NSCI 175: Brain Rhythms and Sleep
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
How long may REM sleep periods last?
30-50 minutes
The external cue that animals use to discern the time of day is called a
zeitgeber
What part of the nervous system generates the fluctuations and oscillations of an EEG
dendrites of many pyramidal neurons in the cerebral cortex
What brain regions and associated neurotransmitters are implicated in changes associated with awakening and states of arousal?
A. Brain stem and forebrain (acetylcholine)
B. Raphe nuclei (serotonin)
D. Locus coeruleus (norepinephrine)
Why is REM sleep referred to as paradoxical sleep?
A. Vivid, detailed illusions called dreams are conjured during REM sleep
B. The EEG for REM sleep is almost indistinguishable from an active, waking brain
C. Rapid eye movements occur during REM sleep
D. The body (except for the eyes and respiratory muscles) is immobilized
B. The EEG for REM sleep is almost indistinguishable from an active, waking brain
The ________ ______ of the ______ requires input from the retina to maintain circadian rhythms that are in phase with the day-night cycle.
suprachiasmatic nucleus of the thalamus (SCN)
The time that elapses between two successive occurrences of a circadian event, such as the commencement of the day's activities, is called the
zeitgeber
period
entrainment
phase
period
Which of the following represents delta rhythms, the hallmark of deep sleep?
Greater than 14 Hz
4-7 Hz
8-13 Hz
Less than 4 Hz
Less than 4 Hz
What brain structure is known to act as a powerful pacemaker for the cerebral cortex?
Brain stem
Thalamus
Midbrain
Cerebellum
Thalamus
Which of the following describes REM sleep behavior disorder?
Dreamers with delta wave terrors
Sleepers who do not generate REM brain waves characteristic of REM sleep
Dreamers have no REM atonia and therefore may act out their dreams.
Sleepers who have narcolepsy
Dreamers have no REM atonia and therefore may act out their dreams.
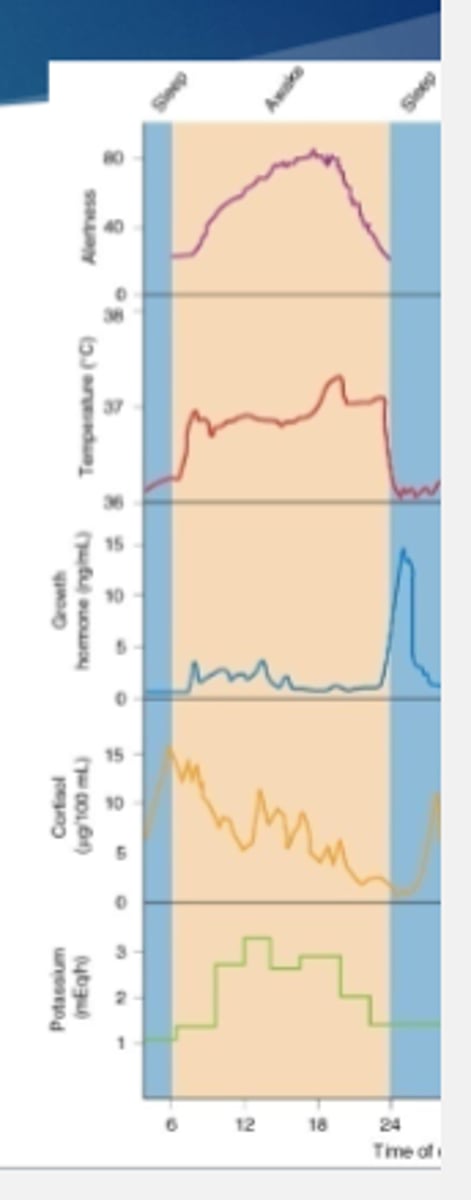
What regulations of the body have been found to demonstrate a circadian rhythm? (3)
body temperature
hair growth
hormone secretion
EEG
Measure of multiple cerebral pyramidal neurons helps detect patterns in circadian rhythm through an electrodes
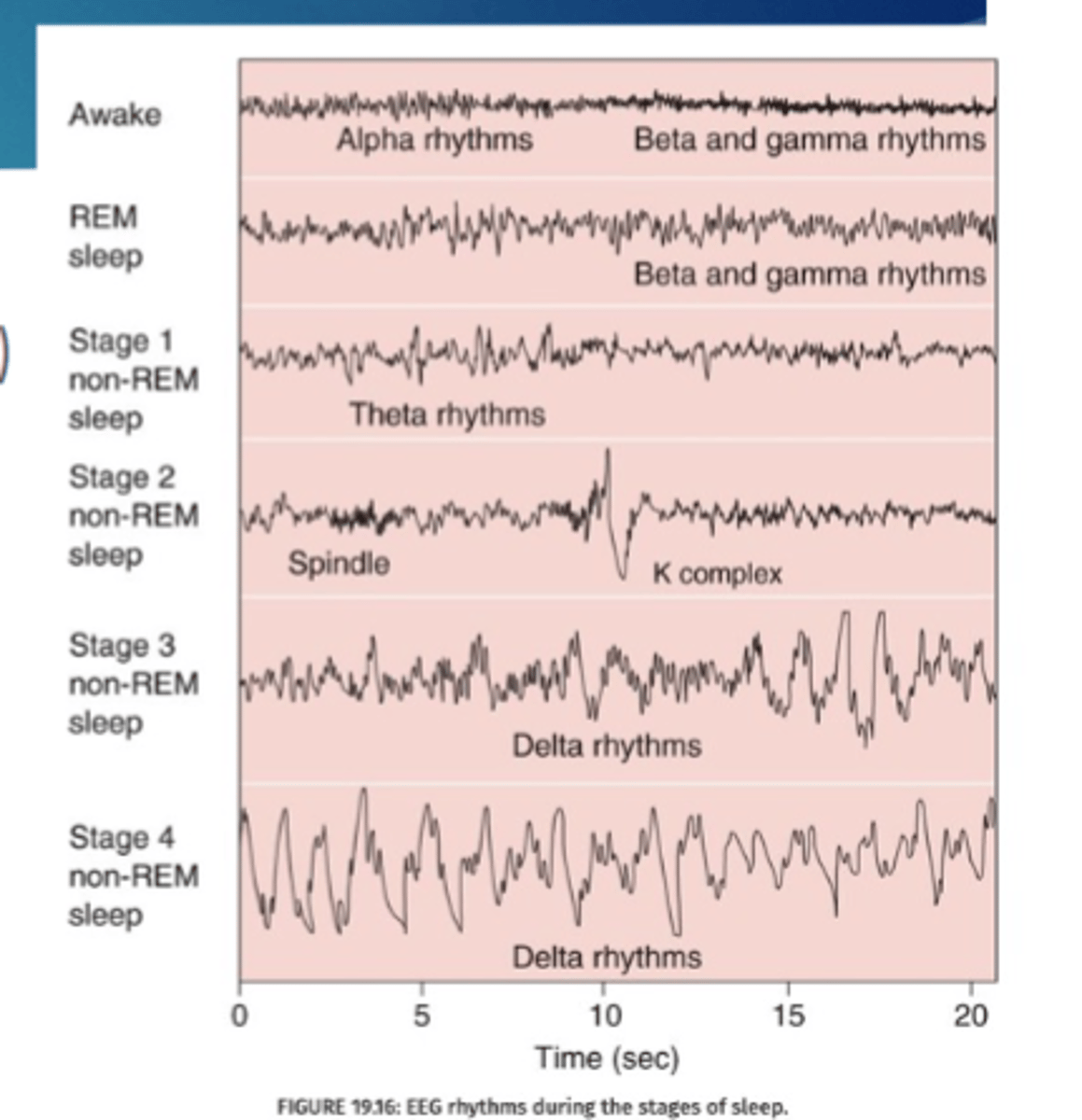
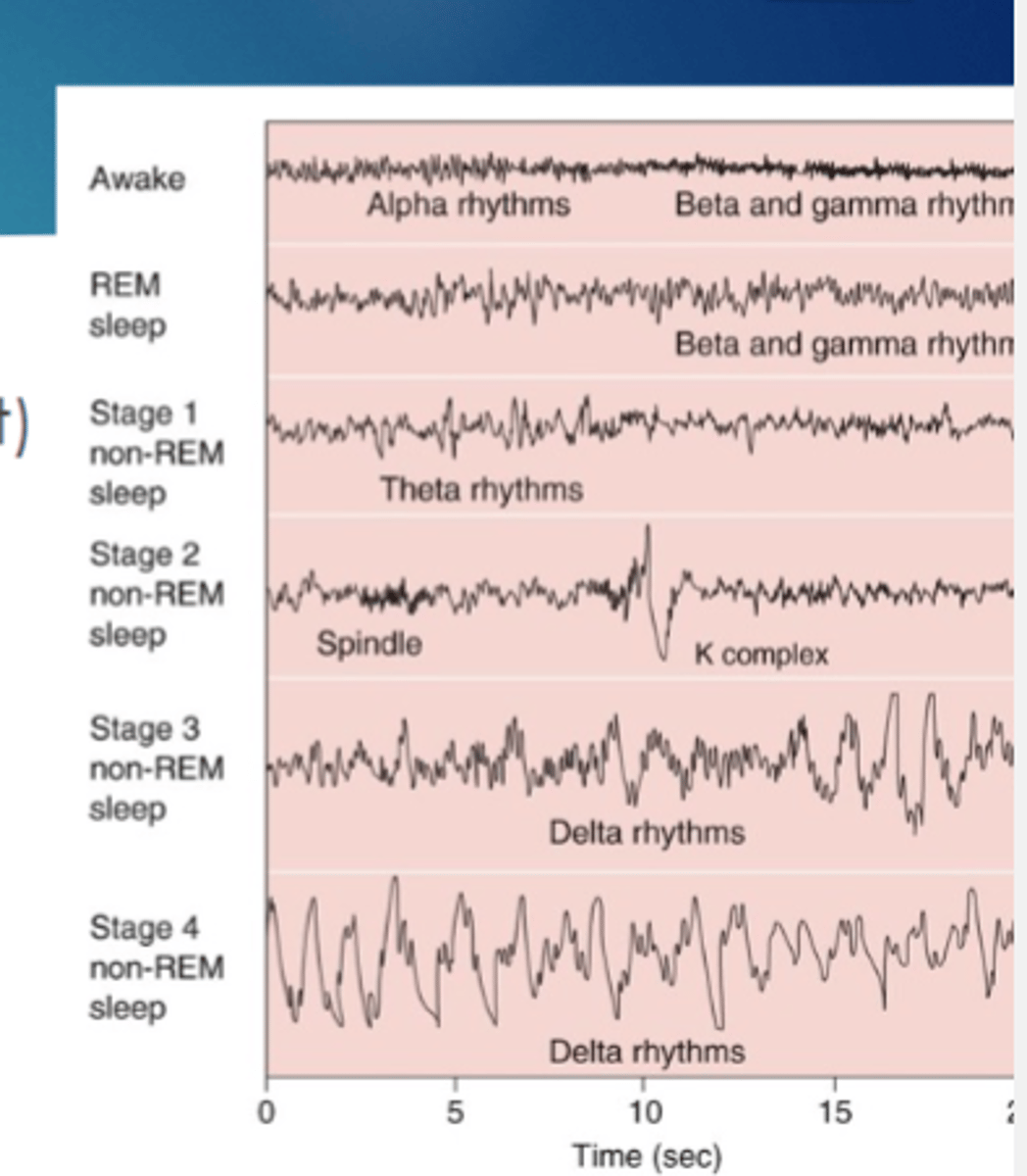
Awake EEG
Low voltage
Fast Vivid
Externally generated Logic
progressive
continuous
voluntary
REM: often
Non REM sleep EEG
high voltage, slow
involuntary
REM Sleep EEG
Low voltage
Fast vivid
illogical
bizarre
muscle paralysis
Awake amplitude and frequncy
low amplitude and high frequency rhythms

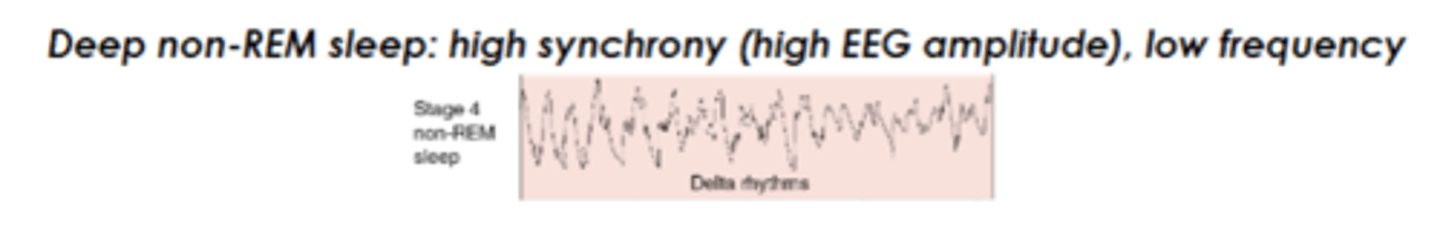
Deep non REM sleep amplitude and frequency
high amp, low frequency
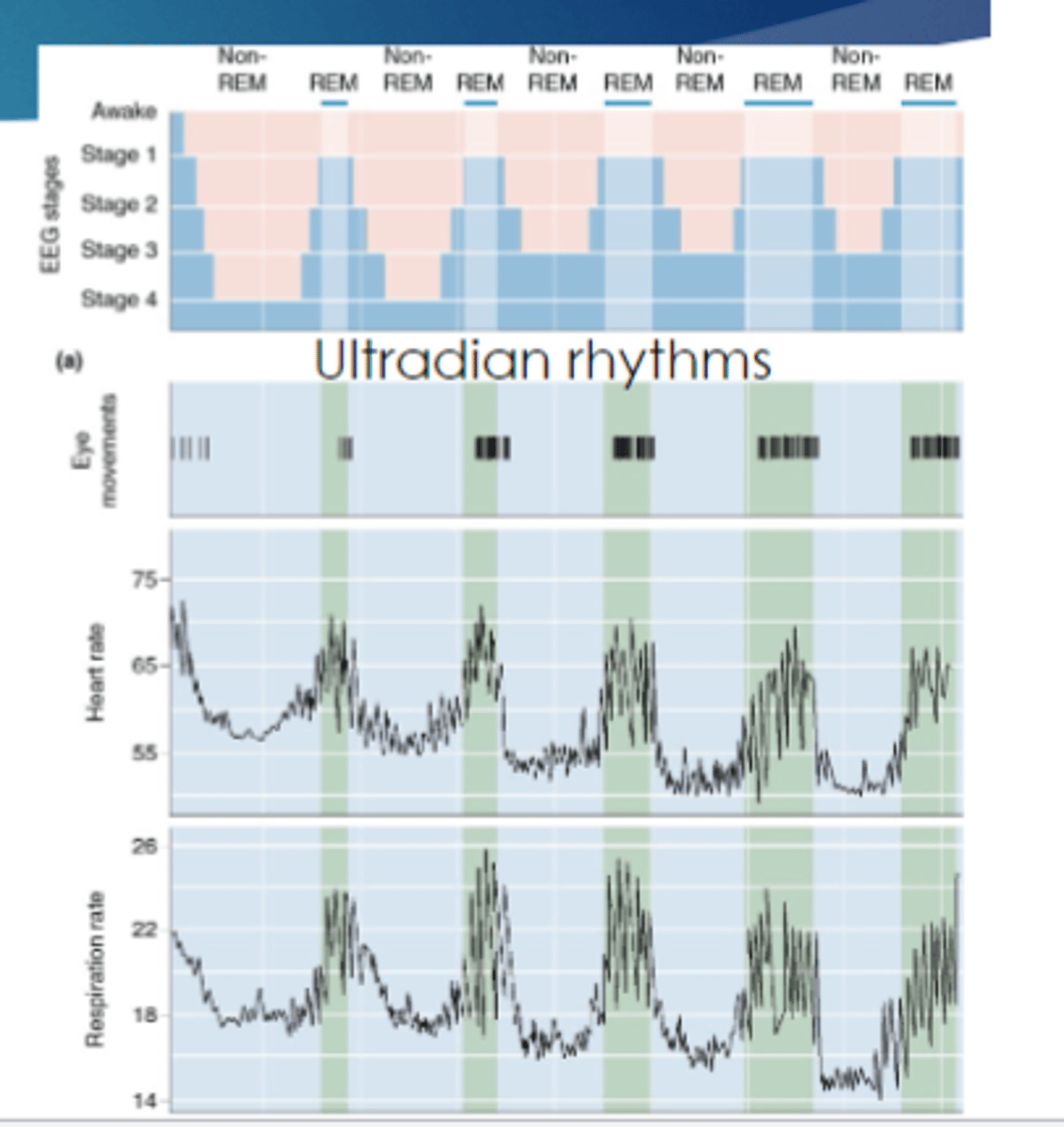
Normal night we cycle through the stages of non REM and REM, repeating every
90 minutes
Four stages of non REM sleep
Transitional sleep (few minutes & lightest)
Slightly deeper (5-15 minutes)sleep spindles & K complex
Delta rhythms, deeper sleep
Deepest sleep (20-40 min)Slow large amplitude delta waves
Major connection in sleep between the __ and the __
excitatory:
hypothalamus and the cerebral cortex
Circadian rhythm vs ultradian rhythm
over 24 hours versus over a few minutes
Atonia, paradoxical sleep and sympathetic activation. fast low amplitudes, beta and gamma rhythms
REM sleep
beta and gamma rhythms
REM sleep
Delta rythmns
Non REM
Kidney function slows, parasympathetic, sleep spindle, K complex, four stages, reduced muscle tension
Non REM sleep
As we age our REM sleep and sleep
decreases
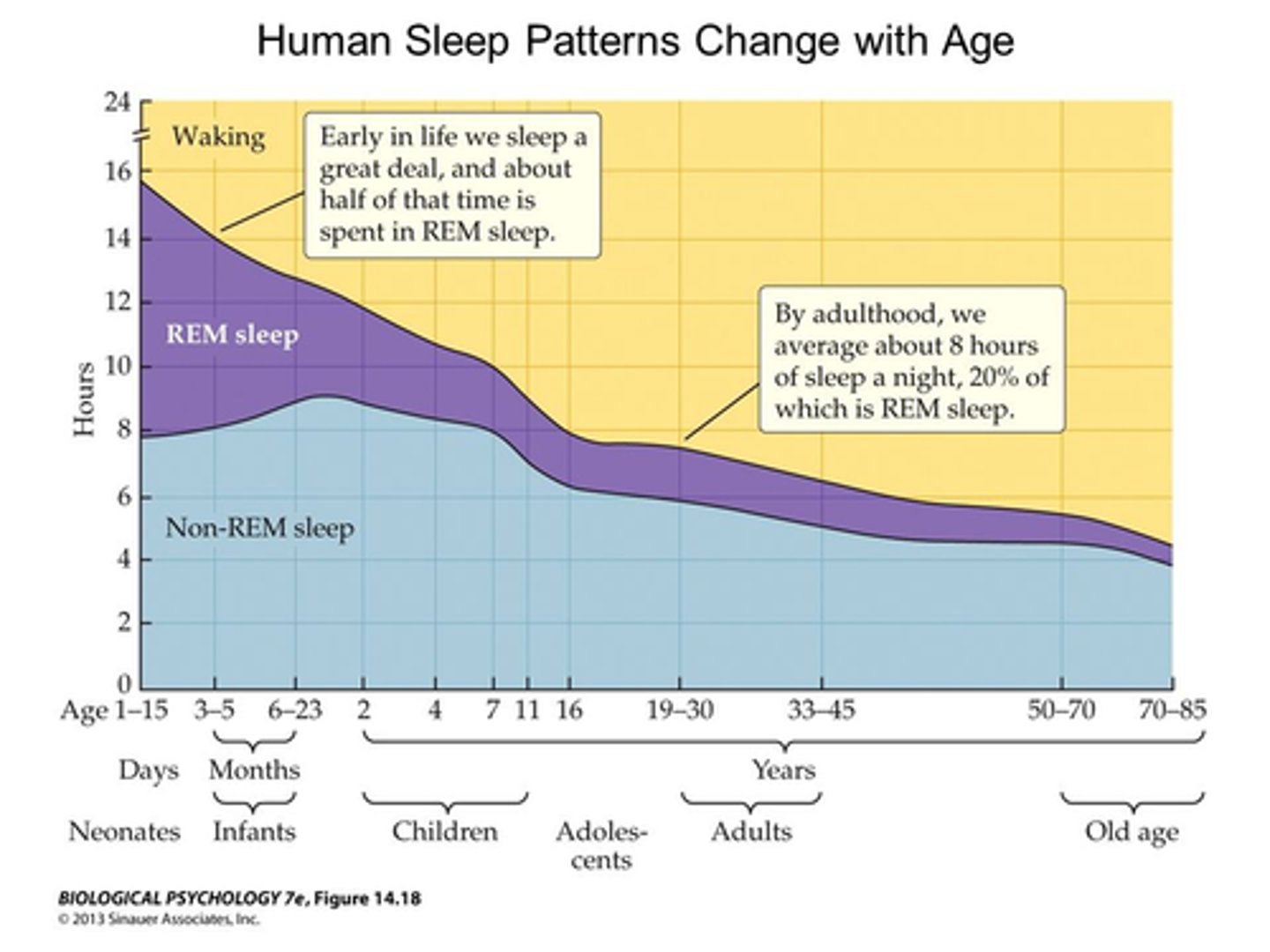
Babies will sleep more for shorter periods with more __
rem cycle
Why we sleep and consequence of sleep deprivation
Restoration: sleep to rest and recovery
Adaptation: hide from predators
Memory consolidation, prevents cognitive impairments
Inactivity Theory
Inactivity at night served as survival function to hide from predators
Energy Conservation Theory
sleep is an adaptation that allows us to conserve energy for gathering food, defeating predators
Brain Plasticity Theory
Changes in structure and organization of brain when we sleep.
Rerouting the neural circut
Restorative Theory
Restore elements impaired and depleted while awake
consequence of sleep deprivation
irritibility, emotional instability
increased heart rate
episodes of disorientation
Fatal Familial Insomnia (FFI)
Rare genetic disorder- Inability to sleep (starts off mild), but progressively worsens leading to significant physical and mental deterioration-
Abnormal variant in the prio-related protein (PRNP) located in the thalamus-
Prognosis: Death within 6-36 months after the onset of symptoms (no cure): spasms, can't eat, fever, rapid heart rate
Episodes of hallucinations.
Shorter sleep predicts
a shorter life because of diseases associated
Sleep deprived individuals have increased activity in the ___
amygdala
Increased Tau buildup causes
Alzheimer's, since sleep deprivation causes lack of filtering the brain
Increased firing rates in which of the following systems likely support the transition from sleep to wake? Select all that apply.
Histamine
Norepinephrine
Acetylcholine
Seritonin
Serotonin and NE enhance ____
5-HT & NE neurons fire during & enhance wake; Different ACh neurons enhance REM sleep while others enhance awake states
What do modulatory systems do to thalamus in sleep cycle
Systems control the rhythmic firing of thalamus which controls EEG rhythms of cortex (slow rhythms of sleep in thalamus block sensory information from reaching the cortex!)
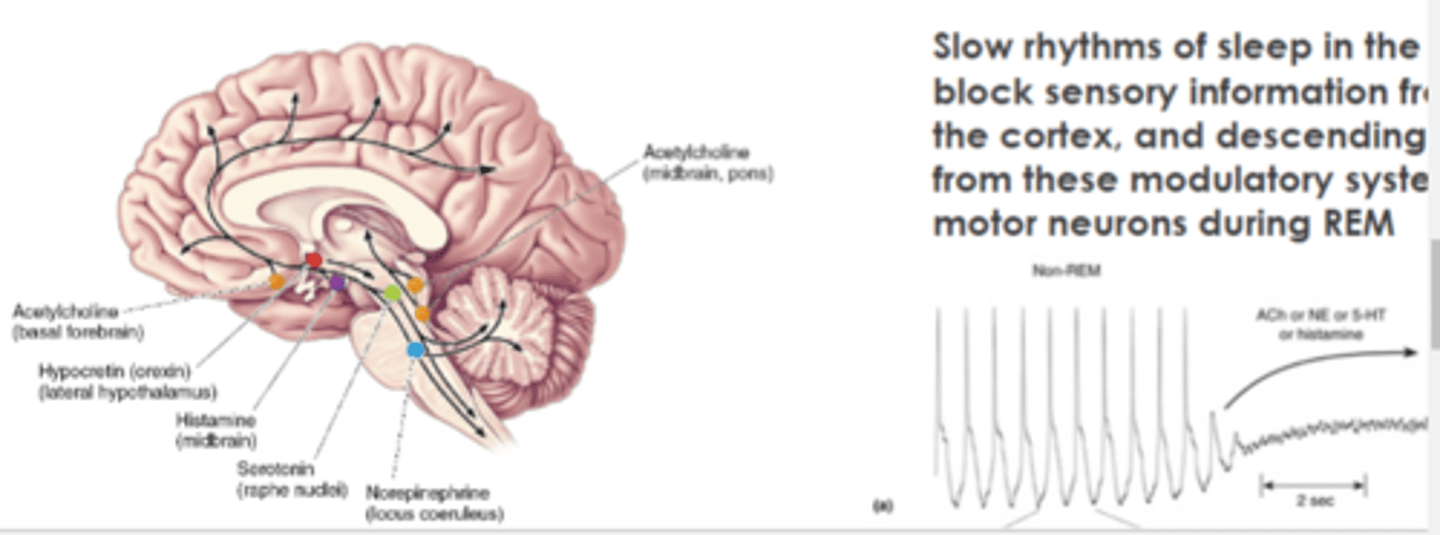
What do modulatory systems do to our motor neurons
Descending branches of these systems inhibit motor neurons during dreaming!
REM on-cells
are cholinergic neurons in the pons that fire to enhance REM events
REM off-cells
include norepinephrine neurons in the locus coeruleus and serotonergic neurons in the raphe nuclei
which decrease firing to almost nothing during REM
Orexin
can excite neurons in modulatory systems
PROMOTES WAKEFULNESS: inhibit REM sleep
Hypocretin
a neurotransmitter secreted by cells in the hypothalamus; helps regulate sleep-wake cycles
Hypocretin is involved in
narcolepsy
narcolepsy is
when you dont go through slow wave sleep before REM,
Makes you sleepy in the day
Melatonin is released when
darkness rises
Melatonin
helps time when sleep will occur. It does not help when sleep occurs.
Helpful for jet lag.
Anti-Histamine promotes
promotes sleep
Caffeine
inhibits sleep signal.
Latches to adenosine sites and masks the receptors.
Once caffeine wears off, adenosine has build up
After ___ hours of being awake, you will start to feel sleepy
16
Zeitgebers:
environmental cues that signals the passage of time
For mammals: primarily light-dark cycle
suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN)
in hypothalamus that function as a biological clock
suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN) receives input from
photosensitive retinal ganglion cells, which allows them to reset the circadian clock
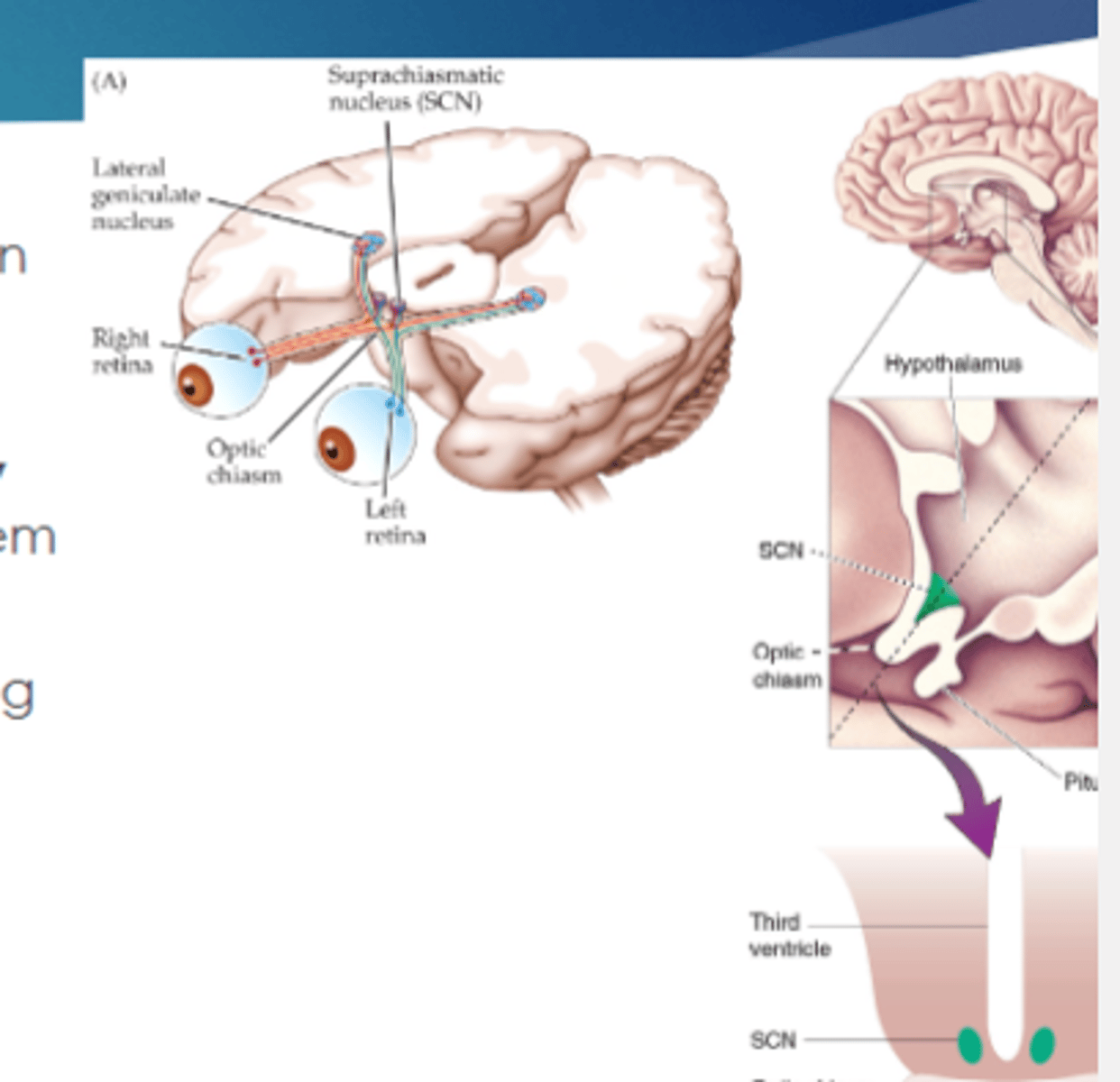
Lesions to the SCN abolishes
the circadian rhythms
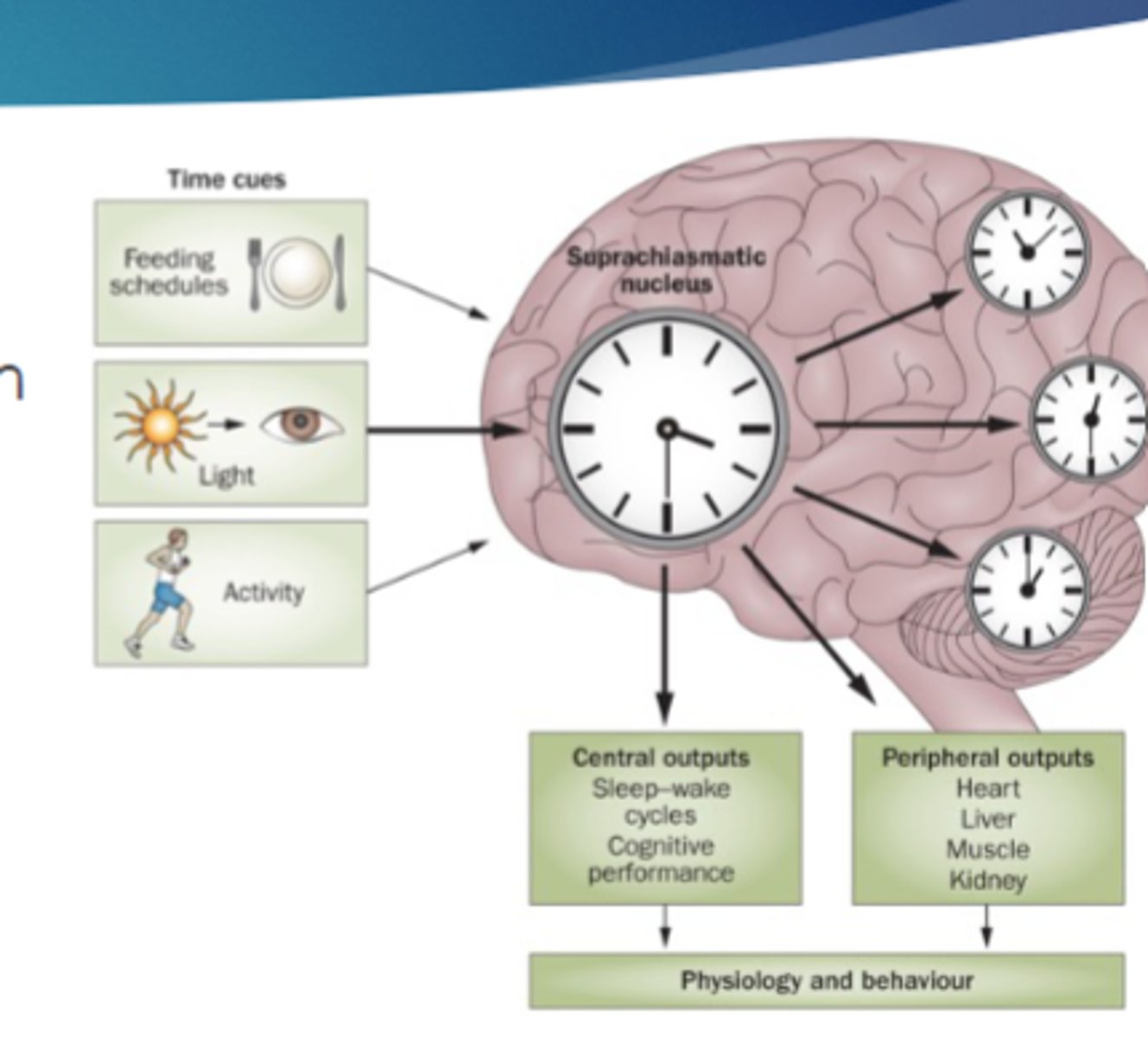
Stimulating the SCN
shifts the circadian rhythms

Transplanting a SCN into a lesioned animal
restores circadian rhythms

In stage __ you have spindle and K complex
2
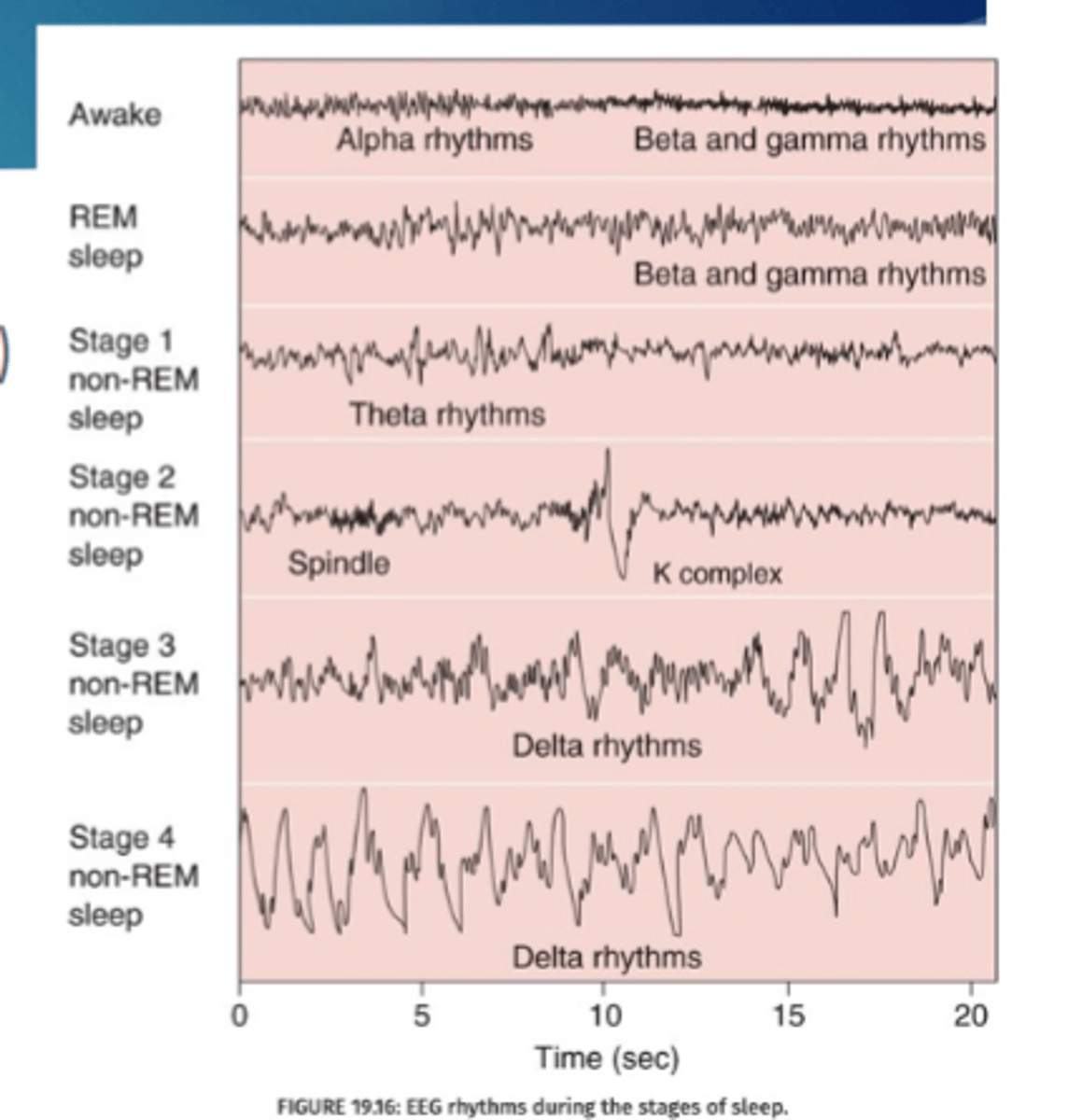
Stages 3 and 4 have ____ rhythms
delta