Chapter 7 - Introduction to T-tests
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Single Sample and Dependent Means
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
T-test
A statistical tool used to compare the means of two groups to see if there's a significant difference between them. Used when:
1. the population SD/variance is unknown
2. comparing two samples
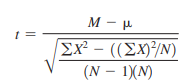
T test for a single sample
A statistical test used to determine if the mean of a single sample differs significantly from a known or hypothesized population mean. It's used to compare a sample's mean to a specific value, often a population mean or a theoretical value.
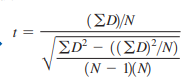
T-test for dependent means (paired t-test)
A test that compares the means of two related groups where the measurements are taken on the same individuals; focuses on differences within individuals or matched pairs, rather than differences between different groups of individuals (Ex. Measuring the same students' test scores before and after a new teaching method, Comparing the same patients' blood pressure before and after taking a new medication, Evaluating the same athletes' performance on a new versus an old baseball bat)
Biased estimate
Estimate of a population parameter that is likely systematically to overestimate or underestimate the true value of the population parameter. For example, SD2 would be a biased estimate of the population variance (it would systematically underestimate it).
Unbiased estimate of the population variance (S2 )
Estimate of the population variance, based on sample scores, which has been corrected so that it is equally likely to overestimate or underestimate the true population variance; the correction used is dividing the sum of squared deviations by the sample size minus 1, instead of the usual procedure of dividing by the sample size directly.
Degrees of freedom (df)
Number of scores free to vary when estimating a population parameter; usually part of a formula for making that estimate—for example, in the formula for estimating the population variance from a single sample, the degrees of freedom is the number of scores minus 1. (N-1) AKA estimated population variance
t distribution
A mathematically defined curve that is the comparison distribution used in a t test.
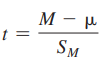
t-score
The number of standard deviations away from the mean of the t-distribution (similar to a z-score)
Repeated measures design
Research strategy in which each person is tested more than once; same as within-subjects design. (AKA within-subjects design)
t test for dependent means
A hypothesis-testing procedure in which there are two scores for each person and the population variance is not known; it determines the significance of a hypothesis that is being tested using difference or change scores from a single group of people
difference scores
Difference between a person’s score on one testing and the same person’s score on another testing; often an after-score minus a before score, in which case it is also called a change score
Assumption
A condition, such as a population’s having a normal distribution, required for carrying out a particular hypothesis-testing procedure; a part of the mathematical foundation for the accuracy of the tables used in determining cutoff values.
Robustness
An extent to which a particular hypothesis-testing procedure is reasonably accurate even when its assumptions are violated