Future of Food Quiz #2 (UNC Chapel Hill 2024)
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Path dependence
Preceding steps induce further movement in the same direction
Agriculture
The practice/science of cultivationg plants and animals to produce food or other usable products.
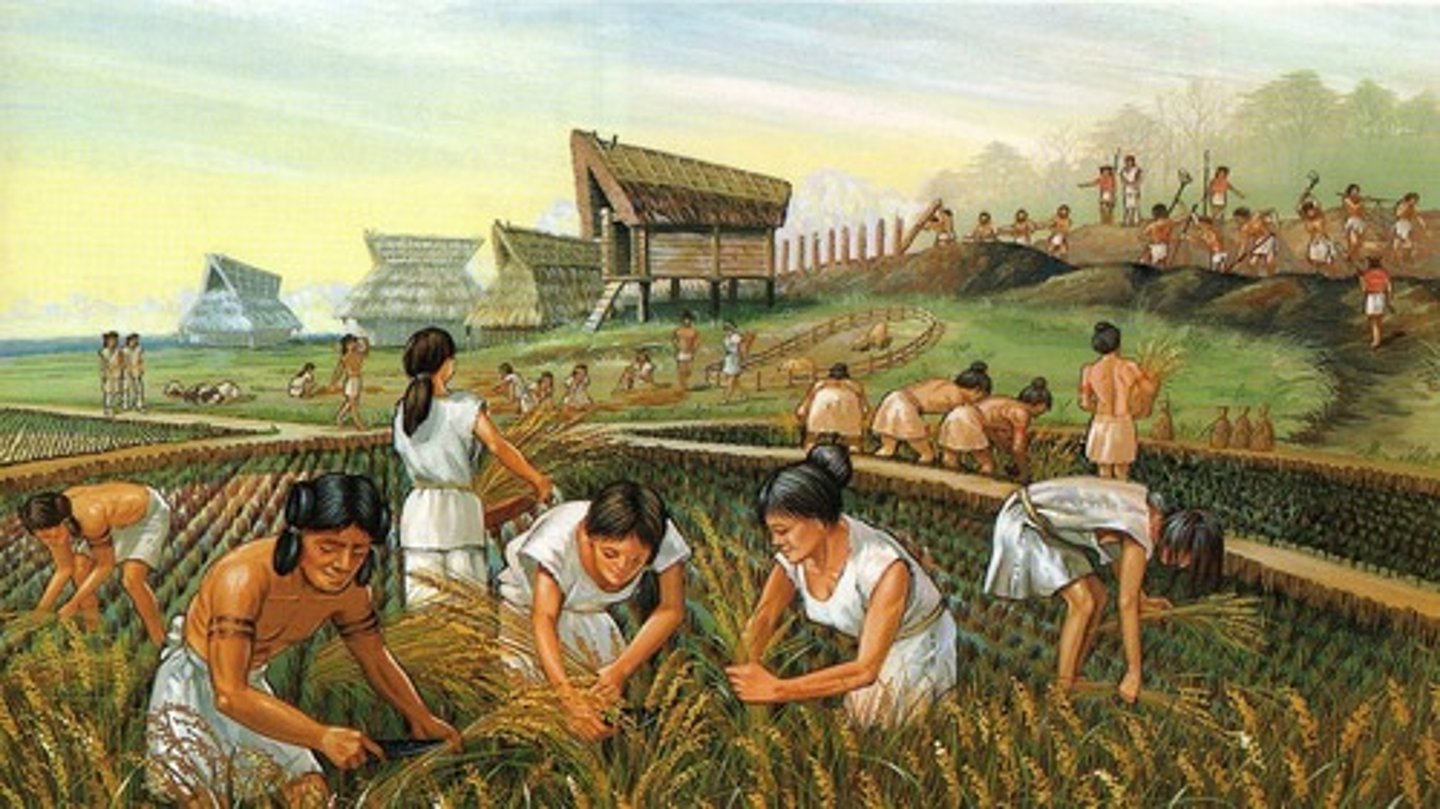

changes in climate, increased population density, overhunting, changing technology
Why did humans adopt agriculture
open-field system
division of large fields into long, narrow strips that are not communal.

Tools for open-field system
Ox-powered plows and hand tools
Enclosure
Fencing or hedging large blocks of land
60%
Average working-class family % of budget on food
Specialization
Narrower range of crops/tasks
Mechanization
Repetative tasks can be performed by machines; fewer people work in agriculture

Consolidation
shift towards fewer and larger farms
Market Concentration
Small number of countries earn most of the sales in one industry
Shifting Baseline
Assuming what we see around us is "natural"
Fishing down the food chain
harvesting at progressively lower trophic levels as higher trophic levels become depleted
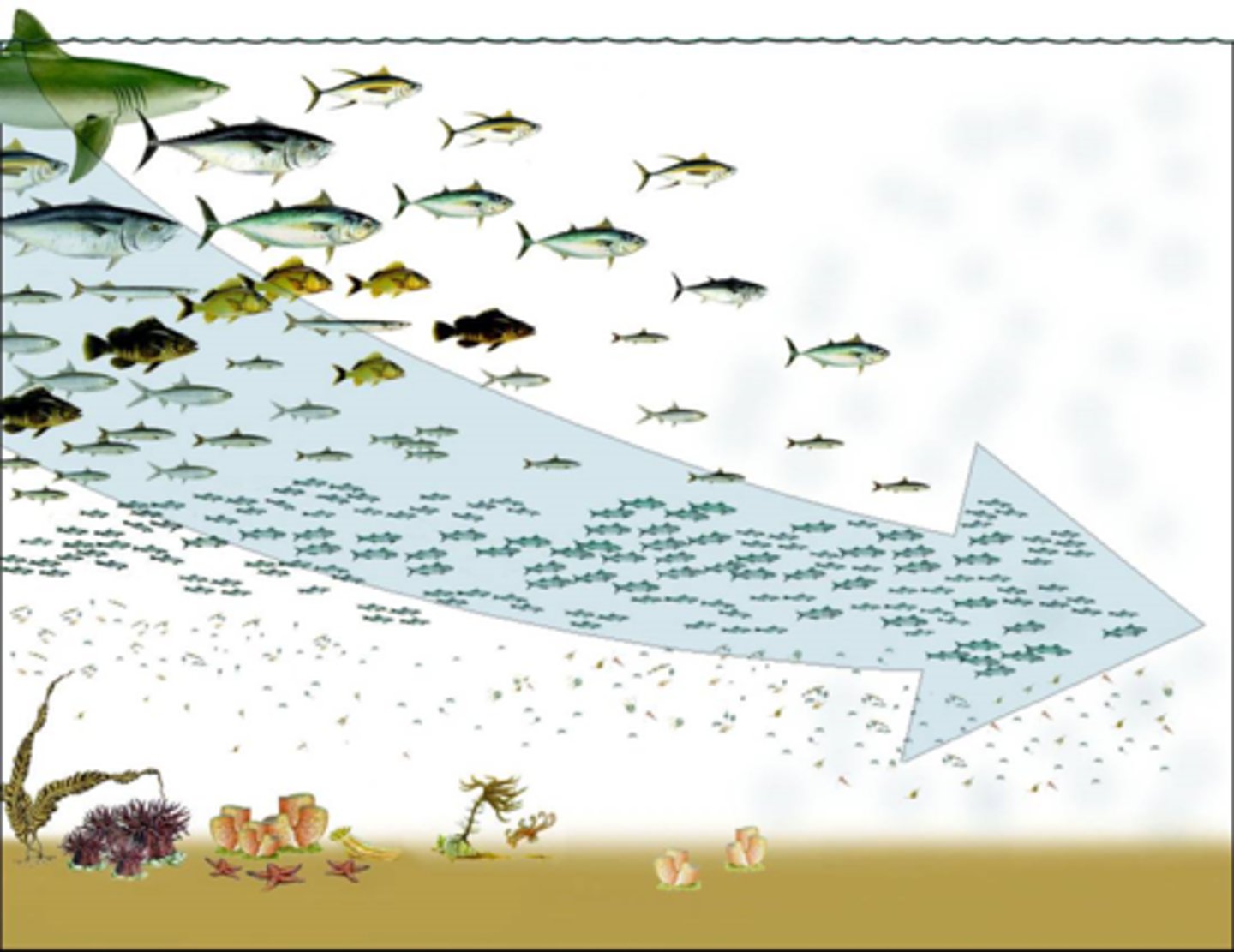
Caribs (Kalinago)
Overfished with small population and massivley affected fish ecosystem
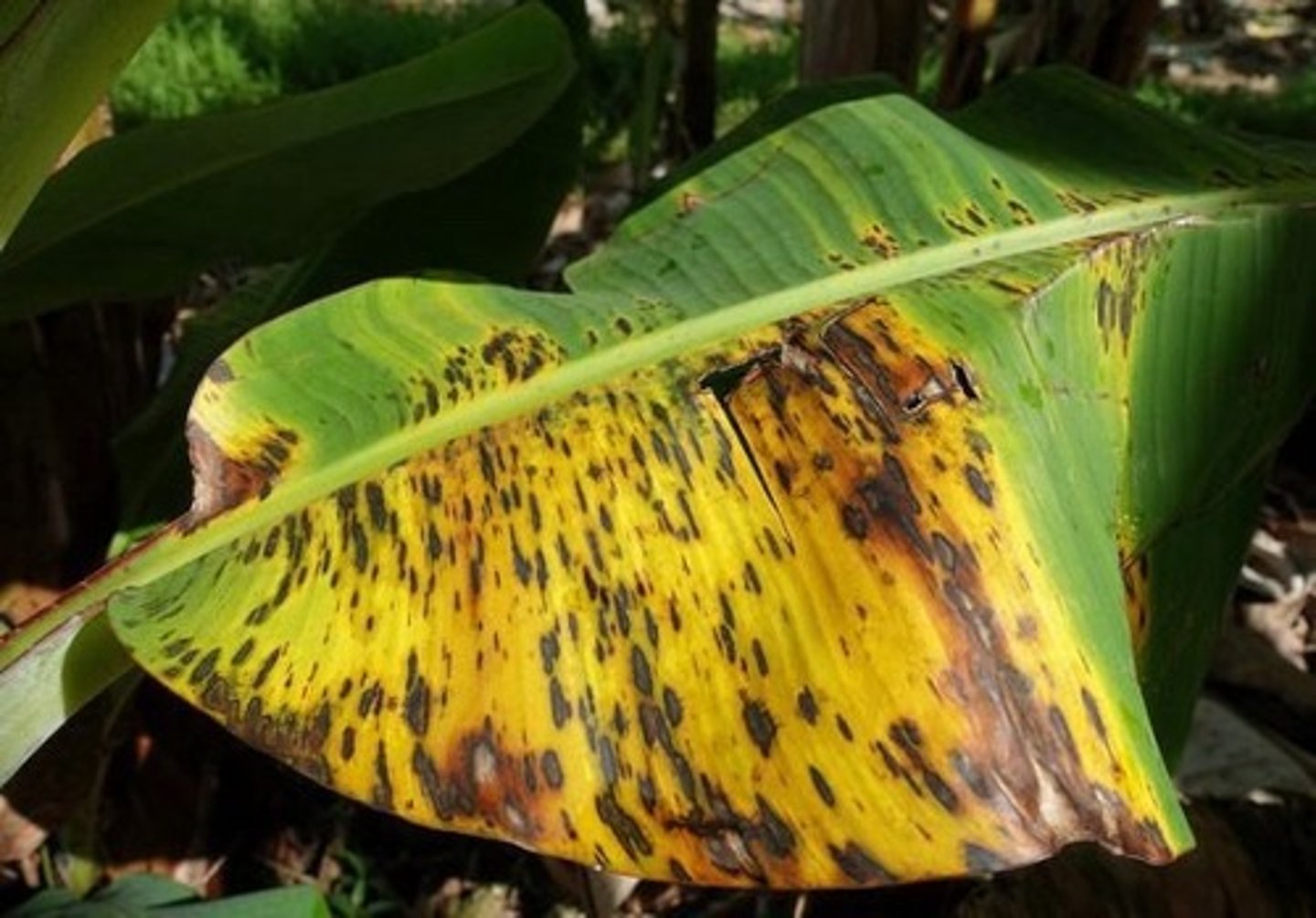
Black Sigatoka
Disease that ruins photosynthesis in banana plants killing the plant. Can ruin whole farm in three weeks.

The Greenhouse Effect
Natural situation in which heat is retained in Earth's atmosphere by carbon dioxide, methane, water vapor, and other gases
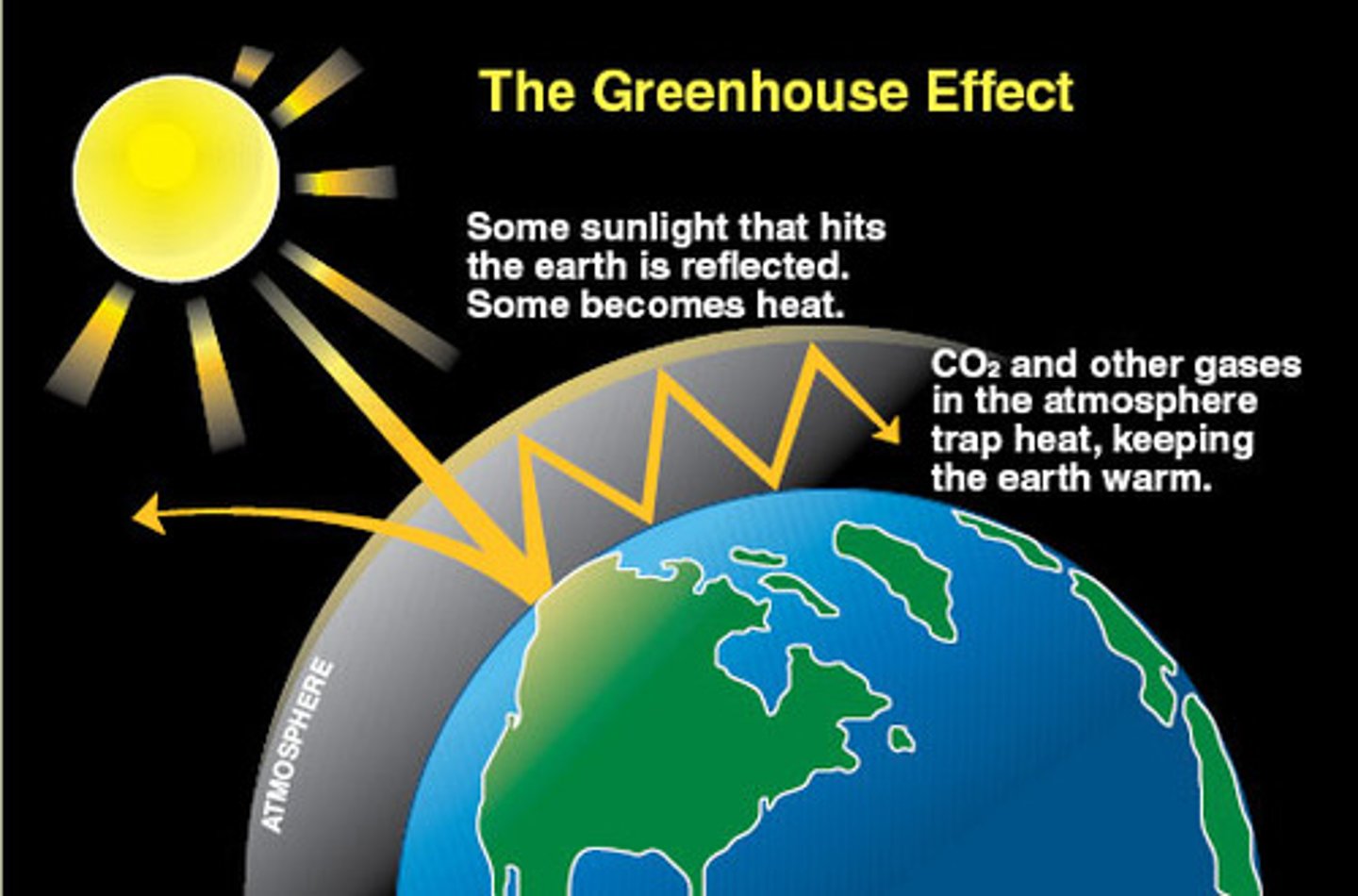
Greenhouse gases
Gases such as carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, water vapor, and ozone in the atmosphere which are involved in the greenhouse effect.
Methane
Very potent but last short amount of time compared to CO2

Sources of CO2 emmisions
Energy (72%), Agriculture use (18.4%), Misc (9.6%)
Methane emmisions main sources
Agriculture: Livestock ruminant animals, rice cultivation, Burning of forests for land use,
Waste
the decomposotion of organic waste in landills
Importance of cereal grains
could feed domesticated animals, good storage, whole plant is useful
Meta-analysis
a procedure for statistically combining the results of many different research studies
Participant observation
doing the same as workers aswell as interviewing and asking questions for research
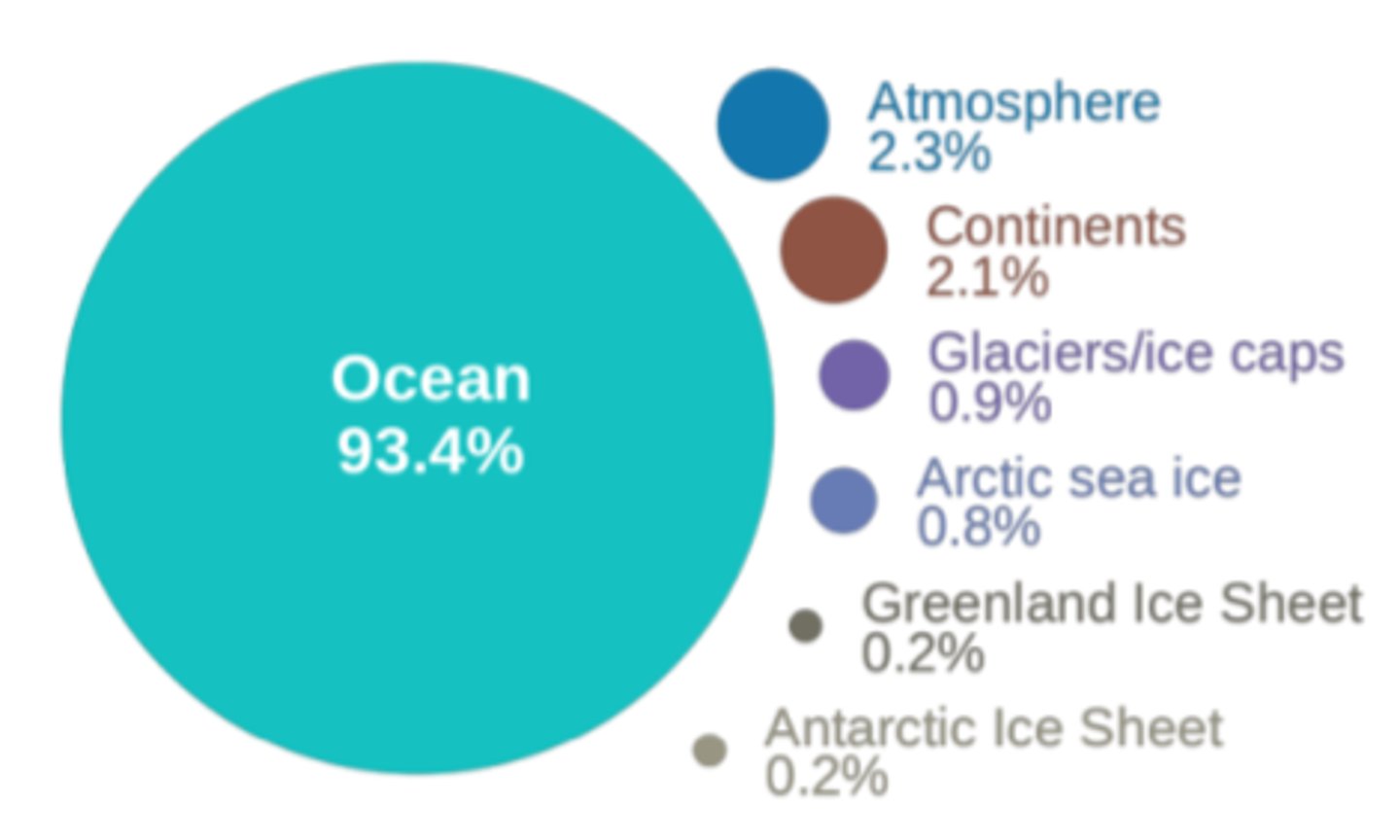
Majority to the Ocean (93.4%)
Where is Global Warming going?
range shifts due to climate change
Warming will shift species distributions poleward (most common in the ocean)
Benefits to zooxanthellae
protection from predators
regulation of environment
nutrient recycling
provision of CO2

change in marine animal biomass
due to increasing metabolism and by stratification and reduced upwelling and primary production
Benefits to coral
productivity
Calcification
nutrient recycling
provision of O2

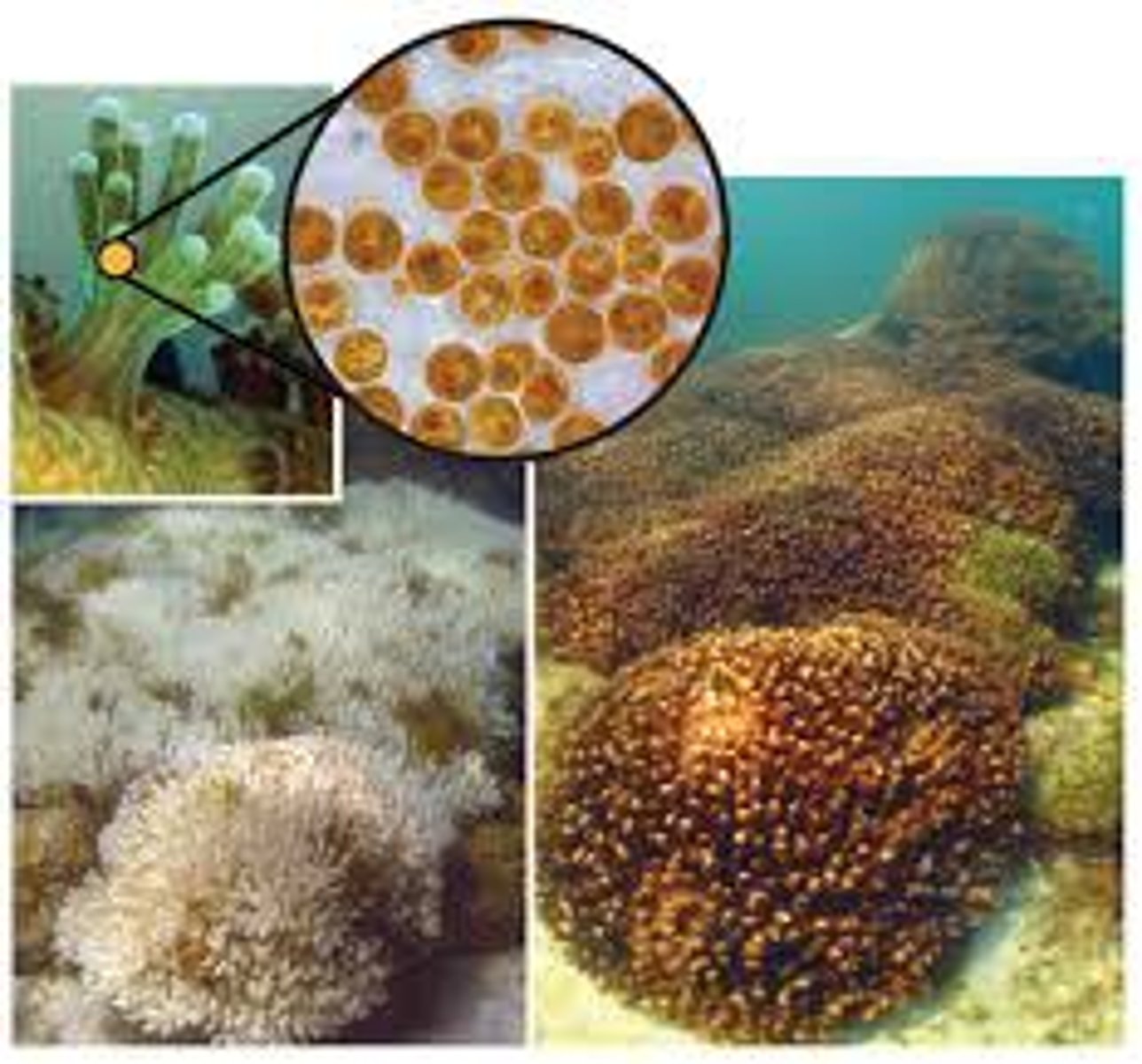
coral bleaching
the loss of color in corals that occurs when stressed corals expel the algae that live in them

Compost
Great solution to food waste?
31-40%
What % of harvested food is wasted in the US?

Food Waste
What is the largest trash item in landfills?
20%
What percent of food waste comes from date labels?
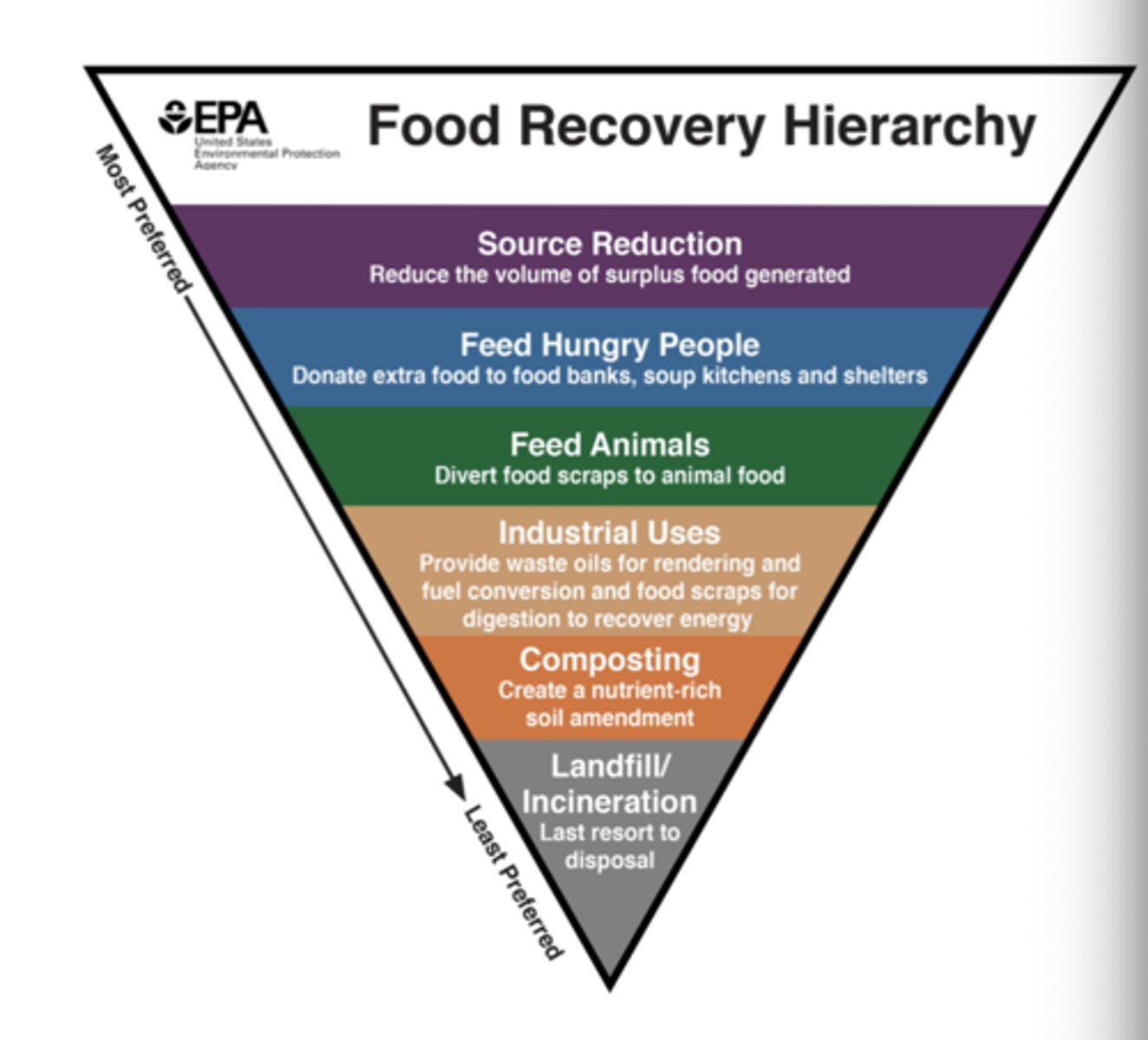
Food Recovery Hierarchy
most preferred --> least preferred
1. source reduction
2. feed hungry people
3. feed animals
4. industrial uses
5. composting
6. incineration or landfill
Colonial Era style of farming
Subsistence or plantation farming

Homestead Act
Provided free land in the West to anyone willing to settle there and develop it. Encouraged westward migration.

Federal Irrigation Projects
provides irrigation for 1/5 of farmers in West
-60% of the nation's vegetables
-25% of fruit/nut crops

government agricultural subsidies
government boosts the farmer's income, not food production
AAA (Agricultural Adjustment Act)
goal to end overproduction and raise crop prices (helped struggling farmers)
Why consolidation?
Federal agriculture programs encourage big farms growing conventional crops.
Farm Bill
a congressional act that is renewed/modified/amended, etc. every 5 years that governs how the Federal government interacts with agriculture in the US
Domestication
the process of changing plants or animals to make them more useful to humans
Fairtrade Organization
A global system that aims to improve the lives of farmers and workers in developing countries by providing better prices, fair terms of trade, and decent working conditions

Fairtrade Principles
- Transparent and democratic farmer-focused decision-making
- Trading partner based on dialogue transparency and respect
- Social, Economic, and Environmental developments