Musculoskeletal Upper Limb
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
Craniovertebral Instability
Symptoms: Neck pain, wry neck posture, headache, myelopathy bowel/bladder dysfunction, ataxia, neurological symptoms
Diagnosis: Sharp-Purer test, neurological exam, Imaging, UMNL signs
Risk Factors: acute trauma, degeneration, congenital conditions
“Excessive movement at C1-C2 vertebrae as a result of bony or ligamentous abnormality”
Cervical Arterial Dissection (CAD)
Symptoms: acute onset neck pain, headache,
Diagnosis: Horners syndrome (constricted pupils, droopy eyelids, inability to sweat), neuro exam
Treatment: refer to ED immediately!
Risk Factors: minor trauma, infection, genetics, younger population
“Tear in the wall of the vertebral artery which may result in a cerebrovascular accident/stroke”
Vertebro-basilar Insufficiency (VBI)
Symptoms: 5 D’s and 3 N’s, lightheadedness, blurriness of vision, vomiting, P&N, pallor
Diagnosis: VBI positional tests, Positive test → dizziness, nystagmus, unwell feeling
Treatment: refer to ED immediately!
Risk Factors: older patients, chronic neck pain/stiffness, atherosclerosis, spondylolysis, trauma
“Decrease blood flow to the posterior portion of the brain via the basilar artery”
Cervical Myelopathy
Symptoms: bilateral neuro symptoms, weakness, bladder/bowel dysfunction, saddle anesthesia.
Treatment: ED or specialist, diagnostic imaging, surgery
Risk Factors: older age
“Compression to the spinal cord from trauma or stenosis”
Whiplash Syndrome (Whiplash Associated Disorders= WAD)
Symptoms: neck pain, headache, decrease neck mobility, arm pain, 5Ds/3Ns,
Diagnosis: history taking, MOI in detail, palpation, ROM, neuro exam
Treatment: stay active, pharmacology, manual therapy
“Acceleration-deceleration injuries to cervical spine“
Acute Wry Neck (Zygapophyseal/Discogenic)
Symptoms of Zygopophyseal:
young children/adults, Upper Cx, locking of C0-C2, limited ROM, sudden movement = sharp pain, trauma
Treatment
joint mobilization, AROM/PROM, posture, traction
Symptoms of Discogenic:
gradual onset, older generation, lower Cx, refer to scapular region
Treatment:
gentle traction, heat, posture, collar, soft tissue mobilisations
Risk Factors: sudden quick movement or waking from sleep
“Sudden onset of sharp neck pain with protective deformity and limitation of movement”
Non-specific Cervical Spine Pain - Spondylosis
“degeneration of the spine”
Symptoms: neck pain, stiff neck, headaches, radiculopathy
Diagnosis: patient Hx, imaging
Treatment: soft tissue, strengthening, medication, ROM, surgery
Risk Factors: age
Disc Prolapse
Symptoms: neck pain, painful AROM/PROM, arm pain
Diagnosis: imaging, patient Hx
Treatment:
Risk Factors: acute trauma, insidious→ degeneration, 51-60yrs, females
Cervical Radiculopathy
Symptoms: neck pain, arm pain, neurological symptoms, tingling/P&N, reflex changes
Diagnosis: patient Hx, Neuro exam, diagnostic imaging, Spurlings test
Treatment: traction, immobilization, soft tissue, manual therapy, steroids, ROM
Stinger and Burner Syndrome
Symptoms: radicular type burning, shooting, stinging, numbness, weakness
Diagnosis: neuro exam, AROM/PROM, MMT
Treatment: treat the deficits, stretching, postural restraining, strength training
Risk Factors: rugby league, contact sports
“brachial plexus traction injury → pulling arm and neck away”
What are the 5D’s and 3N’s for VBI symptoms?
Dizziness (vertigo or lightheadedness)
Diplopia (double vision)
Dysarthria (slurred or impaired speech)
Dysphagia (difficulty swallowing)
Drop attacks (sudden loss of postural control without loss of consciousness)
Nausea (or vomiting)
Nystagmus (involuntary eye movements)
Numbness (especially facial or perioral paresthesia)
Migraine without Aura
Sudden onset - recurrent headache disorder lasting 4-72 hours
Management: Sleep, hydrate, drugs, exercise, diet, lifestyle

Migraine with Aura
Buildup for the migraine - recurrent attacks, symptoms build up followed by headache/migraine
Management: Sleep, hydrate, drugs, exercise, diet, lifestyle

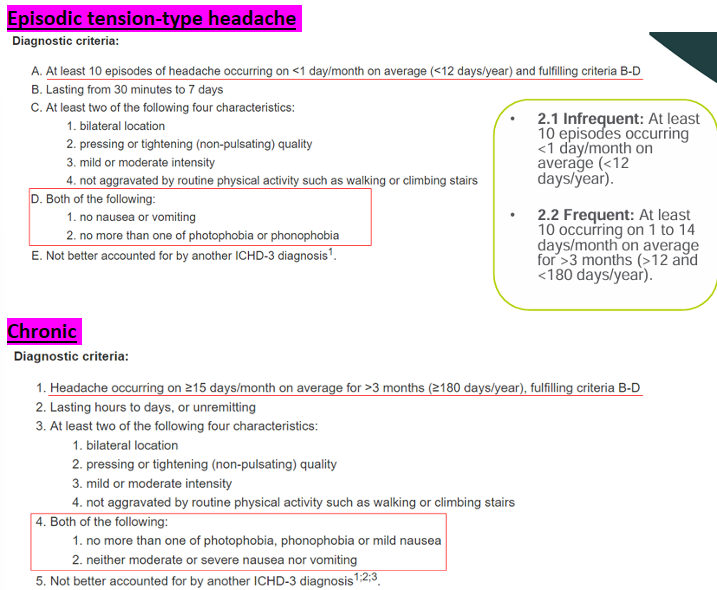
Tension-type Headache - Episodic and Chronic
Symptoms: bilateral, pressing/tightening, mild-moderate, not agg by physical activity
Cause: stress, poor posture, muscular, nutrition, concentration, environmental
Management: Pharmacology, NSIADS< physical activity, CBT, treatment of the cranio-cervical-mandibular region
Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalagias - Cluster or Episodic (TAC)
Symptoms: intense one-sided pain centered by the eye/temple
Ipsilateral pain, lacrimation, rhinorrhea, nasal congestion, sweating, restlessness, miosis
Lasts 15-180 minutes
Management: Triptans, oxygen, pharmacology, physiotherapy, electrostimulation

Primary Cough Headache
Cause: coughing or other Valsalva/straining maneuver

Primary Exercise Headache
Cause: exercise in the absence of any intercranial disorder, hot weather, short duration

HA due to Trauma - Persistent
Symptoms: Dizziness, fatigue, reduced concentration, memory loss, insomnia, anxiety, personality changes
Time frame: HA more than 3 months caused by trauma to the head

HA due to Trauma - Acute
Symptoms: Dizziness, fatigue, reduced concentration, memory loss, insomnia, anxiety, personality changes
Time Frame: less than 3 months caused by trauma to head

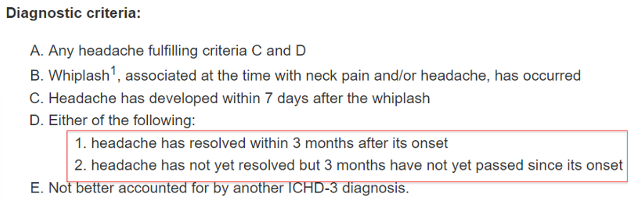
Acute HA due to Whiplash
Symptoms: Dizziness, fatigue, reduced concentration, memory loss, insomnia, anxiety, personality changes
Time Frame: Less than 3 months due to whiplash
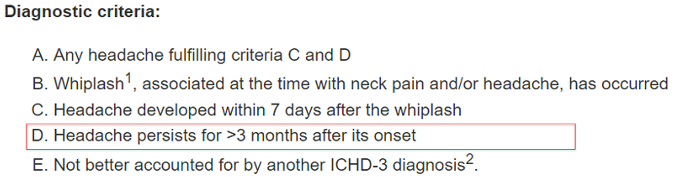
Persistent HA due to Whiplash
Symptoms: Dizziness, fatigue, reduced concentration, memory loss, insomnia, anxiety, personality changes
Time Frame: HA more than 3 months due to whiplash
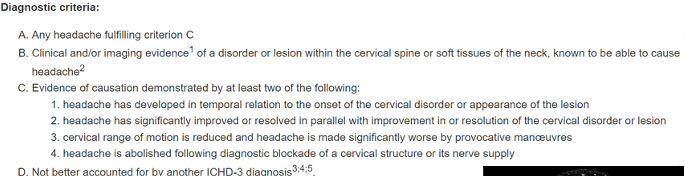
Cervicogenic Headache
Symptoms: Unilateral headache, ipsilateral neck/shoulder/arm pain, migraine-like features
Physical Signs: Anesthetic blockades (gold standard), reduced cervical AROM/PROM, dysfunction, impaired muscle function
Treatment: sleep, drugs, exercise, posture, psych, mobilization
“C1-C3 nerve roots converge in same brain region”
Headache attributed to TMJ disorder
“Referral between Cervical and TMJ - anatomical, neurophysiological, biomechanical, function
Symptoms: Muscle pain, headaches, joint related issues

Headache Differentiation
Myalgia (TMJ)
Symptoms: pain in the jaw, temple, in ear or front of ear AND pain modified with jaw movement, function or parafunction, headaches, difficult to localise, dull pressure, multifactorial
Diagnosis: confirmation of pain in temporalis or masseter on palpation, maximal unassisted/assisted opening
Risk Factor: dental occlusion, molar removals, genetics, depression
Muscle as the primary source of pain
Disc Displacements - Ant. displacement without reduction (ADDwoR)
“Closed lock” limited opening + absence of click
traumatic onset, sudden crack, clicking
painful limited protrusion + deflection to affected side
restricted lateral deviation to contralateral side
Disc Displacement - Ant. displacement with reduction (ADDwR)
click, no lock
deviation to unaffected side during early opening
may achieve full rom
Disc Displacement - Post. disc displacement without reduction
“Open lock” “subluxation”
much less common
Non-specific Thoracic Spine Pain (x3) (mechanical)
Conditions: joint dysfunction, paraspinal muscle sprain. posture related, structural pathologies
Facet Joint:
unilateral/post pain, acute onset, dull pain at rest
reduced AROM, hypomobility of involved facet, muscle spasm guarding
management: manual therapy, gentle ROM
IVD:
central/post/ant pain felt through chest, postural loading, dull and diffuse pain
limited AROM, hypomobility of involved segments
management: manual therapy, gentle ROM, exercises
CVJ/CTJ:
unilateral pain along rib line, conjunction with facet joint injury, respiratory signs,
limited trunk motion, multiple segments involved
Management: manual therapy, gentle ROM
Specific Thoracic Spine Pain - Scheuremann’s Disease (Kyphosis)
Type 1: Thoracic, produces more deformity than pain
Type 2: more pain than deformity in thoracolumbar
Presentation on Imaging: irregularity of end plates, Schmorls nodes, wedge-shaped VB’s, hyperkyphosis
Diagnosis: after long posture, tight hamstrings, respiratory limitation, curvatures,
Risk Factors: adolescents, males, taller/skeletally mature, 13-16 yrs
Management: Education, braces, Tx-Lx-pelvic-hip mobility
Conditions: rib fracture, central canal stenosis, disc prolapse, syndromes
Serious Pathologies of the Thoracic Spine (x4) (PVoPT)
Pyrogenic Spinal Infections
septic discitis, vertebral osteomyelitis, epidural abscess, occurs more in males over 50
Vertebral Osteomyelitis (an infection)
triad of pain, fever and local tenderness, paraspinal abscesses, jaggered N plates
Risks involve malnutrition, IV use, infection, renal failure, spinal surgery
Pyrogenic Discitis
can occur with vertebral osteomyelitis, antibiotics can fix, surgical intervention
Tumors
primary, benign or metastatic, (metastatic spinal disease common)
Specific Thoracic Spine Pain - Scoliosis
Type: Structural: idiopathic (known cause)
usually painless, respiratory issues can be present, lateral curvature
Managment: exercise, bracing, operation
Type: Non-structural (adaptive/maladaptive posture)
leg length differences, hip add/abd deformity, poor lumbar-hip control, muscle asymmetry
Risk Factors: females
Specific Thoracic Spine Pain - Spondyloarthropathies
Inflammatory spinal pain with ONE or more of:
Positive family history in first- or second-degree relatives of patients with ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthropathy, acute iritis, reactive arthritis or IBD.
Psoriasis
Inflammatory bowel disease
Alternating buttock pain
Enthesitis
Acute diarrhoea
Urethritis
Sacro-iliitis: bilateral grade 2-4 changes or unilateral 3-4 changes.
Symptoms: LBP, IT aching, sharp, worse after activity, AM stiffness, limited chest wall excursion
Management: aerobic exercises, manual therapy
Risk Factors: Males, 16-25 years
Specific Thoracic Spine Pain - Central Canal Stenosis
Signs: intermittent aching and clumsiness of both legs, worse with walking, neurogenic intermittent claudication, ataxia, incoordination of LL, cauda equina symptoms, “shopping trolley” sign
Risk factors: older age
Specific Thoracic Spine Pain - IVD protrusion -/+ radiculopathy
Symptoms: localized back pain, radiates around chest wall, myelopathy, +/- cord compression, bladder/bowel changes → UMN
Management: Physio, education, activity, manual therapy, postural control, trunk strengthening
Risk Factors: disc degeneration, disc calcification, below T7
Specific Thoracic Spine Pain - Fractures (x3)
Vertebral body compression #
trauma, high compression
Rib #
blunt trauma (pneumo/hemothorax), ribs 5-10 most common, symptomatic, >3-week recovery
Rib stress injury
shear forces created by muscle contraction, activity related chest wall pain, confirmed by MRI or bone scan
Specific Thoracic Spine Pain - T4 Syndrome
Upper extremity paresthesia and pain +/- symptoms into the neck and/or head
MOI reaching, felt click in thoracic spine, constant thoracic pain, constant glove distribution of paresthesia, altered sensation in the upper limb
Autonomic nervous system role → dysfunctions expressed over lower Cx spine and down the UL
Hypomobility upper Tx region common = responds to joint mobilizations
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
Mechanical compression/entrapment of the cords of the brachial plexus +/ subclavian artery + vein
3 anatomical tunnels → Superior thoracic outlet, Costo scalene hiatus, costoclavicular passage
Neurogenic type: most common, pain, ± paraesthesia in Ulnar nerve, hypothenar atrophy
Vascular type: rare, discoloration, swelling and weakness of fingers/hand
Symptoms: hand weakness/tingling, swelling, atrophy, shoulder pain, ant chest pain, C8/T1 radiculopathy, fatigued gripping
Diagnosis: Roo’s test, Adson’s maneuver, costoclavicular maneuverer
Management: address mechanical interface, address neural mechanosensitivity, identify/reduce agg factors
Risk Factors: congenital, traumatic, overhead athletes, depressed protracted shoulders, scapular dyskinesia
Specific Thoracic Spine Pain - Costochondritis and Tietze Syndrome
Costochondritis:
systemic cause, no local swelling, multi-joint, usually chronic, Inflammation of the costochondral junctions (cartilage attaching ribs to sternum).
Tietze Syndrome
inflammatory disorder of the costochondral, costosternal, or sternoclavicular joints, single joint, idiopathic, local pain and swelling, may occur after chronic coughing, vomiting, viral or trauma
Specific Thoracic Spine Pain - Ankylosing Spondylitis
Symptoms: Hereditary link to HLA-B27, Insidious onset of hip/buttock to LBP, IT aching +/- sharp, Worse after activity, AM stiffness, Limited chest wall excursion, Global limitation of trunk/Tx ROM
Radiographic changes– Sacroiliitis; bamboo spine
Management: exercise, physio, NSAIDs,
Risk factors: 16-25 years, males
Shoulder Impingement
Influenced by thoracic posture and mobility
External (Subacromial)- mechanical encroachment of the soft tissue in the subacromial space between the humeral head and subacromial space, occurs mid-range (60-120 deg “painful arc”)
Internal (post/sup)- Encroachment of the RC tendons in the glenohumeral joint
Primary cause- Structural narrowing of subacromial space (arthritis, AC enlargement, soft-tissue swelling)
Secondary cause- functional problems in shoulder positions (RC weakness, instability)
A cluster of symptoms, NOT a pathology
Shoulder Impingement: Rotator Cuff Related Shoulder Pain (SCRSP)
Supra > Infra > Subscap
Tears: can’t sleep on affected side, pain/weakness with RC testing,
Tendinopathy: multifactorial etiology, chronic pain, pain free past 90deg elevation
Diagnosis:
Tears: MRI, Ultrasound
Tendinopathy: MRI arthorgram
Treatment:
Tears: Conservative treatment surgery, strength, balance/control
Pain relief, RC rehab
Risk Factors: athletes, overhead workers, traumatic event
Shoulder Impingement: Scapular Dyskinesia
Clinical Manifestations: reduced scap upward rotation, post tilt, ER, increased clavicle elevation, decreased strength, Pec minor/post capsule reduced length
Treatment: pain relief, flexibility, muscle training, thoracic spine and STJ mobility, muscle control
Shoulder Impingement: Shoulder Instability - TUBS
^ 3 Types: A.R.P
(Traumatic Unidirectional (+/‐ Bankart lesion) instability +/‐ Surgery (TUBS)
Anterior dislocation
forced shoulder abd + ER, usually a traumatic injury
Recurrent dislocation
chronic shoulder instability
Posterior dislocation
Fall on outstretched hand (FOOSH)
pain, tightening, clicking, decreased ER
Treatment: Scapular rehab, RC control/strengthening, open/closed chain exercises, kinetic chain exercises
Shoulder Impingement: Shoulder Instability - AIOS
(Acquired sport‐specific instability (AIOS))
Symptoms: laxity of ant capsule caused by excessive anterior translation of humeral head
Clinical Manifestations: excessive PROM ER vs IR, recurrent shoulder pain during overhead activity
Diagnosis: “dead arm syndrome,” apprehension/relocation tests positive
Treatment: Scapular rehab, RC control/strengthening, open/closed chain exercises, posterior shoulder stretching, kinetic chain exercises
Risk Factors: overhead athletes, laxity
Shoulder Impingement: Shoulder Instability - AMBRI
(Atraumatic multidirectional instability with bilateral laxity (AMBRI)
Symptoms: pain, repeated subluxation or full dislocation
Clinical Manifestations: dynamic/muscle patterning instability, congenital joint hyperlaxity, repetitive overuse,
Diagnosis: laxity tests positive, altered muscle activation
Treatment: therapeutic exercises ongoing, surgery may be needed, closed/open chain exercises,
Risk Factors: 2-3 atraumatic instabilities
Shoulder Impingement: Biceps-related
Symptoms: All present with shoulder pain
Risk factors: Repetitive overhead activities
Partial tears long head of biceps brachii (LHBB)
Instability of the bicep tendon in the bicipital groove
Superio Labrum Anterior to Posterior (SLAP)
^ Stable/unstable - 4 SLAP sub-types
Degeneration
Superior Labrum and LHB detachment
SL detached, LHB intact
Tear SL +LHB, displaced in the GHJ
Caused By: carrying, dropping, throwing
Symptoms: popping, catching, grinding
Treatment: Conservative treatment for most clients, surgery for traumatic injuries
AC joint - Acute sprain-dislocation
Clinical Presentation: pain at rest over antero-lateral shoulder region, “step down” deformity, swelling, crepitus, possible hematoma
Objective Assessment: TOP over ACJ, hypermobility, pain with all shoulder ROM, check opposite ACj and clavicle length
Diagnosis: X-body abduction test, resisted extension test, X-ray
Management: POLICE, sling, ice, isometrics early, restore ROM, taping
AC joint - Atraumatic Osteolysis
Clinical Presentation: stress reaction of distal clavicle, worse at night, ull ache at rest, bone-stress injury, hypomobile, crepitus
Objective Assessment: TOP, swollen, agg by loading ACJ and pec major
Diagnosis: X-ray, bone scan
Management: conservative treatment
Risk Factors: overuse/overtraining, younger athletes, UL training
Adhesive Capsulitis (frozen shoulder)
“Loss of glenohumeral AROM and PROM resulting from progressive fibrosis and contracture of GHJ capsule”
Phase 1: less than 3 mths, synovitis, no contracture
pain into deltoid insertion, night pain, loss of passive ER with intact RC
Phase 2: 3-9 mths, freezing phase, acute synovitis, contracture
severe night pain, stiffness
Phase 3: 9-15mths, frozen phase
profound stiffness, pain at EOR of motion
Phase 4: thawing phase
profound stiffness, minimal pain
Management: pharmacological, NSAIDS, physical therapy (4 stages), non-operative is favoured, operative → (hydrodilation, manipulation under anaesthetic MUA, arthoscopic release)
Risk Factors: inflammation, fibrosing, female, 40-60, sedentary lifestyle, diabetes, dominant side
Cx as the Source of Pain
Somatic Neck Pain
proximal UL or shoulder girdle pain, C5-7 presents as Upper trap and posterolateral shoulder pain
any structure innervated by the same spinal level will have same distribution
IVD as source (Cloward’s signs), Z-joint as source
Facet Joints
C1-3 = pain in the head
C4-7 = neck -back-shoulder pain, no head pain
Nerve Roots
“Radiculopathy,” scapular, neck, thoracic & shoulder-arm pain (C6-8 only), dermatomes
IVDs
Risk Factors: sustained awkward neck postures, low-level trauma, wry neck
Agg→ looking-reaching behind shoulder, neck flexion, sleeping on unaffected side
Easing → sleeping of affected side, holding arm overhead
Tx as the Source of Pain
Somatic Thoracic Pain
localized to trunk 1-2 levels, disc=central/bilatera/vague, facet= unilateral/local
refer into post shoulder, anterolateral chest wall and iliac crest
C7-T3: pos shoulder > suprascap > medial scapular
Radicular/neurogenic thoracic pain
Tx radiculopathies rare
T4 syndrome can present with bilateral UL paranesthesia, common in ulnar distribution, upper traps/UL pain, P&N
Risk Factors: history of sustained Tx flexion, posture related disc pain, sudden trunk rotation/extension
Agg → deep breathing, looking reaching behind
Easing → lying prone
Shoulder as the Source of Pain
Clinical Presentation: dull aching ± IT aching pain with movement, lateral deltoid pain, upper anterior arm (LHBB tendinopathy), headaches, light-headedness, peripheral nerve entrapments around shoulder
Sternoclavicular joint
Subacromial space
Acromioclavicular joint
Joint sounds:
Glenoid labral tears – ‘deep painful clunk’
Instability – ‘click/clunk’ often not-painful
ACJ degeneration – ‘crunching/grinding’
Impingement/LHBB tendinopathy – ‘click’ +/- pain
Risk Factors: repeated overhead activity, slowly progressing pain and loss of ROM, lifting pain, FOOSH
Agg → overhead activities, reaching behind head/back
Easing → sleeping on unaffected side with affected arm supported
Osteochondritis Dissecans
Clinical Manifestations: insidious onset, acute injury, pain, swelling, poorly localized, catching/clicking/locking, decreased elbow ROM
Diagnosis: crepitus, grip&grind test, valgus stress test, imaging
Differential: Panners Disease
Treatment: rest, NSAIDs, surgery, activity modification, rehab
Risk Factors: children, adolescents, overhead athletes, weight-bearing athletes
“Lesion of the bone and overlying cartilage”
Elbow Fractures (S.L.M.R.O.C)
Clinical Manifestations: acute trauma MOI, pain and swelling, deformity, inability to move elbow
Supracondylar fracture: distal humerus, 60% prevalence, ext/flx type fractures, neurovascular compromise
Lateral condyle Fracture: capitellum fracture, 15-20% prevalence, Milch 1&2
Medial epicondyle fracture: extra-articular fracture, 10% prevalence, repetitive sports, avulsion
Radial head fracture: FOOSH, athletes common, Salter-Harris type 2
Olecranon Fracture: FOOSH or direct contact, limited ability to extend elbow
Coronoid Fracture: combination with radial head # and post dislocation (terrible triad), Regan&Morrey classification
Treatment: immobilization, splint/sling, rehab (strength, ROM, functional) , screws/wires, pinning
Risk Factors:
Elbow Dislocation
Clinical Manifestations: acute trauma, pain, swelling, deformity, inability to move elbow, Two Types (Simple & Complex)
3 Types:
Subluxation of elbow in posterolateral direction (clicking/snapping)
Incomplete dislocation with coronoid perched on trochlea
Complete posterolateral dislocation
Diagnosis: ligamentous stability, vascular supply, palpation, imaging
Treatment: relocation MUA, surgery, bracing/stabilization, rehab (strength, ROM, functional)
Risk Factors: FOOSA injuries, males, young children
Elbow Tendinopathy
“Overuse tendon injury”
Reactive tendinopathy → non-inflammatory (acute overload)
Tendon disrepair → greater matrix breakdown (Chronic overload)
Degenerative → matrix and cell breakdown (ageing, chronic overload, cell death)
Lateral Elbow Tendinopathy (Tennis Elbow)
Factor workers, repetitive gripping sports, Extensor-carpi-radialis-brevis tendon
Resisted wrist extension, resisted finger extension, pain-free grip strength, TOP lateral epicondyle, test ROM
Managed by therapeutic exercise, manual therapy, soft tissue mobilizations, taping/orthosis, cryotherapy, electrotherapy, ergonomics
Medial Elbow Tendinopathy (Golfers Elbow)
Pain over medial epicondyle, adduction movements, pronator teres primarily involved
Pain on palpation, epicondylitis medialis test, Polks test, resisted pronation
Managed by exercises, soft tissue therapy, manual therapy, bracing/taping, stretching
Biceps and triceps Tendinopathy
Clinical Manifestations:
Biceps: pain with resisted elbow flexion or forearm supination, proximal radio-ulnar joint, pain in cubital fossa
Triceps: posterior elbow pain, pain with resisted elbow extension, olecranon tender
Factors: weight lifting, javelin
Bi/Tri Muscle/tendon Rupture
Clinical Manifestations: weakness, altered appearance, bruising, swelling, Limited ROM
Biceps rupture: Hook test, biceps squeeze test, sup-pro test, passive forearm pronation test
triceps rupture: triceps squeeze test
Risk Factors: lifting with high loads, traumatic onset
Treatment: surgery usually
Medial Collateral Ligament Sprain
Diagnosis: Valgus stress test, moving valgus stress test, milking maneuver, POP, instability
Management: education, rest, technique correction, soft tissue therapy, strengthening exercises, strapping, surgery
Risk factors: acute trauma, FOOSH, overuse, throwers
metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joint injury
Little Leaguers Elbow (Apophysitis)
“Affects growth of medial epicondyle”
Clinical Manifestations: POP, deformity, valgus stress test, contraction or forearm muscle that inserts into CFO
Management: education, rest, technique correction, strengthening, strapping, surgery
Risk Factors: overuse, throwing, young children
Olecranon Bursitis (students’ elbow)
Clinical Manifestations: trauma/falling onto elbow, insidious onset (leaning on elbow for too long)
Management: POLICE, aspiration, injection
Posterior Impingement
3 Main Hypotheses:
Younger person – ‘hyperextension valgus overload syndrome’
Valgus instability – olecranon no longer fits in olecranon fossa
Older person – early OA – osteophyte formation
Diagnosis: osteophyte formation, AROM/PROM, valgus instability tests
Management: minimize hyperextension, strengthening, flexibility, surgery
“Impingement of the posterior capsule/bone deformation”
Peripheral Neuropathies and Nerve Entrapments (UMR)
“Pathology/compression to the peripheral nerves”
Clinical Manifestations: ulnar, median, radial nerves & Stingers and Burners
Ulnar Nerve Entrapment (C8-T1)
Cubital tunnel location, pain at elbow, weakness with gripping and wrist flexion, paranesthesia in little and ring finger
Median Nerve Entrapment (C6-T1)
Pain at elbow, paresthesia in digits 1-3 palmer aspect and tips of digits 2-3 (carpal tunnel syndrome), weakness with finger flexion, pronation and wrist flexion
Radial Nerve Entrapment (C5-T1)
pain/altered sensation over dorsal aspect of wrist and digits, common in repetitive pro/sup, TOP of supinator muscle, pain on restricted 90deg flexion, no sensory loss
Diagnosis: neuro assessment, Tinel’s sign, Phalen’s sign, palpation, location of symptoms
Treatment: advice/education, address cause, stretch, neural mobilisation, NSAIDS, surgery, ice, foam pads
Wrist Tenosynovitis (Soft Tissue Classification)
Clinical Presentation: ECU, FCU, FCR, ECR inflammation and swelling
Diagnosis: POP, pain with AROM + resistance, PROM pain
Risk factors: repetitive tasks, Raquet sports, rowers, golfers
De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis (Soft Tissue Classification)
Clinical Presentation: APL and EPB (thumb) inflammation and swelling, pain and tenderness, crepitus
Diagnosis: Patient history, palpation, Finkelstein’s test, AROM/PROM painful
Treatment: Progressive stretching, bracing, corticosteroids, ergonomic adaptations
Risk factors: Raquet sports, rowers, golfers, repetitive tasks
Intersection Syndrome (Soft Tissue Classification)
APL, EPB, ECR
Clinical Presentation: Abductor pollucis longs/Extensor pollucis brevis & Extensor carpi radialis tendinitis/inflammation/swelling
Objective Assessment: pain and tenderness, swelling, crepitus, repetitive movements
Diagnosis: Patient history, palpation, AROM/PROM painful, Finkelstein’s test
Management: Braces, NSAIDs, strengthening, decompression surgery
Risk factors: friction and overuse, rowers, canoeing, weight training, Raquet sports
Wrist Ganglions Cysts (Soft Tissue Classification)
Clinical Presentation: Fluid filled sack arising from joint space, fluid (mucin) creating a soft rubbery ball
Diagnosis: Visible lump, muscle wasting, pain, neurosensory loss
Management: splinting, ice massage, aspiration injection, surgery
Risk factors: repetitive use? ligamentous damage? Females
TFCC Injuries
Clinical Presentation: Ulnar side wrist pain, forced pronation pain, weak wrist rotation, swelling, loss of grip strength, crepitus
Diagnosis: Ulnar foveal sign (point tenderness distal to ulnar styloid), pain with pro/sup/ulnar deviation, +ve TFCC load test, compression test, press test, piano key test, X-ray/MRI/arthroscopy
Management: Splint, dynamic stabilization, progressive WB rehab, early surgical intervention
Risk factors: FOOSH, gymnastics, weightlifting, surfing, increases with age, increased load bearing ulnar side
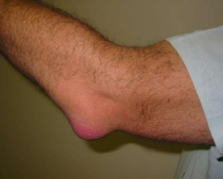
Distal Radius Fracture #
2 Types: Dorsal angulation of distal radius (Colle’s) and Volar angulation of distal radius (Smith’s)
Clinical Presentation: Pain, swelling, visible deformity
Diagnosis: Traumatic MOI, limited ROM, X-ray
Risk factors: low level trauma, ~61 years, FOOSH
Management: casting, conservative (depending on degree of displacement), surgical stabilization, Physio → ROM, strength, control
Scaphoid Fracture #
Diagnosis: Traumatic MOI, pain, swelling, TOP over snuff box, compression test, squeeze test, X-ray
Risk factors: FOOSH, Males
Management: casting, conservative (depending on degree of displacement), surgical stabilization, Physio → ROM, strength, control
Hook of Hamate Fracture #
Diagnosis: MOI, POP, swelling, concomitant ulnar nerve injury, reduced grip and volar/palmar wrist pain
Risk factors: MOI forceful swing when Raquet hits ground
Management: casting, conservative (depending on degree of displacement), surgical stabilization, Physio → ROM, strength, control
Ulnar Styloid Fracture #
Diagnosis: POP ulnar styloid process, DRUJ instability
Management: casting, conservative (depending on degree of displacement), surgical stabilization, Physio → ROM, strength, control
Risk factors: FOOSH, MIO
Keinbock’s Disease
Clinical Presentation: Pain over dorsal wrist, POP of lunate, limited ROM, weakness, wrist swelling
Diagnosis: POP, limited ROM, weakness, confirmed with radiography/CT and/or MRI
Management: Prioritize pain relief, ROM, strength/grip
Stage 1: Immobilization to allow time to heal
Stage 2: Immobilization if necrosis is incomplete
Stage 3-4: surgical intervention
Risk factors: repetitive trauma, increase load on lunate, radial inclination angle, smaller lunate bone, poor vascular supply, males, 20-40 years
“Avascular necrosis of lunate”
Scapulolunate Dissociation
Injury/rupture of scapulolunate ligament complex
Clinical Presentation: MOI/FOOSH, carpal instability, posterior pain, popping, clicking, pain increased with wrist ext/radial dev, swelling, decreased grip strength
Diagnosis: TOP dorsally, consider past trauma, Watsons test, X-ray, MRI
Management: Immobilization with physio, ROM, strengthening, surgical repair, early referral for orthopedic review
Risk factors: In conjunction with a distal radius #,
Lunotriquetral Dissociation
Rupture of lunotriquetral ligament
Clinical Presentation: second common carpal instability, MOI/FOOSH, Ulnar sided wrist pain, pain with pro/ulnar dev, decreased grip strength, clicking w/ movement
Diagnosis: consider fractures, lunate tenderness, pain on pro/ulnar dev, Shuck test, Kelinman’s Shear test, LT compression test, Click Provocation test
Management: Immobilization, injections, bracing, ROM, strengthening, arthroscopy, early referral for orthopedic review
Risk factors: young athletes, high impact sports
Nerve - Neuropathic wrist pain (CUW)
Criterion 1 & 2: subjective examination
Criterion 3: physical tests (sensation, motor as required)
Criterion 4: Objective tests (nerve conduction)
Common Clinical Pathologies
Carpal tunnel syndrome (median nerve)
Ulnar nerve entrapment
Wartenberg’s syndrome Radiculopathy C6-8
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Clinical Presentation: Central volar wrist pain, paranesthesia, weakness and atrophy of thenar eminence muscles
Diagnosis: Neuropathic pain criterion, neuro testing, +ve Tinel’s test, +ve Phalen’s test, Nerve conduction tests
Management: Depends on severity - splinting, corticosteroids, medication, physio, surgery
Risk factors: mechanical trauma, increased pressure, ischemic damage to nerve, females 40-60, diabetes, use of flexor muscles, exposure to vibration
Compression of median nerve within carpal tunnel
Ulnar Nerve Entrapment
Clinical Presentation: Medial volar wrist pain, paresthesia, weakness and atrophy of hypothenar muscles
Diagnosis: Neuropathic pain criterion, Neurological testing, +ve Tinel’s test, Wartenberg sign, X-ray, Nerve conduction
Management: Depends on severity - conservative treatment best, external padding, night splinting, hand therapy, corticosteroids, hand therapy, surgery
Risk factors: mechanical trauma, males, gymnastics
Compression of the ulnar nerve within Guyons canal (pisiform & hook of hammate)
Wartenburgs Syndrome
“Cherialgia paresthetica” - superficial radial nerve compression
Clinical Presentation: Vague lateral wrist pain, paresthesia, night pain, no motor weakness signs
Diagnosis: neuropathic pain criterion, neuro testing, +ve Tinel’s sign, Finkelstein’s test +ve, Nerve conduction tests, imaging
Management: depends on severity - conservative treatment best, removal of compression factors, splinting, corticosteroids, hand therapy
Risk factors: males, 40-70 years, wearing watches/wrist bands or injury to radial forearm
Dupuytren’s Contracture
Progressive contracture of flexor tendons → flx deformity
Clinical Presentation: 4th digit + isolated muscles, painful nodules/cords, limited extension ROM, blanching of the palm
Diagnosis: POP flexor tendons, AROM/PROM, Heuston’s tabletop test, imaging, radiograph
Management: Conservative, splint, injection, surgery, ROM, strength/control
Risk factors: genetic disorders (diabetes, seizures, smoking, alcoholism, HIV, vascular disease), males
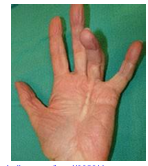
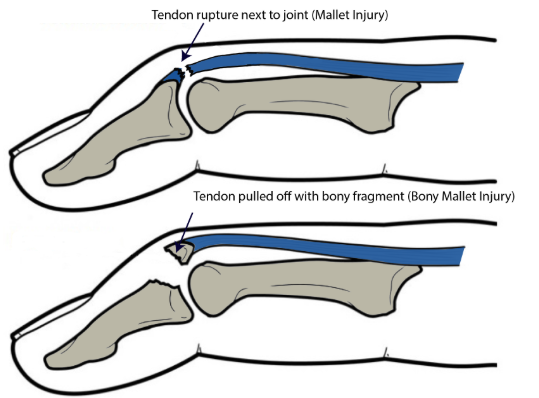
Mallet Finger
Traumatic terminal extensor tendon injury (EDC) Rupture or Avulsion, forced DIPJ flexion
Clinical Presentation: Pain, swelling, fixed flexion deformity, lump, inability to extend, subungual hematoma?
Diagnosis: MOI, observation, TOP to DIPJ, inability to extend DIP, radiograph, palpation of nail bed
Management: Conservative, full time splint, strength & control, surgery, tendon reconstruction, bracing following surgery
Risk factors: cricket, basketball, volleyball, slammed in door, males, dominant side, Swan-neck deformity
Jersey Finger
Traumatic terminal flexor tendon injury (FDP) Rupture/Avulsion
Clinical Presentation: Pain, swelling at DIPJ, inability to flex DIPJ, palpation deformity, pain during gripping
Diagnosis: Acute MOI, inability to actively flex DIPJ, POP, passive finger flexion okay, radiograph
Management: Early surgery, tendon re-insertion, K-wire, splinting post op, ROM, strength & control
Risk factors: trapped in a jersey/shorts/waist band during a tackle, MOI
Skiers Thumb
The thumb is forcefully hyper abducted away from the hand
Clinical Presentation: Localized pain to 1st MCPJ, swelling, weak grip, limited ROM
Diagnosis: MOI, TOP radial side, valgus stress test, weak pincer grip, radiograph
Management: Splinting, ROM, strengthening, surgery
Risk factors: skiing, baseball, javelin, males
Ulnar collateral ligament injury 1st MCPJ (thumb)
Phalangeal, Metacarpal, Boxers, Bennets and Hand Fractures
Phalangeal Fracture
Clinical Presentation: pain, swelling, deformity, unwillingness to move, instability, can occur on any digit
Risk factors: Contact injury, ball sports, crush injury
Metacarpal Fracture
Risk Factors: contact injury, high impact, punch, crushed
Boxers Fracture
Clinical Presentation: Localized pain, swelling, physical deformity, reluctance to move, instability
Risk Factors: Punch injury → axial load with flexion
Location: Fracture of neck of 5th MC
Bennett’s Fracture
Clinical Presentation: localized pain, swelling, physical deformity, reluctance to move, instability
Risk Factors: Punch Injury
Location: fracture of 1st CMC joint
Hand Fractures
Diagnosis: Consider MOI< deformity, POP, pain, imaging
Treatment: Orthopedic referral early, conservative, rehab, surgery
Finger Dislocation
Dislocation of DIP, PIP or NCP joints
Clinical Presentation: Deformity, pain, swelling, discoloration, altered sensation
Diagnosis: MOI, radiograph, imaging, neurovascular exam
Management: PIP focus → splinting, surgery? rehab, physios do NOt “put them back in”
Risk factors: ball or contact sports, MOI= hyperextension and/or axial loads, netball, basketball, consider “Ehlers-Danlos syndrome”
Hand Osteoarthritis
Clinical Presentation: Bouchard’s nodes, Herberden’s nodes, Squaring of 1st CMC, pain, swelling, weakness during grip
Diagnosis: Pt history, deformity, AROM/PROM affected, weakness, radiograph
Management: Strengthening, pharmacological, improve function, surgery
Risk factors: chondral pathology, osteophyte formation, joint space narrowing, older age, female, obesity, weakness
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Clinical Presentation: Joint pain, swelling, AM stiffness, Swan-neck deformity, ulnar deviation/drift, Boutonniere deformity
Diagnosis: Pt history, pain on movement and POP, boggy feeling on palpation, weak grip, deformity, lab testing
Management: Early intervention, lifestyle changes, NSAIDs, anti-inflammatories
Risk factors: HLA-DRB1 gene, female, <30 ears, higher level of autoantibodies