Ultrasound of Abdomen
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
- Liver and spleen
- Biliary system
- Vasculature
- GYN (uterus, ovaries, and cervix)
- Pediatrics
What organs can be examined using ultrasound?
ultrasound
imaging that uses high frequency sound waves directed by a narrow beam into the body. Piezoelectric crystals change electric energy into high frequency sound waves. Each tissue has different acoustic impedance determined by the density. The reflected sound (echo) returns to the transducer and is converted to electrical signal which is converted into an image.
echogenic, gray/white
on ultrasound, solid organs are ___________ meaning they appear ______ on image
anechoic, black
on ultrasound, fluid collections are _____ meaning they appear _____ on image
echogenic
Capable of producing echoes
air and bone
_____ cannot be adequately visualized on ultrasound. The acoustic impedance is too high. They are TOO echoic.
X-ray: Fluid is white
U/s: Fluid is black
What is the color of fluid on X-ray and ultrasound?
anechoic
fluid and blood are ___ on ultrasound
- Linear array
- Curved array
- Phase array
types of transducers used for Ultrasound
isoechoic
region of image that is equal to the surrounding (or another structure it is being compared to)
Linear array
transducer in which each sound pulse travels in the same direction and is perpendicular creating a rectangular image. Near field has high resolution. It is good for limited group of adjacent elements but limited deep field of view.
Linear
____ array transducer is food for superficial structures such as tendons, thyroid, and vessels.
high, poor
Linear array transducers have ____ frequency, but ____ penetration
Curved array
transducers with surface reformed into a convex shape. Has a wider far field with slightly reduced resolution. Large deep and small superficial field of view.
Curved
____ array transducer would be used to visualize deep organs such as Intraabdominal organs.
low, deep
Curved array transducers have ____ frequency and ____ penetration.
Phase array
transducers that are smaller and capable of scanning in areas where acoustic access is limited (between ribs). Small superficial field of view. Poor near field focusing. Limited periphery focusing capabilities. Good for doppler imaging.
Phase
____ array transducers are good for imaging hard to reach areas like the heart.
Hyperechoic
echo-rich structure when compared to adjacent structures; appears as varying shades of lighter gray. Aka echogenic.
isocheoic
having similar echogenicity to an adjacent structure
hypoechoic
less reflective and low amount of echoes when compared with adjacent structures; varying shapes of darker grey
anechoic
totally black on ultrasound, no echoies, aka sonolucent. Usually represents liquids such as blood or fluid collections.
sonolucent
another word for anechoic is ______
artifacts
a structure or appearance that is not natural, but is due to manipulation. Refer to something seen on the ultrasound image that does not exist in reality. Can be helpful in interpreting the image or it can confuse the examiner.
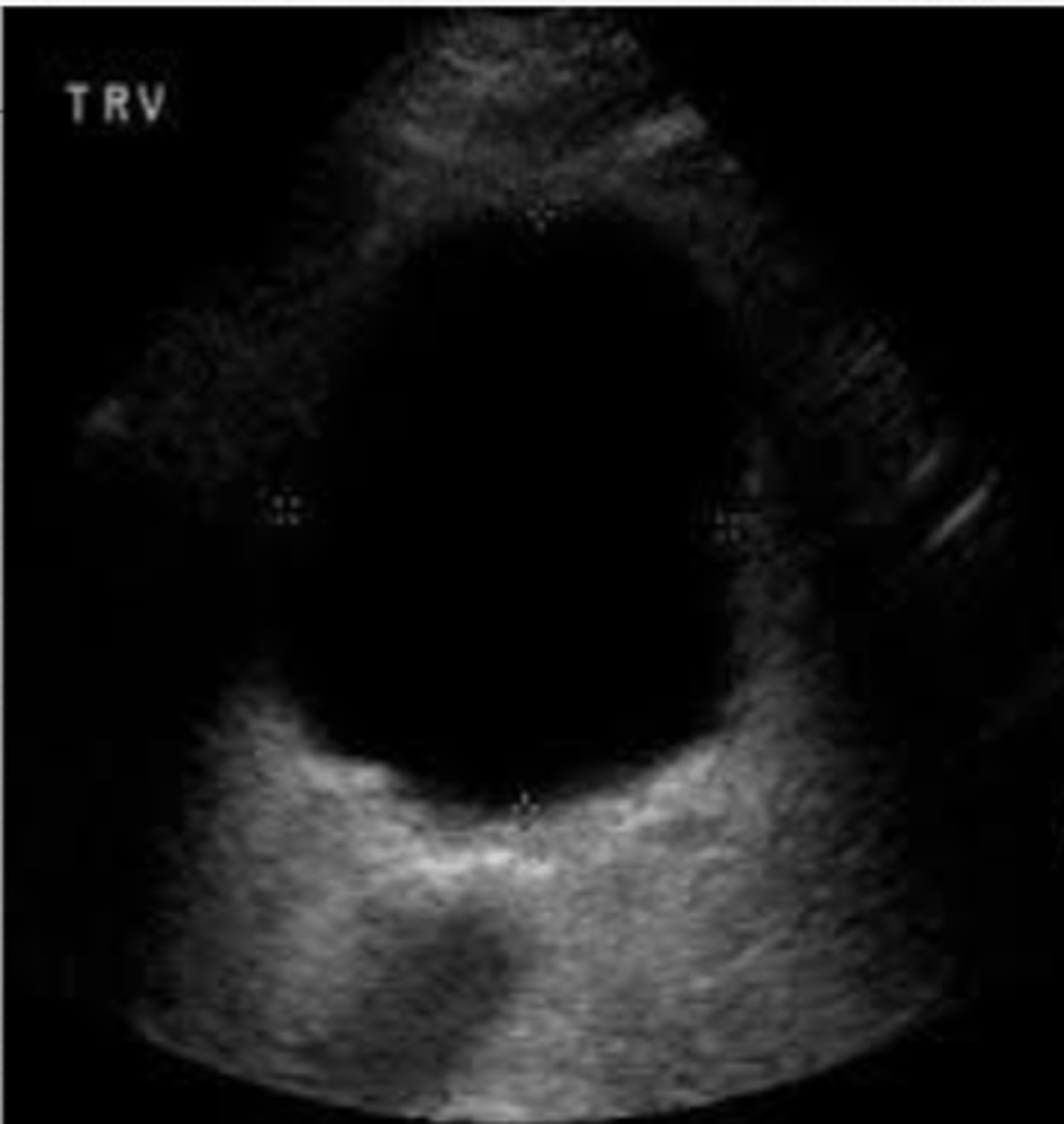
Anechoic
the central fluid accumulation could be described as _____.
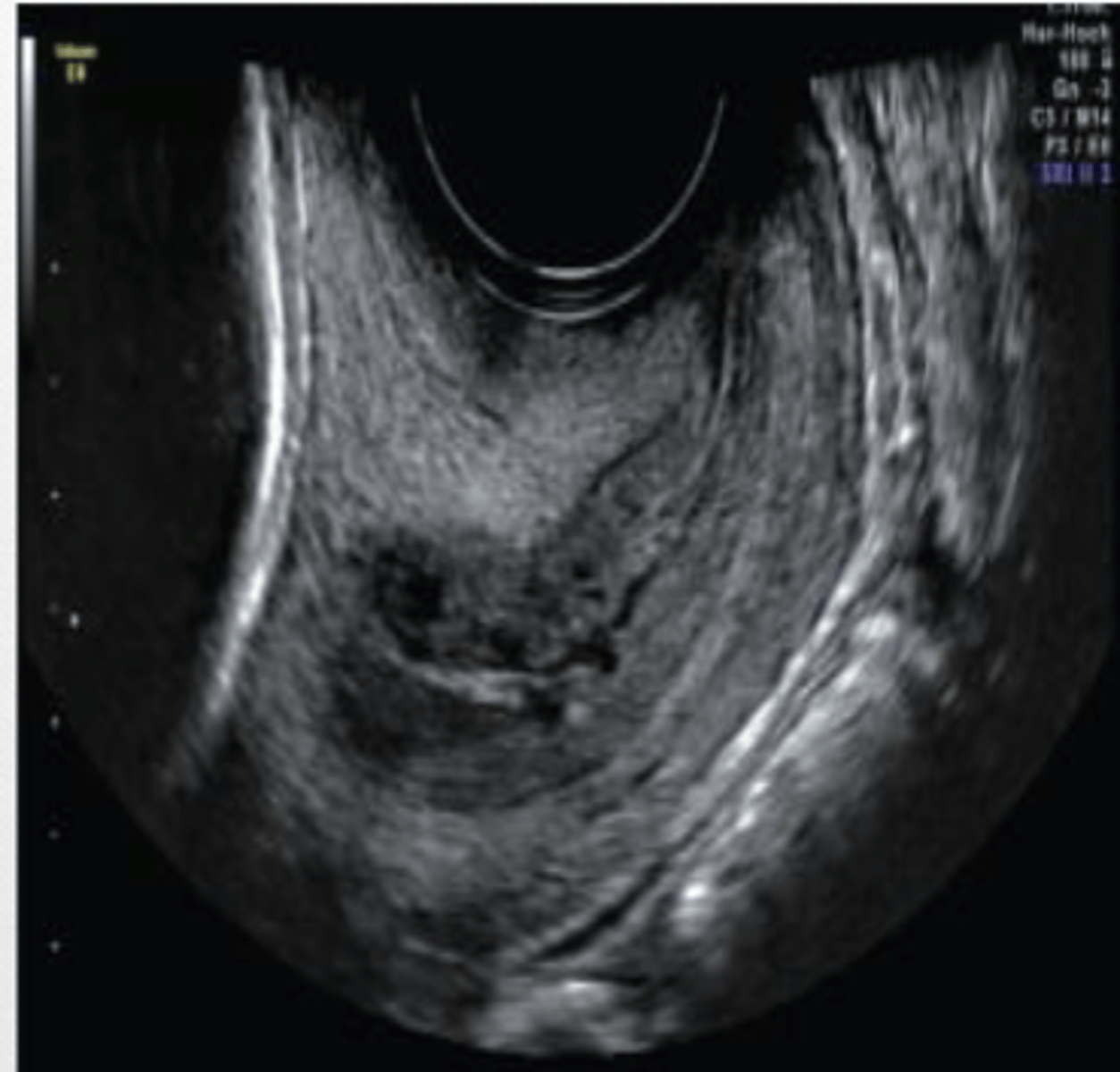
Hypoechoic
the central lesion could be described as ______.
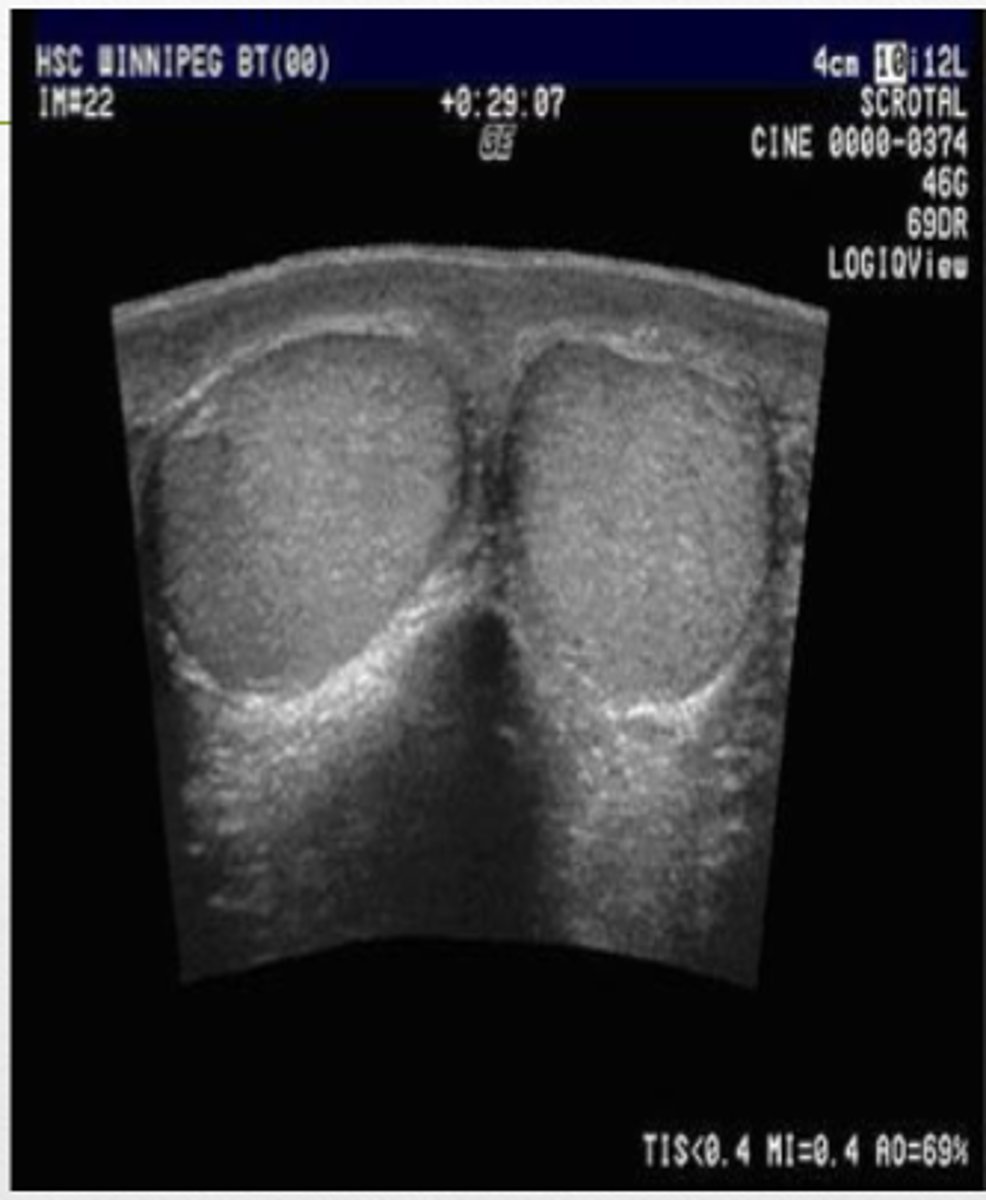
Isoechoic
the testicles are ____ to each other
hyperechoic
the bowel is ____ in comparison to the surrounding tissue
- shadowing
- posterior enhancement
Artifacts that may be seen on ultrasound....
shadowing
artifacts on ultrasound caused by stones, calcifications, and bone
posterior enhancement
artifacts on ultrasound caused by fluid and fluid containing structures.
Acoustic enhancemnet
a manifestation of increased echo amplitude returning form regions beyond an object such as a fluid filled cyst, which causes little or no attenuation of the ultrasound.
acoustic shadowing
______ on an ultrasound image is characterized by a signal void behind structures that strongly absorb or reflect ultrasonic waves. This happens most frequently with solid structures, as sound conducts most rapidly in areas where molecules are closely packed, such as in bone or stones.
acoustic enhancement
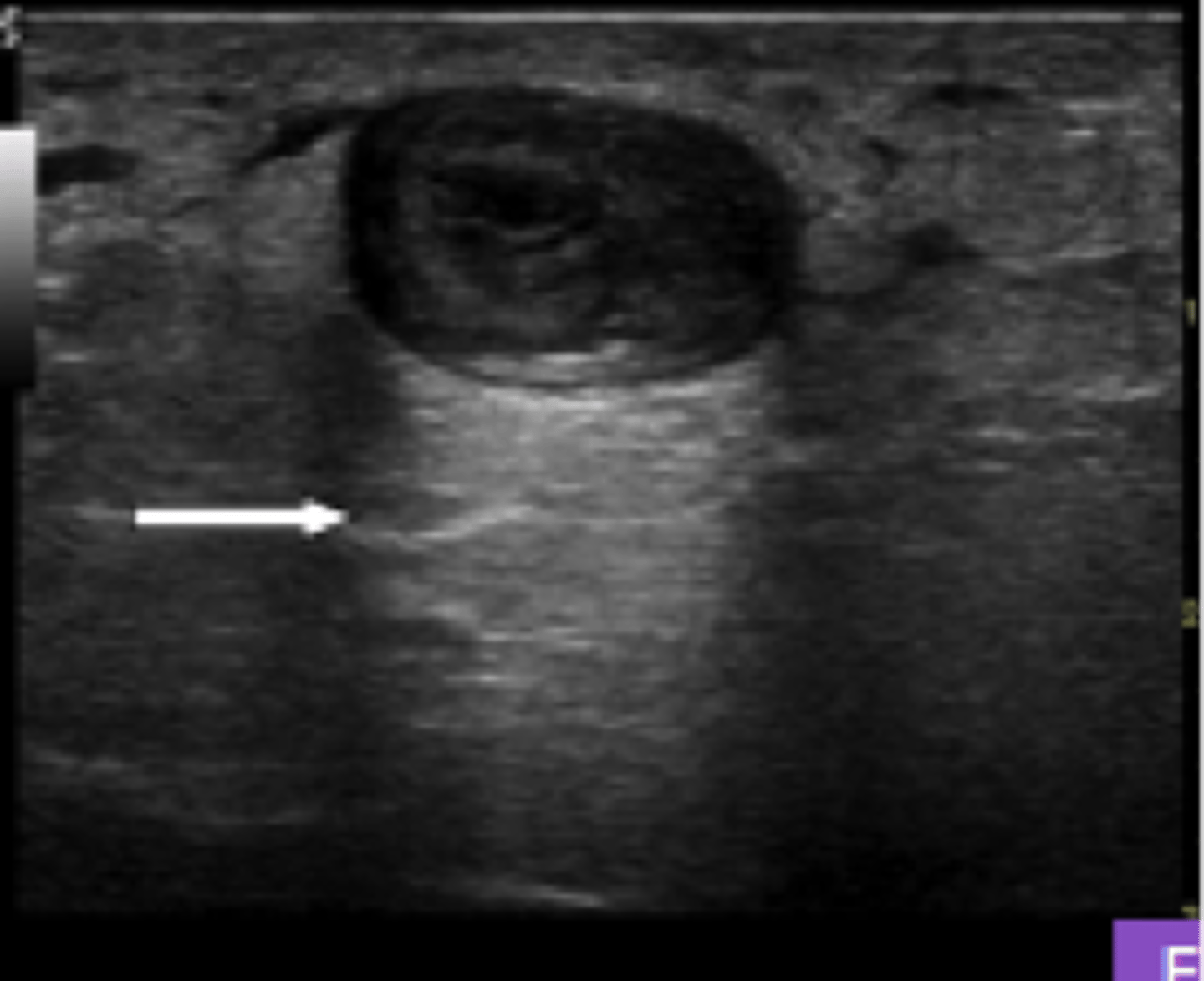
acoustic shadowing
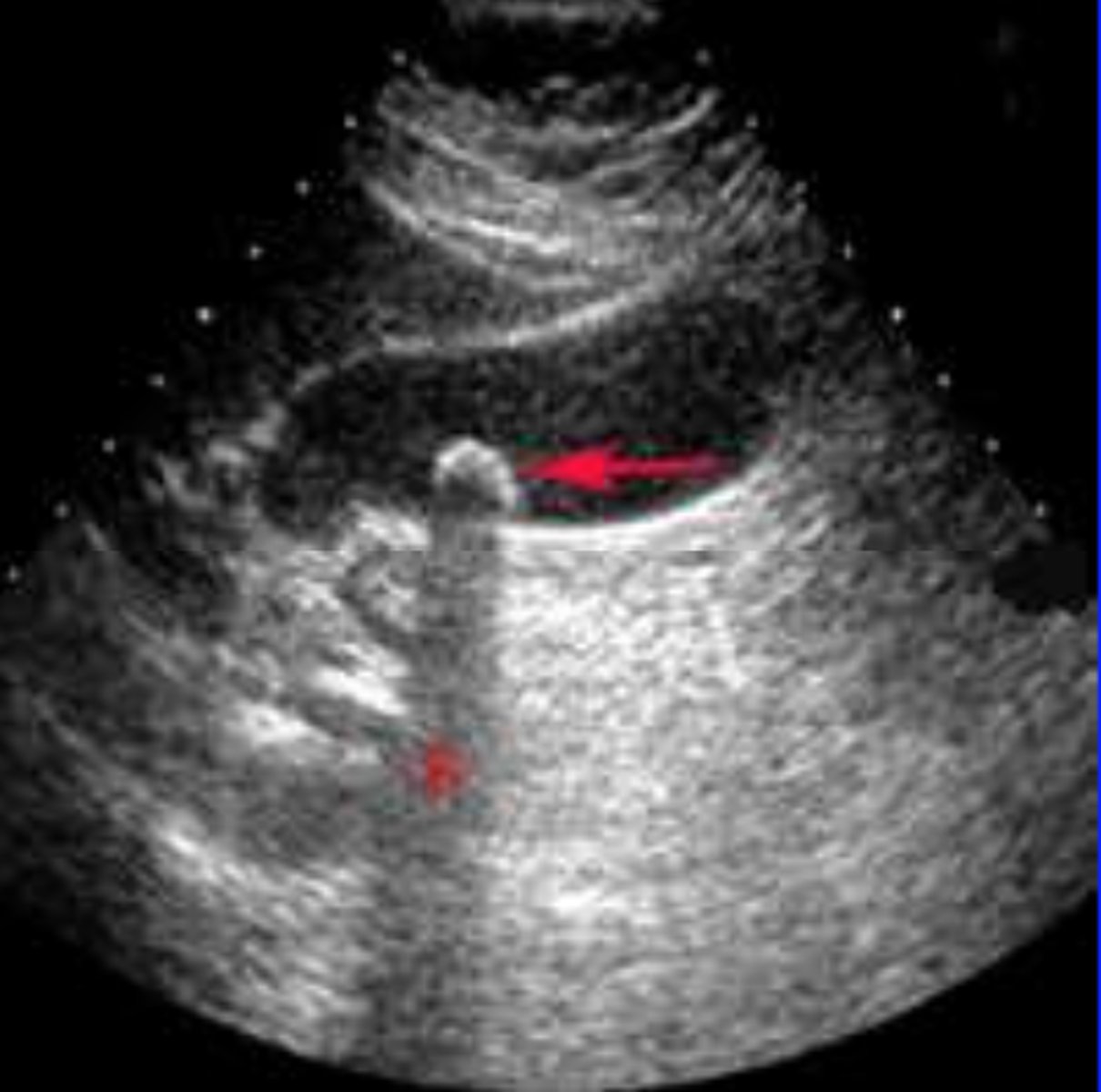
Doppler
measures blood flow toward or away from the transducer. Can measure blood flow and velocity.
Red
on the doppler, ____ indicates flow towards the transducer
Blue
on the doppler, ____ indicates flow away from the transducer
high
____ frequency transducer is used to visualize superficial structures such as the thyroid, MSS, and scrotum.
low
____ frequency transducer is used to visualize deep structures such as the abdomen and pelvis.
brighter
strongly transmitted pulse causing strong returning echoes causes a _____ image
phased array
probe used when you need to image deep structures
linear probe (vascular probe)
probe used for superficial structures.
notch
___ is made to help determine your orientation on the screen to the probe
long view
view the the notch is pointing towards the patients head. Consequently, the left of the screen is superior and the right of the screen is inferior. The top of the screen is anterior and the bottom is posterior.
head
in the long view, the notch should be pointing toward the patients head
superior, inferior
in the long view, the left of the screen is ____ and the right of the screen is _____
anterior, posterior
in the long view, the top of the screen is ____ and the bottom of the screen is _____
trans view
view in which the probe is pointing towards the person scanning. In that case, the left of the image is the patients right.
you must also see it in the trans view
If you see a cyst in the long view, what is the next step?
4 x 10 cm
Fasting GB should measure...
less than or equal to 3 mm
Gallbladder wall should measure...
no more than 4 mm
common hepatic duct should measure
no more than 6 mm
common bile duct should measure
no more than 2mm
pancreatic duct should measure
normal GB
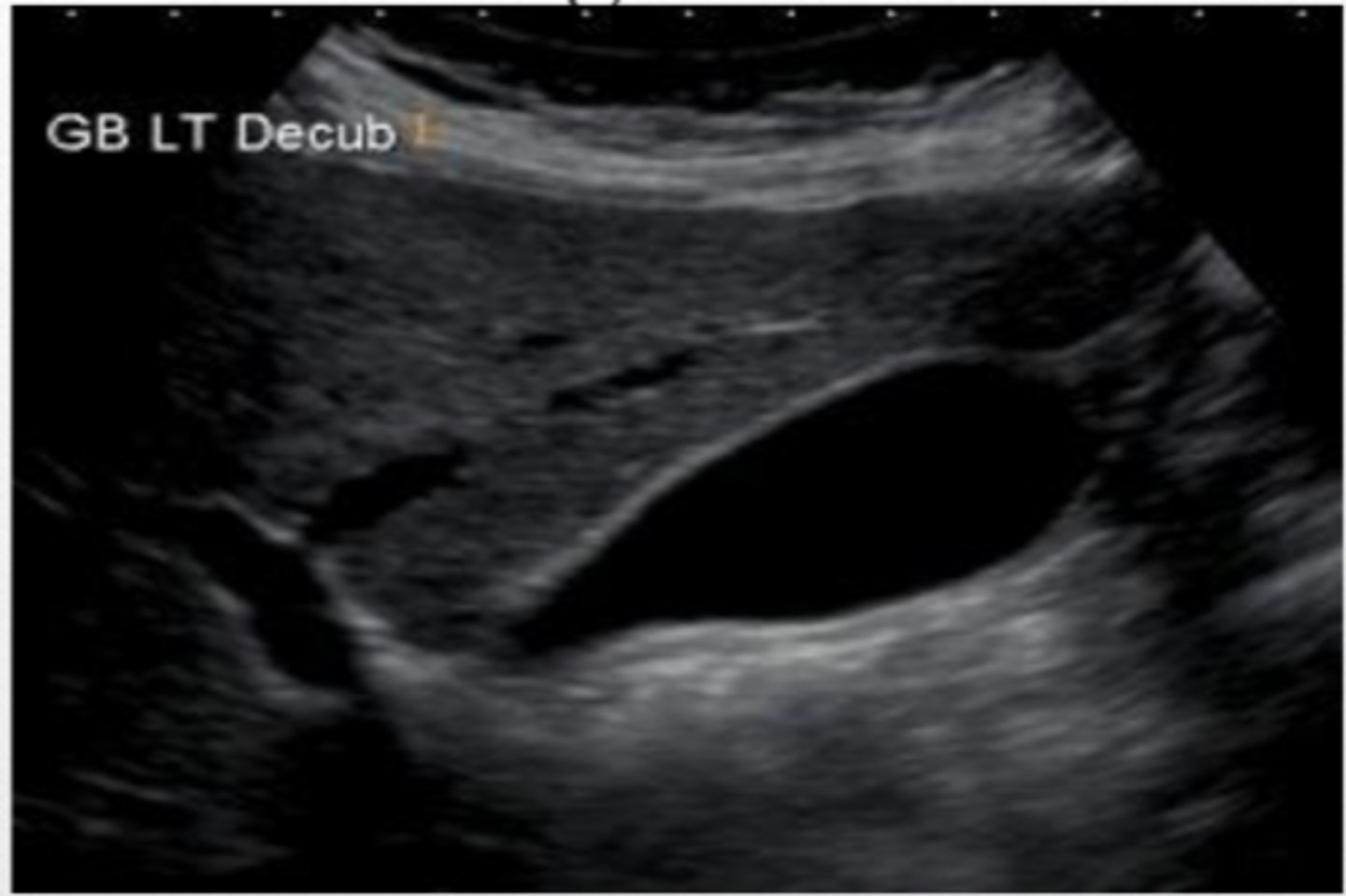
Normal GB (folds on itself)
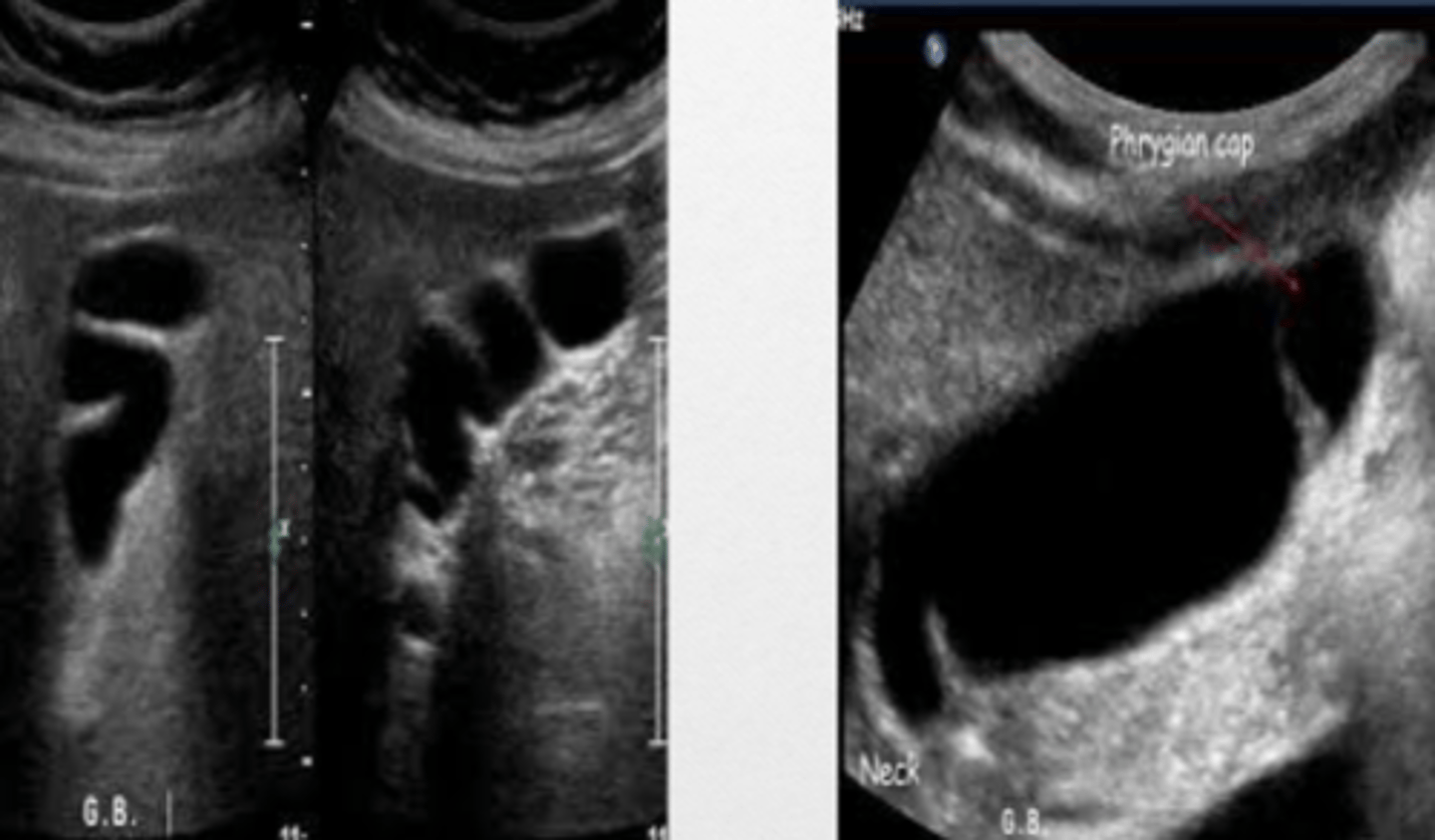
Post prandial Gallbladder (Normal)
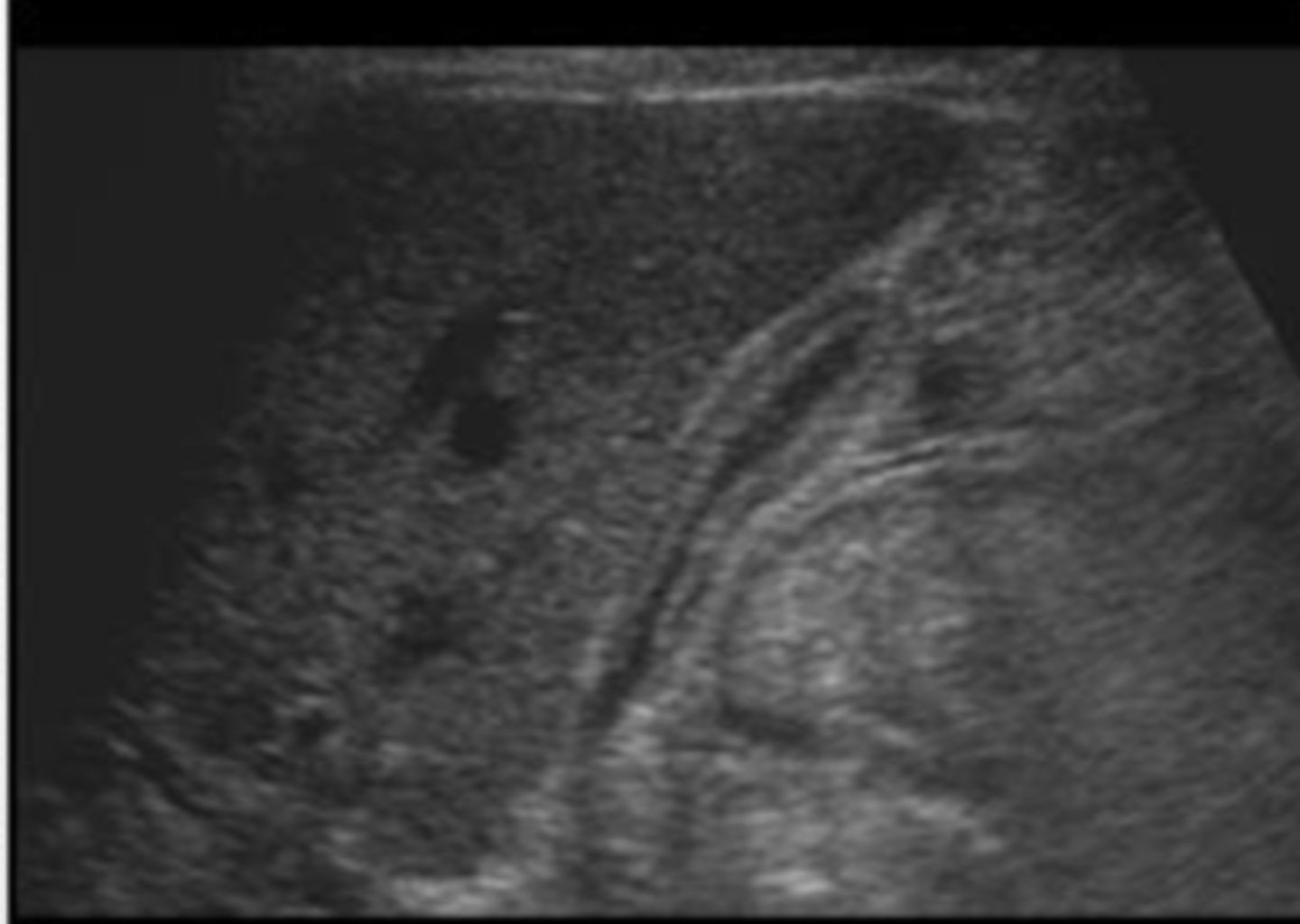
Cholelithiasis
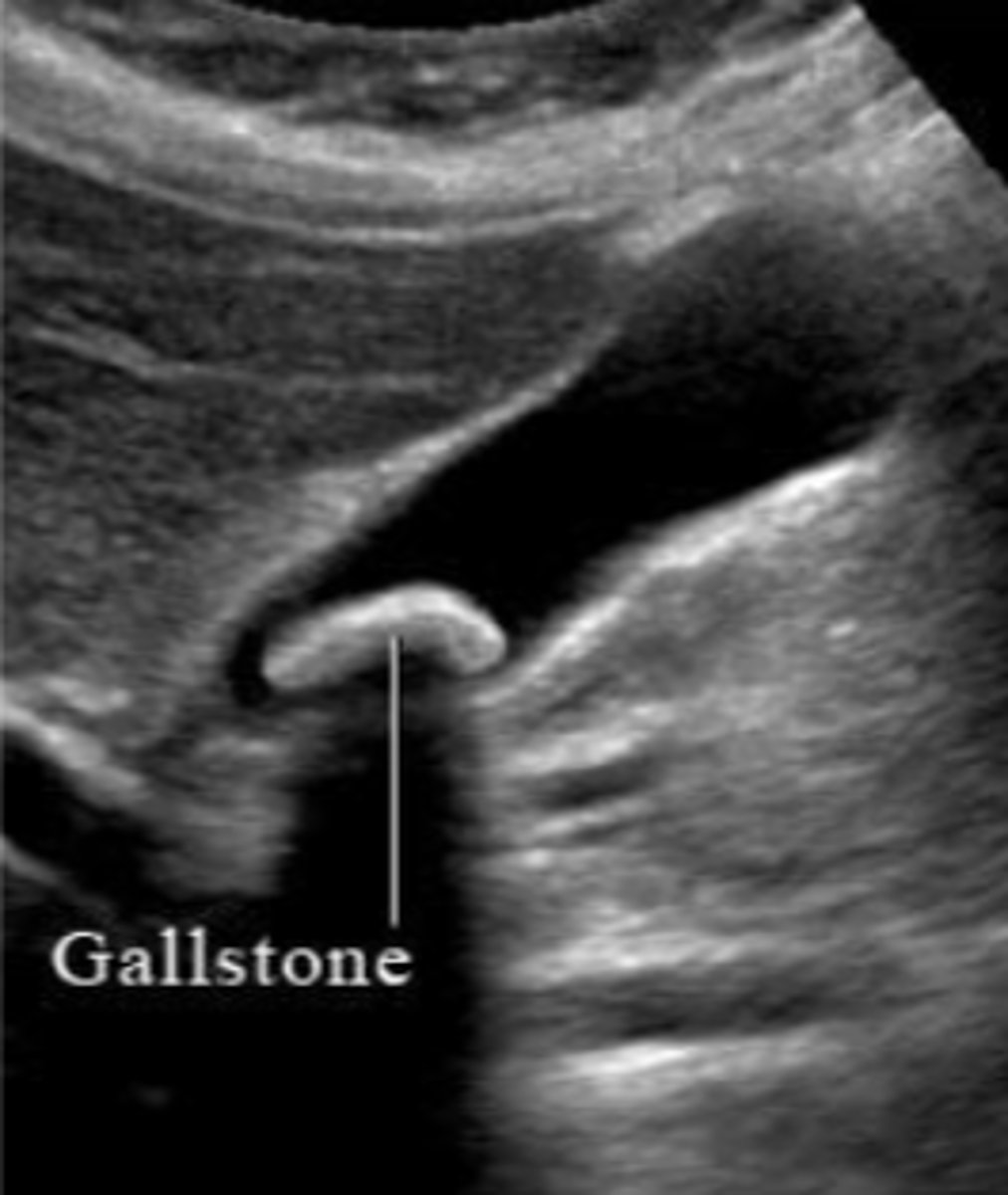
Cholelithiasis
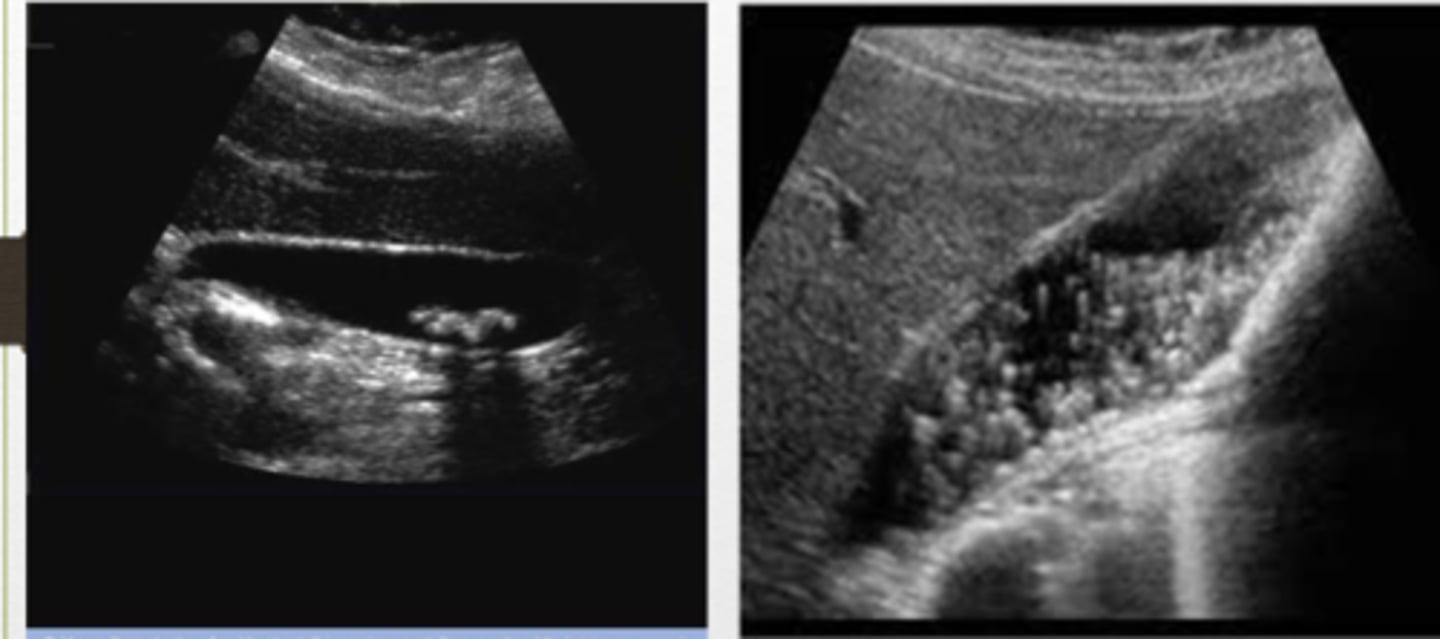
GB sludge
move patient to see sludge move
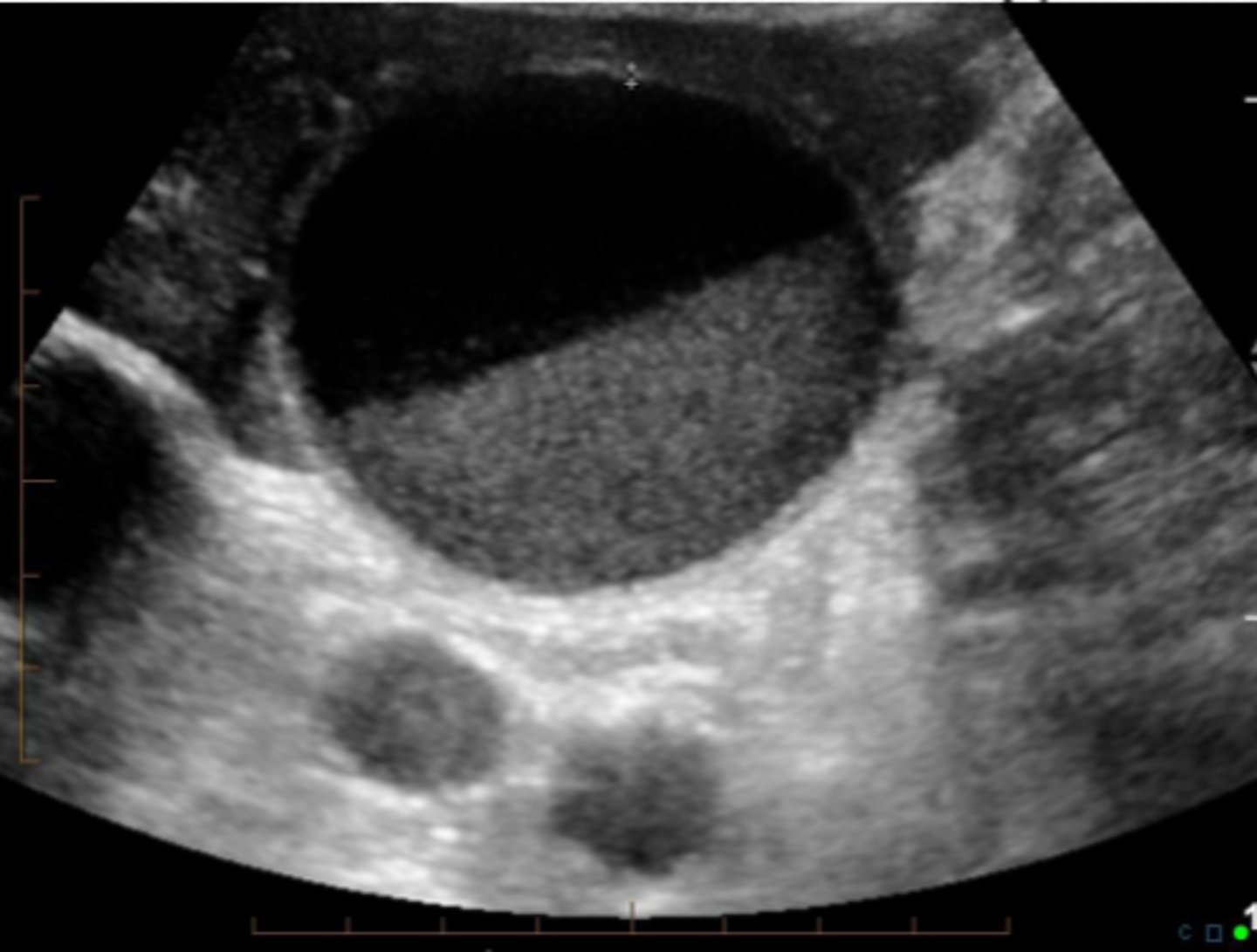
GB with sludge and stones
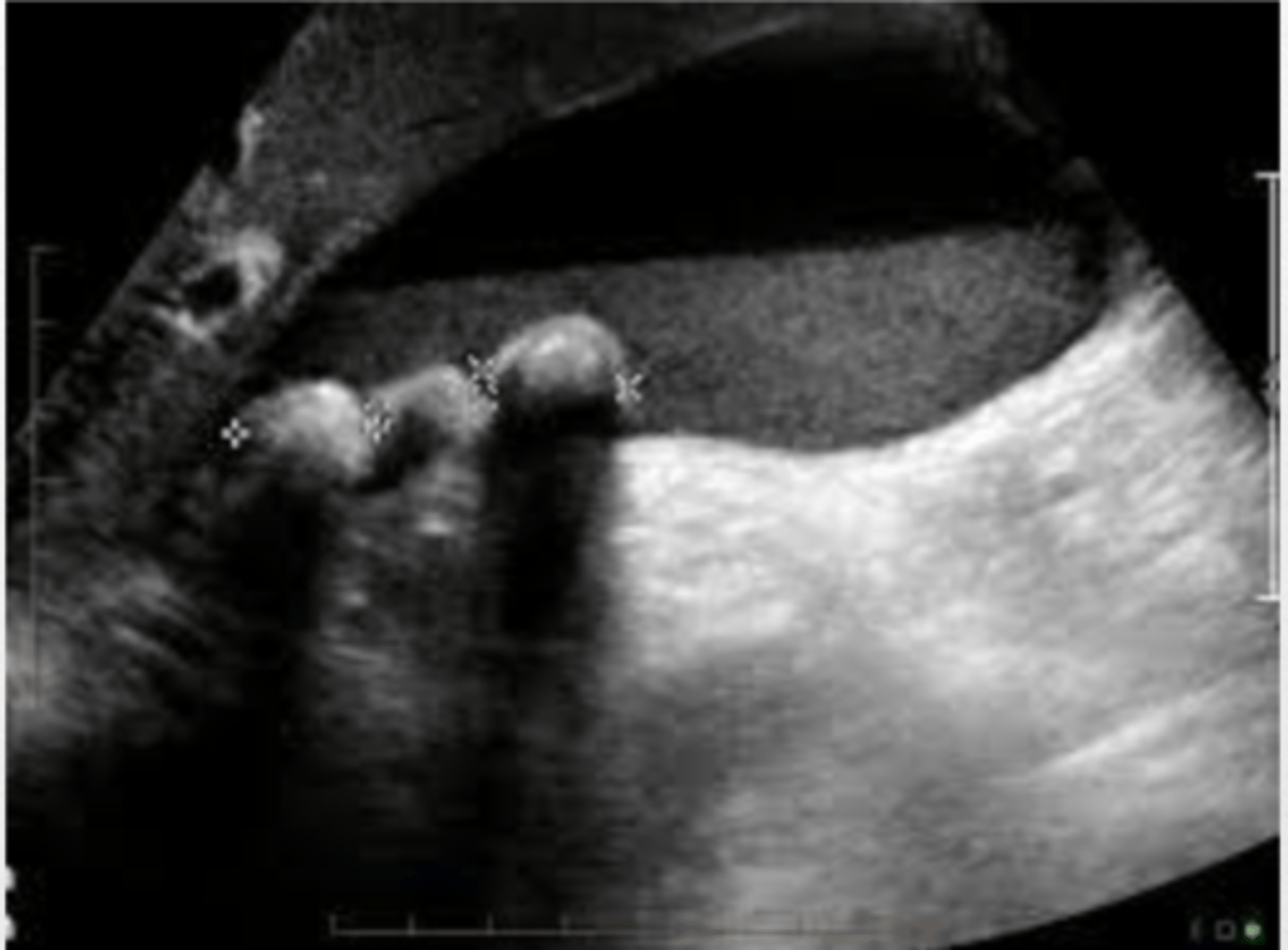
- wall thickening greater than 3mm
- pericholecystic fluid
- Murphy's sign
- with and without stones
What to look for in suspected acute cholecystitis...
Cholecystitis
GB wall thickened with edema, pericholecystic fluid
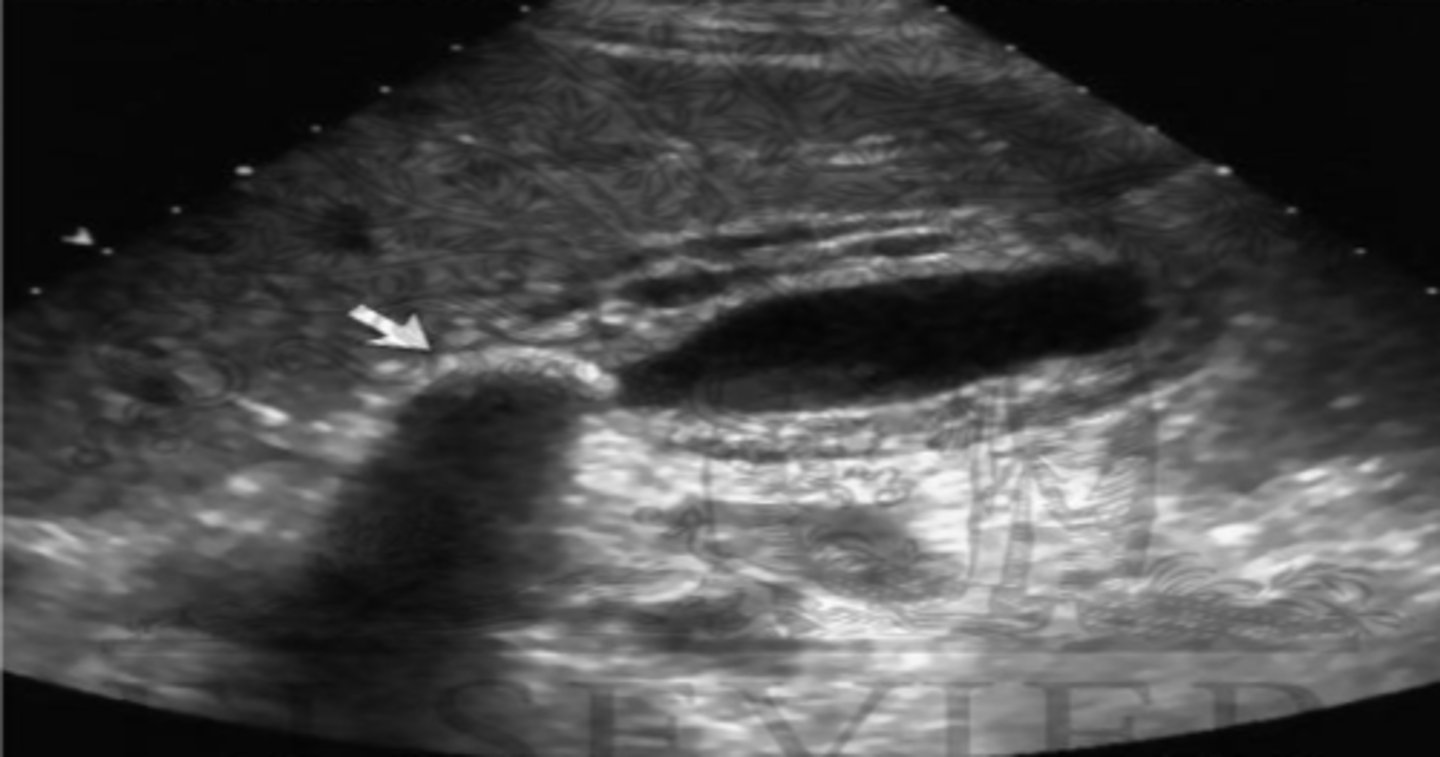
Cholecystitis
Chronic Cholecystitis
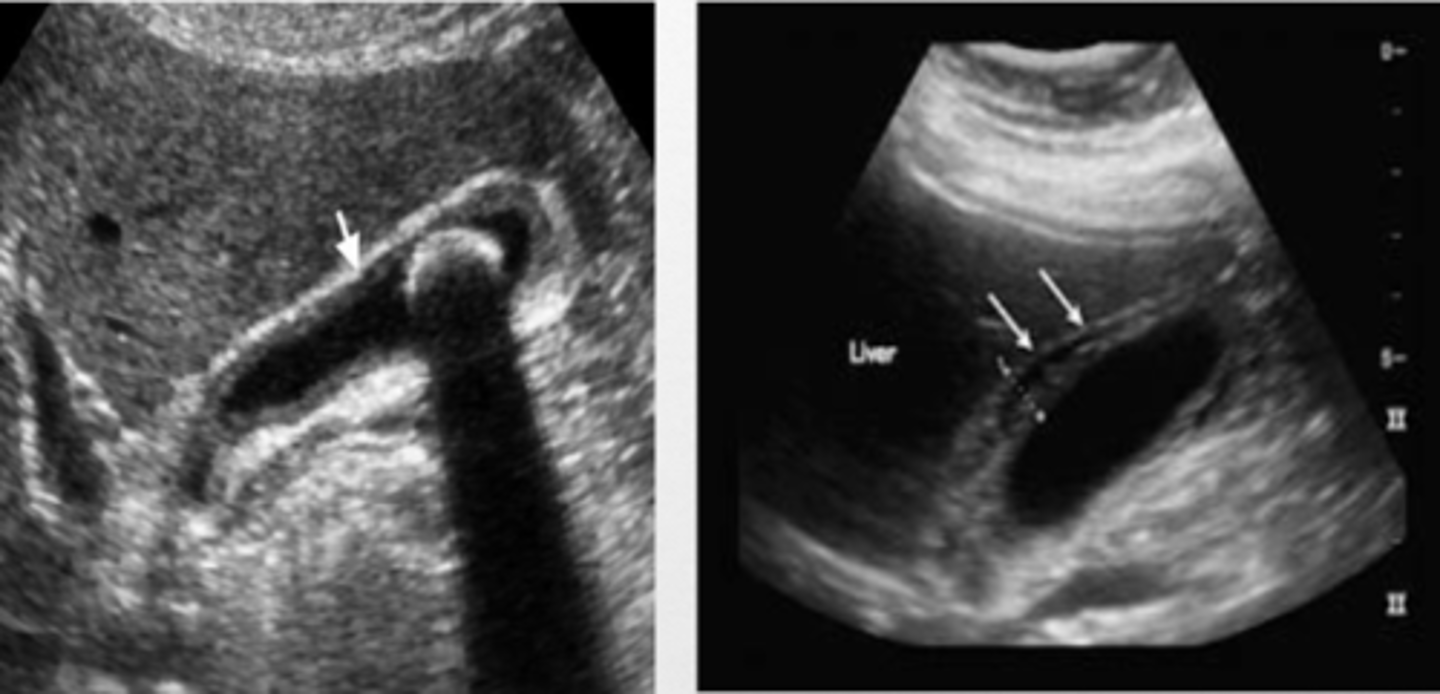
WES sign is indicative of _____.
WES sign...
Wall
Echo
Shadow
What do you look for in suspected chronic cholecystitis?
Chronic Cholecystitis
WES sign
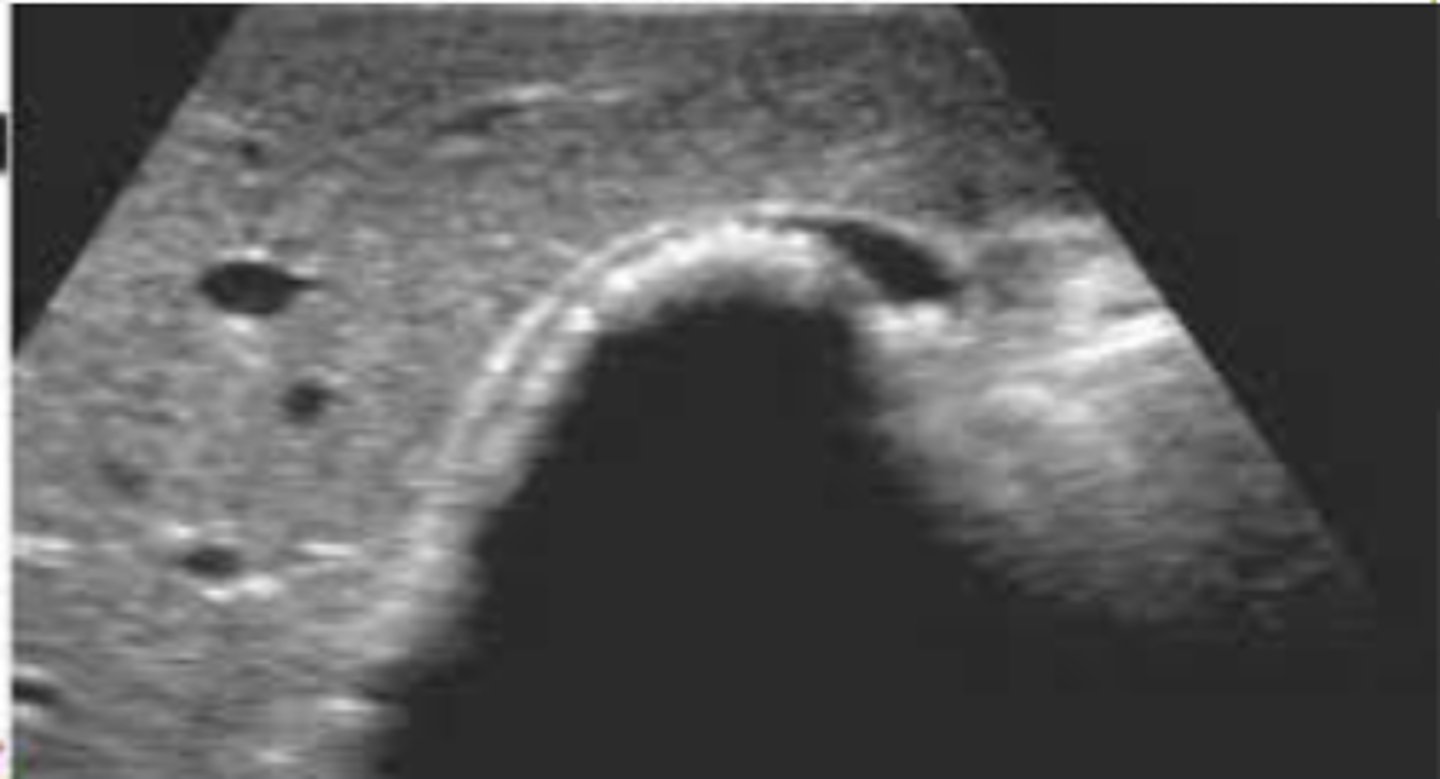
normal CBD
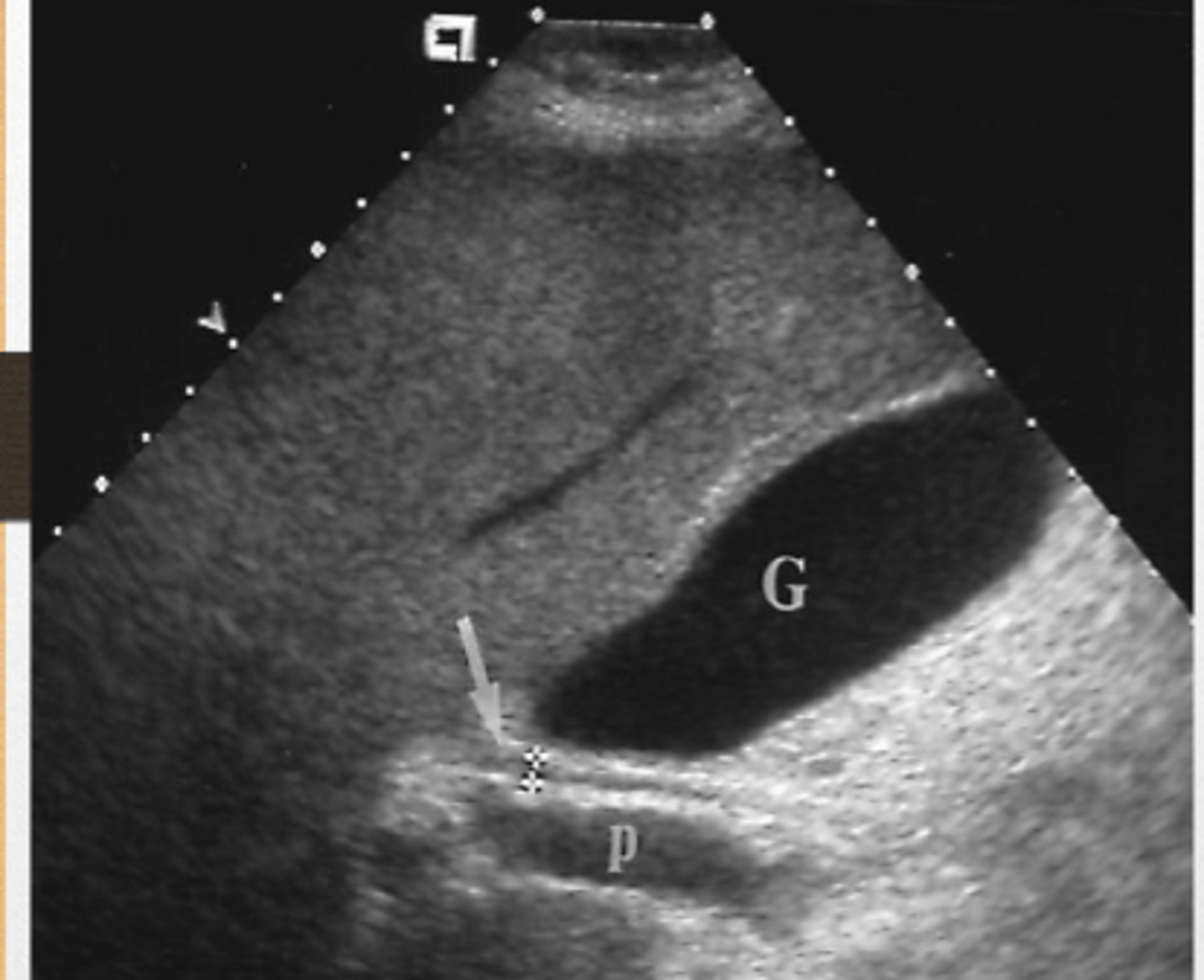
liver
Because flow of blood into the ____ through the portal vin is strongly linked with the spleen, intestines, stomach, ascites, edema, etc. If the ___ is abnormal looking on US then expect problems with the rest of the organs and systems.
normal liver
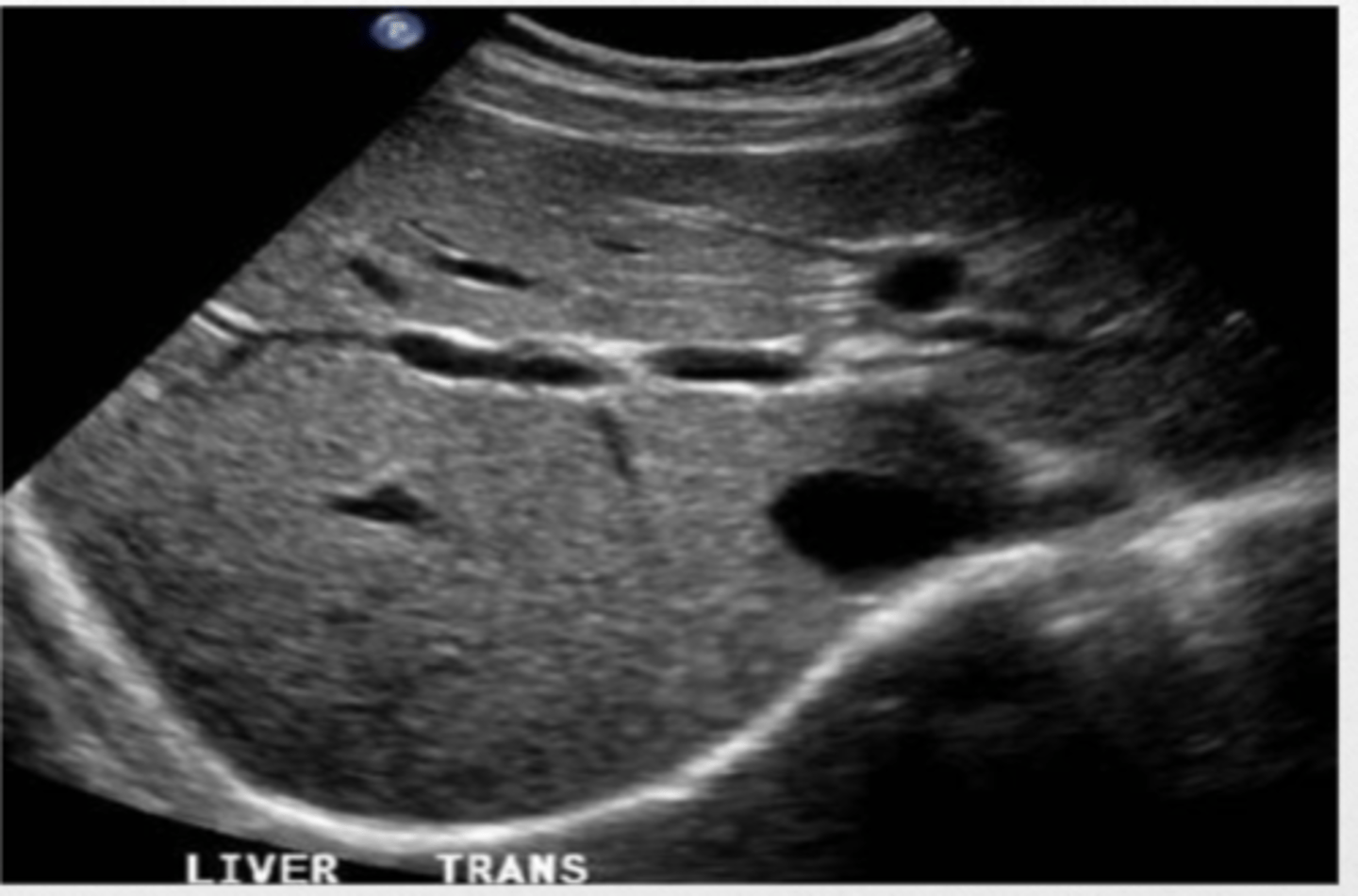
Liver Cirrhosis
liver blackened out
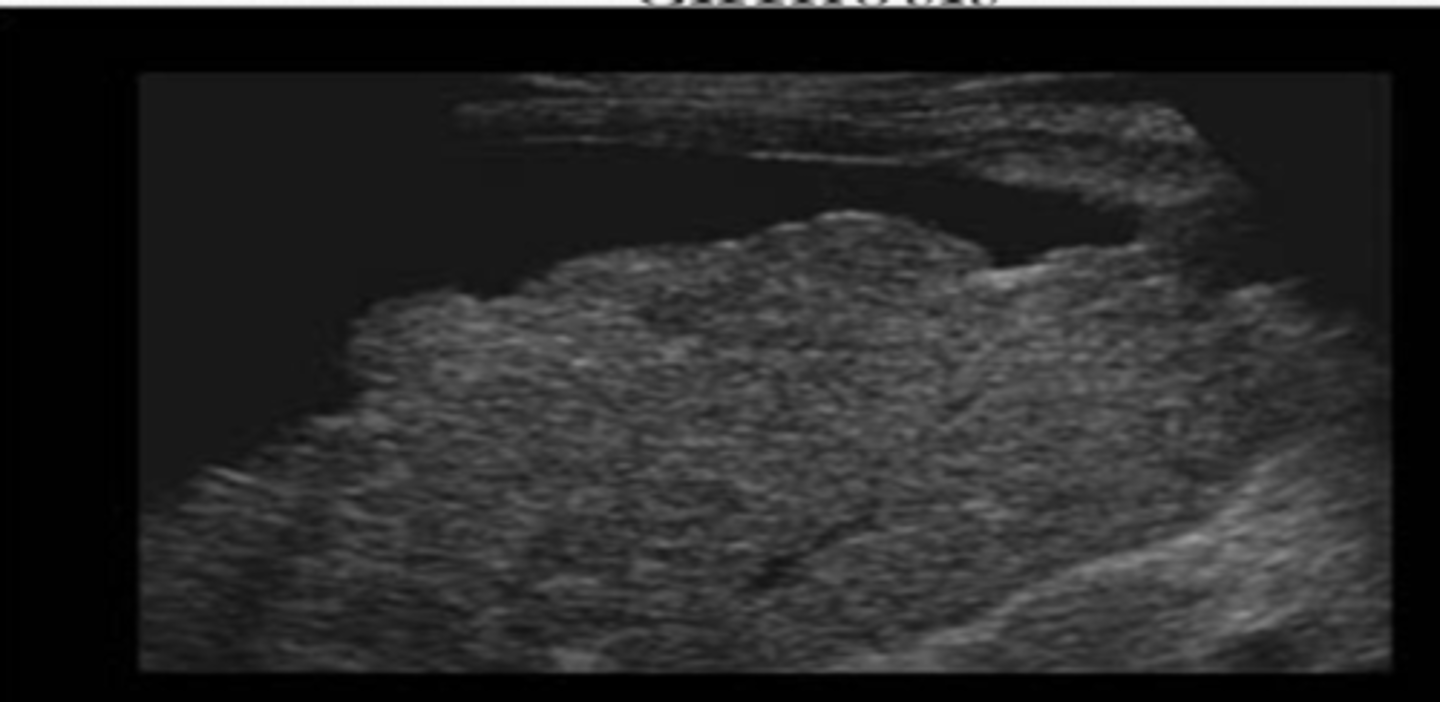
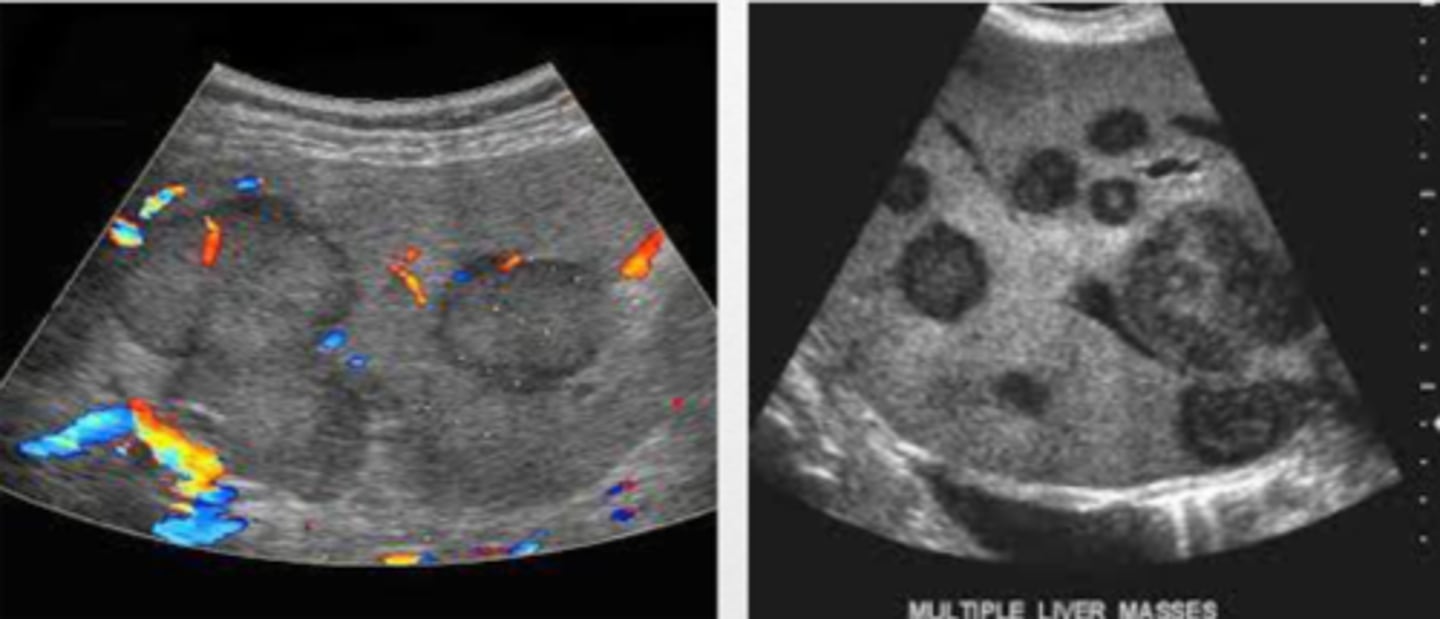
Liver Mets
liver
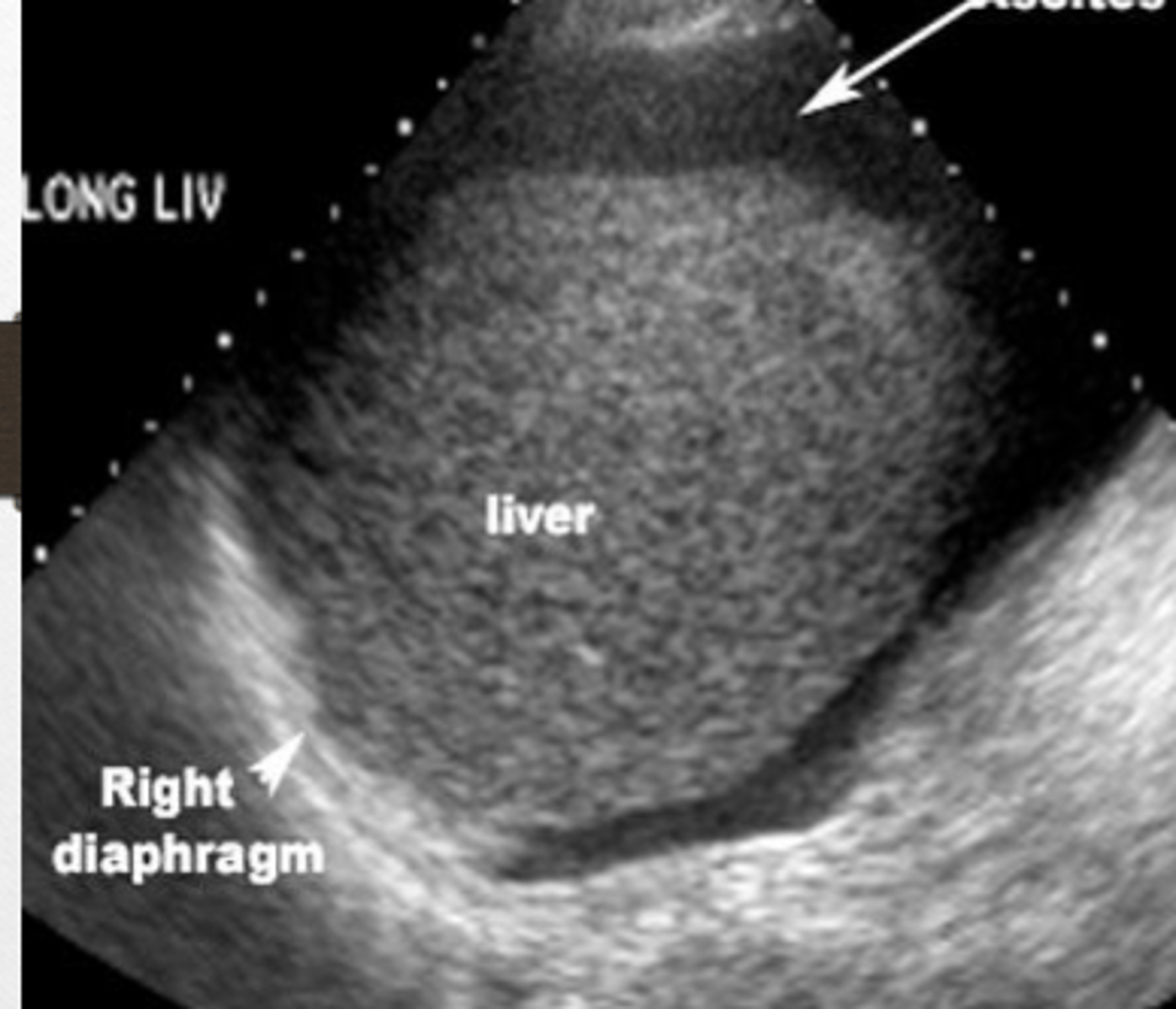
Ascites
Normal kidney
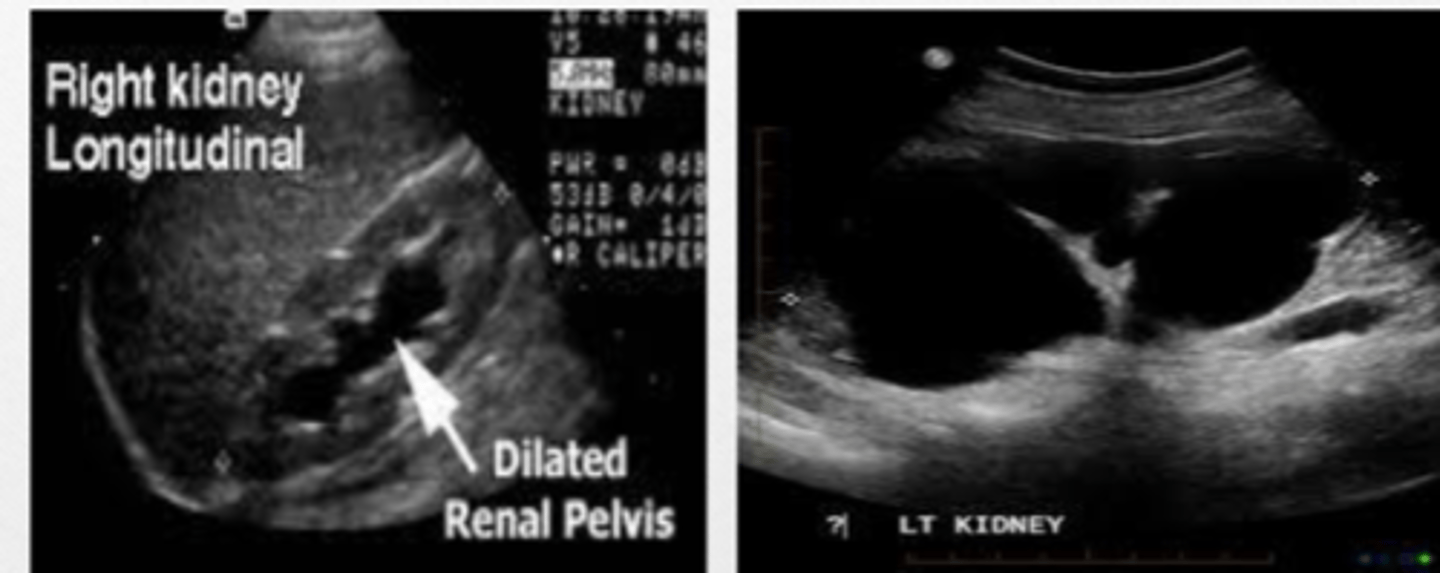
Hydronephrosis
Hydronephrosis
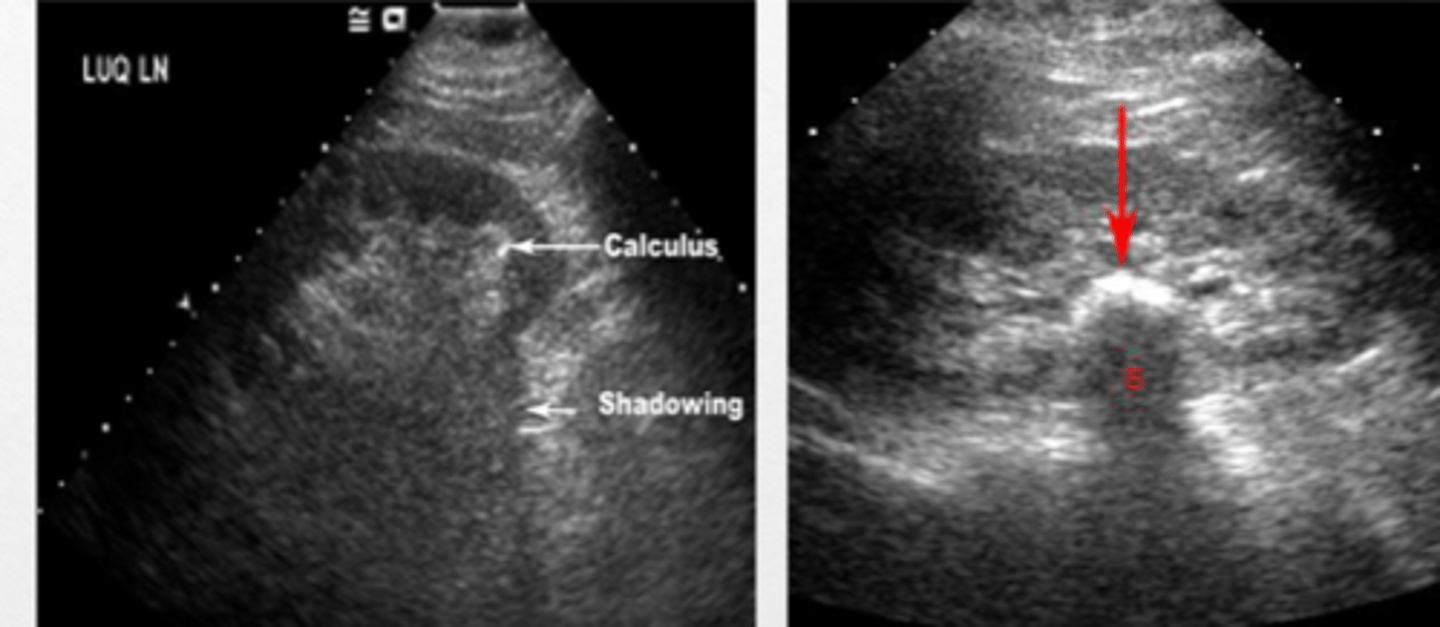
nephrolithiasis
kidney
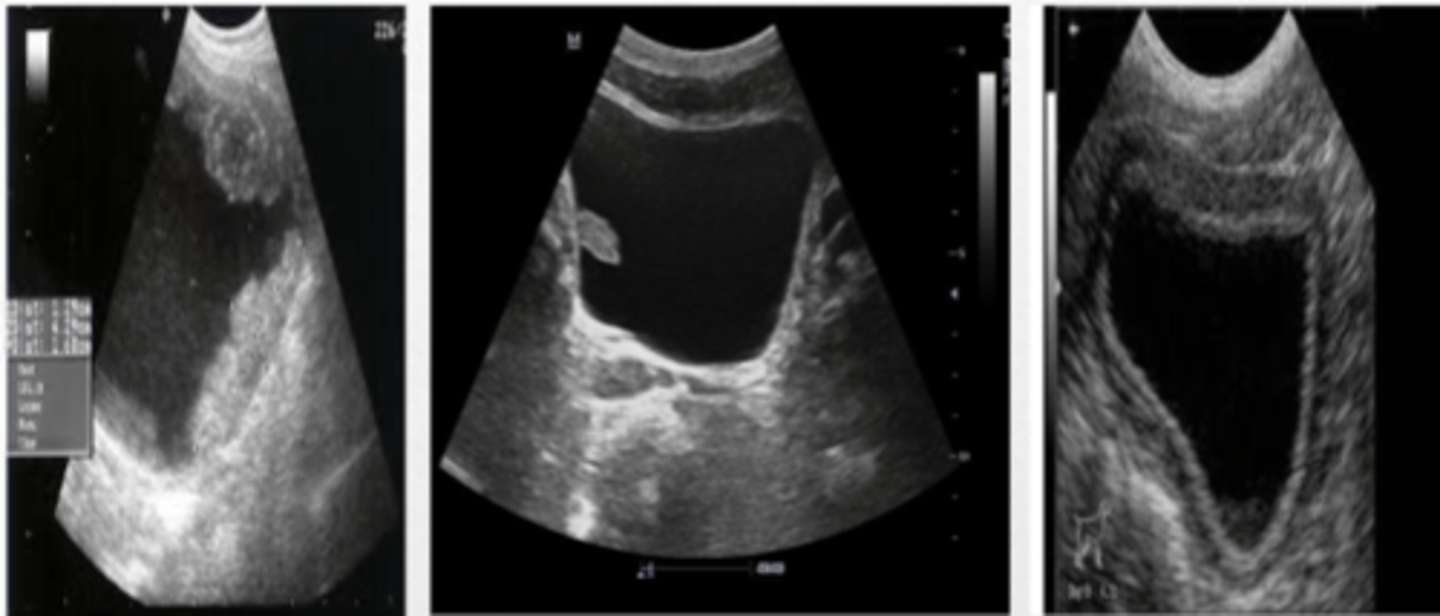
normal urinary bladder
suprapubic US
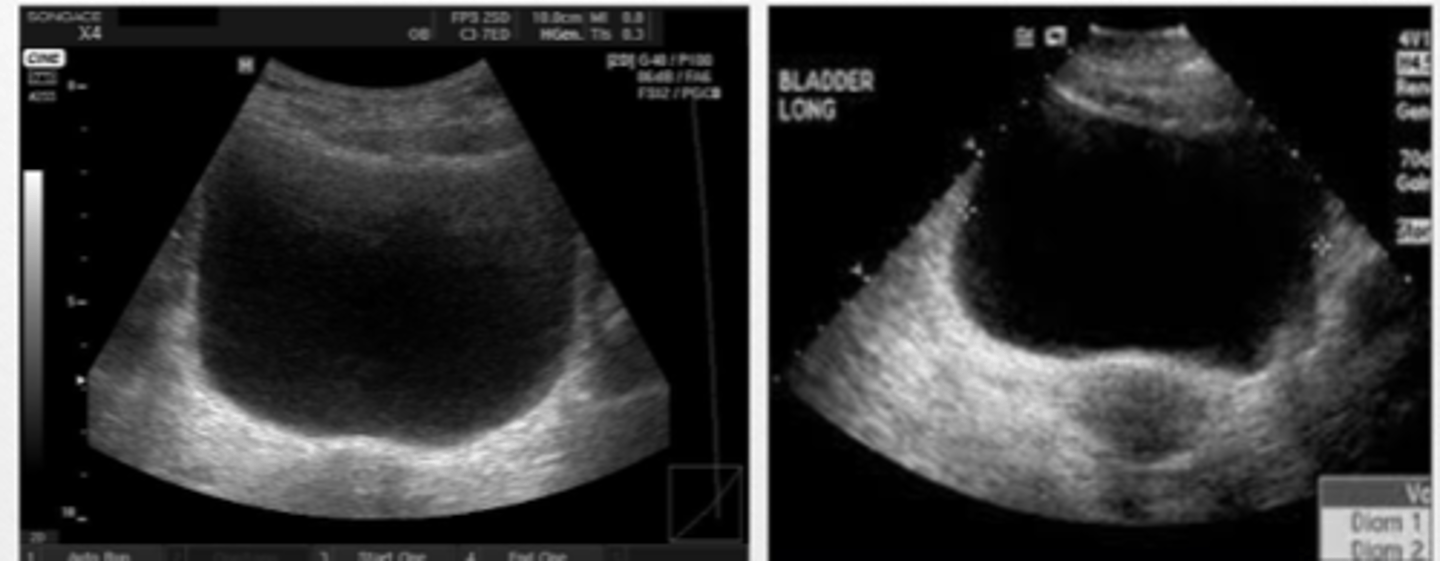
abnormal growths on bladder wall
suprapubic US
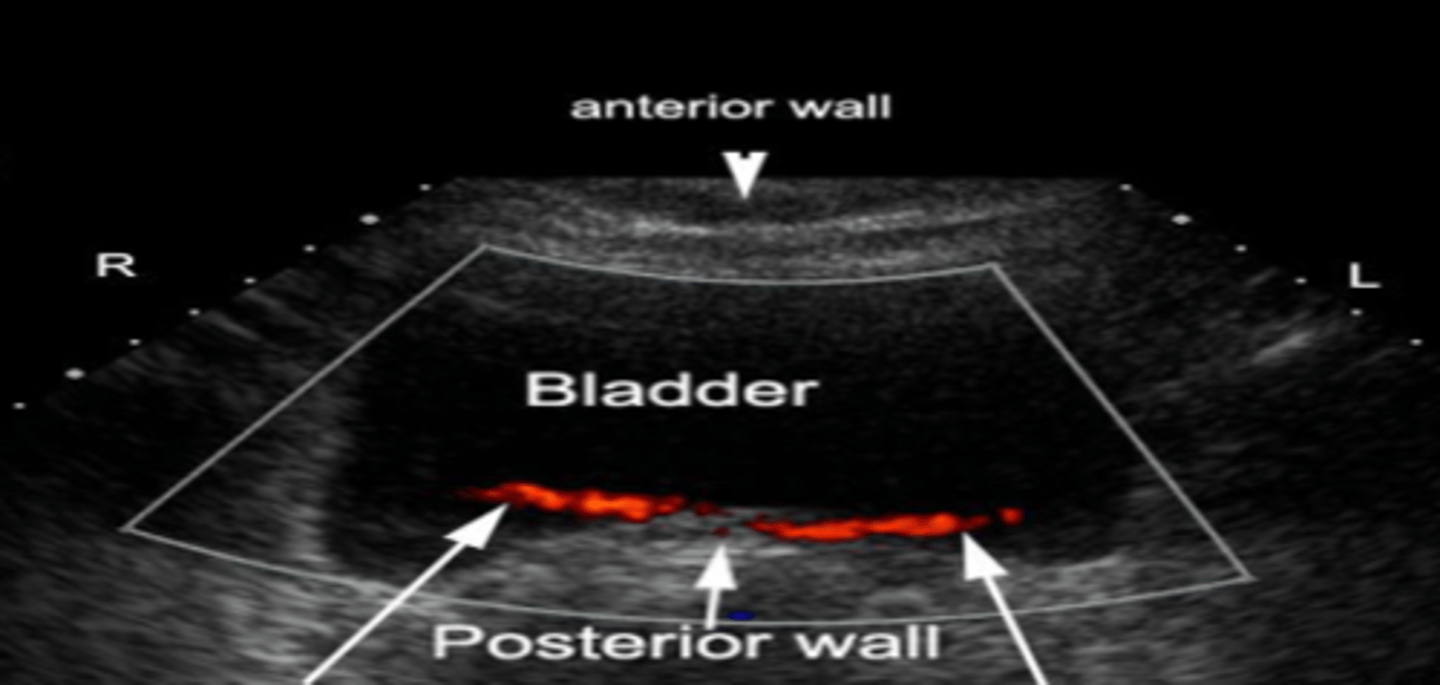
Bladder Jets
normal finding
Foley on bladder US
bladder
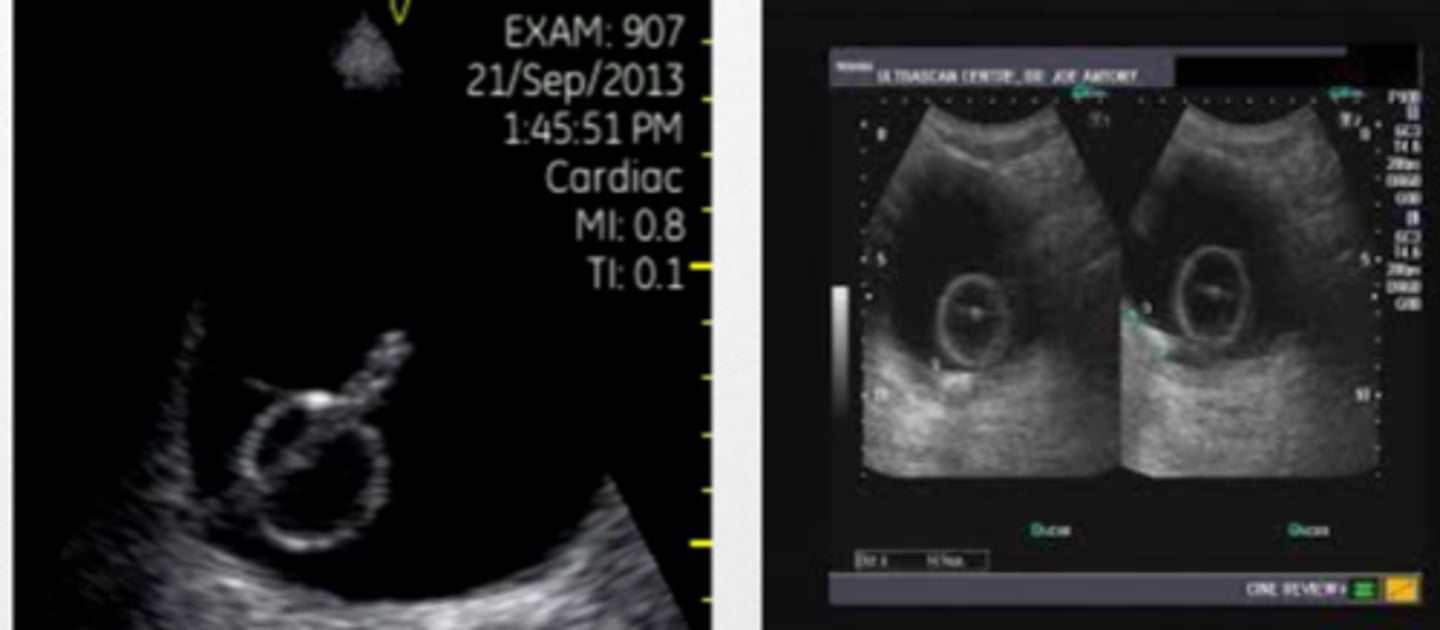
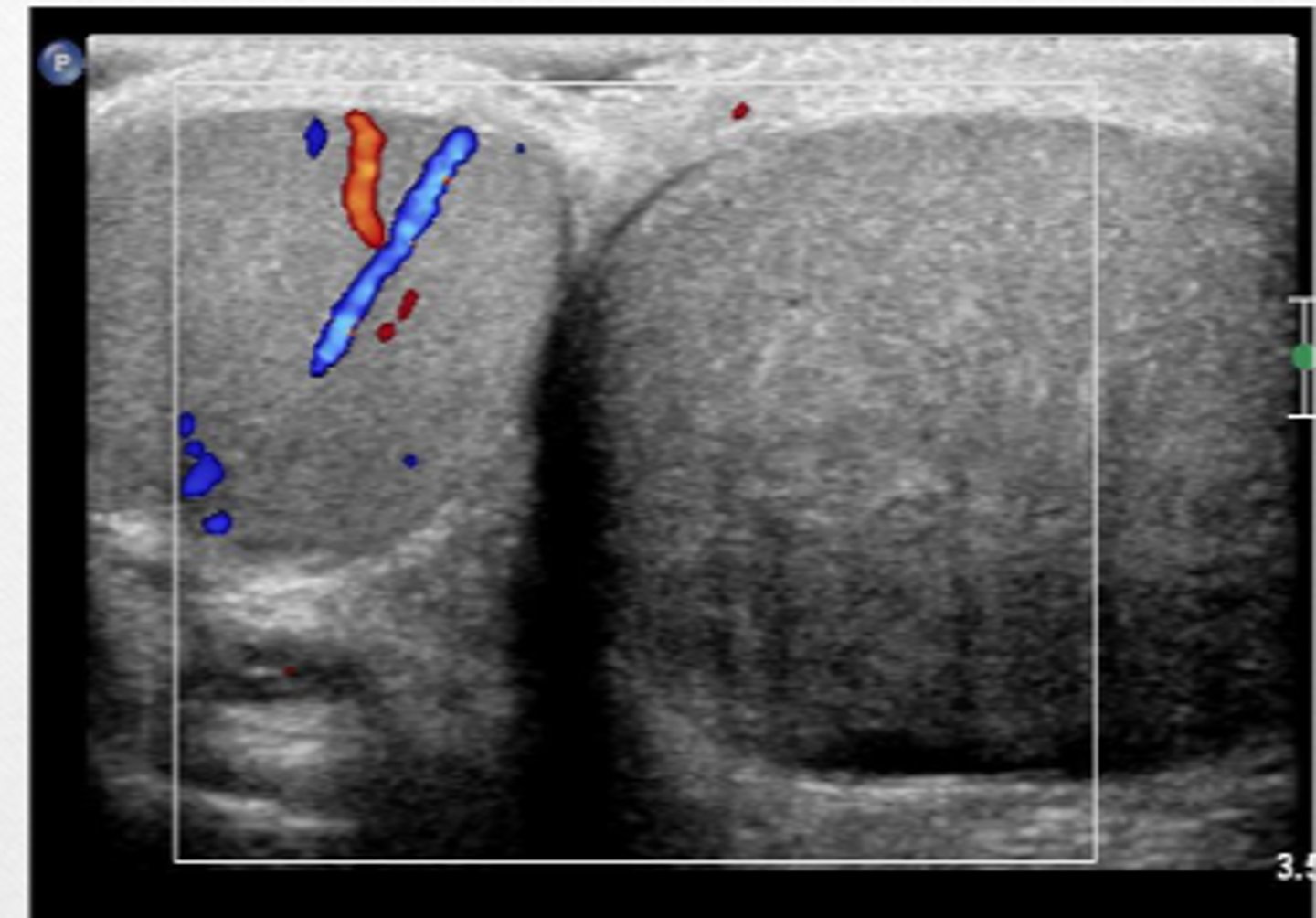
normal testes
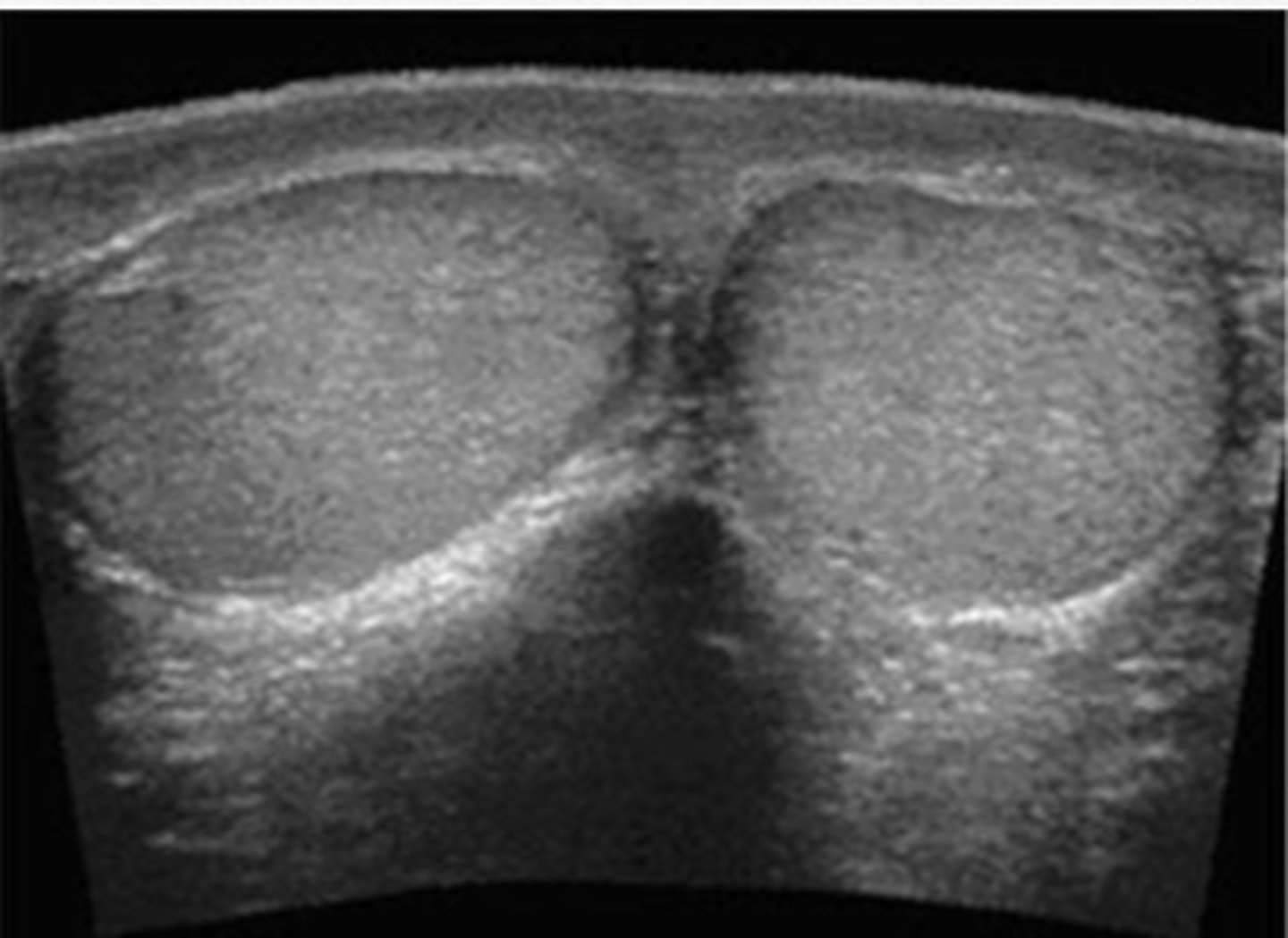
testicle with good blood flow
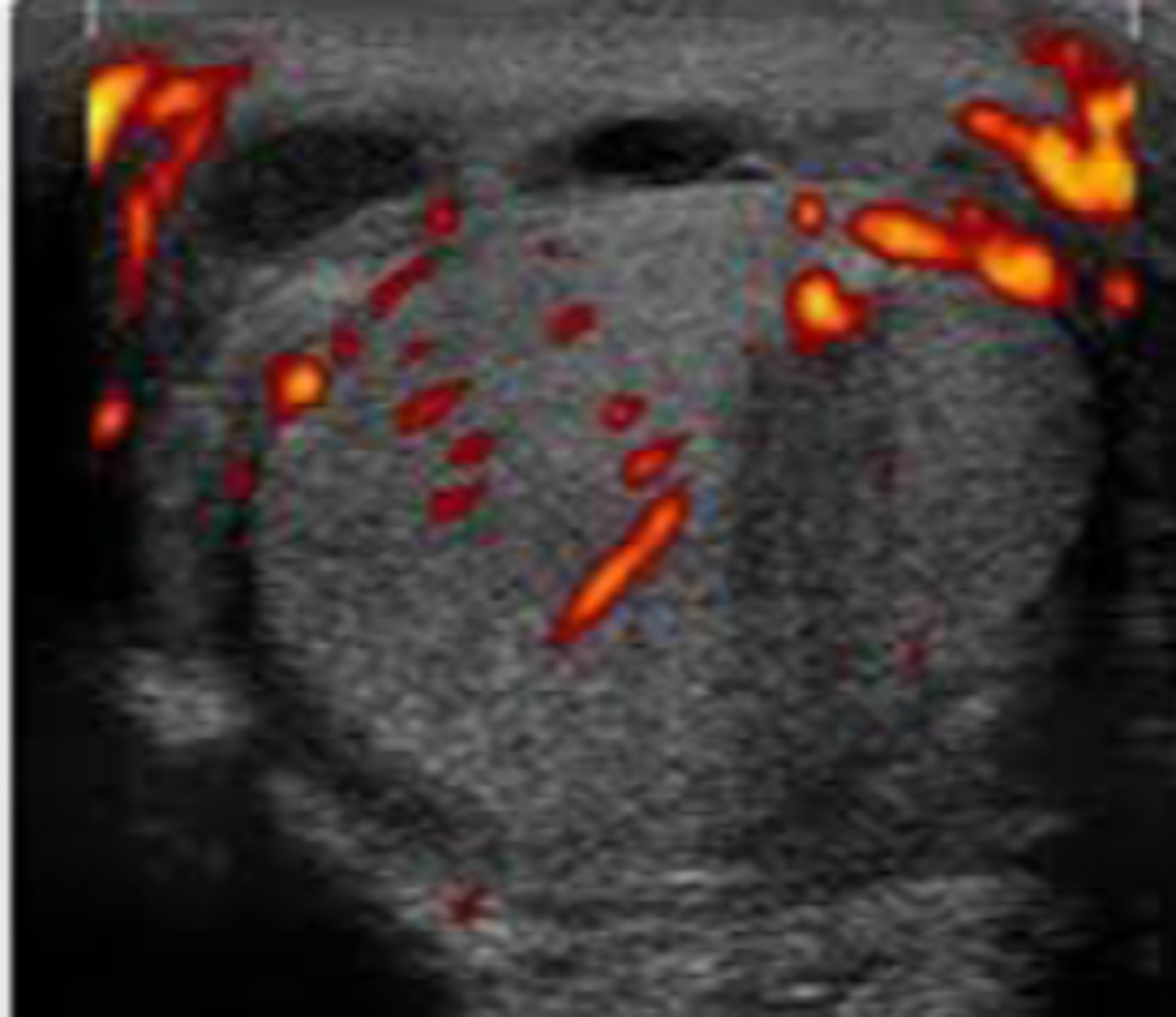
right testicular torsion
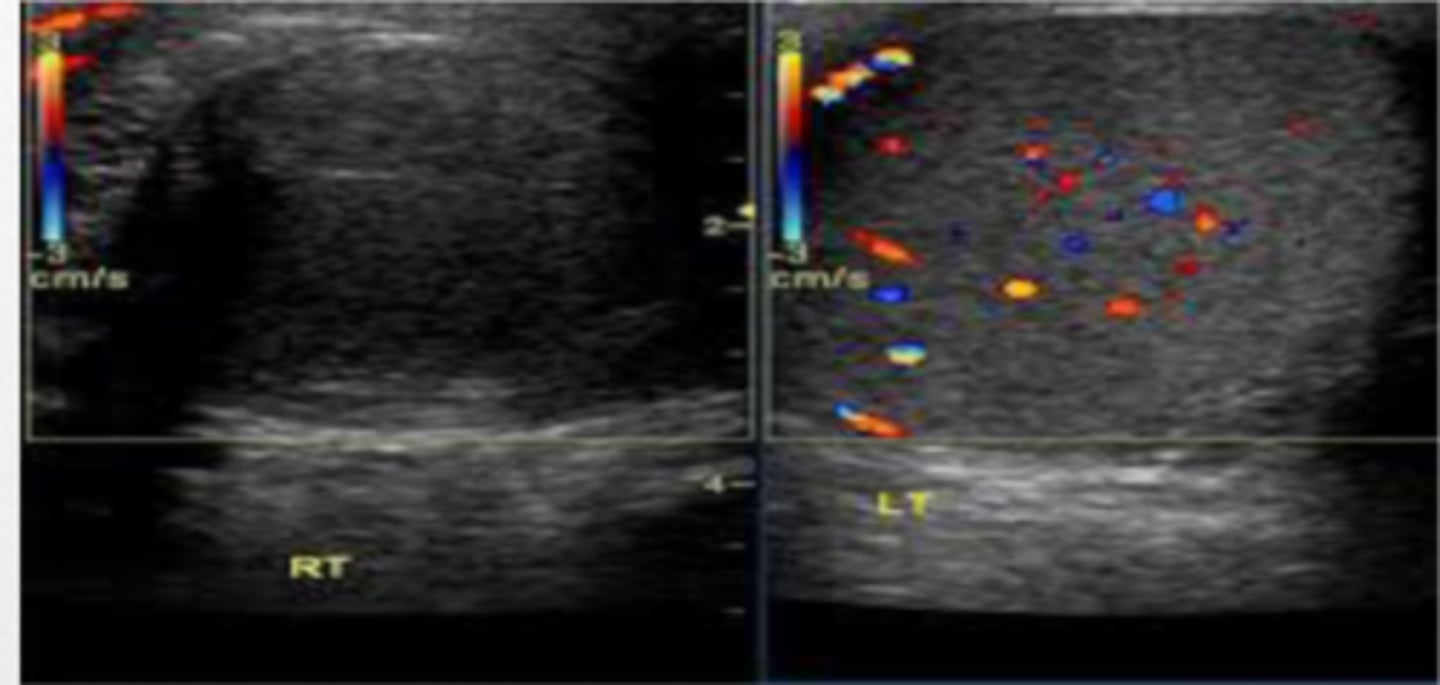
torsion
Phased array probe
Which transducer would you use for performing an abdominal scan?
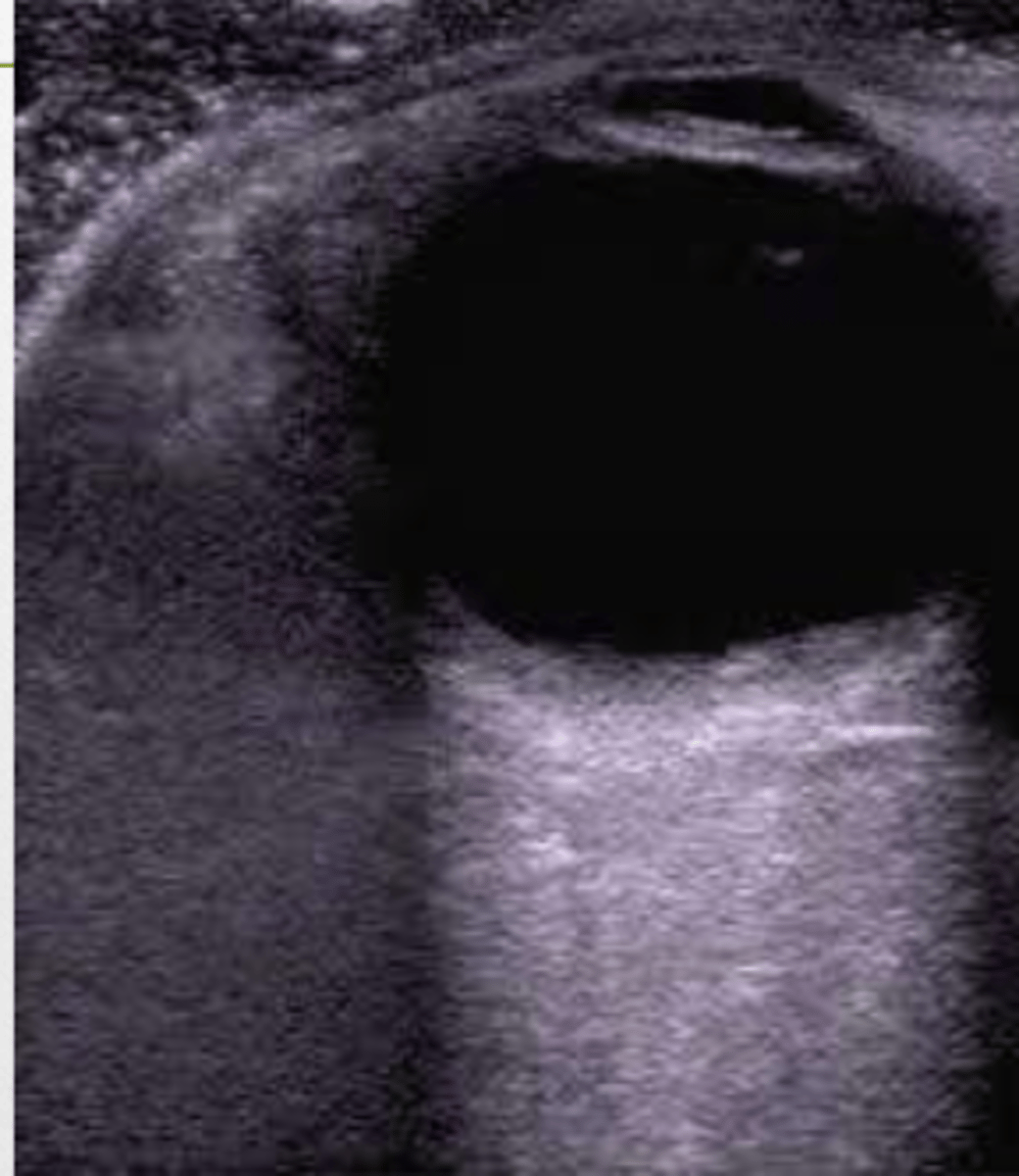
Acoustic enhancement
this image represents...
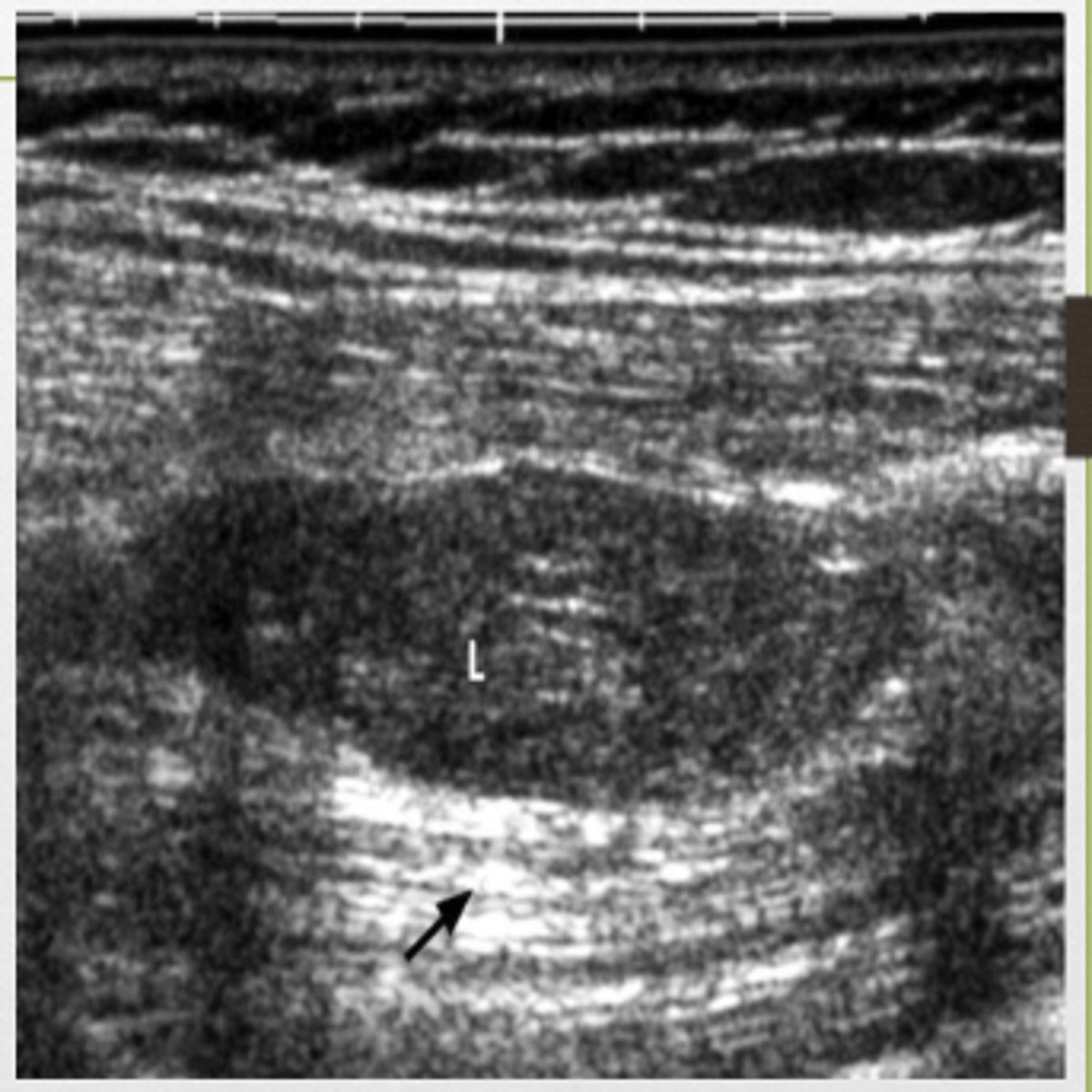
L is hypoechoic structure when compared to surrounding tissue
Describe the structure labeled L in comparison to the surrounding tissue?
head, scanner/operator
in the long view, the notch should be pointing to the ___ of the patient, where in the trans view, the notch should be pointing toward the ______.
False
T/F: Red color on doppler means that the vessel is an artery.
pleural effusion, ascites
fluid superior to the diaphragm is ____, where fluid inferior to the diaphragm is called _____