Nursing 2U03: Test 1
1/175
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
176 Terms
Function of a nurse
assisting the individual, sick or well, in the performance of activities that contribute to health, recovery, or a peaceful death
Definition of nursing
(according to nursing act)
the practice of nursing
is the promotion of health and the
assessment of, the provision of, care
for, and the treatment of, health
conditions by supportive, preventive,
therapeutic, palliative, and
rehabilitative means in order to
attain or maintain optimal functio
Main nursing roles
clinical practice (bedside)
-Includes families, patients, groups, communities and population
education
administration
research
policy
Different types of nurses
RN, RPNs and NPs, all regulated by CNO
What is the difference between RN and RPN
Main difference is foundational education.
study from the same body of nursing
knowledge, RNs study for a longer period of
time, allowing for a greater depth and breadth
of foundational knowledge
Another difference between RN and RPN
level of autonomous practice
-The complexity and stability of the patient being cared for, and the environment, will determine the nursing needs.
As complexity increases and stability decreases there is greater need for the
knowledge and skill of the RN.
ie: care of a stable patient on a ward versus an unstable patient in an IC
What is an NP?
registered Nurses (RNs) in the Extended Class [RN(ECs)] with additional nursing education and experience. NP competencies build and expand upon RN competencies.
-Have legislated authority to diagnose, order and interpret diagnostic tests, prescribe pharmaceuticals and perform procedures
Types of roles
acute hospital setting, community, public health, primary care, hospice, visiting nurse, educator, researcher, administration, occupational health, private sector
What is a profession
An occupation whose work is based on the mastery of a complex body of knowledge and skills. It is a vocation in which the application of science or a practice of an art is used in the service of others. Members are governed by a code of ethics, commitment to competency, integrity and morality, altruism and promotion of public good.
• Considered autonomous in practice and have self-regulation
what is a professional
The primary duty is to the client to ensure
safe, competent, ethical nursing care.
• Demonstrates accountability,
responsibility, ensures safety of client,
models professional behaviour, advocates
for client, demonstrates critical inquiry,
collaborates with others, demonstrates
leadership, analyses and evaluates
practice
Attributes of professional
Knowledge, spirit of inquiry, accountability, autonomy, advocacy, innovation and visionary, collegiality and collaboration, ethicis and values
college of nurses of ontario
Regulatory body for nursing which protects public interest ensuring safe care.
• Self-regulated profession which is governed through CNO
• Must have a Certificate of Registration and College membership in order to practice in Ontario.
• Must practice in accordance of the Standards of Practice.
CNO: 4 Key functions
Article and promote practice standards
establish requirements for entry to practice
administer a quality assurance program
enforce standards of practice and conduct
Regulated health profession act: RHPA
consists of a scope of practice statement
and a series of controlled acts.
• Scope of practice is outlined in the Nursing
Act.
• There are 14 controlled acts which
regulated health professionals can perform
a portion or or all of depending on their
scope of practice. Nurses can perform 5 of
these acts
RHPA: controlled acts
. Performing a prescribed procedure below the dermis or a mucous
membrane.
2. Administering a substance by injection or inhalation.
3. Putting an instrument, hand or finger
i. Beyond the external ear canal
ii. Beyond the point in the nasal passages where they
normally narrow
iii. Beyond the larynx
iv. Beyond the opening of the urethra
v. Beyond the labia majora
vi. Beyond the anal verge
vii. Into an artificial opening into the body
4. Treating, by means of psychotherapy technique, delivered through
a therapeutic relationship, an individual’s serious disorder of
thought, cognition, mood, emotional regulation, perception, or
memory that may seriously impair the individual’s judgement,
insight, behaviour, communication, or social functioning.
5. Dispensing a drug
Nursing Act 1991
define the various classes of nurses that can be registered
outlines the regulations for entry to practice and title protection
outlines the regulations on initiating controlled act
Canadian nursing association
Act in the public interest forCanadian nursing and nurses,providingnationalandinternational leadership in nursing and health
•Advocate for a publicly funded,not-for-profit health system
•Advance nursing excellenceand positive health outcomes
•Promote profession-ledregulation
registered nurses of association of ontario (RNAO)
Foster knowledge-based nursing practice, promote quality
work environments, deliver excellence in professional development, and advance healthy public policy to improve health.
• We promote the full participation of present and future registered nurses, nurse practitioners and nursing students in improving health, and shaping and delivering health-care services.
• Lobbies the government on behalf of nurses; develops Best
Practice Guidelines for care delivery; provides educational resources for nurses
Canadian nursing student organization
To be the primary resource for Canadian nursing students.
• Influence and advance innovation and social justice in the nursing curriculum and the nursing profession
• Strengthening linkages and creating new
partnerships
CNO: practice standards
Nursing standards are expectations that contribute to public protection.
They inform nurses of their accountabilities and the public of what to expect of nurses.
Set the legal and professional basis of nursing practice.
Standards apply to all nurses regardless of their role, job description or area of practice
What are the CNO practice standards?
Confidentiality and
Privacy: Personal Health
Information
• Documentation
• Scope of Practice
• Discontinuing or declining
to provide care.’
Medication
• Nurse Practitioner
• Therapeutic Nurse-Client
Relationship
• RN Prescribing
• Code of Conduct
review!!
RNO; code of conduct
Nurses respect the dignity of patients and
treat them as individuals
• Nurses work together to promote patient
wellbeing
• Nurses maintain patients’ trust by
providing safe and competent care
• Nurses work respectfully with colleagues
to best meet patients’ needs
• Nurses act with integrity to maintain
patients’ trust
• Nurses maintain public confidence in the
nursing profession
McMaster Reflective practice model
look at slides
key components of mcmaster model
Each student comes to the learning experience with expectations influenced
by their lived experience and belonging to communities.
• They engage in new lived experiences with their tutor in the process of
becoming, through acting and knowing.
• Factors that influence this evolution include knowledge, role modelling, Ways
of knowing and political, economic and social structures.
• Outcomes include courage, respect for others and open mindedness.
• Ways of Knowing (Empirical, Ethical, Personal, Aesthetic, Emancipatory
The “What” Model
Developed by Rolf et al. 2001.
Simple, 3 step approach to
reflective practice
Three components: What, So
What and Now What.
Cyclical process that focuses on
action
What happen?
This question prompts the
reflector to describe the
experience.
Involves detailing what
happened, who was involved,
and the context of the situation.
• What happened?
• What was my role in the situation?
• What were the key events?
• What did I observe?
So what?
This question moves beyond
description to analysis.
It encourages the individual to
consider the meaning and
implications of the experience.
• So what does this mean?
• So what did I learn from the experience?
• So what was the significance of the
experience for me and others?
• So what were my feelings during the
experience, and how did they influence
my actions?
Now What?
This question focuses on the
future, prompting the
individual to think about how
they will apply what they have
learned.
Now what will I do differently in the
future?
Now what steps do I need to take to
improve?
Now what actions will I take as a result of
this reflection?
Now what further learning or
development do I need?
Clinical judgement
An interpretation or conclusion
about a patient’s needs, concerns,
or health problems, and/or the
decision to take action (or not),
use or modify standard
approaches, or improvise new
ones as deemed appropriate by
the patient’s response
clinical reasoning
The process by which nurses...make their
judgments, and includes both the deliberate
process of generating alternatives, weighing
them against the evidence, and choosing the
most appropriate, and those patterns that
might be characterized as engaged, practical
reasoning
The gist of clinical reasoning and judgment
In other words, RNs arrive at a clinical judgment through the process of clinical reasoning
Clinical judgemnt model
noticing, interpreting, responding and reflected
Noticing
Knowing the
patient through
understanding
narrative, patient’s
usual patterns
help the nurse to
notice changes.
Factors of noticing
Context: setting, situation, experience of nurse
and patient; knowing the pattern of responses
Background: understanding the narrative of
the patient
Relationship: between the nurse and patient
These combine to inform our expectations and
initial grasp of the situation
Interpreting
Combination of Reasoning patterns analytical,
intuitive and narrative thinking.
Helps to understand key information, prioritize and
what to pay attention to and what to ignore.
What is going on here?
Weighing the option
Responding
Deciding on a course of action and
taking that action.
Think about the rationale for your
actions
How did you decide on the best
option?
Do you use a standard approach, or do
you need to modify it to fit the
situation?
Observe the outcome, patient
response
Refelection
in action and on action
In action
observe and respond to the
patient’s response to your
actions/interventions
“reading the patient
On action
reflect on what worked and
what didn’t; clinical learning
to improve clinical knowledge
in similar future interaction
Learning plan
A learning plan is an agreement between
student and tutor spelling out in detail what
the student intends to learn (learning goals
and questions), how this will be accomplished
(resources and activities) and within what
period of time, the evidence that will
demonstrate the student has accomplished
the learning goals and resolved the learning
questions, and how this evidence will be
evaluated (evaluation criteria)
Nursing documentation
An important component of nursing practice that occurs within the client's health record .It is used to monitior a client’s progress and communicate with other care providers. It also reflects the nursing care that is provided to a client monitor
why do we document
Communication (with other providers)
Accountability (dont get sued)
Security/legislative requirement (needs to be kept for 10 years)
Quality improvement (if something is consistly wrong, see if intervention is being done well)
Research (chart auditing, seeing chart data)
Funding and resource management (workload tool, if you are always busy, you might get more funding. staff, etc)
CNO: Documentation practice standard (2008)
explains the regulatory and legislative requirements for nursing documentation
Communication
Accurate, clear and comprehensive
Accurate, clear and comprehensive
documentation reflects all aspects of care provided; needs, interventions, outcomes (all aspects of care)
objective and subjective data
significant communication with family members/significant others
Informed consent
Written charting includes a full signature and designation (Mac L2, Mac L3, Mac L4)
use approved abbreviation
objective data
what you see, feel, hear, smell
subjective data
what the patient states (goals, concerns, symptoms). What is said as evidence in quotations
Communication: Factual
do not use vague terms (appears, seems, apparently)
No opinions (ex. client seems anxious, patient is difficult)
Reflective of observation not unfound conclusions
Accountability: acccurate, timely and complete
in a timely manner, completing as soon as possible after, the care or event
handwritten documentation is legible and completed in permanent (blue/black) ink
date and time that care was provided and when it was recorded
documenting in chronological order
indicating when an entry is later
ex, 10:45. I did vital at 10:15
do not wait til the end of shift especially things that can change rapidly such as vitals and physcial assessements
Accountability: accurate, timely and complete written documentation
do not leave empty lines; if there are empty lines, draw a line through (paper charting)
never deleting, altering or modifying anyone else’s documentation
the individual who perfomed the action or observed the event completes the documentation
when correcting errors ensure that the original information remains visible/retriable (draw single line through and initial)
Security
ensuring that relevant client care information is captured in a permanent record
accessing only information for which the nurse has a professional need to provide care
maintaaning cofidentality of client health information, including passwords (i.e client information not to leave facilty)
Obtaining consent from patient to disclose information outside the circle of care
ensure the secure and confidental destruction of documents that are no lonegr in use
Abbreviations
see slide 14
Types of documentation
electronic, computerized
flow sheet (vital signs, intake and output)
care plan/critical pathways (CHF and COPD)
narrative
documentation framework
documentations framework
Problem orientated: data is organized bu patient problem or dignosis
DAR: data (objective/subjective), action and response, There most important thinga that happen, what did you do and what did the patient say/react ex. chest pain, gave them meds, they felt less pain (1/10)
SOAP: subjective data, objective data, assessment, plan (This is what doctors do)
Subjective data: what does the patient tell us
symptoms, feelings, perceptions and concerns
object data: what we see
observable and measurable
-vital signs
-physical assessments
lab results
chain of infection
infectious agent
reservoir
portal of exit
mode of transmission
portal of entry
susceptible host
need all six to get someone sick
Infectious agent
most common: bacteria and fungi
1. Infectious Agent:
Bacteria, Viruses, Fungus, Parasite, Prion
Essentials of Bacterial growth:
• Nutrient
• Moisture
• Temperature
• pH (acidity or alkalinity)
• Oxygen (aerobic bacteria only)
Risk factors:
cleaning practices, sharing rooms, sharing equipment, poor hand hygiene by health
care workers
reservoir
A place where an organism/pathogen can survive but may or
may not multiply.
ie. Animals, food, water, insects even inanimate objects
Risk factors:
cleaning practices, sharing rooms, sharing equipment, poor hand hygiene by health
care workers, cleaning practice
portal of exit
how to leave the reservoir
Exits in the human body include
body openings
Mouth, Nose, Rectal, Vaginal,
Urethral, Ostomies, Breaks in skin /
wounds
• Pathogens carried through
the portals through:
Blood
body fluids (urine, feces)
excretions (pus, wound)
Secretions (semen)
Saliva / sputum
Mucus
Risk factors:
Wounds, body fluids, shared equipment
mode of transmission
this is where we can remove/break the chain, the other factors can only be controlled
e
• Direct contact: between the infectious agent and the susceptible host.
• Indirect contact: between a susceptible host and a contaminated intermediate
object (fomite) such as a needle, instrument or other equipment
• Modes include contact, droplet (sneeze), airborne (dust), vehicle (instrument,
food), vector (insect)
Risk factors:
Shared rooms and equipment, poor hand hygiene
Portals of entry
.
• Organisms can enter the body through the same routes they use to exit
• Body openings (GI, mucous membranes, respiratory)
• Breaks in skin
• Breaks in mucous membranes
• Needle piercing the skin
• Devices (ie. catheter; longer in place – greater risk
Risk factors:
Devices: IV, catheter; wound
Susceptible host
person in hospital
Risk factors:
Impaired immunity or physiology, Secondary health problems - ie diabetes, Poor
nutritional status, Altered normal body flora – antibiotic use, Age (children and
elderly more at risk), Exposure to infectious agents, Invasive procedures, Tissue
injury or inflammation, Altered ph of secretion
risk assessment
The first step in the effective use of
Routine Practices is to perform a risk
assessment. A risk assessment must be
done before each interaction with a
client/patient/resident or their
environment in order to determine
which interventions are required to
prevent transmission during the
interaction, because the
client/patient/resident’s status can
change.
4 MOMENTS FOR HAND HYGIENE
beofre intial patient enviornment contact (entering room)
before asptic procedure (dressing change)
after body fluid exposure
after patient envionrment contact (walk out of room, wash hands)
Mcmaster model of nursing
add photo
client-nurse relationship
Trust – client is in a vulnerable position, they need to feel safe;
accountability to client
Respect – inherent dignity, worth and uniqueness of every individual
Professional intimacy –access to personal information and physical
contact (bathing)
Empathy –understanding of the meaning the experience holds for the
client.
Power - appropriate use of power, in a caring manner; partner with the patient
therapeutic client nurse relationship: standards
Therapeutic Communication: introducing yourself, listening, informing, supporting
Client-centred Care: include client in care, negotiate with client; (mutuality McMaster Model of Nursing)
Maintaining Boundaries: set and maintain professional boundaries, refrain from disclosing personal information
Protecting the Client From Abuse: intervene and report verbal or physical abuse; do not neglect the client
What is therapeutic communication
purposeful conversation, goal directed, time limited and focused
self discloser is limited
purpose of therapeutic communication
is related to improving the health and well-being of the clinet client
to provide a safe place for the client to explore the meaning of their illness; to provide information and emotional support
Professional communication: use of names
self introduction
Respect:
use clients’ name (Ms/Mr. X, ask how they would like to be addressed)
no terms of endearment (i.e honey, dear, sweetheart)
no use of pleural (i.e we) as it may be condescending. (are we doing well?)
verbal communication
vocab: language, medical jargon
connotative meaning: interpretation of a work’s meaning influenced bu the thought/ideas one has about the word (“serious condition”)
pacing: enunciate clearly, speak slowly and clearly
tone of voice: respectful vs. condescending
timing and relevance: provide relevant infor at the right time
non-verbal communication
personal apperance
posture and gait
facial expression-smile, avoid negative reactions
nodding, eye contact
sounds: sighing
zones of personal space
intimate zone:
holding an infant
performing a physical assessment
bathing, grooming, feeding, tolieting
changing a dressing
injecting a medication
add chart.
causal: standing at bedside
SOLER (attending behaviours of active listening)
Sitting facing the client
open posture (receptive)
Lean toward the client
Eye contact
Relax
Noticing
Content themes – underlying
feeling
● Communication patterns:
dramatic, exaggerate
● Discrepancies in content, body
language
● Feelings revealed in voice,
facial expressions
● What is not being said as well
as what is
● Your own inner response
strategies to promote communication
Physical environment: private, personal space
Open-ended questions: allow client to elaborate, telling
their story
Focused question: “can you tell me more about….”
Close-ended questions: “do you smoke?”, initiate discussion
Theraputic listening responses
use minimal cues: smiling, nods, go on…
clarification: expressed as a question “can you give me an example”
restament: you mean
Paraphrasing: transform the original message and into own words
without losing meaning
Reflection: “it sounds as if you are really angry about…”
Summarization
Use of silence, touch
Non-theraputic communication techniques
False re-assurance: “it’s going to be OK”
Giving personal opinion: “I feel you should….”
False inferences: making unsubstantiated assumptions about what the client
means
Moralization: expressing your own values about what is right or wrong
Value judgments: approval/disapproval of the client’s behaviour
Automatic responses: polite, superficial comments, use of clichés (“You can’t win
them all”)
Sympathy versus Empathy: empathy more therapeutic
client factors that effect communication
age, culture, health, education, emotion and language
four phases of therapeutic relationship
pre interaction, orientation, working and termination phase
pre-interaction
review/client information, talk to caregivers, private location
orientation phase
nurse and patient/client get to know each other: introduction, confidentiality, set the tone by being warm/comforting/caring, purpose of interview/discussion, time frame
Working phase
explore clients thoughts and feeling
establish goals mutually with client
identify issues
resolve: nurse and client work together to solve issues and meet goals
termination phase
Ending the
relationship - notify
the client/patient
Summarize key
points
Evaluate goal
achievement with
client
Offer follow up or
other actions
Ask client if they
have any
questions /concerns
May facilitate
transition to another
care give
importance of health assessment
Subjective data: what the patient tells you about his or herself
Objective data: what you observe or measure or record in your
exam and diagnostic tests.
Provides a complete picture of the patient’s past and current
health and includes detailed record of the health problem
Provides a record of health strengths and coping skills
key components
iographical
data
Reason for
seeking care
History of
present illness
Past
medical/surgical
history
Childhood
illnesses
Accidents &
Injuries Hospitalizations Surgeries Obstetrical
history Immunizations
Allergies Medications Family History Review of
systems
Functional
Assessment &
ADL’s
make acronym for this.
Health History
1) biological data: name, DOB, martial status, occupation, gender
2) reason for seeking care: what brings you in today?
3) History of presenting illness: tell me about your pain, use PQRSTU
PQRSTU
P-provocative and palliative
• Q-quality and quantity
• R- region and radiation
• S-severity
• T-timing (onset, duration, frequency)
• U-understand patient’s perception
Health history continued
Past Medical/Surgical History
Childhood Illnesses: measles, mumps etc
Accidents/Injuries: fractures, head
injuries
Serious/Chronic Illnesses: diabetes, HTN,
seizures, heart disease
Hospitalizations: reason, length of time
Surgeries: types, dates
Obstetrical History: pregnancies,
deliveries
obstetrical history-GTPAL
G – Gravida (pregnancies)
T – Term births
P – Pre-term births
A – Abortions (spontaneous, induced, miscarriage, ectopic)
L – Living children
go by number. start with can you get pregnant, then # of pregnancy, then # of children, if do not match ask about A.
Health history pt 3
• immunixations: MMR, hepatitis, flu shot e:
• Allergies:Food, drug, environmental and reactions
• Meds:
Prescribed and over the counter
• Name, dose, frequency and purpose and
compliance
Health history pt 4
Family History:
• Ask about age and health of parents, grand parents and siblings
• Consider diabetes, heart disease, stroke, cancers, blood disorders, HTN, allergies, seizures, arthritis
Functional Assessment:
• Gordon’s Patterns: self-esteem, activity, sleep, nutrition, relationships, spiritual, coping, ADLs
Social history:
• smoking, alcohol, drugs
family tree
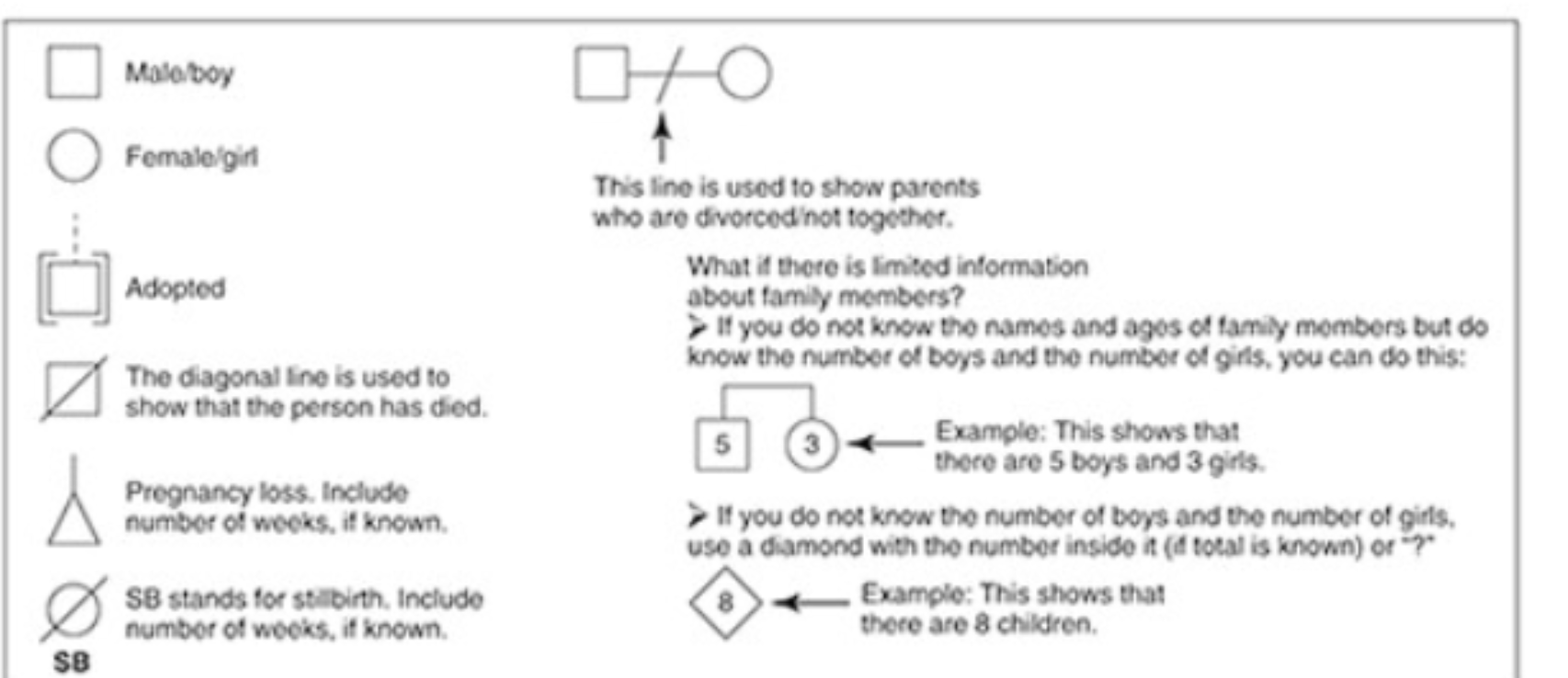
Gordon’s functional health patterns
there are 11
Health Perception-Health Management, Nutritional-Metabolic, Elimination, Activity-Exercise, Sleep-Rest, Cognitive-Perceptual, Self-Perception-Self-Concept, Role-Relationship, Sexuality-Reproductive, Coping-Stress Tolerance, and Value-Belief
Health Perception –
Health Management Pattern
describes client’s
perceived pattern
of health and well
being and how
health is managed
Nutritional
Metabolic Pattern
describes pattern
of food and fluid
consumption
relative to
metabolic need
Elimination Pattern
Elimination Pattern
describes pattern
of excretory
function (bowel
and bladder) and
use of aids
Activity – Exercise Pattern
• describes pattern of exercise, activity, leisure, and
recreation
Cognitive – Perceptual Pattern
• describes sensory, perceptual, and cognitive pattern