BMS 590 Gross Anatomy H&N Oral cavity
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
What are the Oral region components ?
Oral Cavity,
Teeth,
Gingivae
tongue
palate
palatine tonsils
what is Vestibule?
space between lips and cheeks and teeth and gingivae
What are the part of the Oral cavity proper boundaries ?
Anterolaterally
Roof
Floor
Posteriorly
What is in the anterolaterally part of the cavity ?
dental arches
what is in the roof of the oral cavity ?
hard and soft palate
What is in the floor of the oral cavity ?
tongue and mucous membrane
What is in posteriorly part of the oral cavity ?
communicates with oropharynx
What are the lips ?
musculofibrous folds surrounding the mouth formed of skin exteriorly and mucous membrane internally, between these is the obicularis oris m.
What is the nasolabial sulk ?
shallow depressions attached to upper lip
What are the parts of the lips?
Nasolabial
Mentolabial
Labial frenulum
Philtrum
Vermilion
What is the mentolabial sulci ?
shallow depression attached to the lower lip
What is the labial frenulum?
Fold of mucous membrane in the midline, extending from vestibular gingiva to mucosa of upper and lower lip?
What is the philtrum ?
depression aboe upper lips and below nose in the midline
what is the vermilion ?
exposed red portion of the upper and lower lips
What is apart of the oral cavity of the vasculature ?
upper lip vasculature
lower lip vasculature
What is the Upper lip Vasculature?
superior labial branches of the facial and infraorbital aa.
what is the lower lip vasculature?
inferior labial branches of facial and mental aa.
What is apart of the nerves of the oral cavity ?
upper lip nerves
lower lip nerves
What is the Nerves of upper lip?
Superior labial branches of the infraorbital nerve (CN V2)
What is the Nerves of lower lip?
Inferior labial branches of the mental nerve (CN V3)
What is the Gingivae?
fibrous tissue covered with mucous membrane
What is are teeth ?
participate in mastication and articulation
What are deciduous teeth?
20 teeth in children
What are permannent teeth ?
32 in adults
What are the types of teeth ?
incisors,
canines,
premolars,
molars
What is the Incisors?
thin cutting edges
What is the Canines?
single prominent cones
what are the premolars ?
two cusps (bicuspids)
What are the Molars ?
three or more cusps
What are the Surfaces of teeth ?
Vestibular (Buccal or labial),
lingual,
medial,
distal,
occlusal
What is the vestibular (labial or buccal) surfce of the teeth ?
outwards
What is the vestibular surface of the teeth ?
inwards, on side of tongue
What is the Medial surface of the teeth ?
toward facial portion of cranium. contact surface.
What is the Distal surface of the teeth ?
towards the middle on cranium (back side) contact surface
What is the Occlusal surface of the teeth ?
masticatory surface, biting surface
What are the Parts of teeth ?
crown, root, neck, dentine, enamel, cement, pulp cavity, root canal, periodontist, periodontal ligament, dento-alveolar syndesmosis
What is the crrown of tooth?
project from gingivae
What is the Neck of tooth?
between crown and root
What is the Root of tooth?
below neck, fixed in the tooth socket by periodontist
What is the Dentine of tooth?
composes most of tooth, contains pulp cavity
What is the Enamel of tooth?
covers dentine over crown. this is the hardest substance in human body.
What is the cement of the tooth?
covers detin over root
What is the Pulp cavity of tooth?
covered by dentin, contains connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerves
What is the Root canal of tooth?
transmits nerves and vessels to and from pulp cavity through apical foramina
What is the Periodontium of tooth?
collagenous fibers, located between cement of root and periosteum of alveolus
What is the Periodontal ligament?
group of specialized connective tissue fibers that essentially attach a tooth to the alveolar bone within which it sits
What is the Dento-alveolar syndesmosis?
fibrous joint connecting the root of teeth to the bone of maxilla or mandible
what is the Palate ressponbile for ?
-arched roof of mouth and floor of nasal cavities,
-separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavities and nasopharynx,
-superior (nasal) portion covered with respiratory mucosa and the inferior (oral) with oral mucosa.
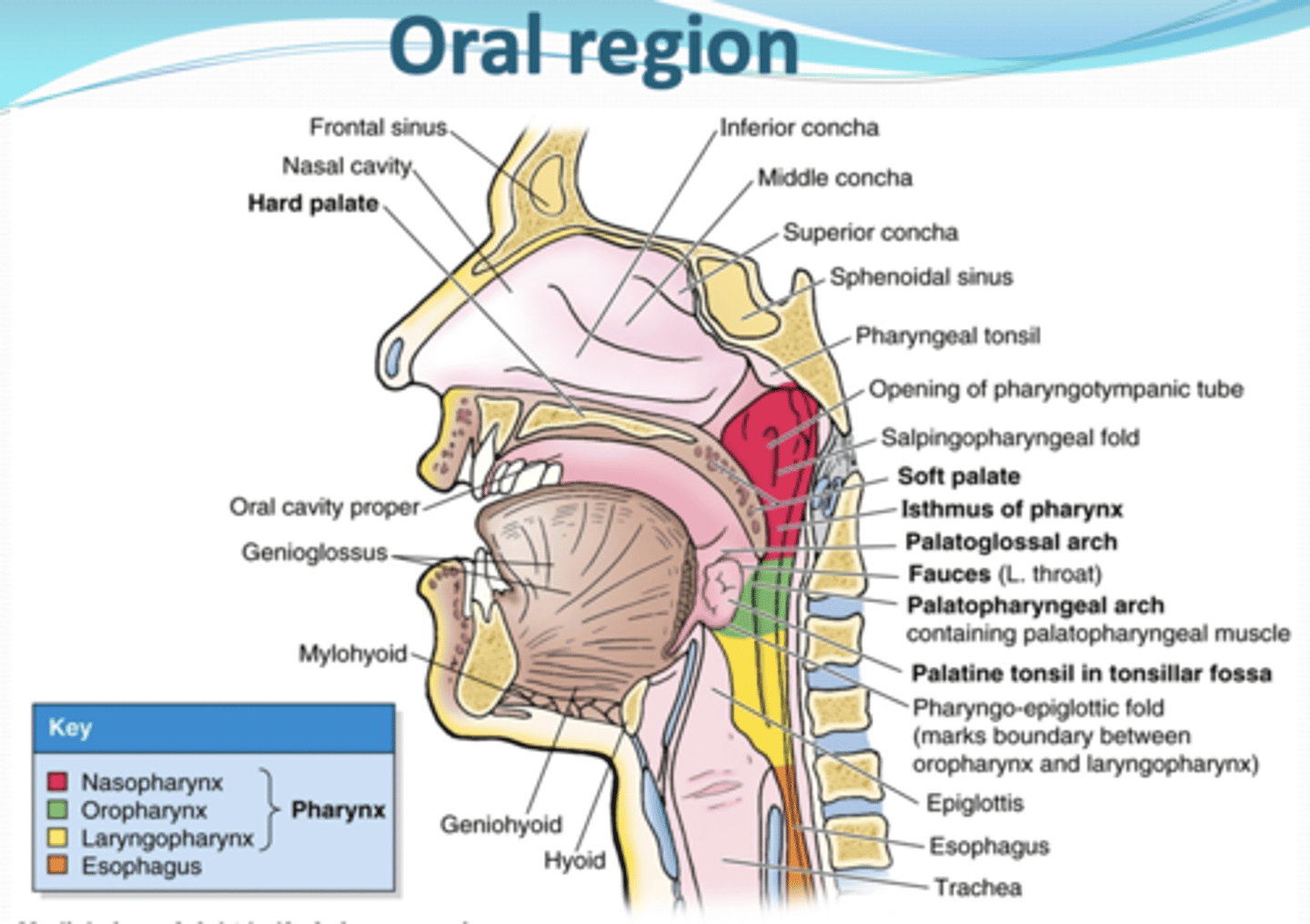
What is the anterior palate is ?
hard palate
What is the posterior palate is ?
soft palate
What does the hard palate ?
occupies anterior 2/3rd of palate. compromised of palatine process of maxillae and palatine bone.
Where is the Incise fossa located in the hard palate?
posterior to central incisor teeth. located at hard palate.
What is the Nasopalatine artery and nerve in the hard palate?
pass from nose through foramina leading into the incisive fossa.
What is the Greater palatine foramen (GPF) in the hard palate?
medial to 3rd molar. Nerve and artery emerge from this foramen and run anteriorly to meet and anastomose with the nasopalatine nerve and artery and innervate and supply hard palate.
What is the Lesser palatine foramina in the hard palate?
Posterior to GPF. Nerve and artery energy from this foramina and run posteriorly to innervate and supply soft palate.
What is the mucous membrane in the hard palate?
tightly bound to and covers hard palate
What is the transverse palatine folds in the hard palate ?
assist with manipulation of food during mastication
What is the palatine raphe in the hard palate ?
extending posteriorly from the incisive fossa to the uvula, is a fold of mucosa membrane that represents the site of fusion of palatal processes
What is the Soft palate ?
occupies posterior 1/3rd of palate and is moveable. suspended from the posterior border of hard palate by the palatine aponeurosis.
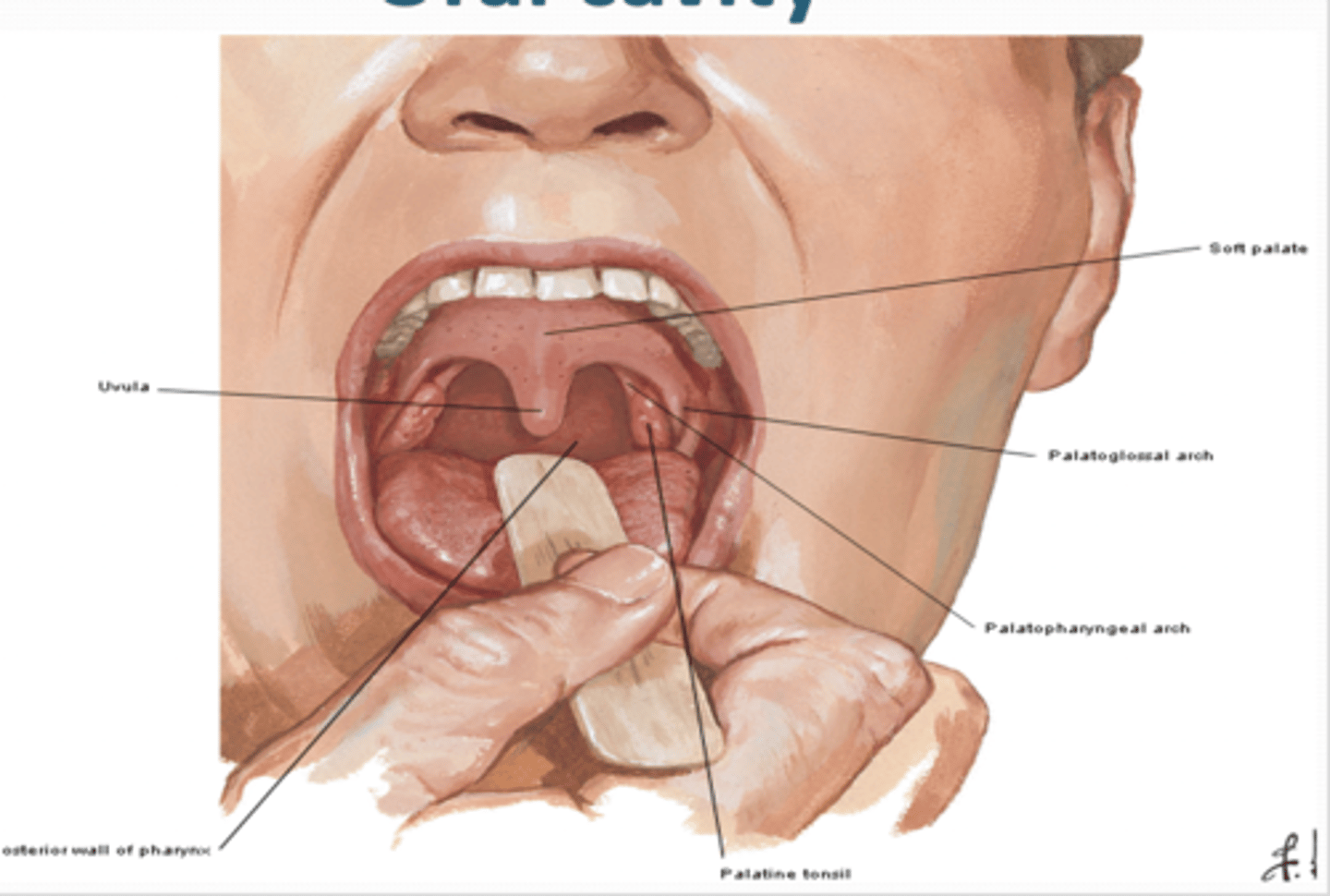
What happens in the soft palate when you sallow ?
During swallowing the ____ tenses to squeeze bolus of food posteriorly and then elevates it posteriorly and superiorly against wall of pharynx to prevent passage of food into nasal cavity
What is the Uvula in the soft palate?
Conical process hanging from posteroinferior curved, free margin of soft palate
What is in the soft palate?
uvula
palatoglossal arch
palatopharyngeal arch
What is the Palatoglossal arch in the soft palate ?
mucous membrane covering the palatoglossal m. Joins soft palate to tongue
What is the Palatopharyngeal arch in the soft palate ?
mucous membrane covering the palatopharyngeal m. Joins soft palate to pharynx
Fauces (L. throat)
space between cavity of mouth and pharynx
Boundaries of Fauces
S: soft palate
I: root of the tongue
L: pillars of fauces (palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal arches)
isthmus of fauces
space between oral cavity and orophaynx
palatine tonsils
masses of lymphoid tissue on each side of oropharynx and are bounded by the palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal arches
Muscles of soft palate
Tensor veli palatini, levator veli palatini, palatoglossus, palatopharyngeus uvular
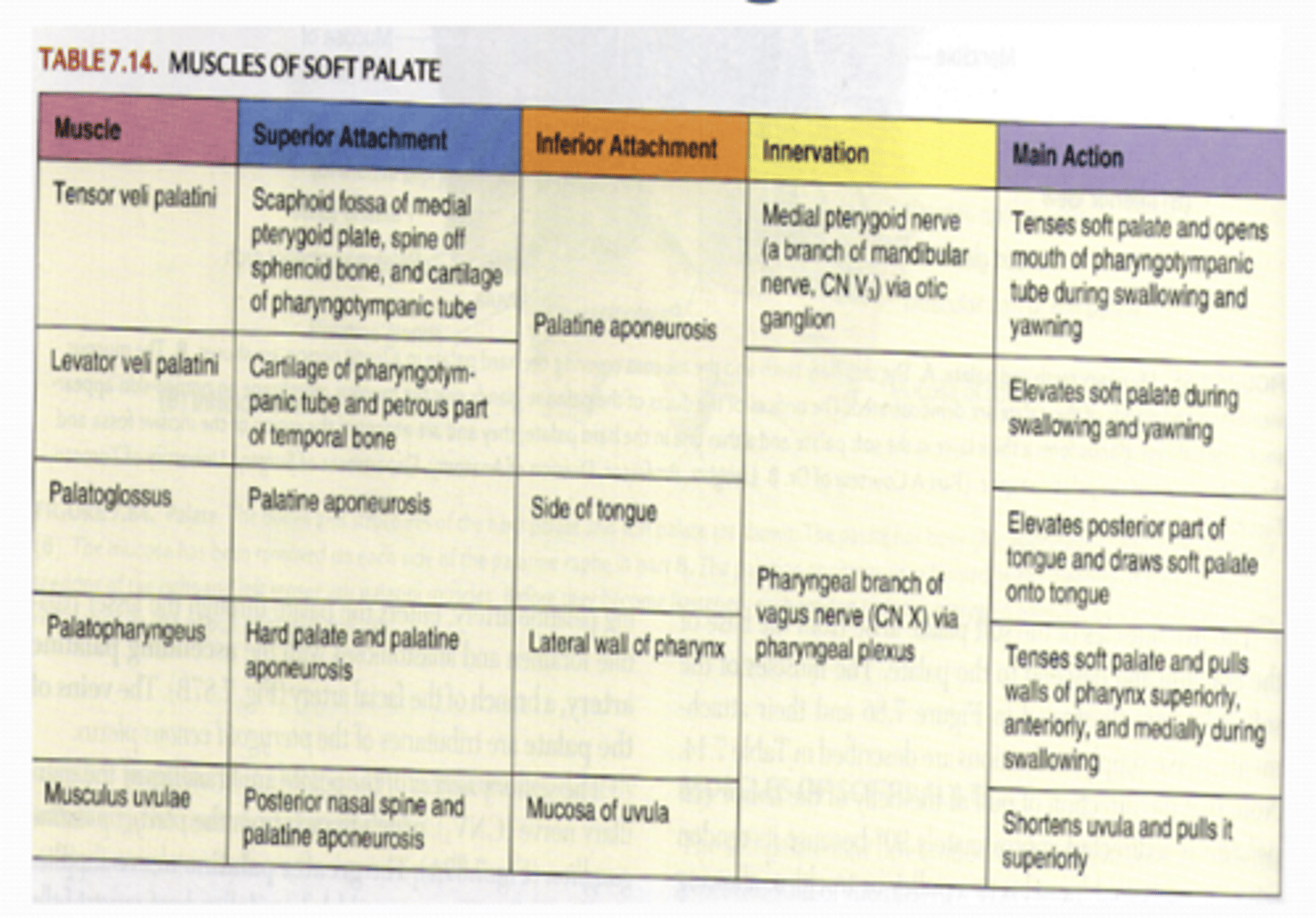
Palatine aponeurosis
flatten, extended tendon of the tensor veli palatini m. that attaches to the posterior border of the hard palate
Tongue
anterior 2/3rd in oral cavity and posterior 1/3rd in oropharynx. participates in articulation, swallowing, taste and oral cleansing
Parts of tongue
root, body, apex
root of tongue
attached posterior portion
body of tongue
between root and apex
apex of tongue
tip of tongue
What are the surfaces of the tongue?
dorsum: (superior surface) terminal sulcus, foramen cecum, midline groove, lingual papillae, vallate, foliate, filiform, fungiform, lingual tonsil
inferior: frenulum, sublingual caruncle (papilla), sublingual folds
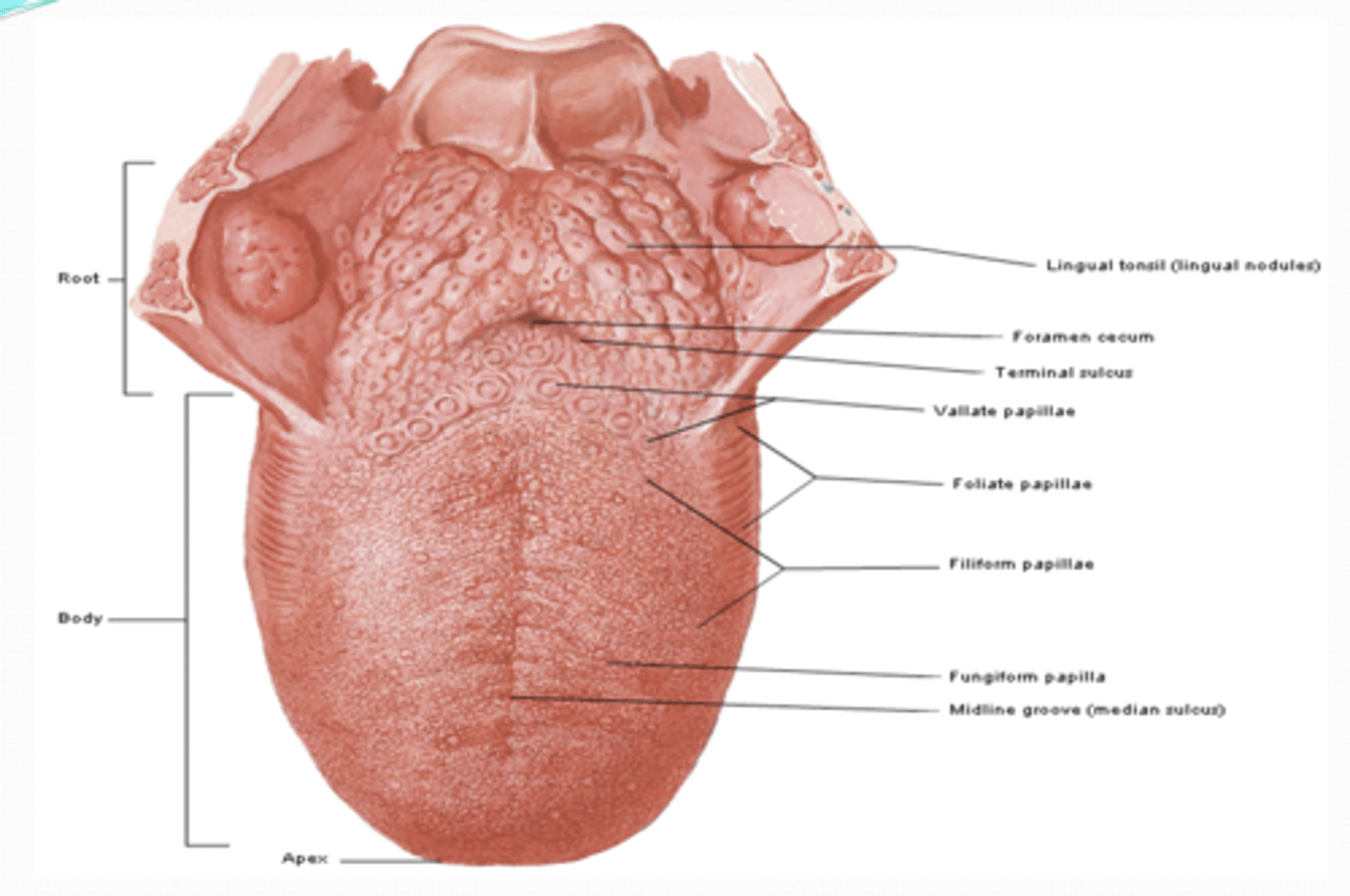
what is the Terminal sulcus in the tongue ?
V-shape demarcation, separating ant. 2/3rd and post. 1/3rd
What is the Foramen cecum in the tongue ?
opening at the end of the terminal sulcus, developmental remnant of the thyroglossus duct
What is the Midline groove in the tongue ?
divides anterior part of tongue into R & L parts
What is the Lingual papillae in the tongue ?
vallate, foliate, and fungiform contain taste rec. and buds
what is the Vallate in the tongue ?
large and flat topped, lie anterior to terminal sulcus in V-shaped row
What is the foliate in the tongue ?
small lateral folds of lingual mucosa
What is the fungiform in the tongue ?
mushroom shaped, scattered among the filiform papillae, most numerous at apex
What is the Lingual tonsil in the tongue ?
cluster of lymphoid nodules on posterior 1/3rd of tongue
What is the Frenulum of the tongue ?
connects tongue to floor of mouth
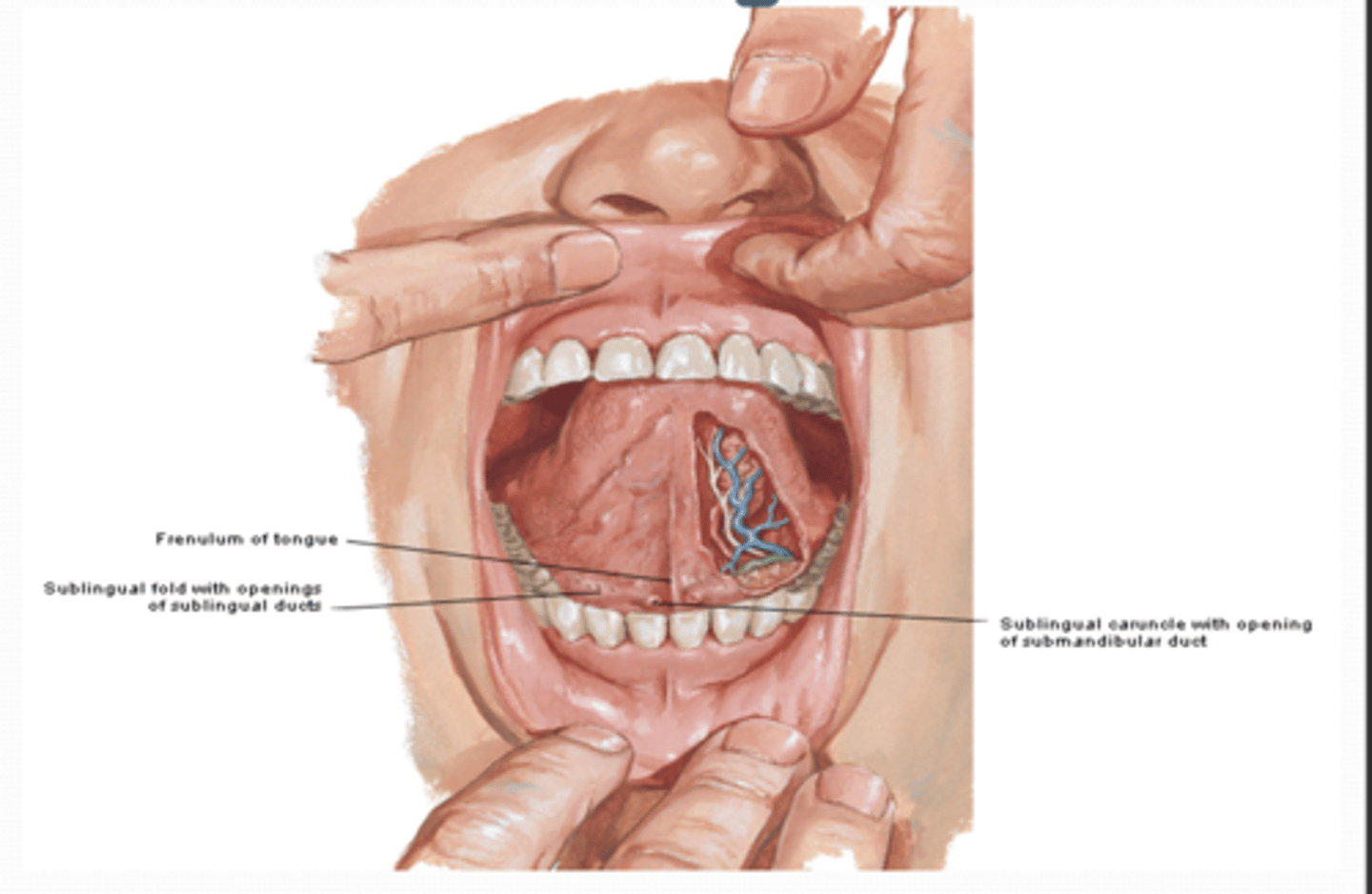
What is the Sublingual caruncle (papilla) tonuge ?
on each side of lingual frenulum, includes the opening of the submandibular gland duct
What is the sublingual folds of the tongue ?
elevations of sublingual mucosa, containing the openings of the sublingual gland ducts
What are the Extrinsic muscles of tongue?
Genioglossus
Hyoglossus
Styloglossus
Palatoglossus
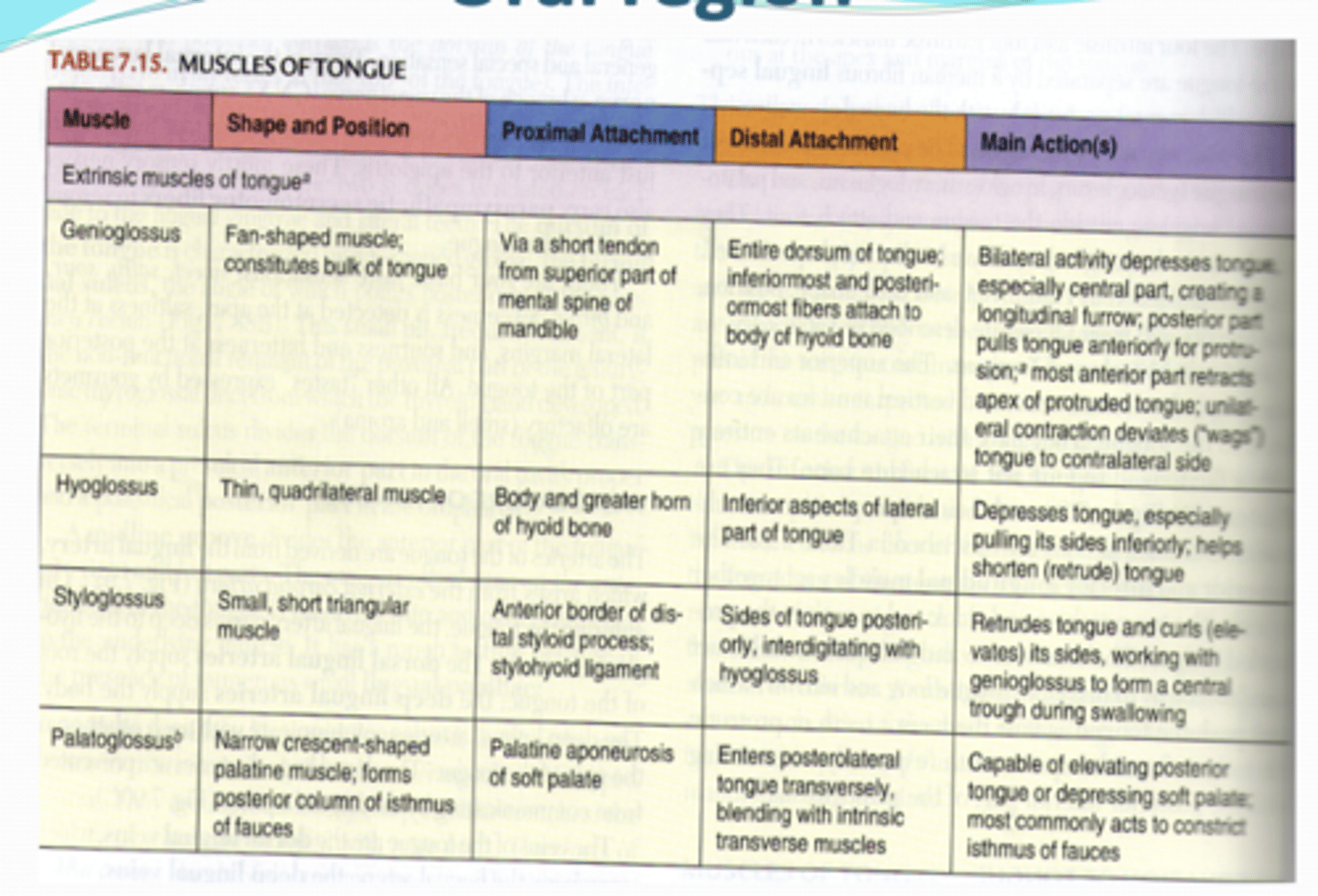
What is the extrinsic muscles of tongue is all innervated by
CN XII except for?
palatoglossus (CN X)
What is the Intrinsic muscles of tongue?
superior longitudinal, inferior longitudinal, transverse, vertical
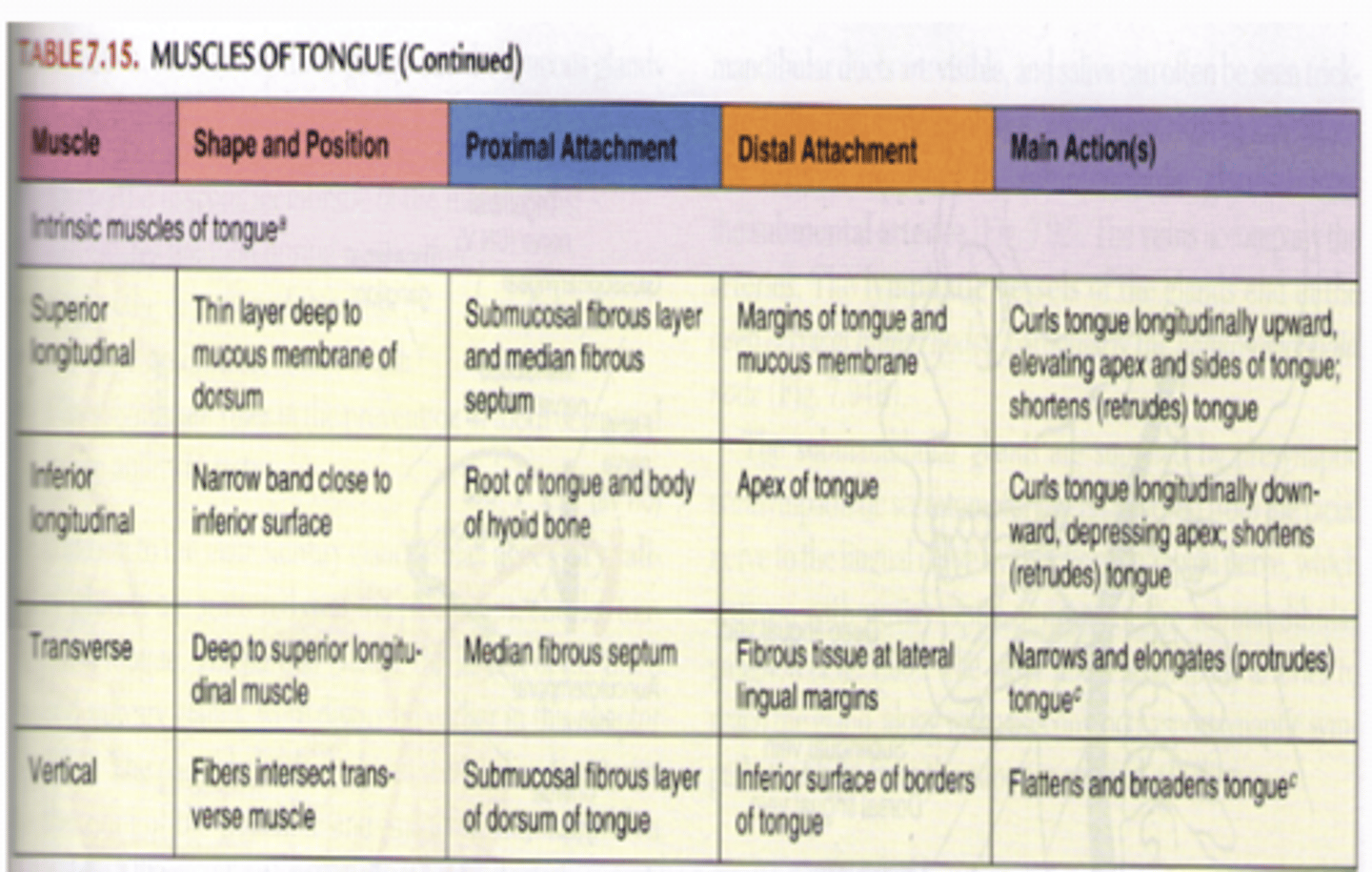
What is the all intrinsic tongue muscles are innervated by?
CN XII (hypoglossal)
What is in the Tongue vasculature?
Lingual artery
- dorsal lingual + deep lingual
Lingual vein
- dorsal lingual +deep lingual
What are the Salivary glands?
parotid, sublingual, and submandibular glands. secret saliva.
What does the secret salivado ?
moisturizes mucous membrane of oral cavity. lubricates food during mastication. begins starch digestion. intrinsic mouthwash, prevents tooth decay. taste.
Parotid glands
largest of the salivary glands
location: anteroinfeior to external acoustic meatus between the ramus of mandible and mastoid process.
Parotid glands Embedded with the gland (superficial -> deep)
Branches of fascial nerve (CN VII)
Retromandibular vein
ECA
Parotid duct
passes anteriorly from the gland, crosses masseter m., pierces the buccinator m., enters oral cavity opposite 2nd maxillary molar.
submandibular glands
Location: along body of mandible in the submandibular triangle, partly superficial and party deep to mylohoid m.
Submandibular duct
runs medially to open on each side of the lingual frenulum in the sublingual caruncle
sublingual glands
smallest and most deeply situated of salivary glands
Location: Lie in floor of mouth between mandible and genioglossus m.