Chemistry 1.2 Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
What does an atom contain?
A positively charged nucleus with orbiting negatively charged electrons.
What is a proton?
A particle with a positive charge of +1 and a relative mass of 1.
What is a neutron?
A particle with no net charge and a relative mass of 1.
What is an electron?
A particle with a negative charge of -1 and a relative mass of 1/2000.
What does a nucleus contain?
Protons and neutrons make up the nucleus. The nucleus contains most of an atom’s mass.
What is an atom’s electrical charge?
Atoms have no overall charge because the number of protons and electrons are equal. Therefore, the positive and negative charges balance out to an overall charge of 0.
What is atomic number?
The number of protons in the nucleus—this dictates what element it is.
What is mass number?
The relative mass of the atom given by the total number of protons and neutrons.
What is an isotope?
Atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. As a result, they have different masses. They are known as isotopes of the same element.
How do you calculate the relative atomic mass of elements with more than one isotope?
Relative atomic mass = ((isotope 1 mass × abundance) + (isotope 2 mass × abundance)) ÷ 100. Keep repeating for all isotope masses. Abundance is in %.
How are elements arranged in the periodic table?
In order of increasing atomic (proton) number, which places elements with similar properties in the same column (group).
What are the columns of the periodic table called?
Groups.
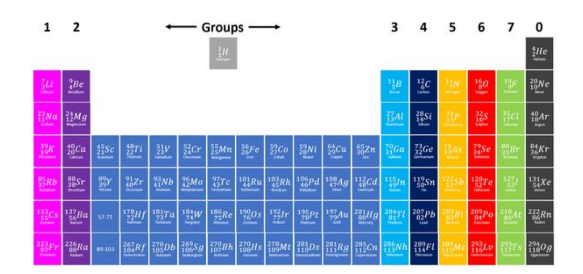
What are the rows of the periodic table called?
Periods.
Where are metals found in the periodic table?
The left side and centre of the periodic table.
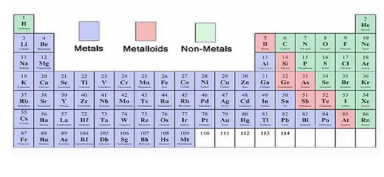
Where are non-metals found in the periodic table?
Right side.
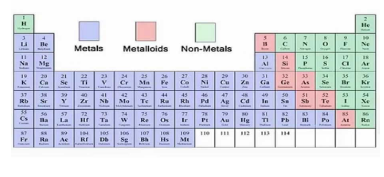
What type of elements lie between the metals and non-metals in each period?
Elements with intermediate properties.
List the electronic configurations of the first 20 elements.
H - 1,
He - 2,
Li - 2.1,
Be - 2.2,
B - 2.3,
C - 2.4,
N - 2.5,
O - 2.6,
F - 2.7,
Ne - 2.8,
Na - 2.8.1,
Mg - 2.8.2,
Al - 2.8.3,
Si - 2.8.4,
P - 2.8.5,
S - 2.8.6,
Cl - 2.8.7,
Ar - 2.8.8,
K - 2.8.8.1,
Ca - 2.8.8.2.
What is the relationship between electronic structure and position in the periodic table?
The group number of an atom is equal to the number of electrons in its outer shell.
What similarities do elements in the same group have?
Similar chemical properties, as they have the same number of electrons in the outer shell.
What are the Group 1 elements known as?
The alkali metals.
What are Group 7 elements known as?
The halogens.
What physical trends do the alkali metals show?
Atomic radius increases down the group. Densities gradually increase down the group. Melting and boiling points gradually decrease down the group.
What is involved in the reactions between Group 1 and Group 7 elements?
The loss or gain of electrons, forming ions:
● Group 1 elements lose one electron to form a +1 ion.
● Group 7 elements gain one electron to form a -1 ion.
What is the reactivity trend of the alkali metals down the group?
Electrons are lost more easily down the group. Reactivity increases down the group as alkali metals react by losing an electron.
What is the reactivity trend of Group 7 elements down the group?
Electrons are attracted less down the group. Reactivity decreases down the group as there are more electron shells and so the ability to attract another electron decreases.
What does the reaction of an alkali metal with oxygen produce?
An oxide.
What does the reaction of an alkali metal and a halogen produce?
A white precipitate (crystalline halide salt). The reaction occurs very quickly.
What does the reaction of an alkali metal and water produce?
Fizzing that produces an alkaline solution and hydrogen.
What is the test to identify hydrogen gas?
Collect some of the gas in an upturned test tube. Place a lighted splint into the test tube. A squeaky pop sound means hydrogen gas is present.
What does iron + fluorine produce?
Cold iron wool reacts almost instantly to form white iron (III) fluoride.
What does iron + chlorine produce?
Reacts vigorously to form an orange-brown precipitate of iron chloride.
What does iron + bromine produce?
Reacts quickly to form a red-brown precipitate of iron bromide—the reaction has to be warmed.
What does iron + iodine produce?
Reacts slowly in iodine vapour to form a grey iron iodide precipitate—the reaction has to be heated strongly.
What are the relative reactivities of the halogens as demonstrated by precipitation reactions?
A decrease in reactivity down the halogen group means that a more reactive halogen can displace a less reactive one:
● Chlorine will displace bromine and iodine.
● Bromine will displace iodine but not chlorine. ● Iodine will not displace chlorine or bromine.
What are the uses of chlorine?
Chlorine is a disinfectant and kills bacteria, so it is used to sterilise drinking water and clean swimming pools. Reacts with sodium hydroxide and water to form bleach. Used in manufacturing chemicals, including insecticides, PVC, and chlorofluorocarbons.
What is iodine used for?
Iodine is an antiseptic, so it can be used to prevent infection in hospital procedures.
What are the flame test colours for Li+, Na+, K+, Ca²⁺, and Ba²⁺ ions?
Li⁺ Crimson flame.
Na⁺ Orange-yellow flame.
K⁺ Lilac flame.
Ca²⁺ Orange-red flame.
Ba²⁺ Green flame.
What are the precipitates for Cl⁻, Br⁻, and I⁻ reaction with silver nitrate solution?
Cl⁻ precipitate is white. Br⁻ precipitate is cream. I⁻ precipitate is yellow.
What are the ionic equations for the reactions of Cl⁻, Br⁻, and I⁻ with silver nitrate solution?
Ag⁺(aq) + Cl⁻(aq) → AgCl(s).
Ag⁺(aq) + Br⁻(aq) → AgBr(s).
Ag⁺(aq) + I⁻(aq) → AgI(s).
Why are the Group 0 gases unreactive?
Group 0 gases (noble gases) are unreactive because they have full outer electron shells, making them stable and unlikely to gain or lose electrons.