Edexcel IGCSE Biology Paper 1
1/139
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
140 Terms
What are the characteristics of living things?
Move, respire, sensitivity, grow, respire, excrete, nutrition, control
Describe eukaryotic cells
Example
Complex large cell
Contain Nucleus
Any mammal/insect cell
Describe prokaryotic cells
Example
Small simple cell
No nucleus
Floating DNA
Amoeba/Chlorella
Animal cell:
Structure
Carbohydrate store
Example
Multicellular
Contain: No cell wall
Store carbs as Glycogen
Any mammal/insect
Plant cell:
Structure
Carbohydrate store
Example
Cell wall, vacuole, chloroplasts
Store carbs as starch or sucrose
Beans/maize
Fungi:
Structure
Feeding method
Store carbohydrates
Example
Body called mycelium made up of hyphae (thread like structures)
Cell walls made of chitin
Saprotrophic nutrition - release enzymes into surroundings to dissolve food
Store carbs as glycogen
Yeast
Describe the levels of organization
Organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system
What is the function of the mitochondria?
cellular respiration for energy
function of ribosomes
protein synthesis
function of chloroplast
Contains chlorophyll which absorbs light energy for photosynthesis
function of vacuole
Stores water, salts, proteins and carbs and provides structure
Define pathogen
disease causing organism
Describe viruses
Example
small cells, can only reproduce in living cells, no cellular structure, protein coat and contain DNA or RNA
HIV
Describe bacteria
single celled, no nucleus, contain circular chromosomes of DNA, contain plasmids (extra bits of DNA)
Lactobacillus
Define cell differentiation
the process by which cells become specialized in structure and function
Structure and elements in carbohydrates
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen
Starch/Glycogen
Structure and elements in lipids
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen
fatty acids and glycerol
Structure and elements in proteins
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen
Amino acids
How to test for starch
addition of Iodine (orange) reacts with starch to produce brown/blue color
How to test for lipids
Add drops of Sudan III
Shake
Red lipids settle on top
How to test for proteins
Biuret test
Add biuret solution and shake
blue -> pink if present
How to make a food sample
Break food in pestle and mortar
stir with distilled water
filter solution to remove solids
How to test for glucose
Benedict Solution in a hot water bath - blue -> turns green-yellow-brick red
Describe the process of photosynthesis
light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll in chloroplasts
used to convert carbon dioxide and water into
sugar (glucose) (oxygen is released)
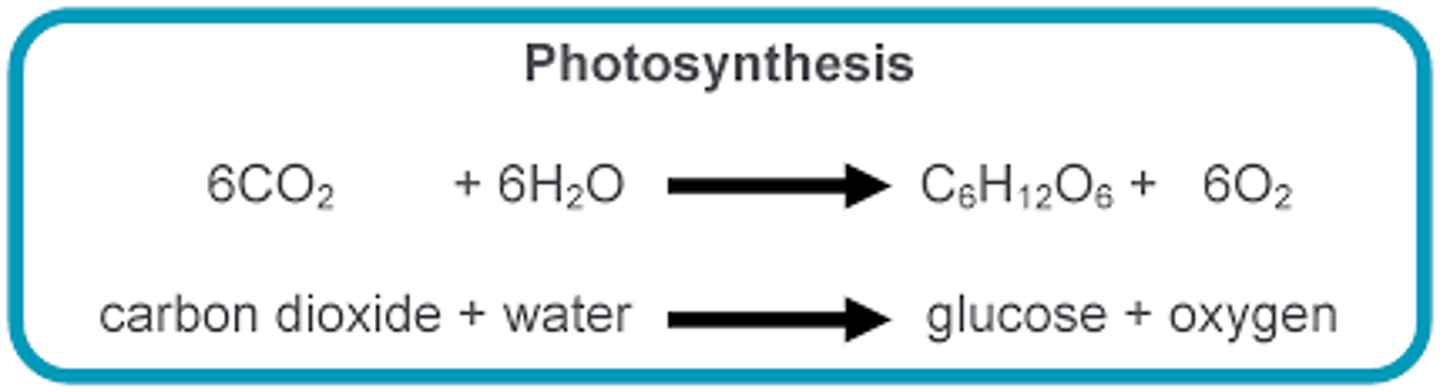
word and chemical equation for photosynthesis
Carbon dioxide + water > glucose + oxygen
6CO2 + 6H2O = C6H12O6 + 6O2
Adaptations of a leaf
Large surface area
Upper epidermis transparent allows light in
most chloroplasts found in palisade cells near top
waxy cuticle prevents water loss
What do plants need mineral ions for
Growth
What is a plants use for nitrates
Deficiency symptoms
Used for supply of nitrogen to make amino-acids and protein which is used for growth
Stunted growth
Leaves go yellow
What is a plants use for Phosphates
Deficiency symptoms
Used for making DNA and cell membranes as well as for respiration and growth
Poor root growth
Leaves turn purple
What is a plants use for Potassium
Deficiency symptoms
Help enzymes for photosynthesis and respiration
Poor flower/fruit growth
discoloured leaves
What is a plants use for magnesium
Deficiency symptoms
Used for making chlorophyll
Yellow leaves
Bodies use for Carbohydrates
Found in
Energy
Pasta, rice, sugar
Bodies use for Lipids
Found in
Energy, energy storage, insulation
Fish, butter
Bodies use for Protein
Found in
Growth and tissue repair
Meat, fish
Bodies use for Vitamin A
Found in
Improve vision - hair and skin
Liver
Bodies use for Vitamin C
Found in
Prevent scurvy
Citrus fruits - lemons, orange
Bodies use for Vitamin D
Found in
Increases calcium absorption
Eggs
Bodies use for Calcium
Found in
Strong bones and teeth
Dairy products
Bodies use for Iron
Found in
Make haemoglobin for blood
Red meat
Process of food digestion
Mouth
Oesophagus
Stomach
Duodenum
Ileum
Colon
Rectum
Anus
Digestion - what happens in the mouth
Mastication - more surface area for enzymes
Amylase in saliva breaks starch into maltose
Digestion - what happens in the oesophagus
Peristalsis - circular muscle contraction moves boluses of food down
Digestion - what happens in the Stomach
Mechanical digestion - churning food
Hydrochloric acid kills bacteria
Pepsin breaks protein down into amino-acids
Digestion - what happens in the Duodenum
Pancreatic juice added - protease/trypsin - protein
- amylase - starch
- lipase - lipids
Bile added - neutralises acid
- emulsifies lipids
Digestion - what happens in the Ileum
Food absorption
Villi (covered in microvilli) Very high surface area
Adaptations of Villi and the Ileum
Ileum is very long so time to absorb all nutrients
Villi and micro-villi create high surface area
Villi have a one layer thick surface - short diffusion pathway - increased rate
Lots of capillaries assists good absorption
Digestion - what happens in the Colon
Water absorbed
Digestion - what happens in the Rectum and Anus
Rectum - Faeces stored
Anus - Egestion - Faeces removed
Digestion - what happens in the Liver
Bile produced
Stored in Gall bladder
Digestion - what happens in the Pancreas
Protease, amylase and lipase produced
Released into Duodenum
Describe aerobic respiration
Word and chemical equation
Lots of oxygen available
Lots of ATP produced
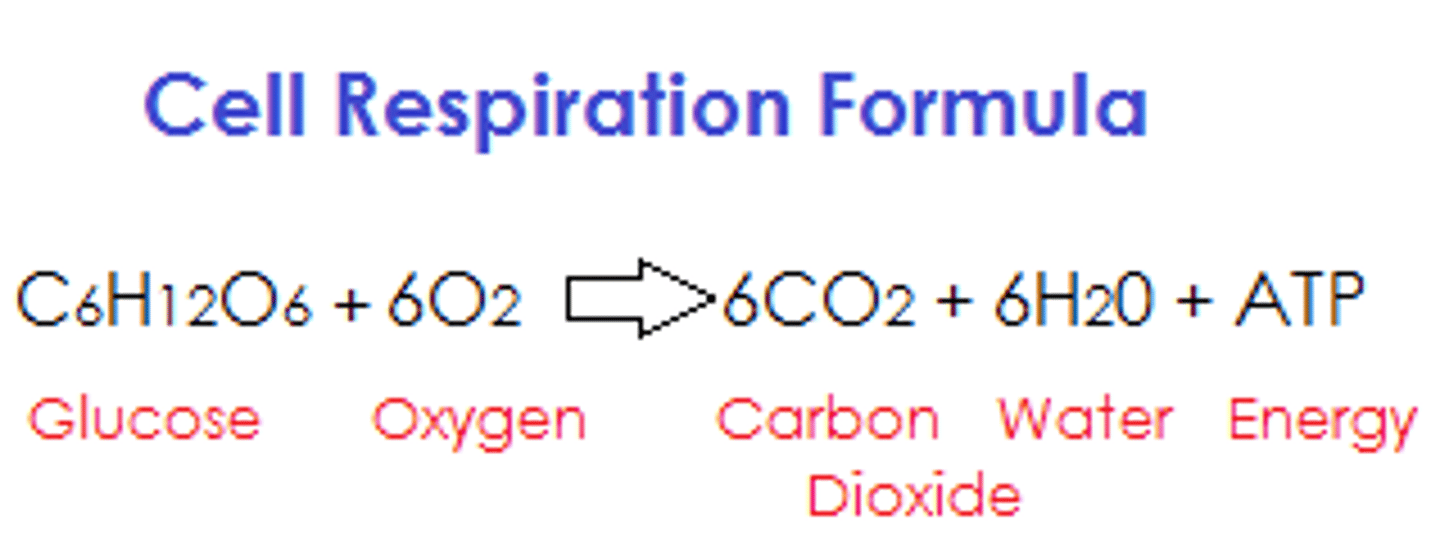
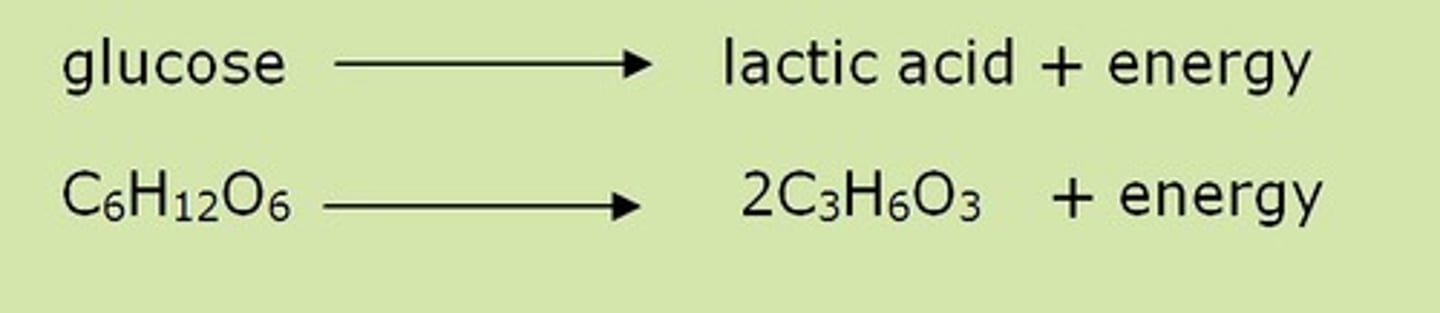
Describe anaerobic respiration
Word equation
Insufficient oxygen available
Produces much less ATP
Lactic acid produced in Humans
Ethanol and C02 produced in plants
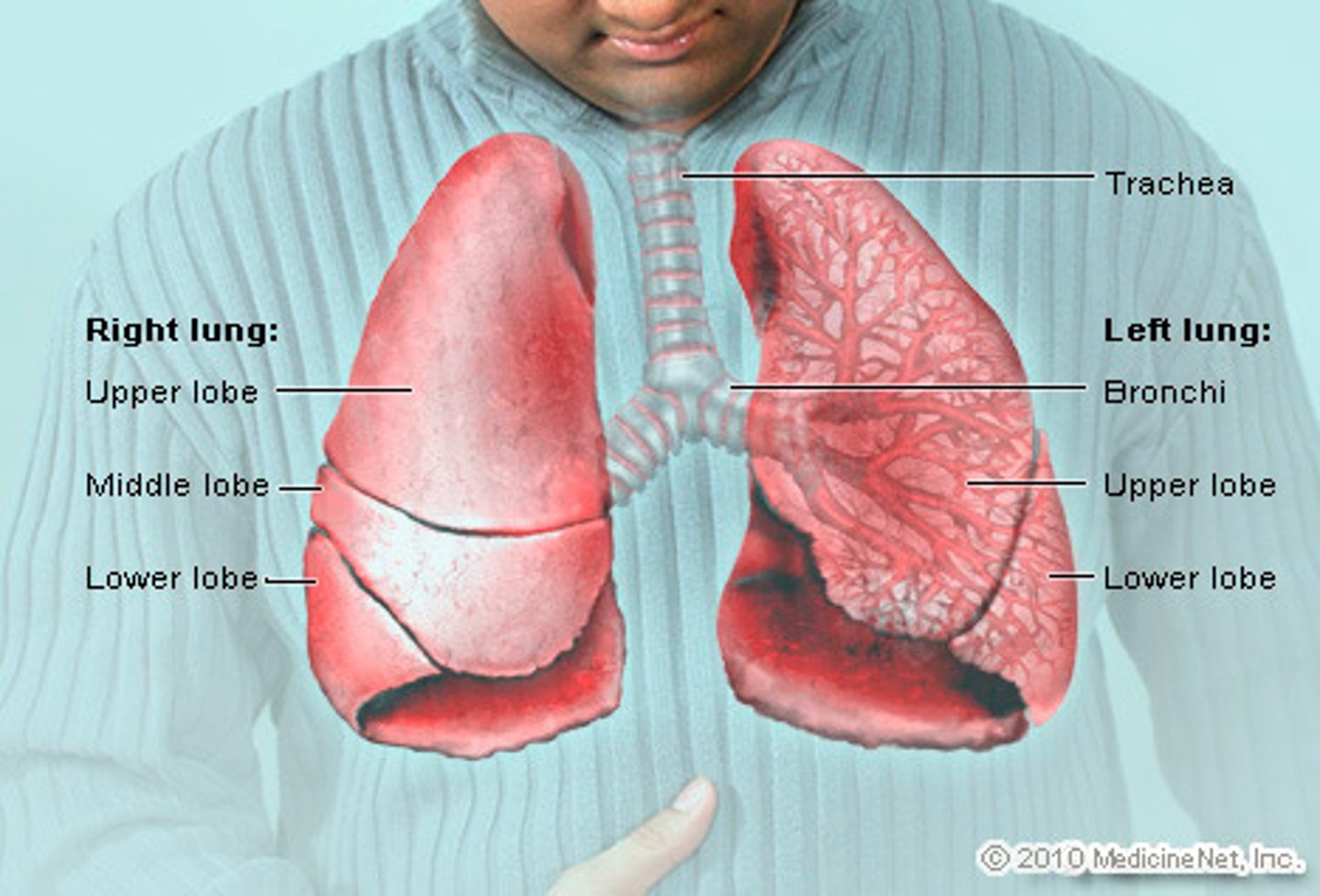
Gas Exchange:
Describe the Thorax
Trachea (surrounded by cartilage prevents collapse)
Bronchi
Bronchioles
Alveoli
Surrounded by ribs with intercostal muscles
Diaphragm at bottom
Thoracic cavity surrounded by airtight pleural membranes
Describe breathing in
Intercostal muscles and diaphragm contract
Thorax volume increases
Decrease in pressure drawing air in
Describe breathing out
Intercostal muscles and diaphragm relax
Thorax volume decreases
Pressure increase forcing air out
What are the adaptations of alveoli for gas exchange?
Huge number in lungs
Very small means increased surface area
One cell thick walls - short diffusion pathway
many capillaries to maintain a high concentration gradient
Effects of smoking on the lungs
List 5 in detail
Damages the alveoli reducing their surface area
leading to diseases like emphysema
Tar in cigarettes damages the cilia in the trachea and lungs
These stop dust and bacteria entering the lungs
Increases risk of chest infections
Tar irritates bronchi and bronchioles causing excess mucus production - smokers cough
Carbon monoxide in the smoke reduces the oxygen in blood
The body counters by increasing heart rate and blood pressure, which damages artery walls.
Increases chance of blood clots
Increases risk of coronary heart disease
Smoke contains carcinogens that cause cancer
(Nicotine also increases heart rate)
Why can unicellular organisms rely on diffusion for movement of substances
They are very small so have a large SA:Volume ratio
Why do multicellular organisms need a circulatory system for movement of substances
They are large so have a low SA:Volume ratio meaning substances cannot diffuse through them and so they need a system
Name the main components of blood
Red blood cells
White blood cells
platelets
plasma
Blood:
What is plasma?
Pale yellow liquid that carries everything in blood
including:
Digested food products
CO2
Urea
Hormones
List 3 adaptations of red blood cells
Biconcave shape - high surface area for absorbing oxygen
Contains haemoglobin which contains Iron
allows blood to carry oxygen
No nucleus creates space for more haemoglobin
Describe how the immune system works including descriptions of the two types of white blood cell.
Phagocytes - detect foreign things
Digest the object using enzymes
Non-specific - destroy everything foreign
Lymphocytes - Find foreign antigens (attached to pathogens)
Produce antibodies that are specific to the antigen
antibodies attach to the pathogen and mark them to be destroyed
Memory cells remember a specific antigen and can produce antibodies very quickly if the pathogen enters the body ever again.
How does exercise affect heart rate?
During exercise muscles contract more
So need more energy
So the body respires more
More CO2 produced
Receptors in aorta detect increased CO2 - signal brain
so heart pumps faster to increase blood flow to remove it
How does adrenaline affect heart rate?
Adrenaline binds to heart receptors
Heart pumps faster and harder
more oxygen gets to muscles
ready to escape/for action
List 3 factors that can lead to coronary heart disease
High saturated fat in diet
Causes fatty deposits in arteries.
Smoking causes arterial damage
Fatty deposits more likely to form.
Low exercise leads to high blood pressure which damages the arteries.
Fatty deposits more likely to form.
What causes a heart attack? (Coronary heart disease)
Coronary arteries to the heart get blocked by fatty material.
Blood flow is restricted causing lack of oxygen to the heart.
Can cause a heart attack.
Describe an artery
Carry blood away from the heart
High pressure
Strong elastic sides
Thick layer of muscle
Medium Lumen
Describe a capillary
Very tiny
Permeable walls
One cell thick walls - increase rate of diffusion
Very small lumen
Describe a vein
Culmination of capillaries
carry blood to the heart
Low pressure - valves prevent blood changing direction
Large lumen
What does Pulmonary mean?
To do with the lungs
What does Hepatic mean?
To do with the liver
What does Renal mean?
To do with the kidneys
How does the body respond to the environment?
Receptors in sense organs (eyes, ears etc) detect stimuli
Effectors (muscle, glands etc) communicate with the receptors by the nervous system or hormonal system
Define homeostasis
Maintaining a stable internal environment (including water content and body temperature)
What is geotropism?
a plant's response to gravity
What is phototropism?
A plant's response to light
When a shoot is exposed to light, where does the auxin go?
To the shade which increases growth on that side bending the shoot towards the light.
How does the sensory nervous system work?
Consists of brain and spinal cord only
•Receptors detect stimuli
•Send electrical impulses along sensory neurones to the CNS
•CNS sends impulses to an effector using motor neurones
•Effector responds
How are neurones connected?
•Synapses are connections between two neurones
•Signal is transferred by chemicals called neurotransmitters which cross the gap
•causing a new signal on the other side
Describe the reflex arc
stimulus → receptor → sensory neurone → central nervous system → motor neurone → effector → response
Label the structure of an eye
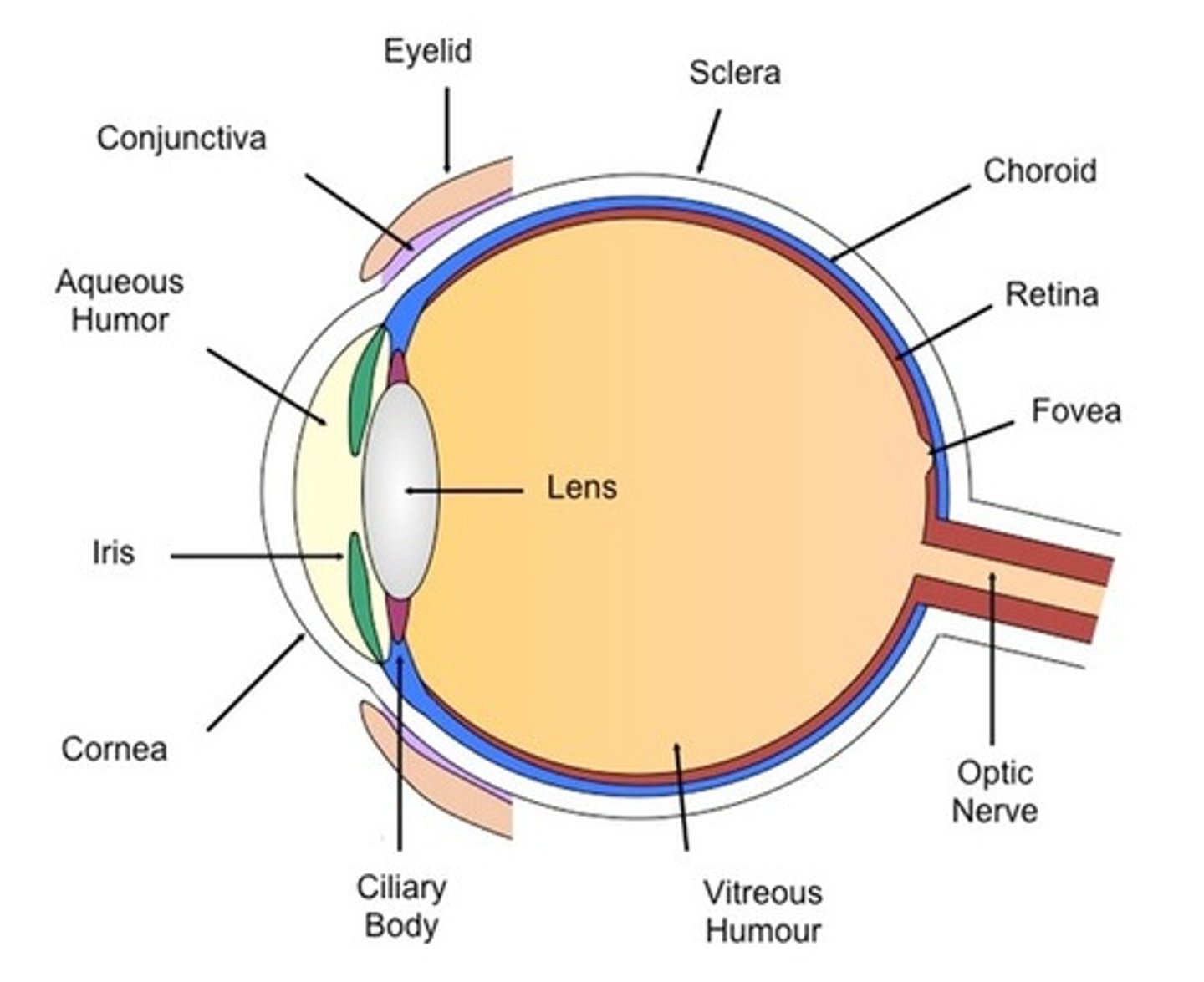
Eye: What does the conjunctiva do?
Lubricates and protects the eye surface
Eye: What does the Sclera do?
tough outer layer - protects the eye
Eye: What does the cornea do?
Refracts light into the eye
Eye: What does the iris do?
it contracts and expands to let enough light into the eye so it can focus on the retina
Eye: What does the optic nerve do?
Carries impulses from the eye to the brain
How does the eye respond to dim light?
Radial muscles contract making the pupil larger
Circular muscles relax
How does the eye respond to bright light?
Circular muscles contract making pupil smaller
Radial muscles relax
What is the optimum temperature for the body?
37 degrees celsius
How does skin react when you are too hot?
Lots of sweat produced - evaporates taking heat away
Blood vessels near skin widen - vasodilation - more blood near skin so more heat lost
Hair lies flat
How does skin react when you are too cold?
Blood vessels near surface constrict - less blood to lose energy - vasoconstriction
Shivering increases respiration so more heat created
Hairs stand up to insulate the body with air
Adrenaline source/role/effect
Adrenal Gland/Fight or flight/Increases heart rate, blood flow to muscles and blood sugar levels
Insulin source/role/effect
Pancreas/Control blood sugar level/stimulates the liver to convert glucose into glycogen
Testosterone source/role/effect
Testes/male sex hormone/(see puberty)
Progesterone source/role/effect
Ovaries/Supports pregnancy/Maintains the lining of the uterus
Oestrogen source/role/effect
Ovaries/female sex hormone/controls menstrual cycle and (see puberty)
What is asexual reproduction?
The production of genetically identical offspring from a single parent
What is sexual reproduction?
Reproduction involving fusion of a male and a female gamete to create diverse offspring.
Define mitosis
cell splits to form two cells with identical sets of chromosomes