Architecture.
Validate architecture: Ensure the architecture supports all essential information processing needs of the organization.
Address stakeholder concerns: Identify and address any stakeholder concerns that may have been overlooked in prior architectural work.
Guide improvement: Provide insights into areas that need enhancement or development to achieve the desired future state.
Support roadmap development: Inform the creation of architecture roadmaps by identifying the steps needed to transition from the current to the target state.
What architectural domains are typically examined during a Gap Analysis?
Business architecture (e.g., processes, capabilities)
Data architecture
Application architecture
Technology architecture
What is “Architecture Governance”?
It is:
A system that directs and controls the current and future state
Decision-making process with a defined structure of relationships that direct and control the enterprise to reach their goals
Controls on the creating, monitoring of components and activities, ensuring the evolution of architectures through implementation
Ensuring compliance with internal and external standards and regulations
Ensures accountability to stakeholders
What is the purpose of the Architecture Board?
It is responsible for overseeing the development and implementation of enterprise architectures. It ensures alignment with organizational goals, compliance with standards, and decision-making.
What are the key responsibilities of the Architecture Board?
Responsibilities include:
Decision-Making - approve/reject architecture proposals and changes; ensures compliance with standards
Governance - oversees the ADM lifecycle and manages risks and resolves cross-domain (Biz Arch vs Tech Arch) conflicts
Compliance - Conducts Architecture Compliance Reviews and enforces adherence to the Architecture Repository and the Standards Information Base
Strategic Alignment - Validate that architectures support business objectives
Resource management - allocate budgets and resources for architecture projects and monitor progress and outcomes
What is an Architecture Contract?
It is a joint agreement between development partners and sponsors on the deliverables, quality, and purpose of architecture, basically a “Statement of Work”.
What are some interplay between the ADM and Architecture Contracts?
The “Statement of Architecture Work” produced during Phase A is an Architecture Contract.
Architecture Domains may be contracted out and would have their own Architecture Contract(s)
Implementation of the EA may be contracted out at the end of Phase F / Beginning of Phase G
What are the benefits of performing Compliance Reviews?
Strategic Alignment - ensure alignment with business goals
Risk Mitigation - catch problems early, reduce operational risks, minimizes project deviations
Cost Efficiency - lower development costs, prevent redundant investments
Improved Governance - ensures conformance to contracts
Standards & Regulatory Compliance - Validates adherence to industry standards
Quality Assurance -
Enhanced Communication -
Strategic Agility -
What are architectural Building Blocks?
They are the fundamental components used in the ADM to create and implement enterprise architectures.
What are the two main types of Building Blocks?
Architecture Building Blocks (ABB’s) - define what functionality will be delivered based upon the business and technical requirements and guide the development of the SBB’s
Solution Building Blocks (SBB’s) - define what products and components will implement the functionality.
What are the characteristics of a Building Block?
Functionality Package: A Building Block is a package of functionality defined to meet business needs across an organization
Metamodel Type: Actor, Business Service, app, data entity
Published Interfaces: Building Blocks have published interfaces to access their functionality
Interoperability: They may interoperate with other, interdependent Building Blocks
Composability: Building Blocks may be assembled from other Building Blocks or serve as subassemblies for larger Building Blocks
Reusability and Replaceability: Ideally, a Building Block is reusable and replaceable, and well-specified
Loose Coupling: A Building Block's boundary and specification should be loosely coupled to its implementation
Service Description: For each Building Block, a service description portfolio should be built up as a set of non-conflicting services
What is the ADM?
The Architecture Development Method describes the development and management of the EA lifecycle and forms the core of the TOGAF Framework.
What does the ADM provide?
It provides a tested and iterative process for developing architectures. It also demonstrates essential information flow.
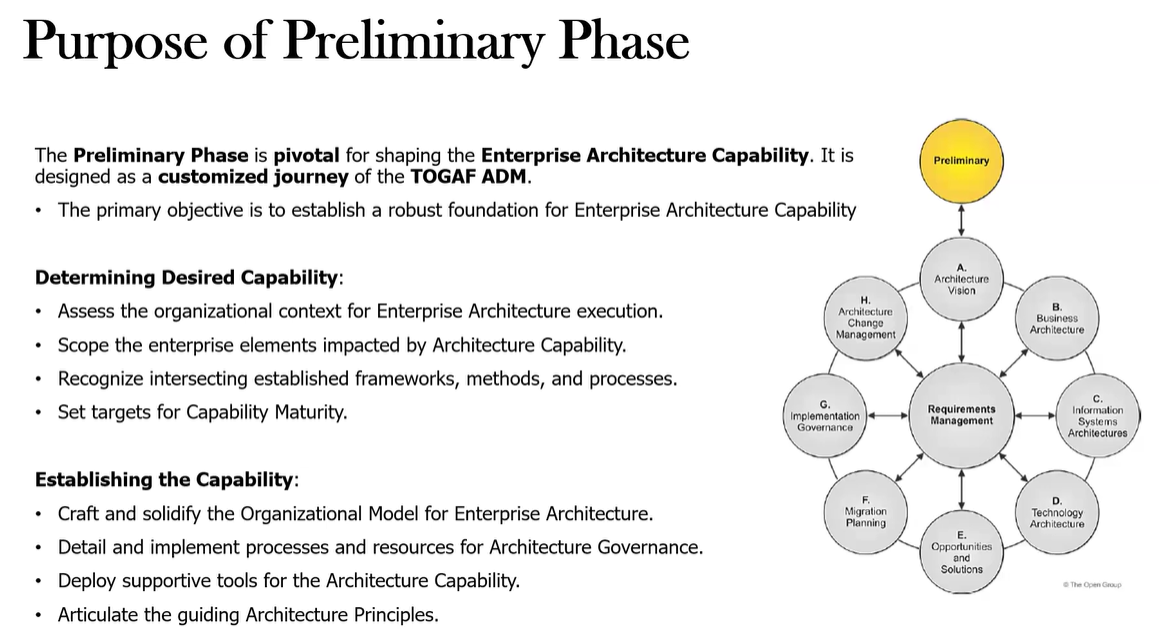
What is the purpose of the Preliminary Phase?
Define and establish the architecture capability within the organization
Customize TOGAF where necessary
Define Architecture Principles
Establish relationships between management frameworks
Establish capability maturity target
Define tools to support the architecture capability
Establish the Org model for EA
What are the primary steps in the Preliminary Phase?
Scope the enterprise orgs impacted
Confirm governance and support frameworks
Define and establish EA team and Org
Identify and establish Architecture Principles
Tailor the TOGAF and other Frameworks
Develop a strategy and implementation plan for tools and techniques

What are the key deliverables produced in the Preliminary Phase?
Org model for EA
Tailored Architecture Framework - for the org
Architecture Principles - guiding principles
Architecture Repository (initial setup) - structure for storing artifacts
Architecture Capability assessment (maturity)
Architecture Governance Framework - structures & processes for architecture decision making
What is the name for ADM Phase A?
Architecture Vision
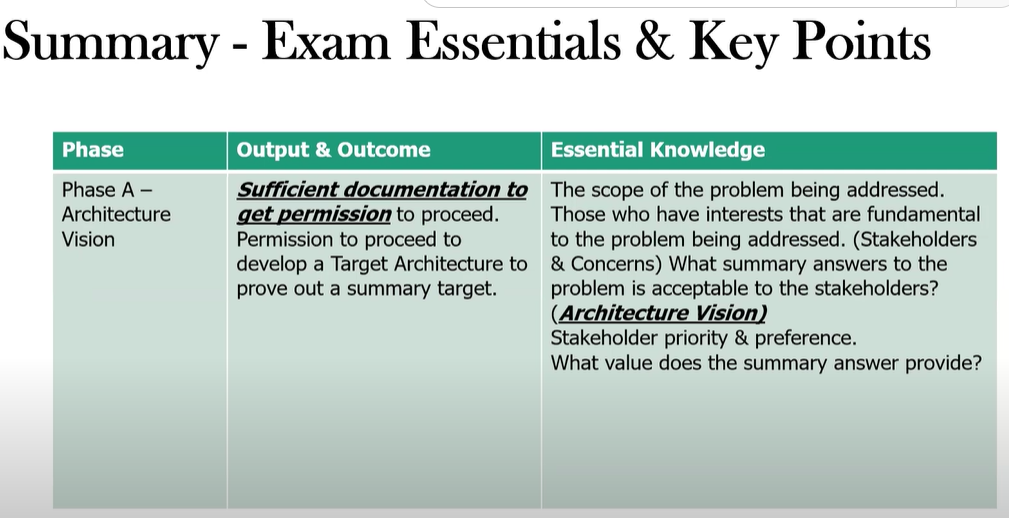
Define Phase A: Architecture Vision and its primary purpose.
It is the initial phase of the ADM and its primary purpose is to:
Develop a high-level aspirational vision of the capabilities and value to be delivered as a result of EA activity
Create a high-level target vision of the Target Architecture
Define the scope of the architecture development effort
Identify key stakeholders and their concerns
Obtain formal approval to proceed with architecture development (Statement of Architecture Work)
What are the key activities in Phase A?
Establishing the architecture project and its scope
Identifying stakeholders, concerns, and business requirements
Confirming and elaborating business goals, drivers, and constraints
Evaluating business capabilities
Developing an Architecture Vision
Defining value propositions and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Identifying risks and mitigation strategies
Assess readiness for business transformation
Develop the Statement of Architecture Work and obtain approval
Stakeholders, concerns, and business requirements
Identify the key stakeholders
Create the Stakeholder map
Capture the concerns and viewpoints in the Architecture Vision
Which of these concerns and viewpoints will be developed to satisfy the requirements

What are the key deliverables produced in the Phase A: Architecture Vision?
Architecture Vision document - High-Level description of the Baseline and Target Architectures; Also includes a summary of architecture work and stakeholder’s concerns, capability assessment, and tailored Architecture Framework
Statement of Architecture Work - Defines cope and approach for the architecture work; includes a statement about what work products will be produced, resources required, and timeline
Stakeholder Map - id’s key stakeholders & their concerns
Communication Plan - out to engage with stakeholders throughout the project
Initial Architecture Repository content - populate with existing architecture artifacts and reference materials
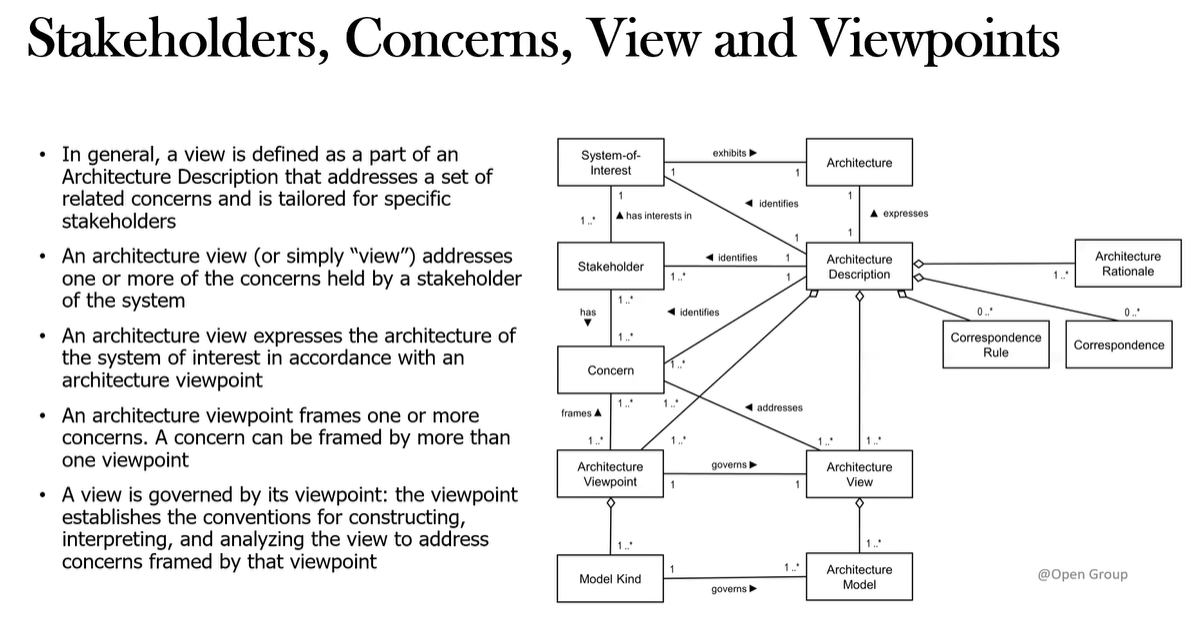
What is the name of ADM Phase B?
Business Architecture
What does Phase B focus on?
Phase B focuses on the developing the Target Business Architecture that describes how the enterprise needs to operate to achieve business goals.
It also identifies the candidate Architecture Roadmap components based upon the Baseline/Target gaps.
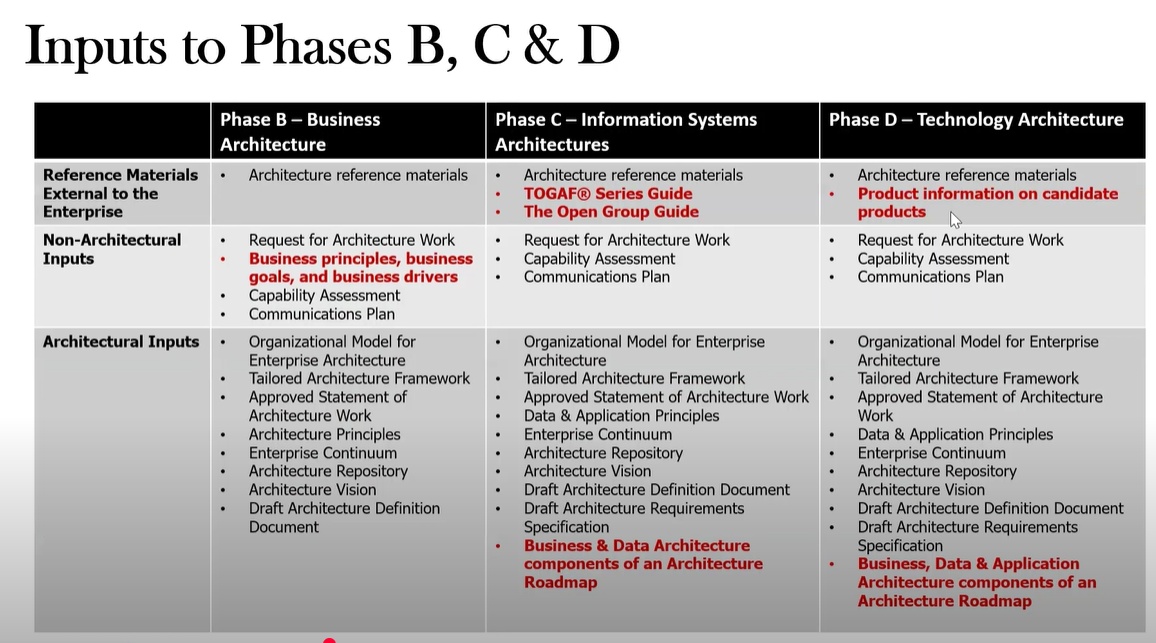
What are the inputs to Phase B?
Refernce Materials: Architecture Reference materials
Request for Architecture Work
Business principles, business goals, and business drivers
Capability assessment
Communication Plan
Org Model for EA
Tailored Arch Framework
Statement of Arch Work
Arch Principles
Enterprise Continuum
Arch Repository
Arch Vision
Draft Arch Definition Document
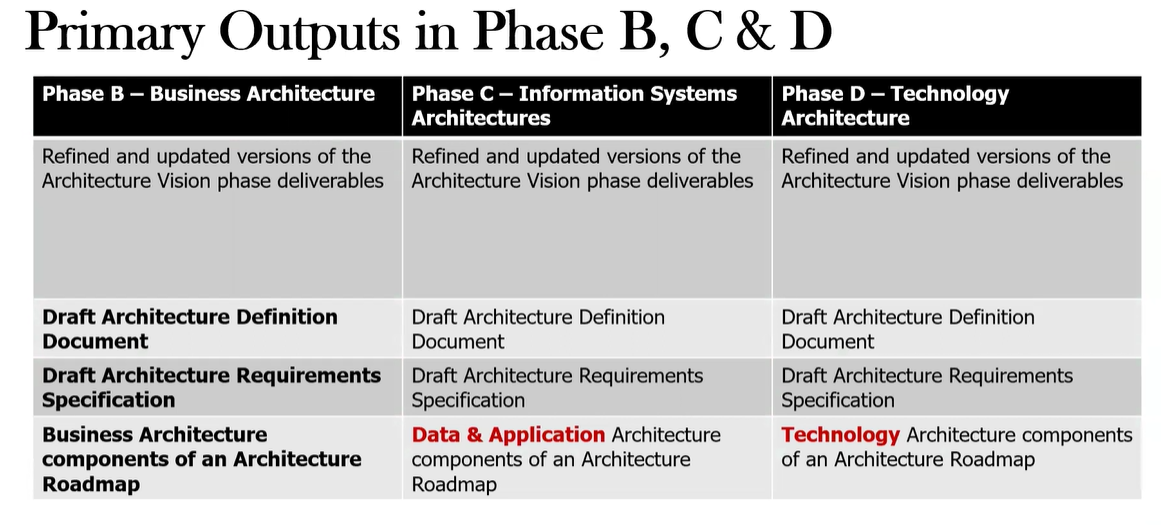
What are the key deliverables produced in the Phase B: Business Architecture?
Business Architecture components of an Architecture Roadmap (e.g., business models, operating models, capability models, process models)
Updated Architecture Repository / Architecture Definition Document
Draft Architecture Requirements Specification
update the Architecture Vision phase deliverables if necessary
What does the Business Architecture Document typical include?
Detailed description of Baseline and Target Business Architectures
Business service/information diagram
Functional decomposition diagram
In Phase B, what is typically updated in the Architecture Repository?
Business architecture artifacts, such as, Org Charts, Process models, and Capability Maps
What are some of the techniques and tools used in Phase B?
Business capability mapping
Business process modeling (e.g., BPMN, APQC Process Classification Framework)
Organizational modeling
Use case diagrams
Value stream mapping
Stakeholder maps
SWOT analysis
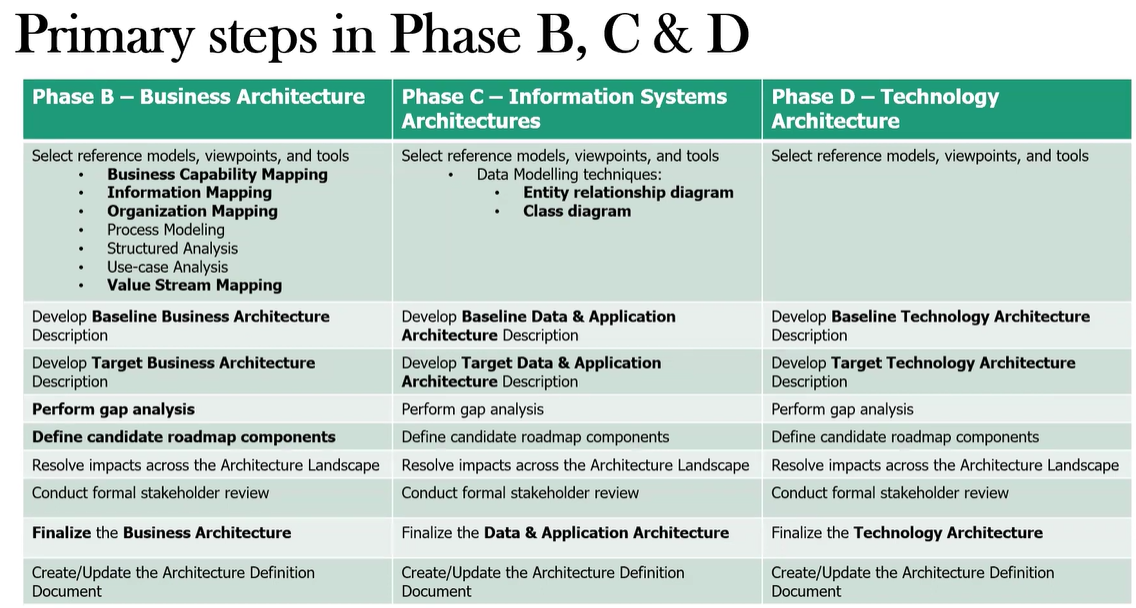
What are the key activities performed within Phase B?
Select reference models, viewpoints, and tools - Choose appropriate business models and tools for architecture development
Develop Baseline Business Architecture description - Document current business processes, organizational structure, and information flows
Develop Target Business Architecture description - Define future business processes, organizational structure, and information flows; Ensure alignment with business strategy and stakeholder concerns
Perform gap analysis - Compare Baseline and Target Architectures; Identify required changes to reach the target state
Define roadmap components - Prioritize activities for moving to the Target Architecture; Identify opportunities for quick wins
Resolve impacts across the Architecture Landscape - Ensure consistency with other architecture domains (Data, Application, Technology)
Conduct formal stakeholder review - Present Business Architecture to key stakeholders for feedback and approval
What is the name of ADM Phase C?
Information Systems Architectures
What are the main objectives of Phase C?
Phase C is called the Information Systems Architectures and its main objectives are:
Develop the Target Information Systems Architectures, describing how the enterprise's Information Systems will enable and support the business goals
Identify gaps between the Baseline and Target Information Systems Architectures
Define candidate roadmap components to bridge these gaps
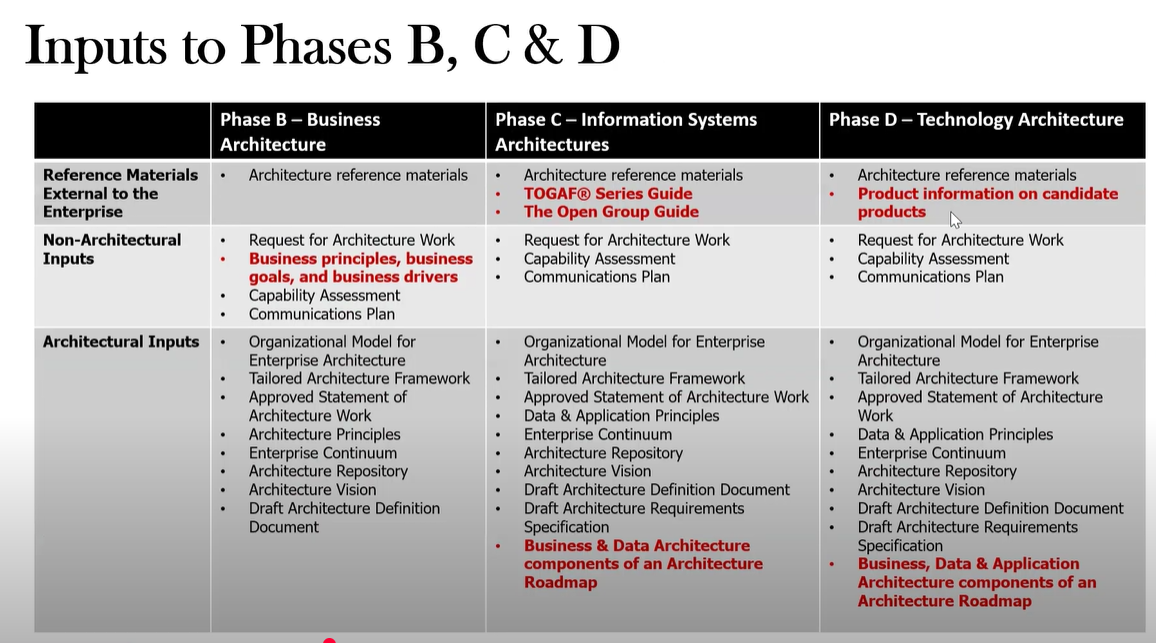
What are the main inputs of Phase C?
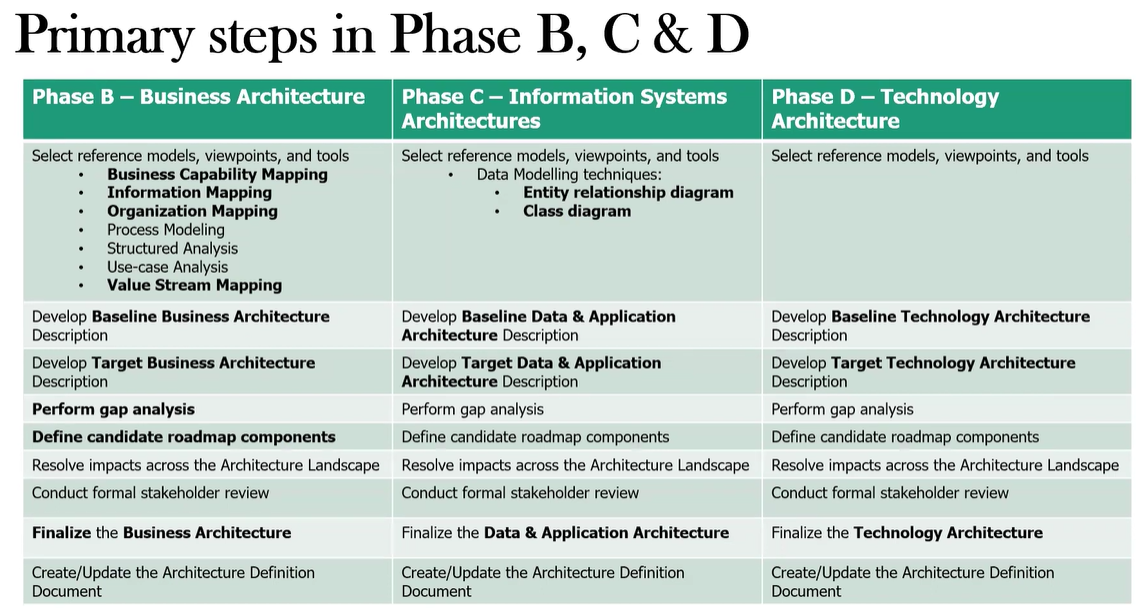
What are the key activities in Phase C?
Develop Data Architecture (major types and sources of data, logical and physical data models, id data management processes and tools)
Develop Application Architecture (major kinds of application systems, interactions between systems, app relationships to business processes)
Performing gap analysis between Baseline and Target of these architectures
Defining Roadmap components to move between current and target architectures
Resolving impacts across the Architecture Landscape
Conducting formal stakeholder reviews
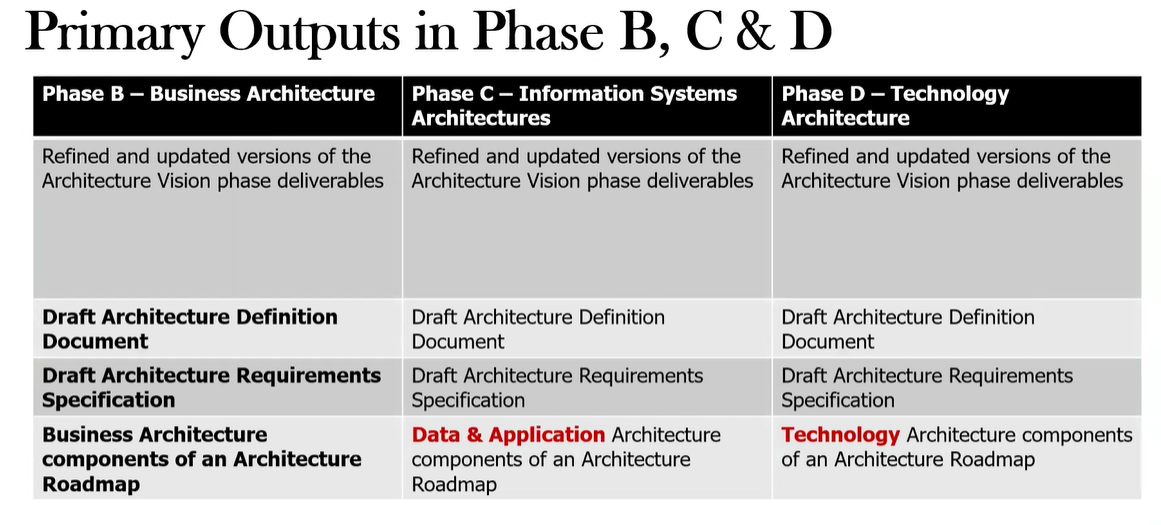
What are the key deliverables produced in the Phase C: Information systems Architecture?
Data Architecture document (data entity catalog, data component catalog, data entity/business function matrix)
Application Architecture document (app portfolio catalog, interface catalog, app/org matrix)
Updated Architecture Repository (Architecture Requirement Spec, Architecture Roadmap)
Update the Architecture Vision phase deliverables
What is the name of ADM Phase D?
Technology Architecture
What is the main objectives of Phase D?
Define the target Technology Architecture that enables the data and application components developed in Phase C
Identify gaps between the Baseline and Target Technology Architectures
Develop candidate roadmap components to bridge these gaps
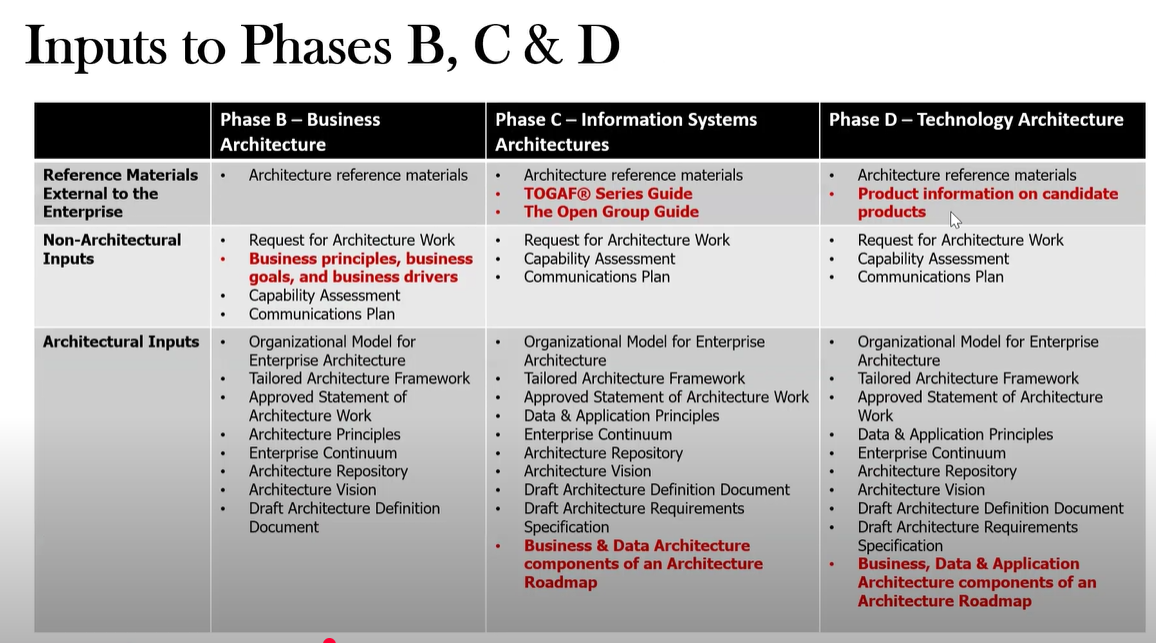
What are the inputs for Phase D?
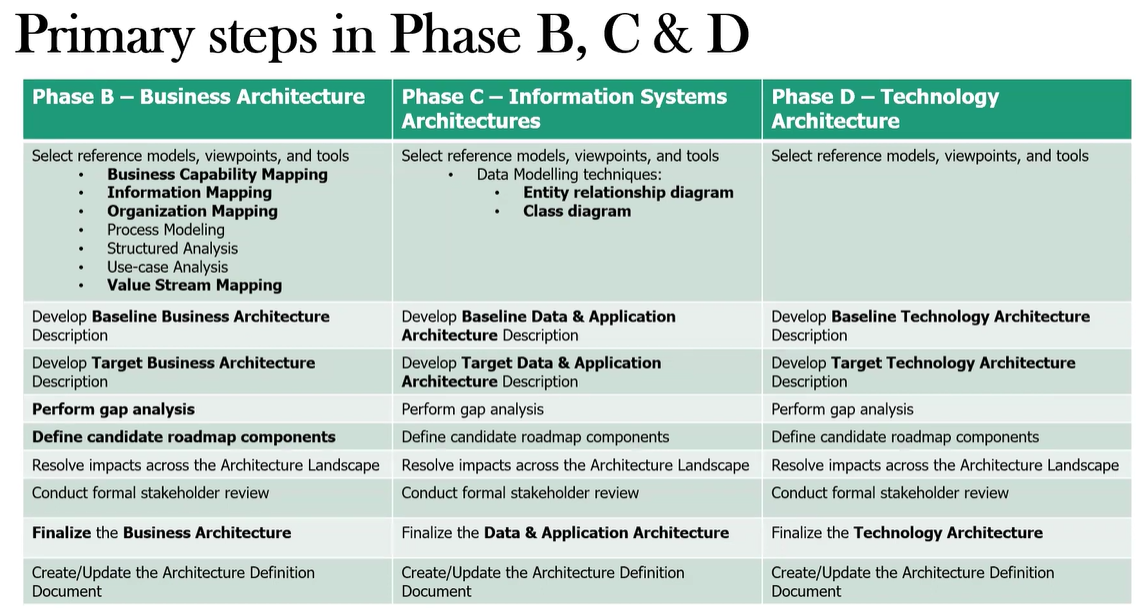
What are the key activities in Phase D?
Identifying major technologies and defining technology requirements
Developing Technology Architecture models
Assessing the current technology environment
Creating a Target Technology Architecture
Performing gap analysis
Defining roadmap components
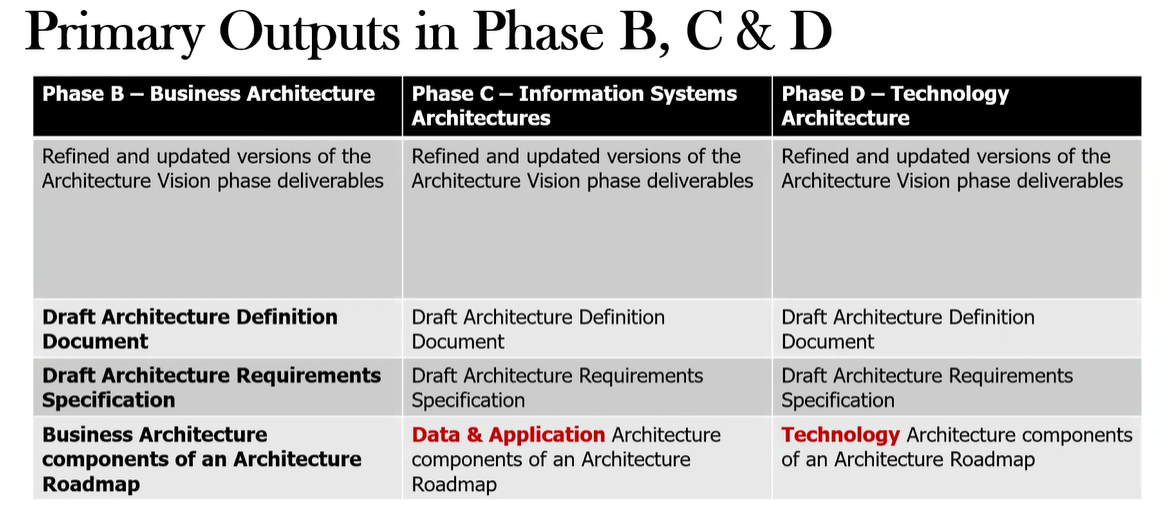
What are the key deliverables produced in Phase D : Technology Architecture?
Technology Architecture Definition Document
Updated Architecture Requirements Specification
Technology Architecture models
Technology standards and guidelines
Updated Architecture Roadmap
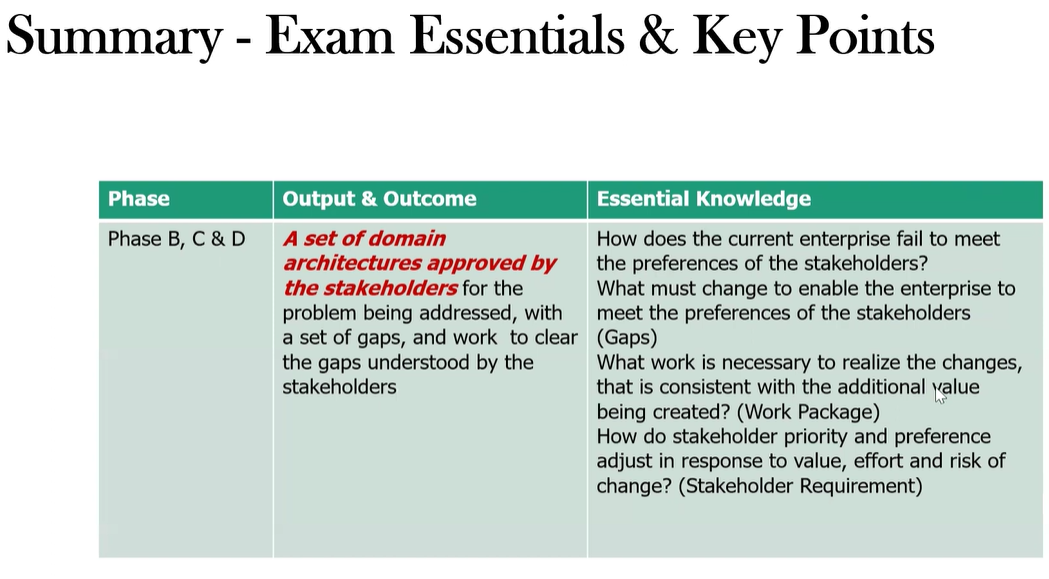
what are the Outputs and Outcomes for Phase B, C, D?
Output & Outcomes
A set of domain architectures approved by the stakeholders, with identified gaps and the target arch to address those gaps and is understood by the stakeholders.
Essential Knowledge
How does the current enterprise fail to meet the needs of the stakeholders?
What must change to enable the enterprise to meet stakeholder needs?
What work is required to realize the changes to create additional value (work packages)?
How to adjust stakeholders priorities based upon value, effort, and risk?

What is the name of ADM Phase E?
Opportunities and Solutions
What are the main objectives of Phase E?
Generate the initial complete version of the Architecture Roadmap
Determine overall Solution Building Blocks (SBBs) to finalize the Target Architecture
Identify delivery vehicles (projects, programs, or portfolios) for implementing the Target Architecture
Transitions Architectures, if applicable,
Create the Implementation and Migration Plan
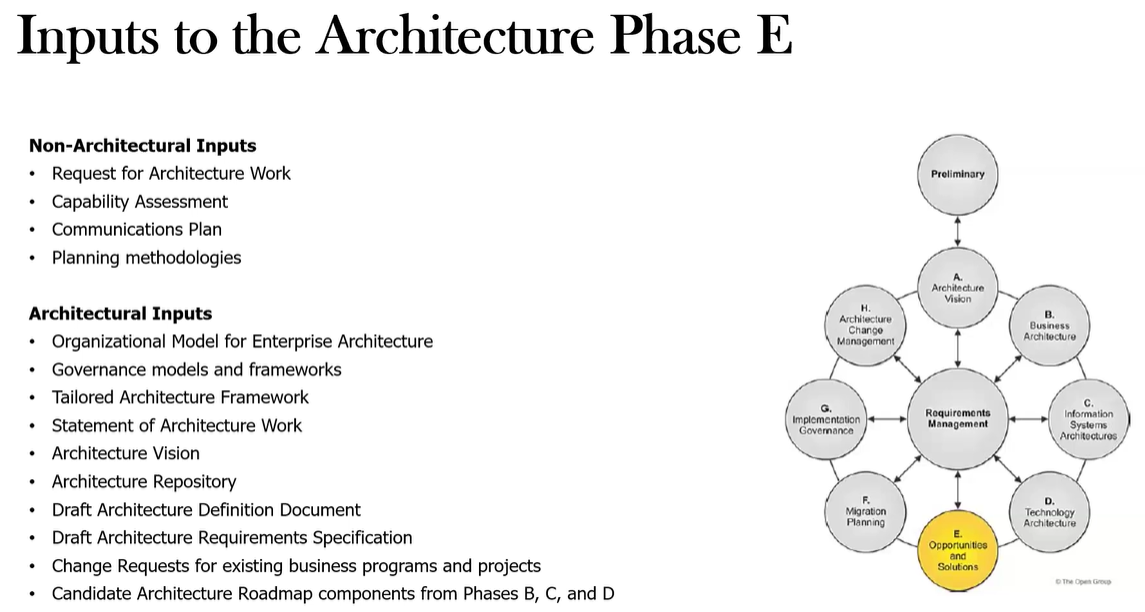
What are the key Inputs to Phase E?
What are the key activities of Phase E?
Consolidate gap analysis results from Phases B, C, and D
Review consolidated interoperability requirements
Determine the business constraints for implementation
Refine and validate dependencies
Formulate the implementation and migration strategies
Create the Architecture Roadmap & Implementation and Migration Plan
Identify and group major work packages
Identify Transition Architectures if needed
Confirm Business readiness and risk
Determine Solution Building Blocks (SSBs)
Assess Dependences, costs, and benefits
What are the key deliverables produced in Phase E: Opportunities and solutions?
Draft Architecture Definition Document (ADD)
Draft Architecture Requirements specification
Capability Assessments
Architecture Roadmap
Implementation and Migration Plan (initial version)
Architecture Building Blocks (ABBs)
Solution Building Blocks (SBBs)
Transition Architectures
Update Statement of Architecture Work (SoAW)
What is the name of ADM Phase F?
Migration Planning
What are the main objectives of Phase F?
Finalize the Architecture Roadmap and Implementation and Migration Plan
Ensure coordination with the enterprise's overall change portfolio
Analyze costs, benefits, and risks of the transition architectures and work packages
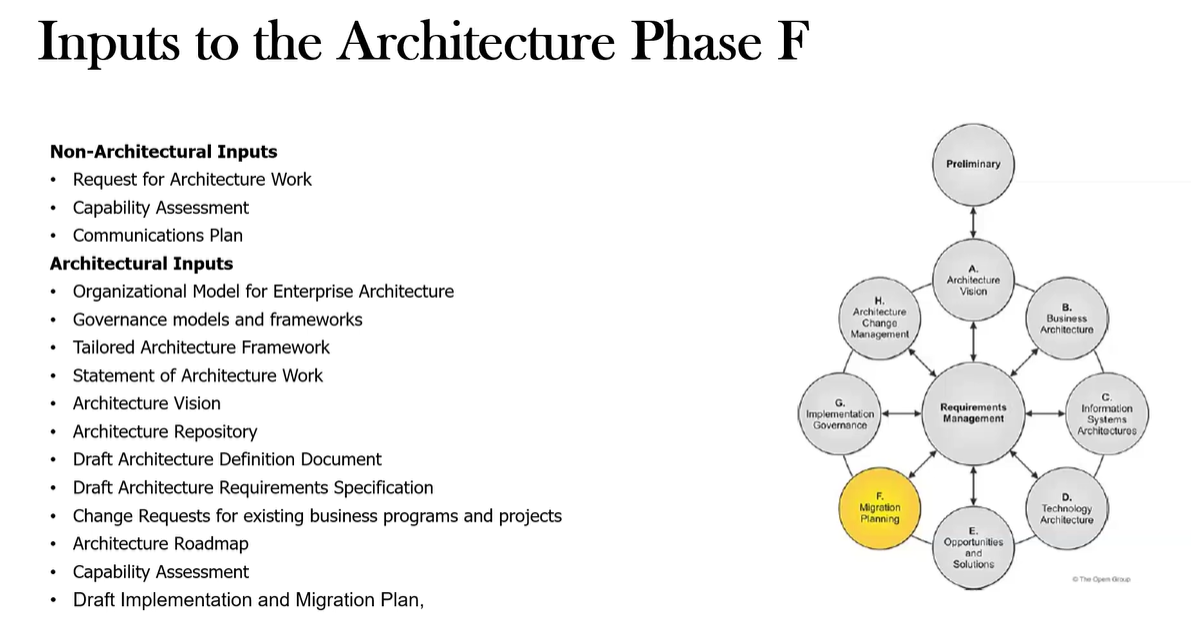
What are the Inputs to Phase F?
What are the key activities of Phase F?
Identify Work Packages: Break down the overall implementation into smaller, manageable work packages and assign value to each package.
Define / Finalize the Migration Strategy: Determine the approach to transition from the current architecture to the target architecture, including prioritizing and sequencing work packages.
*Prioritize Migration Projects: Conduct a cost/benefit assessment and risk validation to prioritize the migration projects.
*Estimate Costs and Resources: Provide an estimate of the costs, resources, and time required for each work package, facilitating better budget and resource allocation.
*Develop a Detailed Migration Plan: Create a structured timeline and roadmap, detailing when and how each work package will be executed.
Identify Risks and Mitigation Strategies: Analyze potential risks associated with the implementation and propose measures to mitigate those risks.
Engage Stakeholders: Ensure that relevant stakeholders are involved in the planning process to gain insights and support.
*Confirm Management Framework Interactions: Validate that the management framework interactions for the Implementation and Migration Plan are confirmed.
*Assign Business Value: Assign a business value to each work package to prioritize and justify the investments.
*Confirm Architecture Roadmap: Finalize the Architecture Roadmap and update the Architecture Definition Document accordingly.
*Document Lessons Learned: Complete the architecture development cycle and document any lessons learned for future reference.

What are the key deliverables produced in Phase F: Migration Planning?
Refined/Approved Implementation and Migration Plan
Finalized Architecture Definition Document
Finalized Architecture Requirements Specification
Finalized Architecture Roadmap
Finalized Transition Architecture documents
Architecture Implementation Governance Model
Requests for Architecture Work
Change Requests for Architecture capability based on lessons learned

What is the name of ADM Phase G?
Implementation Governance
The main objectives of Phase G?
Ensure implementation projects conform to the Target Architecture
Provide architectural governance for the implementation
Monitor and evaluate the implementation progress
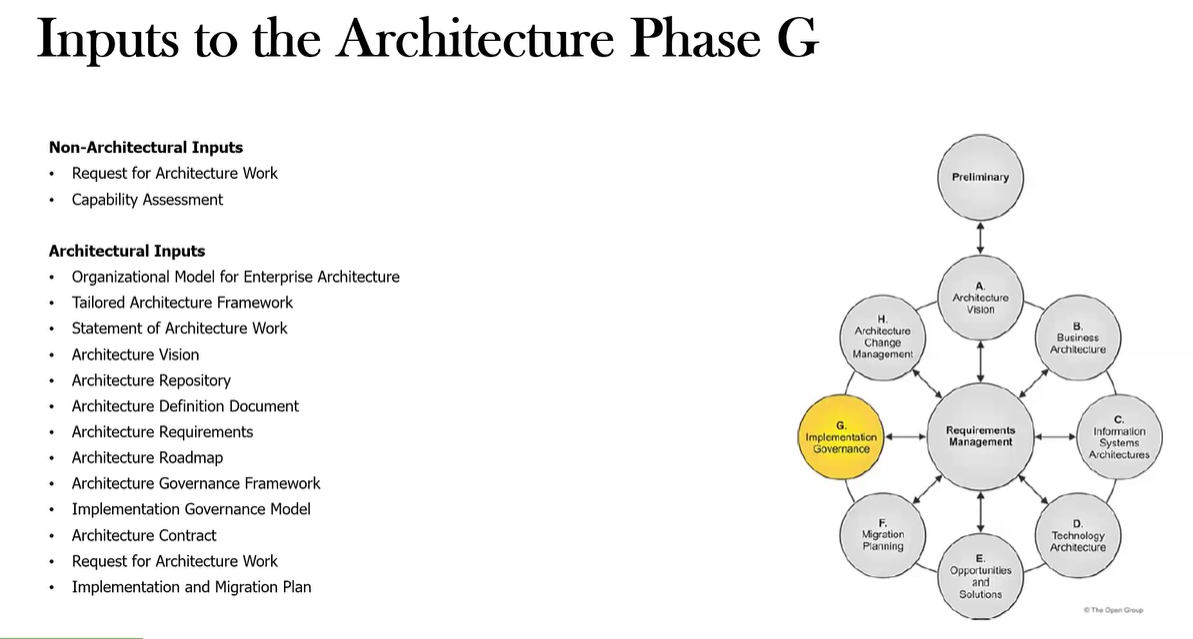
What are the inputs to Phase G?
The key activities of Phase G are?
Performing architecture governance functions
Confirming scope and priorities for deployment with Dev organization
Identifying deployment resources and skills
Guiding solution development
Conducting Enterprise Architecture compliance reviews
Implementing business and IT operations
Performing post-implementation reviews

What are the key deliverables produced in Phase G: Implementation Governance?
Architecture Contract (updated if necessary)
Compliance Assessments
Provide recommendations for non-compliant implementations
Provide guidance / oversight as necessary
Manage changes
Address Issues / Conflicts
What is the name of ADM Phase H?
Architectural Change Management
The main objectives of Phase H?
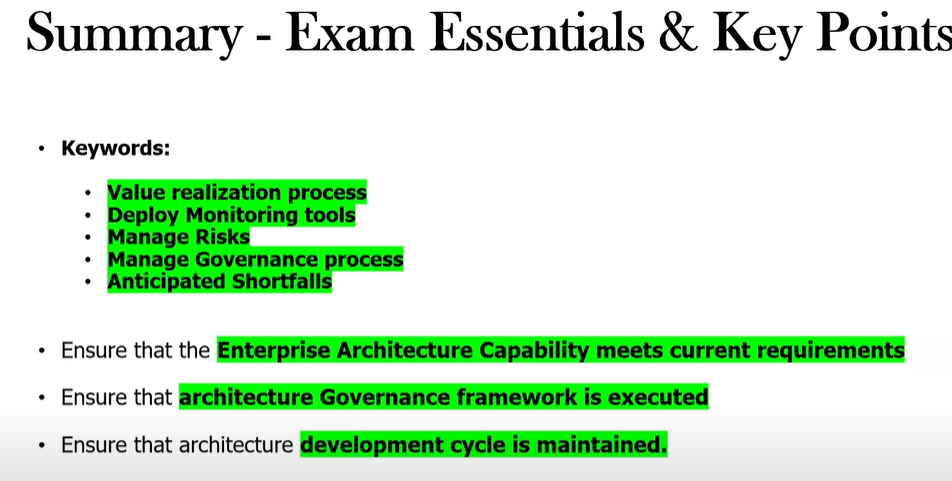
Ensure the architecture development lifecycle is maintained
Execute the Architecture Governance Framework
Ensure that the Enterprise Architecture Capability meets the current requirements
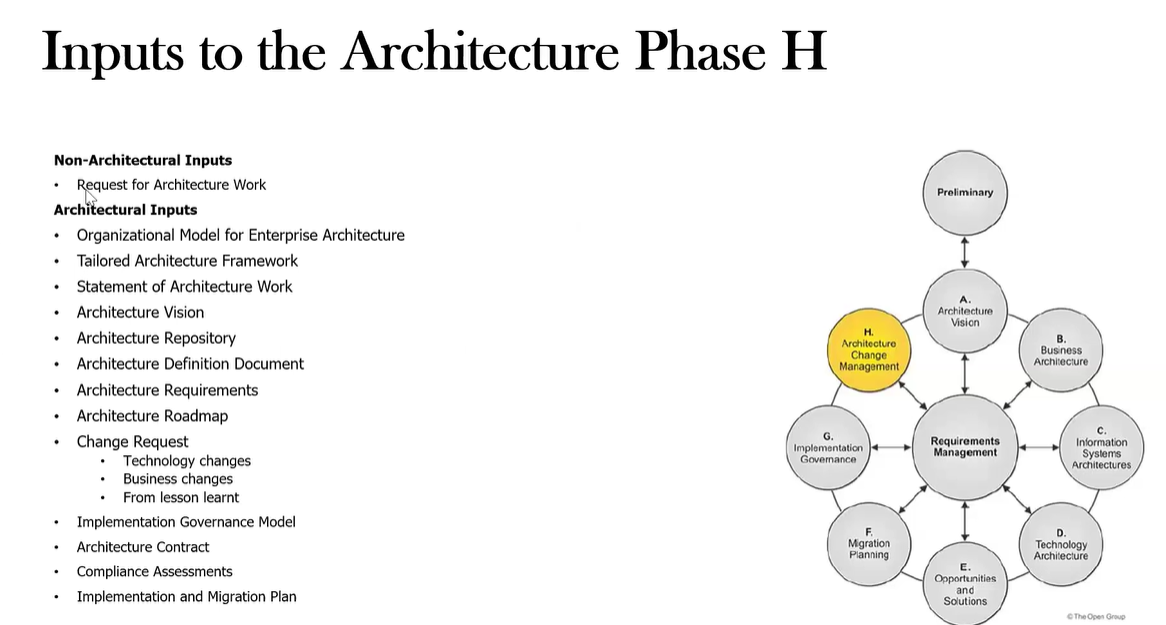
What are the Inputs to Phase H?
The key activities of Phase H are?
Establishing a value realization process
Deploying monitoring tools to track architecture changes
Managing risks associated with architectural changes
Providing analysis for architecture change management
Developing change requirements to meet performance targets
Managing the governance process
Activating the change implementation process
What are the key deliverables produced in Phase H: Architecture Change Management?
Architecture Updates
Changes to the Architecture framework and principles (if necessary)
New Architecture work requests
Change Request documents
Updated Architecture Repository
Implementation value assessments
Threat and opportunity assessments

What is the purpose of the Requirements Management phase?
Identifying, documenting, and managing requirements…
Identify, store, and manage architecture requirements across all ADM phases
Ensure requirements remain aligned with organizational goals and adapt to changes
Maintain traceability between requirements and architecture artifacts
Facilitate impact analysis when requirements change
Support the evaluation and selection of architecture alternatives
Provide a basis for defining architecture scope, objectives, and deliverables
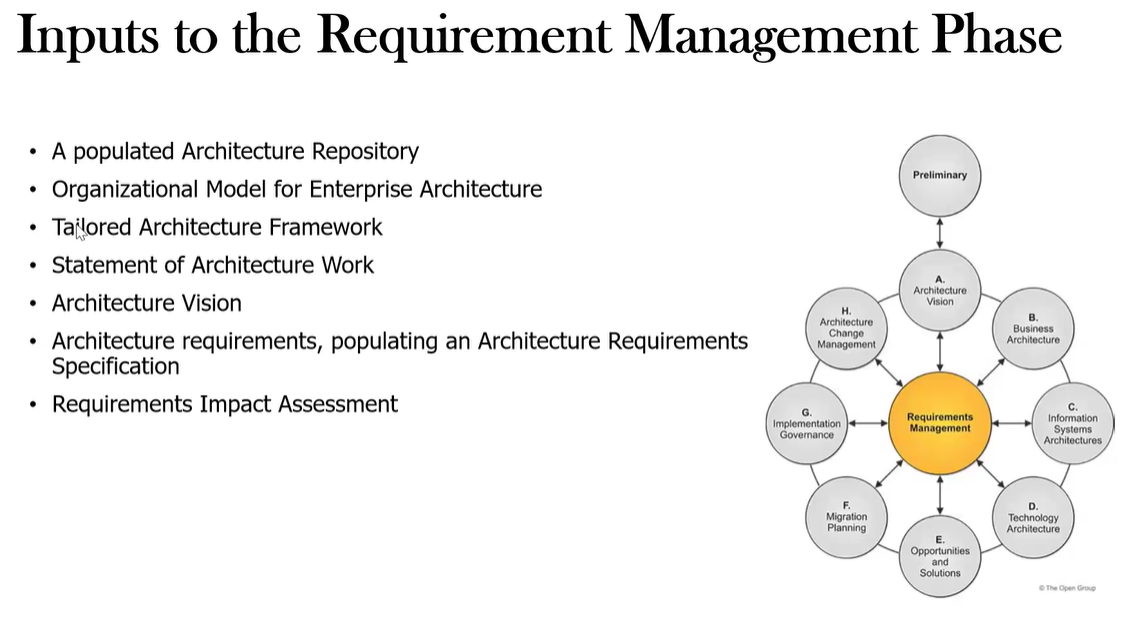
What are the Inputs to the Requirements Management Phase

What are the primary outputs in the Requirements Management phase?
Requirements impact Assessment
Updated Architecture Requirement Specification
In TOGAF, the Business Scenarios technique may be helpful when identifying what?
Business Requirements
What are the 4 main iteration cycles?
Architecture Capability Iteration - ensuring the org has the skills & processes to execute architecture development effectively
Architecture Development Iteration - focuses on preparing the actual architecture ensuring Business, Data, Apps, Tech architectures are integrated into transition plans
Transition Planning Iteration - creating change roadmaps to go from baseline to target
Architecture Governance Iteration - ensuring compliance to standards, providing guidance
What two phases are typically part of the Architecture Capability Iteration?
Preliminary
A: Architecture Vision
What three phases are typically part of the Architecture Development Iteration?
B: Business Architecture
C: Information Systems Architecture
D: Technology Architecture
What two phases are typically part of the Transition Planning Iteration?
E: Opportunities and Solutions
F: Migration Planning