insects tracheal system
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
what is an exoskeleton
waterproof outer layer which is rigid and prevents insects drying out
how do insects reduce water loss?
small SA:volume means less water loss
waterproof exoskeleton
spiracles (pores in the exoskeleton which can open or close)
where do spiracles lead to?
they run along the length of the abdomen and lead to network of tubes called trachea, which branch into tracheoles.
what holds tracheae open?
rings of hard chitin which is impermeable to gases
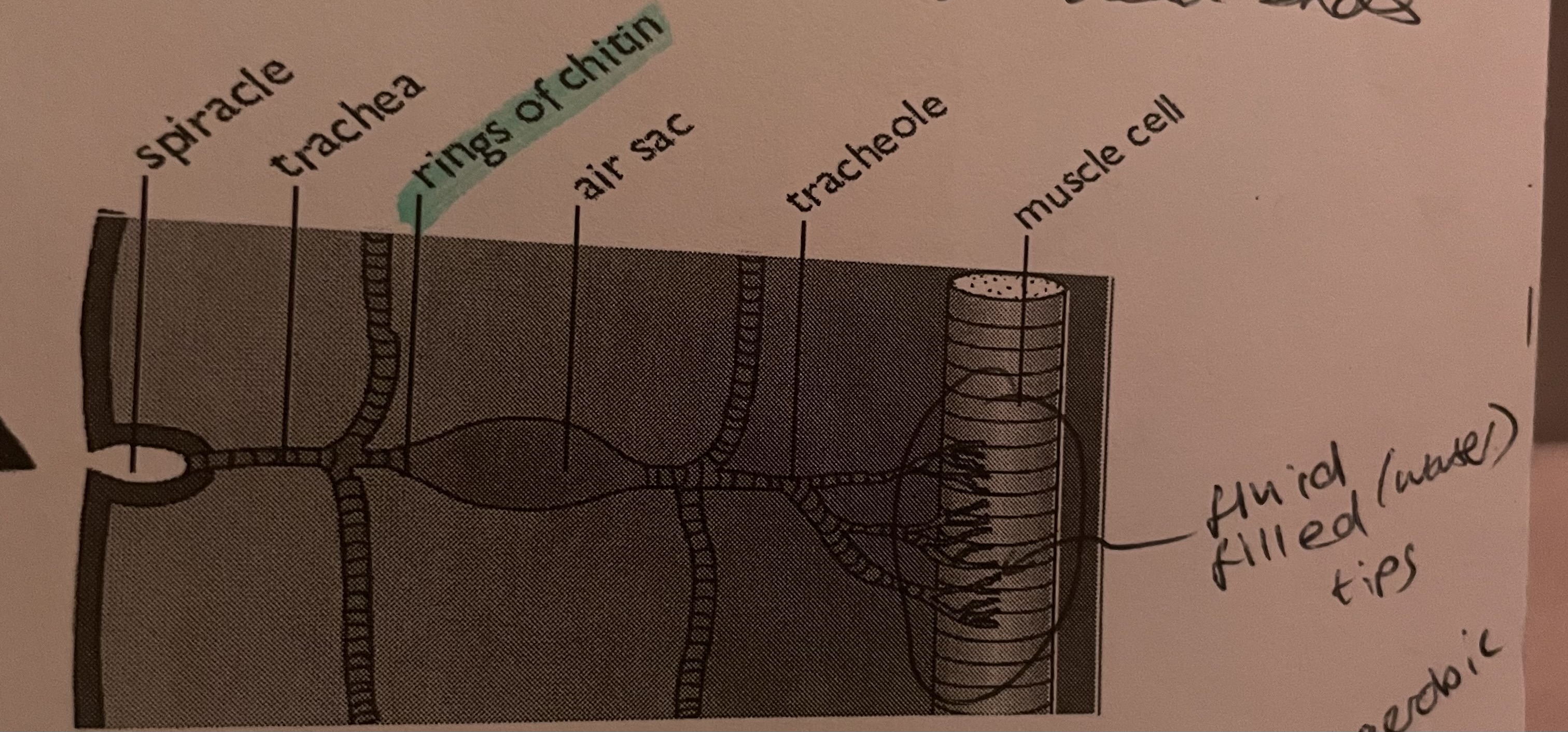
why are tracheoles so efficient?
they penetrate deep into the tissues of an insect to deliver air quickly and directly to cells.
what does the insect do at rest?
the water diffuses out of cells into the tips of tracheoles (tracheal fluid), this means oxygen has to diffuse through the water before the cells - slow process.
what happens when an insect is flying?
anearobic respiration occurs and buildup of lactic acid lowers water potential, so water diffuses by osmosis from tracheoles into the cells - faster process.
what do larger insects do?
use their muscles (thoracic and abdominal) to ventilate, and squeeze trachea to suck air in and out.
how do some insects counteract water loss?
hairs around spiracles which can close spiracles when inactive, they also have a rigid waterproof cuticle
how do spiracles reduce water loss?
trapping moist air, reduces water potential between inside and outside the insect, which slows down evaporation and water loss.
insect adaptions for sufficient diffusion
large number of tracheoles - large surface area
walls of tracheoles are thin and short distances between spiracles and tracheoles - short diffusion pathway
use of oxygen and production of carbon dioxide - steep conc grad