Money & Banking Ch. 22 Flashcards
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
7 Factors that affect the Aggregate Demand Curve (all autonomous)
C (consumption)
I (planned investment)
G (government purchases)
T (taxes)
NX (net exports)
f (financial frictions)
r (real interest rate)
Shows the relationship between inflation and Real GDP
Aggregate Demand
Changing the real interest rate:
a. shifts the IS curve and shifts the AD curve
b. shifts the AD curve and moves along the IS curve
c. moves along the ad curve and shifts the IS curve
d. moves along the AD curve and moves along the IS curve
B; shifts AD, moves along IS
T/F A change in inflation shifts the AD curve
False; it moves along the AD curve
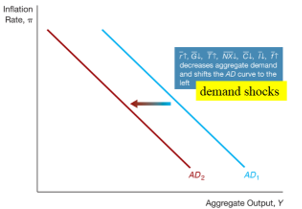
Using the attached image, draw a negative demand shock and show the effects
Demand curve shifts left, reducing aggregate output
AD curve
If autonomous real interest rate increases, aggregate output will
decrease
AD curve
If government purchases increases, aggregate output will
increase
AD curve
If Taxes increase, aggregate output will
decrease
AD curve
If autonomous net exports decreases, aggregate output will
decrease
AD curve
If autonomous consumption increases, aggregate output will
increase
AD curve
If autonomous investment decreases, aggregate output will
decrease
AD curve
If financial frictions decrease, aggregate output will
increase
This curve shows the relationship between the quantity of output supplied and the inflation rate
Aggregate supply curve
A vertical line that is determined by the amount of capital, labor, and available technology
Long Run Aggregate Supply (LRAS) curve
The LRAS curve is vertical at the _____ generated by the _____
The LRAS curve is vertical at the natural rate of output generated by the natural rate of unemployment
4 factors that shift the LRAS curve
Capital, Technology, Labor, Natural rate of unemployment
An increase in Capital would cause the LRAS to _____, which would effect aggregate output in what way?
shift right, increasing aggregate output
An increase in technology would cause the LRAS to ____, which would effect aggregate output in what way?
shift right, increasing aggregate output
A decrease in labor would cause the LRAS curve to ____, which would impact aggregate output in what way?
Shift left, decreasing aggregate output
An increase in the natural rate of unemployment would cause the LRAS to _____, which would impact output in what way?
shift left, decreasing output
An upward-sloping line based on 3 factors that drive inflation.
What are the three factors?
Aggregate Supply; Expected inflation, output gap, supply shocks
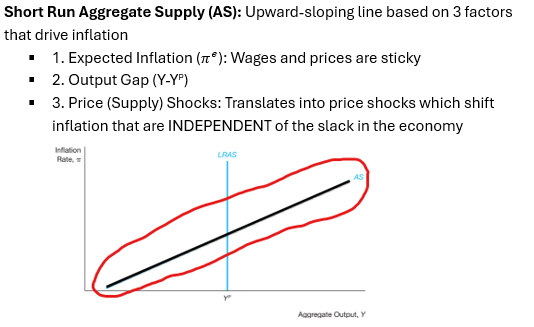
This kind of shock translates into price shocks which shift inflation that are INDEPENDENT of the slack in the economy
Price (supply) shocks)
3 factors that shift the Aggregate Supply curve
Expected inflation, supply shocks, a persistent output gap
AS curve
An increase in expected inflation would ____
shift the AS curve up
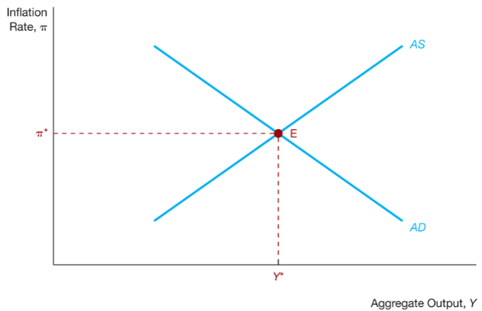
AS curve
A negative price shock would cause the AS curve to
shift up, increasing inflation and reducing output
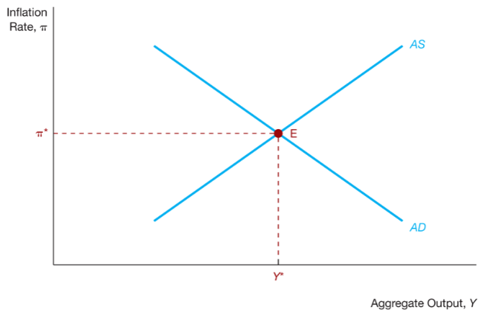
AS curve
A positive price shock would cause the AS curve to
shift down, reducing inflation and increasing output
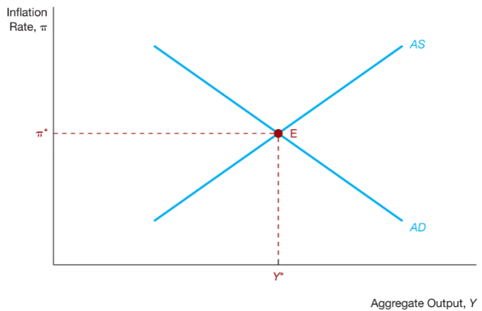
AS curve
An increase in a persistent output gap would cause the AS curve to
shift up, increasing inflation and reducing aggregate output
this mechanism claims that regardless of where output is initially, it’ll always return to the equilibrium natural rate of output.
Self-correction mechanism
When the self-correcting mechanism is slow,
Wages are _____ (flexible/inflexible)
Active government policy is _____ (needed/not needed)
Wages are inflexible
Active government policy is needed
When the self-correcting mechanism is rapid,
Wages and prices are _____ (flexible/inflexible)
Active government policy is _____ (needed/not needed)
Wages are flexible
Active government policy is not needed
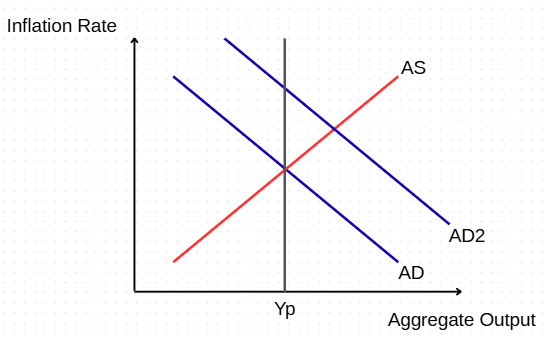
Assume an aggregate demand shock where AD shifts right. What happens to the LRAS and AD equilibrium?
AS curve shifts upward to equilibrium causing a higher inflation rate.
(notice how it initially caused higher output, but in the long run it only increased inflation and output remained unchanged)
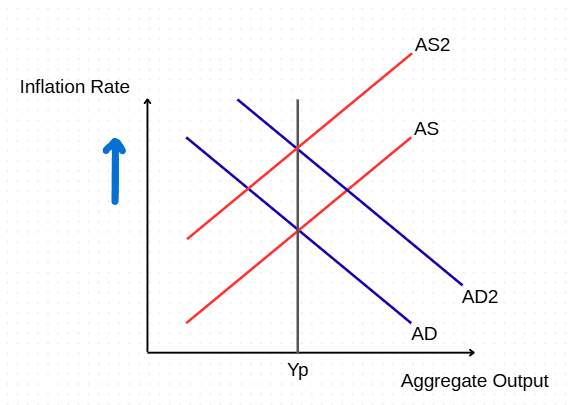
Aggregate Supply can shift from (2)
Define whether or not LRAS shifts from each
Temporary supply shocks (LRAS doesn’t shift)
Permanent supply shocks (LRAS does shift)
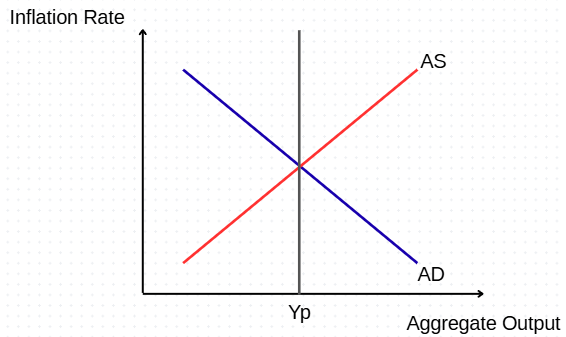
Assuming market equilibrium, draw a temporary negative supply shock. What would be the short term and long term impact?
Short term: Inflation increases, output decreases
Long term: No change in inflation or output

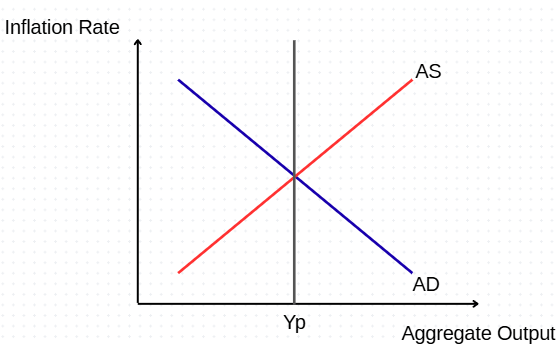
Assuming market equilibrium, what would happen in a temporary positive supply shock? What would be the short run and long run effect?
Short run: Fall in inflation, rise in output
Long run: No impact on inflation or output

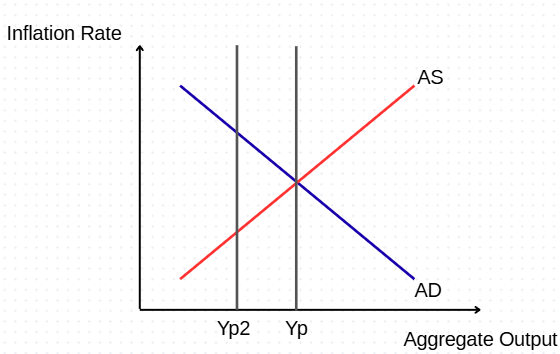
Assuming market equilibrium, what would happen in a permanent negative supply shock? Draw the impact on the graph.
AS shifts up along the AD curve until equilibrium, causing permanent higher inflation and lower output
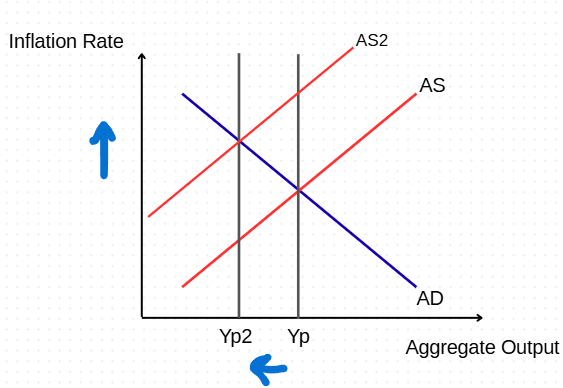
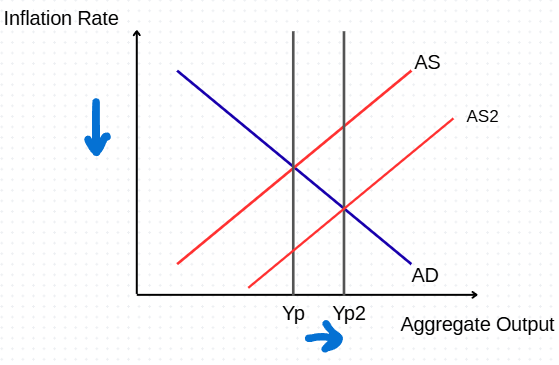
Assuming market equilibrium, what would happen in a permanent positive supply shock? draw the impact on the graph.
AS shifts down along the AD curve until equilibrium, causing permanent lower inflation and higher output
T/F a shift in aggregate demand curve affects output only in the short run, and has an effect in the long run
False; no effect on long run
T/F a temporary supply shock effects output and inflation only in the short run, and has no effect in the long run
True
T/F A permanent supply shock affects output and inflation both in short run and long run
True
T/F the economy has a self-correcting mechanism that returns it to natural output and potential rate of unemployment.
False; potential output and natural rate of unemployment