psychology final part 2 cumulative
1/89
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
introspection
Process to objectively examine own conscious activity
William Wundt: “father of pyschology”
structuralism
Conscious experience understood when broken into parts (underlying components)
Edward Titchener:
Used introspection to identify structure of the mind
functionalism
To understand purpose (function) of thoughts, feelings, etc
William James: Studied functionalism, Argued cognition is adaptive
psychoanalysis therapy
Talk therapy to access unconscious. personality develops from navigating unresolved unconscious conflicts.
Sigmund Freud: Believed Early life experience and influence from parents in sense of self
pyschodynamic therapy
therapy that focuses on relationship between conscious and unconscious motivation.
humanistic
self-actualization: humans inherently “good” drive for positive growth. Concept of humanistic psychology
Carl Rodgers and Abraham Maslow
behaviorism
Environment produces behavior, objective observations are ONLY suitable topics for study
B.F. Skinner:
Believed Behavior is determined from consequences. Developed operant conditioning
cognitive perspective
Renewed focus on mental processes in the 1950s
EEG: shows activity via electrical signals
fMRI: shows activity via blood flow
independent variable
Manipulated and changed by researcher
dependent variable
variable that is Measured on how it changes
extranous variable
any factor that is not the independent variable that can affect an experiment's dependent variables
ex: can be natural characteristics of the participant, such as age or gender, or they could be features of the environment such as noise or lighting
confounding variable
variable that influences independent and dependent variable
ex: weight loss study and we didn’t account for the diet habits. the diet habits would be this variable
structure of a neuron
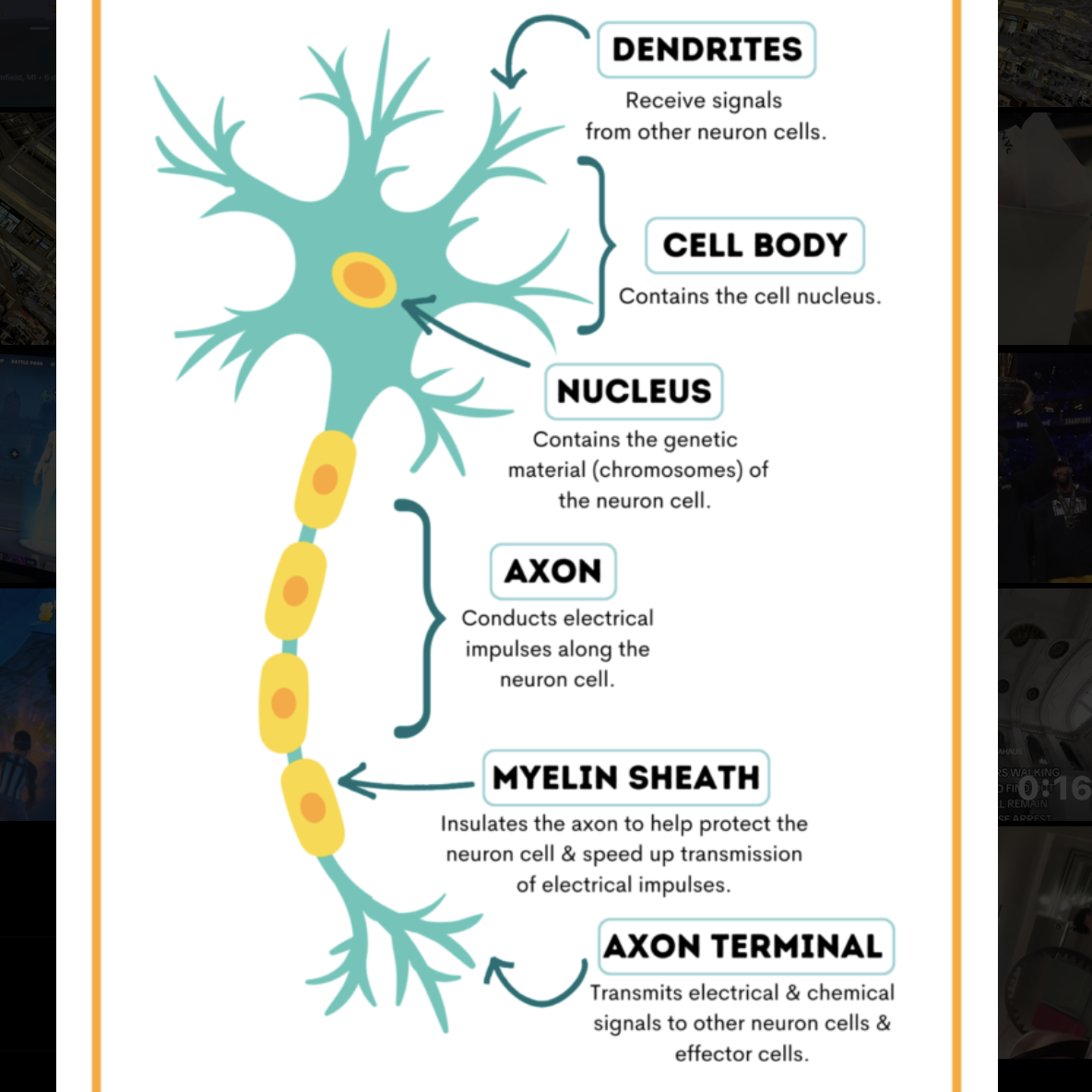
Acetylcholine (neurotransmitter)
Most abundant neurotransmitter in brain. movement, memory, arousal, attention. Too much = muscle spasms, too little = paralysis
Glutamate (neurotransmitter)
Excitatory neurotransmitter, increases action potentials. Wanting to learn. Most abundant neurotransmitter in brain. (elf)
GABA (Neurotransmitter)
neurotransmitter that regulates sleep and wakefulness (elf dad)
dopamine (reward)
Neurotransmitter. “reward”.
Low = low motivation low mood, poor concentration.
High = euphoria, pleasure, tends to be addictive
serotonin
neurotransmitter “Regulator of brain”
Regulates emotion, Impulse control, dreaming, appetite, sleep, aggression, breathing.
SSRIs
Med that increases seratonin. Can treat depression and eating disorders
Central nervous system
made up of Brian and spinal cord
peripheral nervous system
Made of Autonomic Nervous System and Somatic Nervous System. Connects CNS to rest of body
autonomic nervous system
Involuntary (Ex: pumping blood, stomach). Made up of sympathetic nervous system and parasympathetic nervous system
Somatic Nervous System
collects sensory info and controls voluntary muscle movement
sympathetic nervous system
fight or flight response
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Rest and digest; returns body to resting state
hypothalamus
subcortical structure, REGULATOR of organ and body functions
hippocampus
subcortical structure, processes MEMORY
amygdala
negative EMOTION; involved in fear, motivates defensive behavior
left hemisphere of brain
specializes in language
right hemisphere of brain
specializes in visual-spatial tasks
temporal lobe
hearing
Occipital lobe
vision
parietal lobe
Sensory perception (senses) and language
frontal lobe
thinking, memory, behavior
classical conditioning
a type of learning in which one learns to link two or more stimuli to find what stimuli causes involuntary response and modify emotional and voluntary response
unconditioned stimulus (US)
stimulus naturally causes response (Ex: taking dog on walk causes happiness)
unconditioned response
natural response to US (Ex: happiness dog receives from walk)
neutral stimulus (NS)
Stimulus doesn't do anything before learning.(Ex: "wanna go for a walk" does nothing for a new puppy)
conditioned stimulus (CS)
learned stimulus produces response after pairings
conditioned response (CR)
Learned response to CS after pairing.
Same response as UR, just now caused by CS
response acquisition
the moment when a response is established based on conditioning
extinction
occurs when the conditioned stimulus is applied repeatedly without being paired with the unconditioned stimulus
Ivan Pavlov
Russian physiologist who observed conditioned salivary responses in dogs (1849-1936). Dogs salivated when food was infront of them then over time starting salivating when they heard assistant walking down hall.
spontaneous recovery
is when a behavior that is believed to be extinct (the conditioned behavior has disappeared or stopped occurring when the stimulus is present) unexpectedly and quickly returns after a period of rest or lessened response.
stimulus generalization
A similar stimulus to CS elicits same response. Ex: Pavlov's dogs salivate when hearing any bell tone
stimulus discrimination
Learning to tell apart CS from similar non-CS. Ex: Pavlov's dogs can tell different tones apart when one is paired with food but the other isn't
operant conditioned
individuals associate behavior with specific consequences (positive or negative). Goal is creation or modification of behavior
reinforcement
An event following a response that increases the tendency to make that response.
positive reinforcement
addition of an outcome (consequence) following a behavior
punishment
an outcome (consequence) that decreases the likelihood of a behavior to be repeated in the future
positive punishment
adding an adverse outcome after an unwanted behavior to decrease the chance that a person engages in the behavior again
negative punishment
you remove a pleasant stimulus to decrease a behavior
shaping
you don't teach the final behavior but rather break it down into smaller steps that build toward it.
ex: So, if you want to teach your dog to roll over, you could lure them all the way over, or you could shape it by starting with them lying on the ground.
information process model
Progression of memory (sensory memory ➡ short term memory ➡ long term memory)
sensory memory
everything sensed at given time(taste, touch, smell); Enables accurate encoding. Info that captures attention is processed. Large capacity & short storage
short term memory
Information currently in use.
Small capacity = short time in storage (+ or - 7)
Duration = 20-30 seconds if not actively "worked on" or encoded
encoding
perception -> code. Code represents experience in a way that the brain can read. Code sent from sensory to Long-Term memory.
Type of information activates different brain areas.
storage
code "placed" in store. Placed in to long-term memory.
Type of information determines where it is stored
retrieval
stored info accessed, brought into short term memory, and remembered. Stored code might be inaccessible. (Ex: tip of the tongue phenomenon)
long-term memory
Permanent storage of memory. Unknown capacity; Long lasting indefinite storage of memory. stored as meaningful concepts, not timeline.
recognition
matching stimuli with stored info with retrieval cues
retrieval cues
help sort through our memory to find information. Thinking of things associated with info makes retrieval easier
elaborative rehearsal
Builds connections to already existing info. Incorporates meaning and improves retention and storage (ex: songs, rhythms)
chunking
Combining small pieces of information into larger clusters or chunks that are more easily held in short-term memory.
maintenance rehearsal
Repeating info to keep it in short memory
encoding failure
the inability to recall specific information because of insufficient encoding of the information for storage in long-term memory
retrieval failure
information not stored properly, OR information cannot be stored
proactive interference
old information disrupts recall of newer information. (pro = forward)
retroactive interference
new information disrupts recall of older memories (retro = backward)
misinformation effect
new or misleading information distorts memory
germinal stage
prenatal stage. (weeks 0-2) = fertilization to implantation
embryonic stage
prenatal stage. (weeks 3-8) = implantation to 8 weeks. early organs begin to form
Highly susceptible to damage (teratogens); most vulnerable period
fetal stage
prenatal stage. (9 weeks to birth-infancy)
sensorimotor stage
individuals develop by exploring environment through senses and motor activities. goal is to develop object permanence (0-2)
Preoperational stage
use of symbolic thinking. goal is to develop imagination and theory of mind (2-7)
concrete operational stage
logical thought, strict rules, objectivity. goal is to develop conservation of mass and volume (7-11)
formal operational stage
systematic, abstract and hypothetical thought criticisms.
Erik Eriksons stages
assumes that individuals go through specific psychosocial challenges at different stages of life. These challenges are necessary fir a healthy development and formation of strong identity, each challenge builds upon previous one.
(Trust vs mistrust, autonomy vs shame and doubt, initiative vs guilt, industry vs inferiority, identity vs confusion, intimacy vs isolation, generativity vs stagnation, integrity vs despair)
fundamental attribution error
More likely to make an internal (dispositional) attribution about others bad behavior, but an external (situational) attribution about your own bad behavior
self-serving bias
Attribute success to our dispositions, whereas our failures are due to the situation. (if we did good on test we are brilliant, if we did bad it was unfair)
just-world hypothesis
People get what they deserve - the world is fair
conformity
Tendency to modify behaviors, attitudes, and opinions to match others around us.
Follows social Norms - expected by social environment (workplace, culture, gender, etc.)
obedience
compliance with authority
compliance with a person with greater situational power
bystander effect
individuals are less likely to offer help to a victim or react to a situation when others are present
Ex: car accidents on highways. Do you stop? Do you keep going, assuming someone else will take action?
groupthink
tendency for group members to maintain cohesiveness and agreement in their viewpoints with a failure to consider alternative or contradicting view-points
stereotype
inferences we make about a person based on their perceived group membership
prejudice
hostile attitudes and judgements about a person based on their group membership “pre-judging”
discrimination
different TREATMENT that is motivated by prejudice towards individual or group
group polarization
group opinions and positions on issues tend to SHIFT to the extreme pole of the initial attitudes of members attitudes that already agree. Can lead to groupthink