1.3 bacterial growth and phys
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
bacteria usually divide via?
binary fission
do bacteria grow linearly or exponentially
exponentially
energy to make macromolecules needed for bacterial growth is obtained via?
respiration or fermentation
bacteria use hexoses by changing _______ to _________. what is the net ATP of this process?
glucose; pyruvate; 1
anaerobic bacteria build up pyruvate and convert it into? what is the purpose of this?
lactic acid; regenerate NAD+
if oxygen is available, bacteria can convert pyruvate to ______ and then is completely oxidized into ______ via the ______ cycle
acetyle CoA; CO2; Krebs
where is the ETC found in gram negative bacteria
inner cytoplasmic membrane
what other ions can bacteria use as the final e- acceptor in anaerobic respiration
nitrate, sulfate, carbonate, etc
most bacteria are facultative anaerobes meaning?
can grow in presence or absence of O2
oral and gut microbes are ______ ________ meaning that they cannot tolerate O2
obligate anaerobes
very few bacteria are strictly ________
aerobic
some bacteria have high nutrient requirements and can only live ______ _______
inside cells
all bacteria have peptidoglycan except for what genus
mycoplasma
mycoplasma contribute to?
pelvic inflammatory disease
chlamydiae genus are gram _____ and require ______ from the host cells
negative; ATP
chlamydiae can cause?
eye infections, urethritis, genital infections, pneumonia
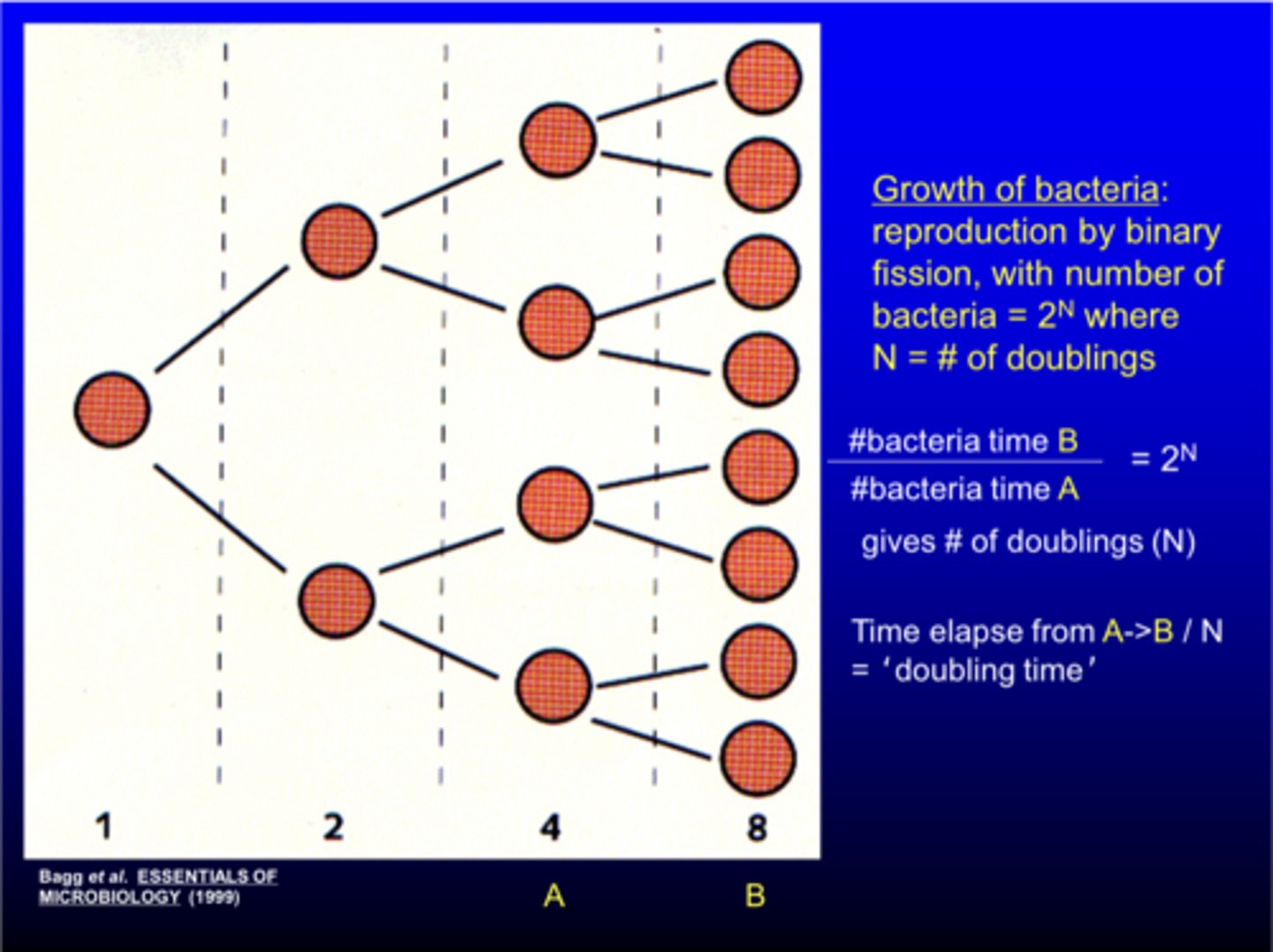
review growth/doubling of bacteria slide
growth can be calculated via 2^N where N = # of doublings
what are the growth phases in batch culture
lag, exponential, stationary, decline
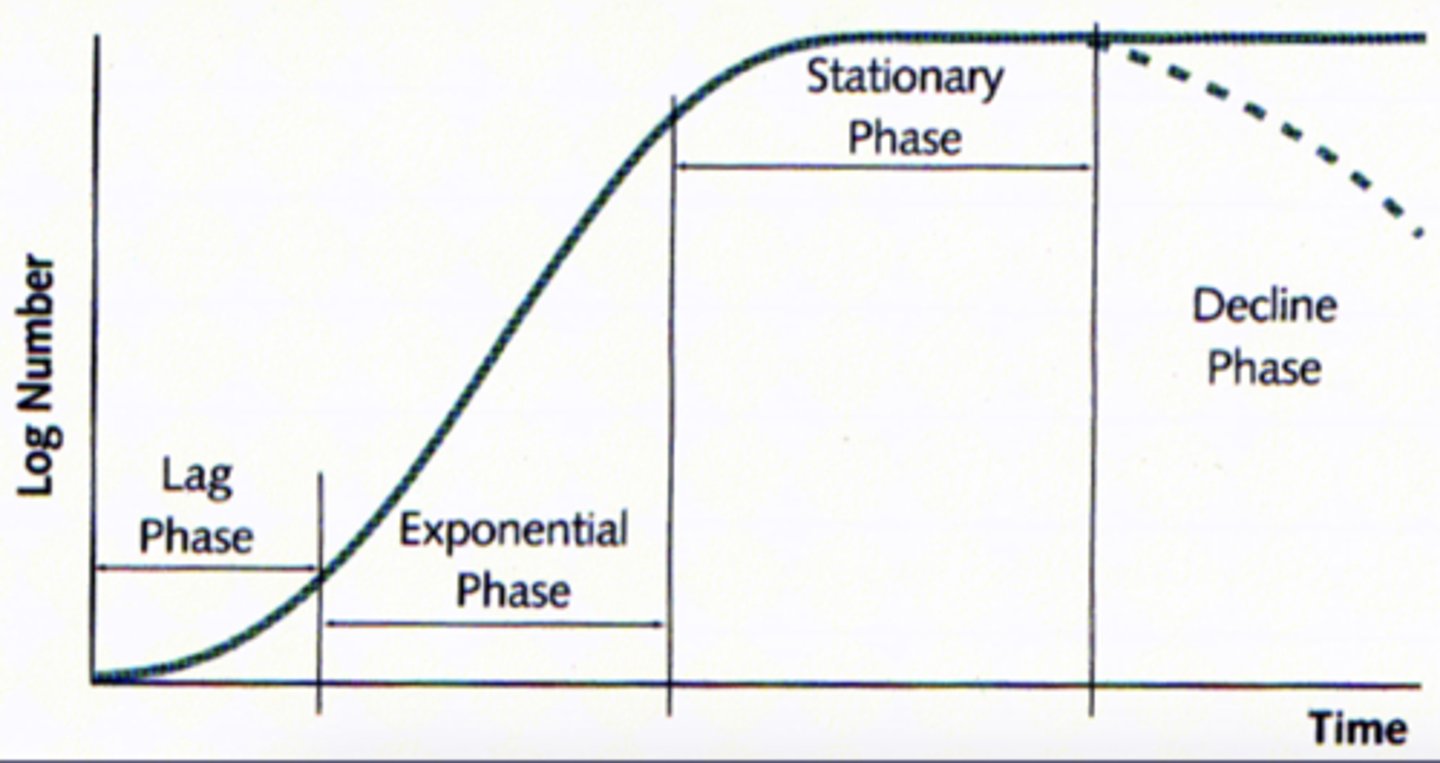
during which growth phase are toxins or spores normally made/expressed
stationary
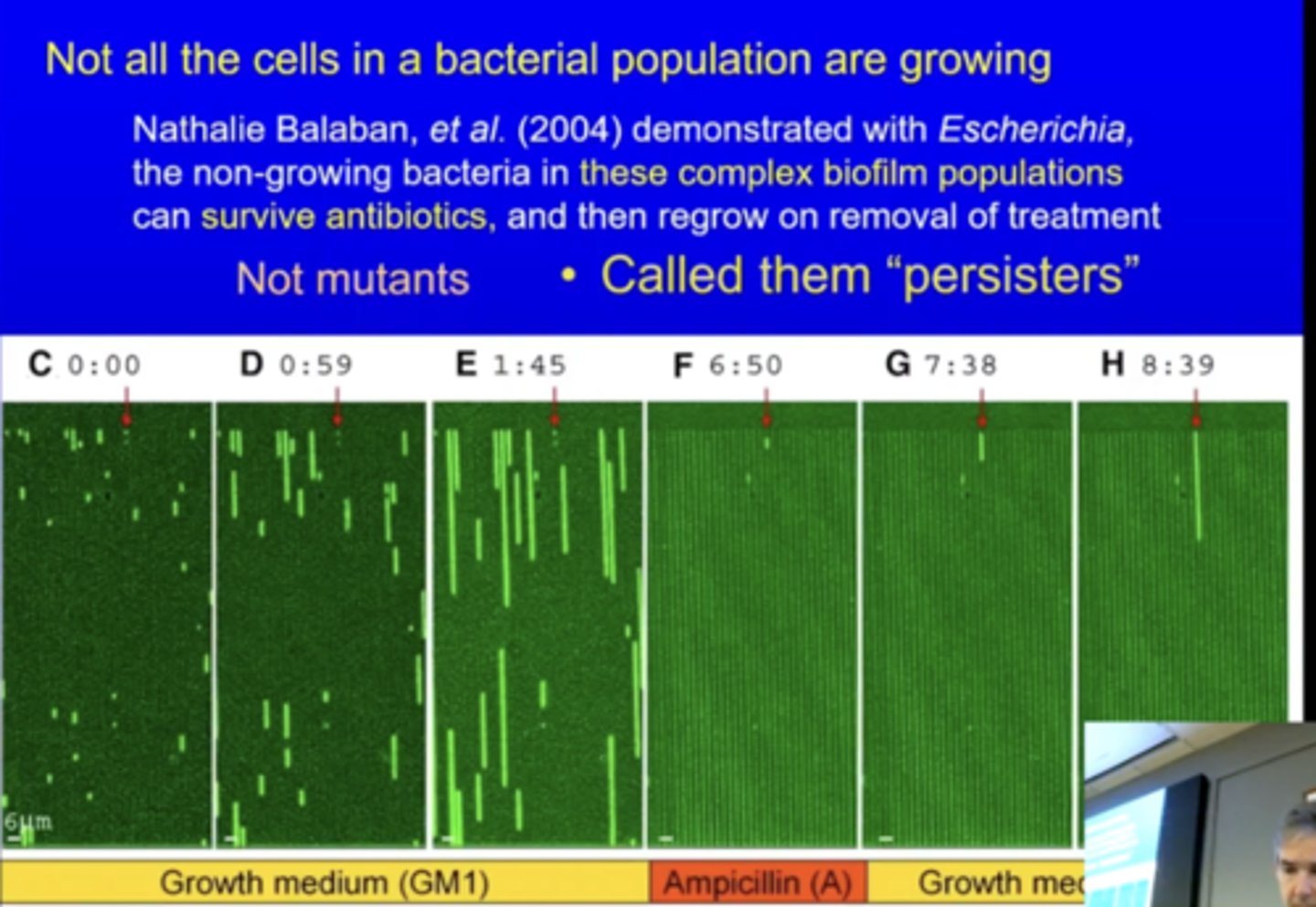
what is the difference between mutated bacteria and "persisters"
mutated bacteria have a specific gene that allows them to resist abx while resisters are dormant or slow growing bacteria that can survive abx without having specific genes
what is an alternative to binary fission? does it occur in gram + or -
sporulation; +
during which growth phase can sporulation occur? this is when ______ are limited or the ______ ______ are stressful
stationary phase; nutrients; environmental conditions
what form of division produces spores?
asymmetric
do gram - or gram + more commonly produce spores
gram +
which two bacterial genus' most commonly produce spores
bacillus, clostridium
spores are metabolically _______
inert (no growth or division)
what two things can kill bacterial spores
-heat/steam from autoclave
-bleach (via the free chloride within it)
what is one thing to be cautious of if using bleach to kill spores?
it goes down in half strength every month (so if your bleach is old it may not be effective in killing spores)
what structural component makes the spore resistant of harsh conditions
peptidoglycan layer and protein coat
can ethanol or detergent kill bacterial spores
no
in nature, bacteria often grow in ______ _________
mixed communities
what is biofilm
structured community of micro-orgamisms that is adhered to a surface and enclosed in carbohydrates and proteins