ROMANESQUE ARCHITECTURE
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
“Roman-like” or Roman Style
Romanesque
Architectural Character of Romanesque Architecture.
Sober and Dignified │ Picturesqueness
Structural System of Romanesque Architecture.
Romanesque Vaulting
Northern Extent
Republic of Florence
Northwestern Extent
Republic of Pisa
Southern Extent
Duchy of Naples
Capital of Kingdom of Lombardy. High degree of prosperity.
Milan
Trading links with the east.
Ravenna and Venice
Had influences with Greece and North Africa
Kingdom of Sicily
Is practically on the high road between south and north of Europe, and the relative position of each district influenced the various prevailing type of architecture.
France
On the banks of the Rhine, and in the south, cities had been established during the Roman occupation, and it was in these parts that Christianity took root, while in the north and east, paganism still existed.
Germany (Holy Roman Empire)
Isolated Island Kingdom
British Isles (Norman Conquest)
Ordinary building material of Rome.
Bricks (Central Italy)
Abundant, especially in Tuscany.
Stone (Central Italy)
Material obtained in Tivoli
Volcanic Stone, Travertine (Central Italy)
Material obtained in Carrara or Paros
Marble (Central Italy)
Primary building material in the plains of Lombardy.
Brick (North Italy)
Contributed to the wealth of the Island.
Sulphur (South Italy)
Primary influence of its architectural style.
Limestone (South Italy)
Building material that is rich in France.
Stone (France)
Quarried from the banks of the Rhine Valley.
Stone (Germany)
Due to the lack of stone in Northern Germany, this material was used as an alternative.
Bricks (Germany)
Transferred by sea to different isles.
Stone (British Isles)
Obtained in Cornwall and Devonshire.
Granite (British Isles)
Colder in the north and sub-tropical in the south.
France
Experiences extreme heat in summer and colder winters.
Germany
Cool, temperate, mild and moist climate.
British Isles
Chief source of education, civilization, and culture.
Christianity
Erection of a _______ is often the foundation of a city.
Church
The _______ had been rising to great power and influence.
Papacy
The separation of the _______ and _______ Christianity has grown wider.
Eastern and Western
Bishops conferred with authority over provincial and municipal governments.
Pragmatic Sanction (554 BCE)
Under religion, _________ ____________ were established.
Monastic Communities
Holding of land on the condition of military service. Constant warfare rendered the condition of the people unsettled.
Feudal System
Skill in __________ is at its lowest ebb.
Craftsmanship

Independent Peasants
They gave foods and crops to the knights in exhange of protection.
Freemen (The People)

Tenant Vassals (Kinghts and Abbots)
They gave protection to the freemen, and gave foods and protection to the Bishops in exchange of Land.
Lords (Knights)

Suzerain Vassals (Barons and Bishops)
They gave lands to the knights in exchange of protections, and gave lands and goods to the king in exchange of more lands.
Nobles (Bishops and Seigneurs)

They are in the same position as the Priest and the Church.
They gave lands to people in exchange of goods, protection, and lands.
The King/Duke
They are in the same position as the King/Duke.
They gave blessing to the King/Duke in exchange of lands, protections, and goods.
The Church
Highly religious people where the Pope and King reigns the land.
Holy Roman Empire
Germany was never Romanic, they were _________ ________.
Germanic People
The age were most of the people died in their 30’s because of war and plague.
Dark Ages (Medieval Period)
Election of the frankish King, Charlemagne; End of the Roman Empire; Formation of the Holy Roman Empire
799
Belief of the world’s end resulted to less construction projects; Most European nations had its time to come into full existence; France, Germany, and Spain becoming powerful; Foundation of Nordic Kingdoms; Norman Conquest of England
1000
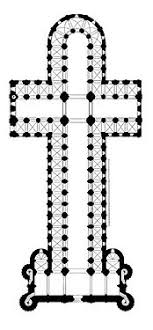
Common plan used in Romanesque Architecture.
Latin Cross Plan
_______ was usually employed at the side aisles to address _____-______.
Vaulting; Fire-Proofing
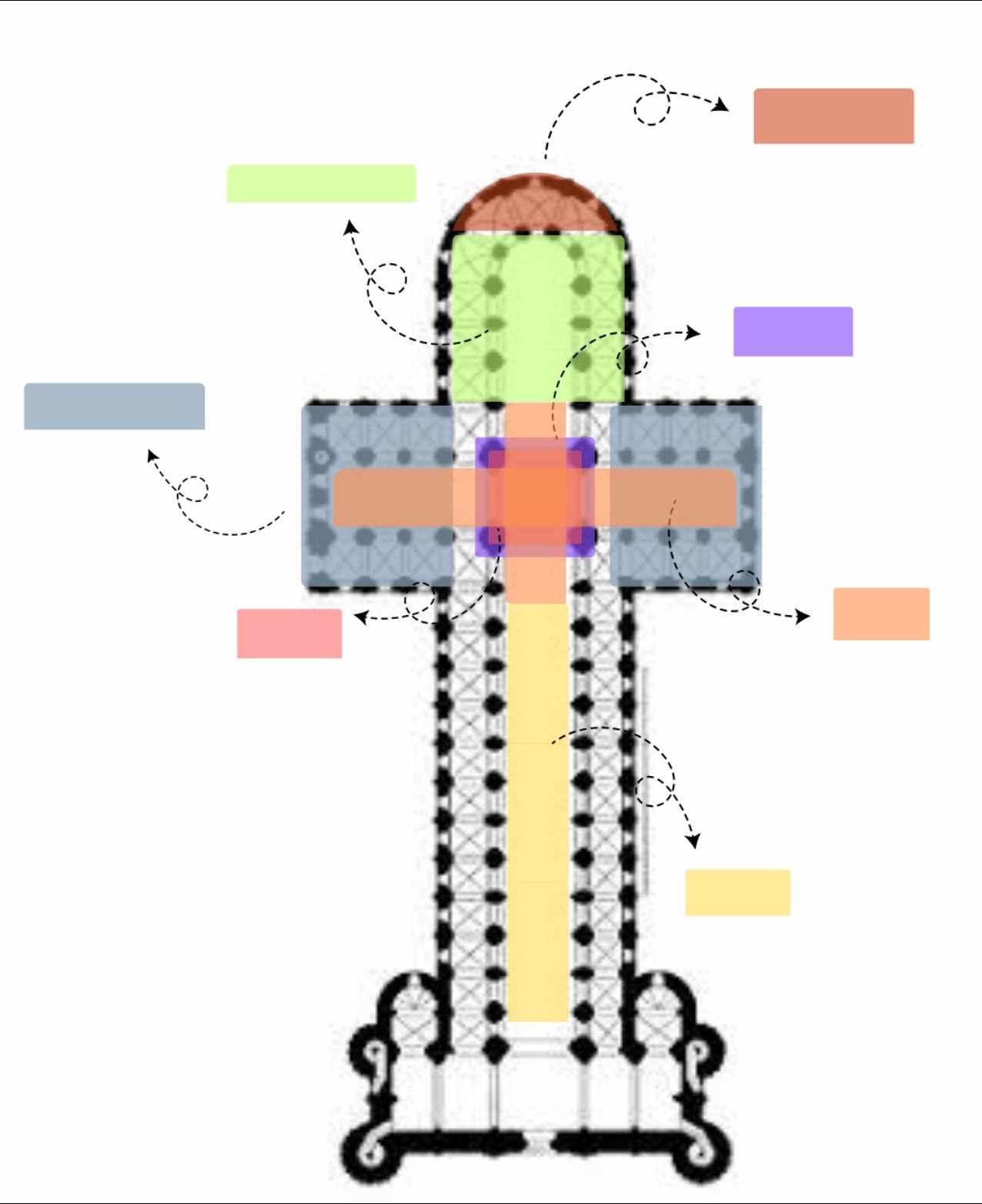
More pronounced and are as wide as the nave.
Transepts
________ was prolonged further east.
Chancel
The ______ was raised and a crypt was located below.
Choir
The saints and bishops were buried in the _______ to make a church a legitimate church. Burial site of saints and martyrs.
Crypt
Great example of a cathedral in the Philippines that has a crypt.
Manila Cathedral
Special features and of great prominence in the design. They are either square, octagonal, or circular. Placed at the east and west ends and crossings.
Towers
Rough and coarsely built.
Walls
True or False
Most Romanesque churches are dim due to the small openings because of thick walls and buttresses.
True
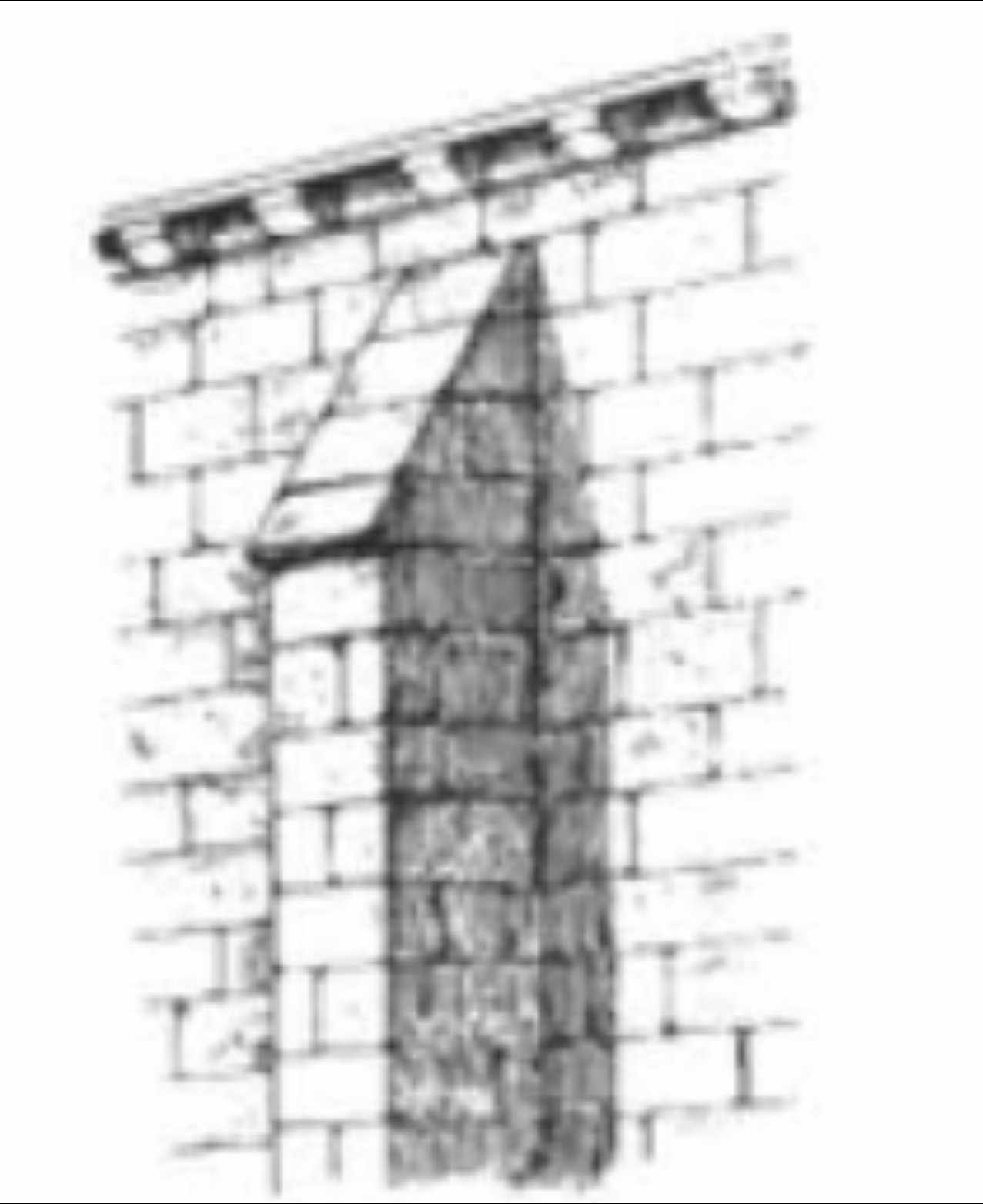
________ are employed formed by pilaster strips.
Buttresses
True or False
Buttresses are built because the foundations of the walls are deep.
False
The need for buttresses is not due to the depth of the foundations but rather to support and stabilize the upper walls of a structure.
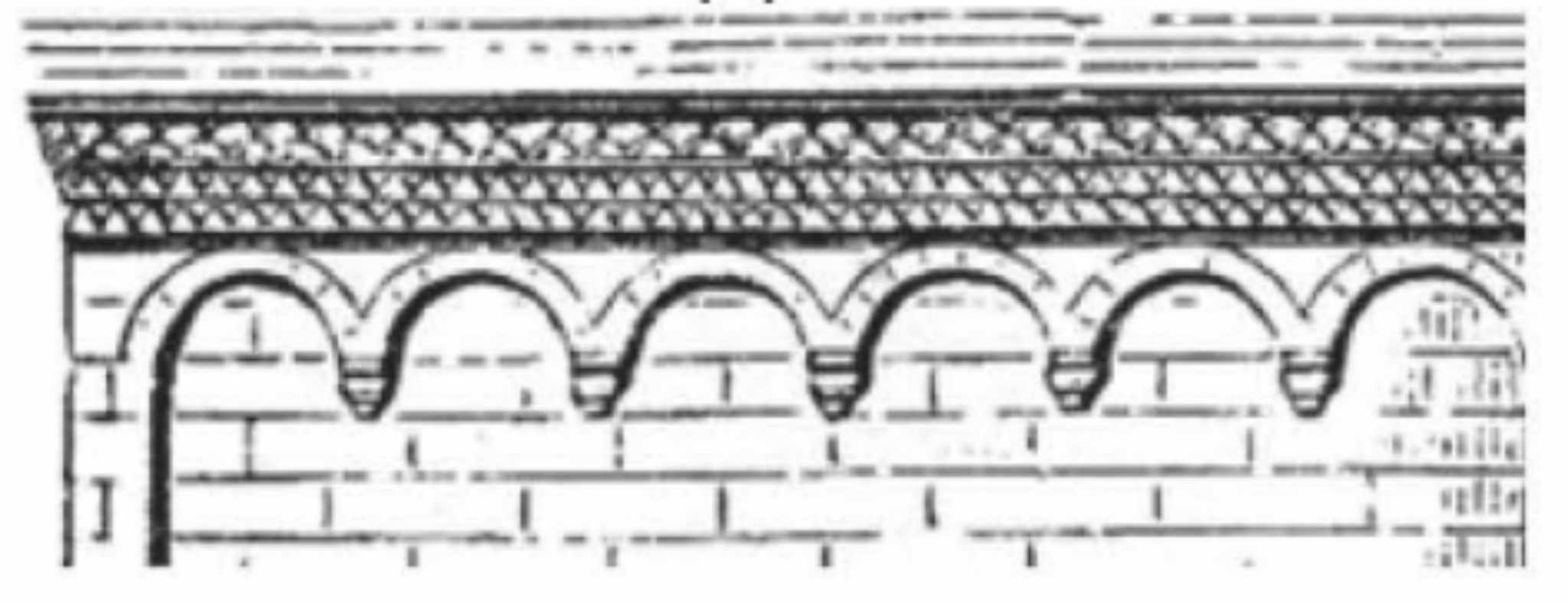
Ornaments/Decorations on top of the walls.
Arched Corbels
They use ____________ arches as openings.
Semicircular
_______ are formed with __________ or _____________.
Jambs; Receding Planes or Rectangular Recesses
They are usually placed in the transepts.
Principal Doorways
Usually placed over the principal door of the church in the west front.
Rose/Wheel Window
Rose and Wheel Window are common in ___________.
Southern Italy
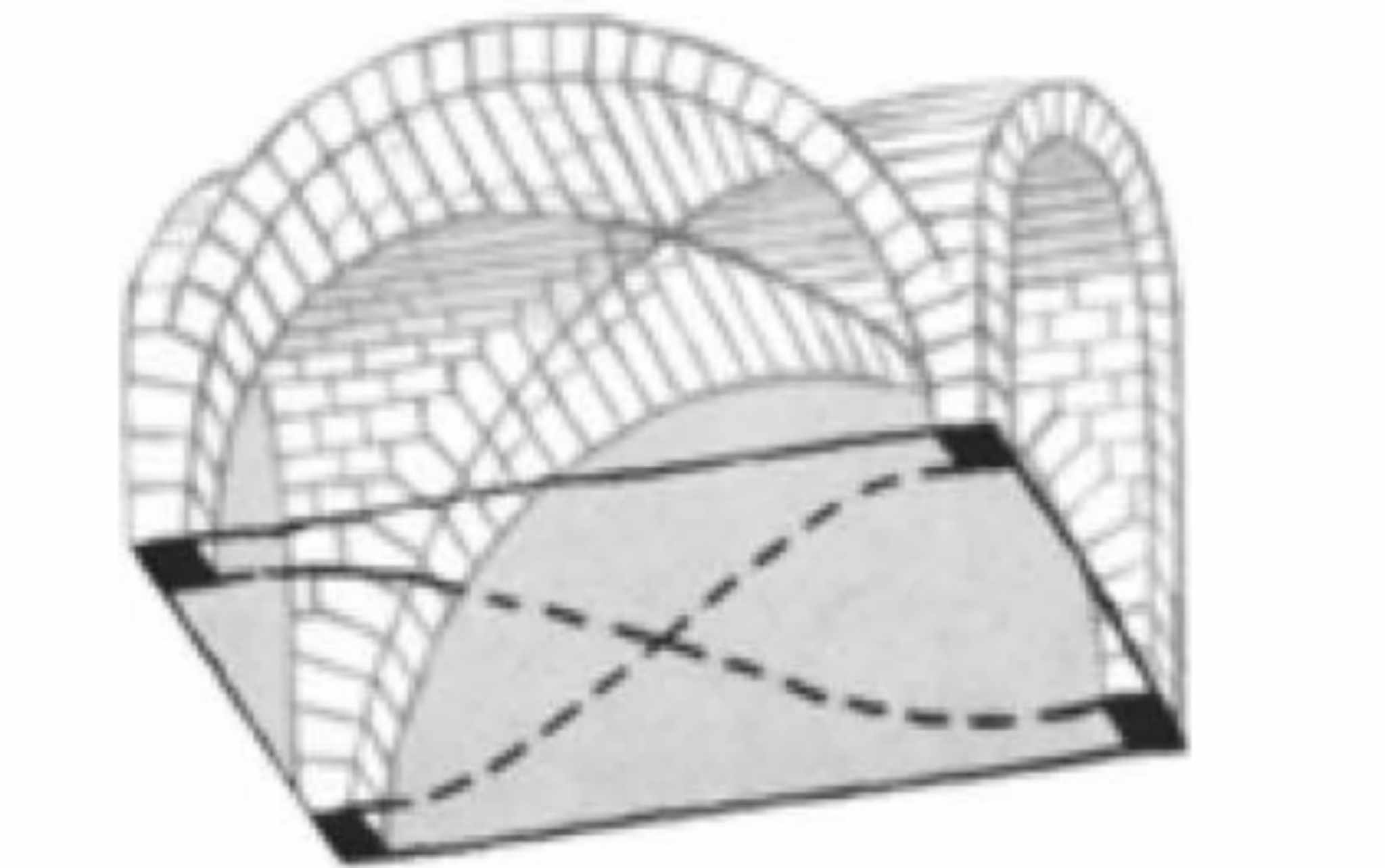
A type of vaulting introduced in the Romanesque Period:
Quadpartite Vaulting
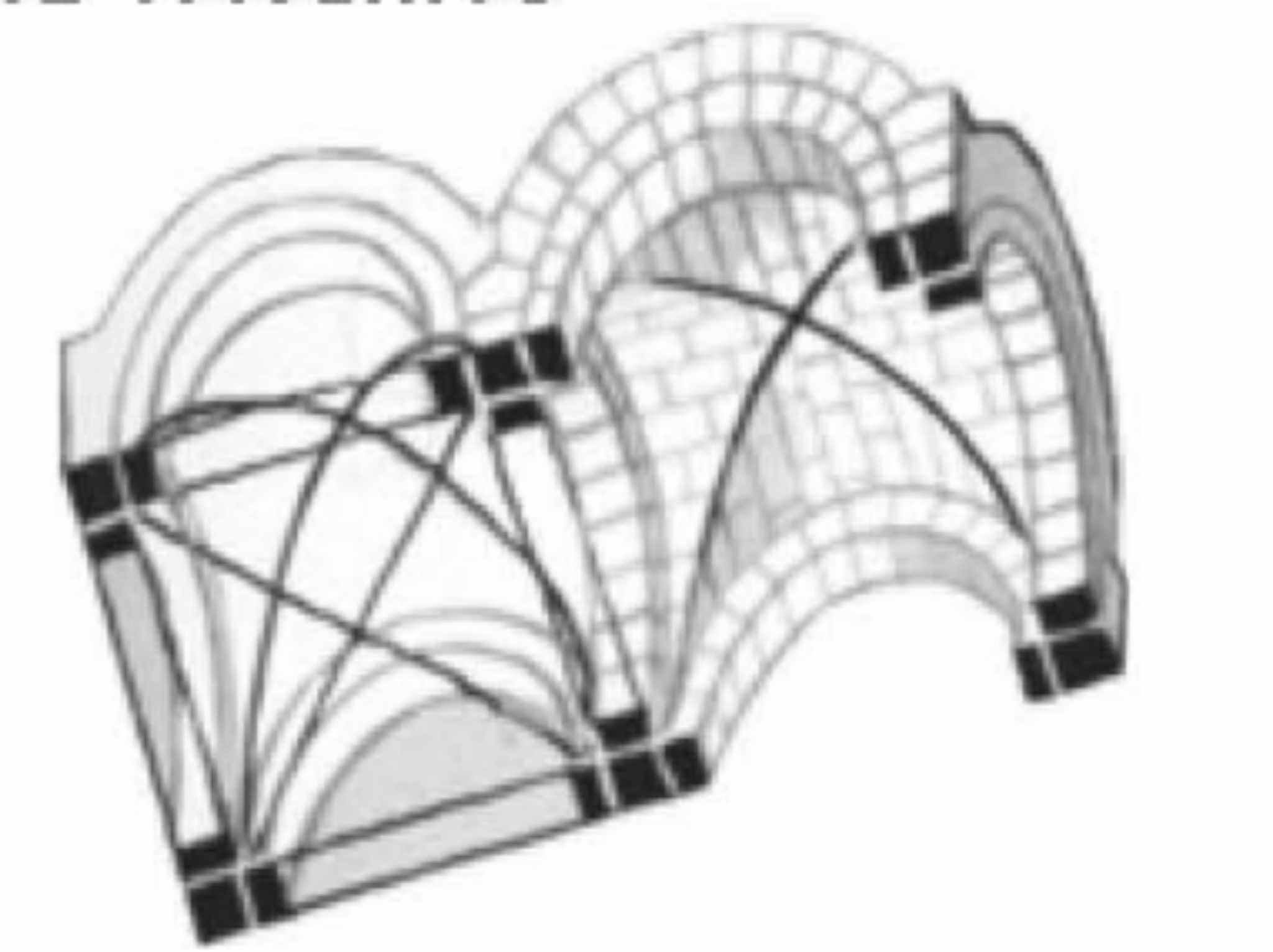
A type of vaulting introduced in the Romanesque Period:
Sexpartite Vaulting
The ________ of the columns varies is treatment.
Shaft
_________ was employed of vertical, spiral, or trellis work form.
Fluting
Shaft if sometimes covered with ___________ __________.
Sculptured Ornaments
Early examples of the capitals are patterned from the __________ and __________ capitals.
Corinthian and Ionic
Later examples of the capitals are in _____________ shape.
Cubiform (Cushion)
The mouldings are carved elaborately usually depicting ________ or _____________ ________.
Vegetable or Animal Motifs
______________ were more commonly used than mosaic which required great technical skill.
Fresco Paintings
Facade has ornamental wall passages which rose one above the other sometimes even into gables.
Central Italy
Flat facade with projecting porch.
Arched corbel table.
Northern Italy
Has Byzantine and Islamic Influences.
Southern Italy and Sicily
Aisle-less naves; Pointed Arches.
Southern France
Two flanking towers at the western facade.
Northern France
Helm Roof and Colored Bricks
Germany
Defensive Forts; Administrative Center of Fiefdoms; Residence
Medieval Castles
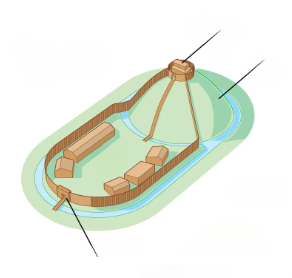
Type of Medieval Castle
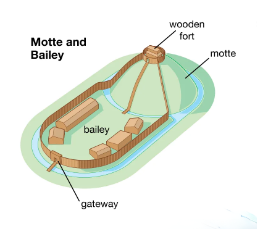
Motte and Bailey
Type of Medieval Castle
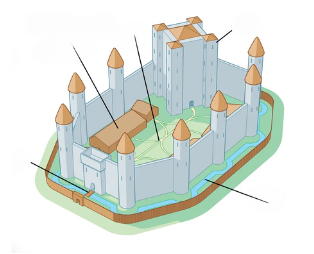
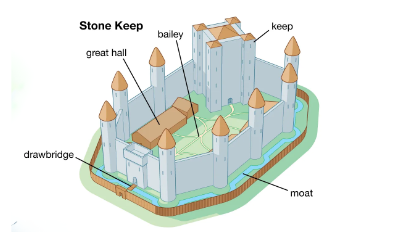
Stone Keep Castle
Type of Medieval Castle
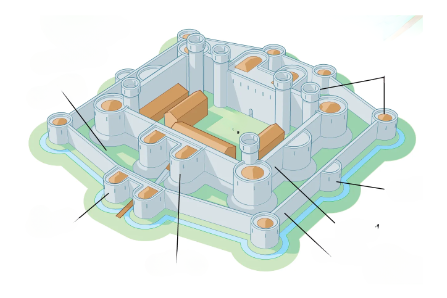
Concentric Castles
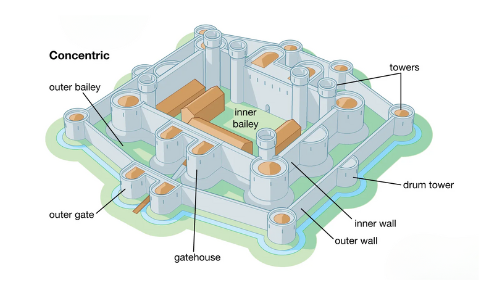
A raised earth mound on which a wooden or stone keep (fortified tower) was built. It was often an artificial hill, providing a strategic height advantage to defend against attackers.
Motte
A water-filled ditch that surrounds a castle or fortification. It was designed to hinder attackers by creating a physical barrier that was difficult to cross.
Moat
Arrow Slits
Crenellations
Murder Holes, they usually pour boiling water or large rocks to the enemies.
Machicolations
Battlements
Merlons
Close to the bed, corbelled out of the wall over either a moat or river.
Latrine/Garderobe
Inner Tower, Important Residence
Keep/Donjon