Lab 7: PowerLab 4 - Respiratory Air Flow and Volume
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
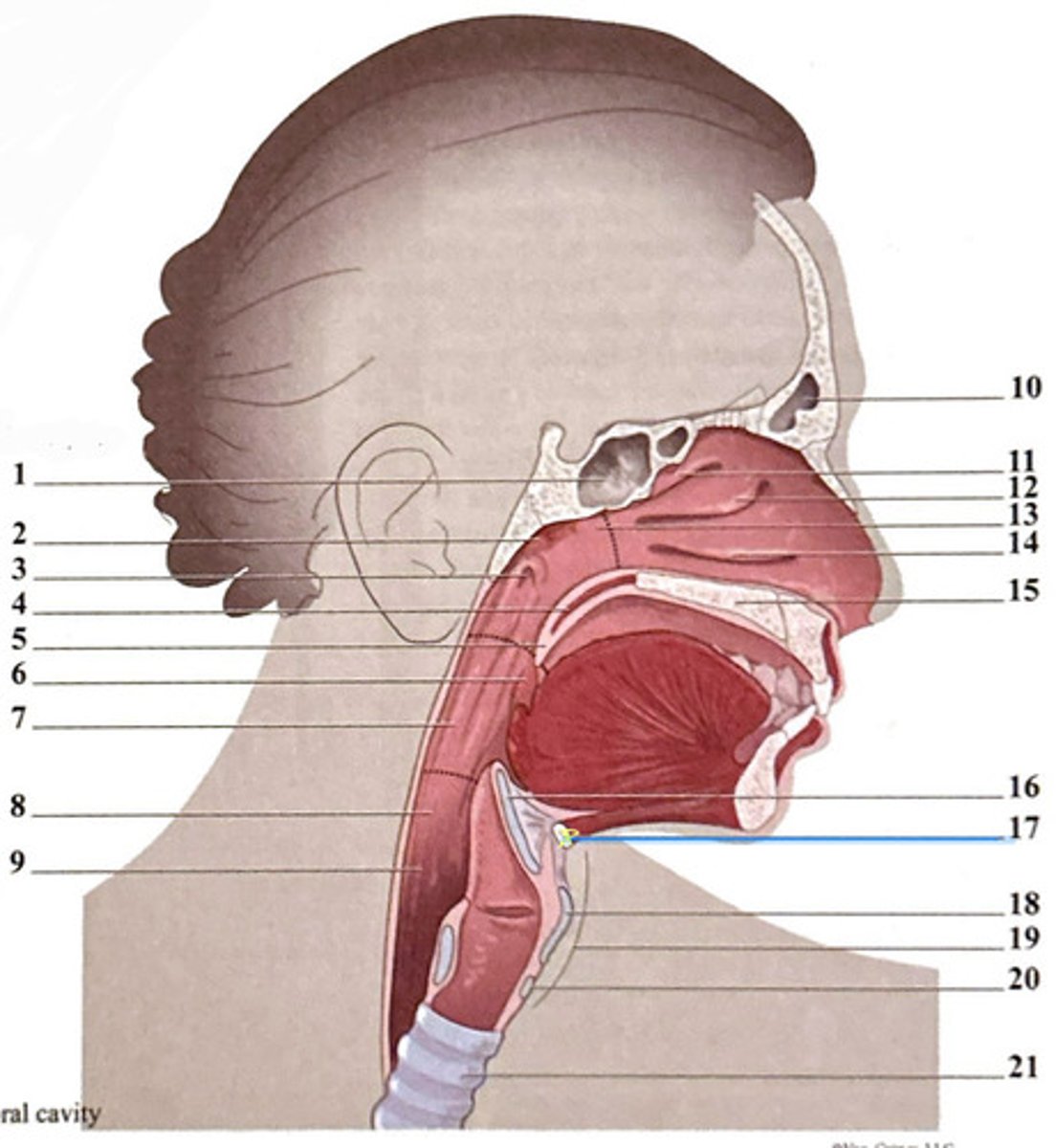
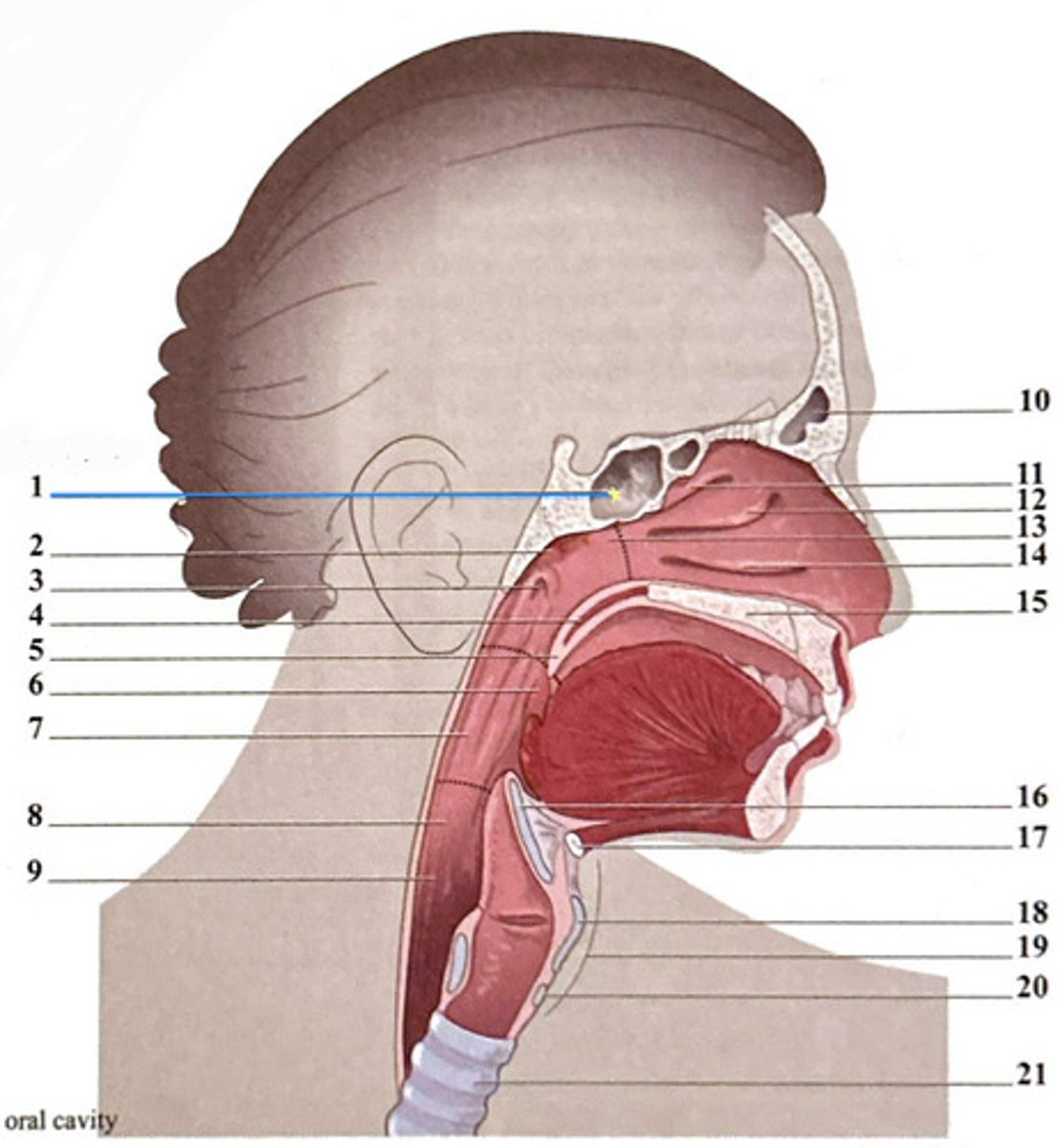
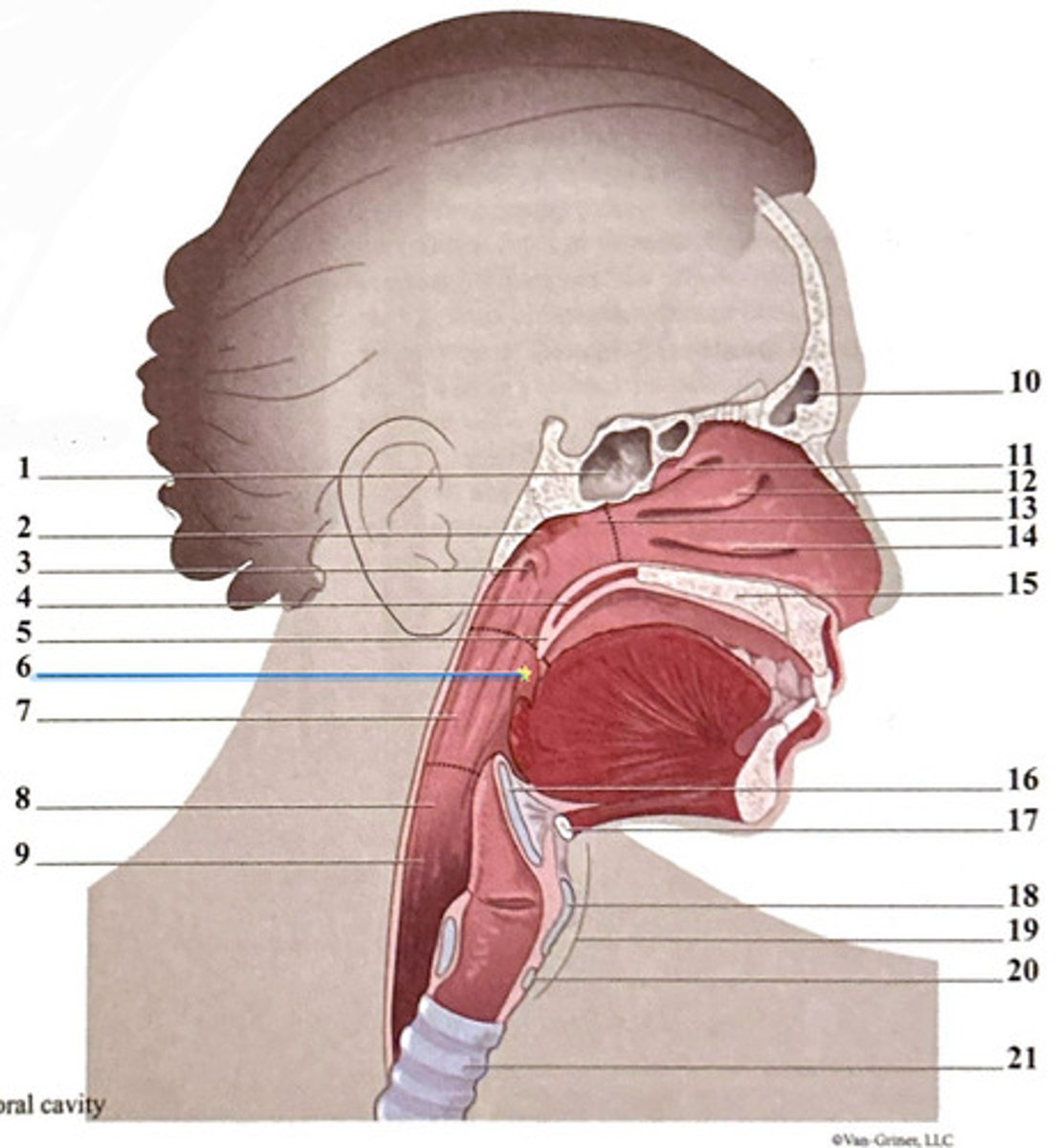
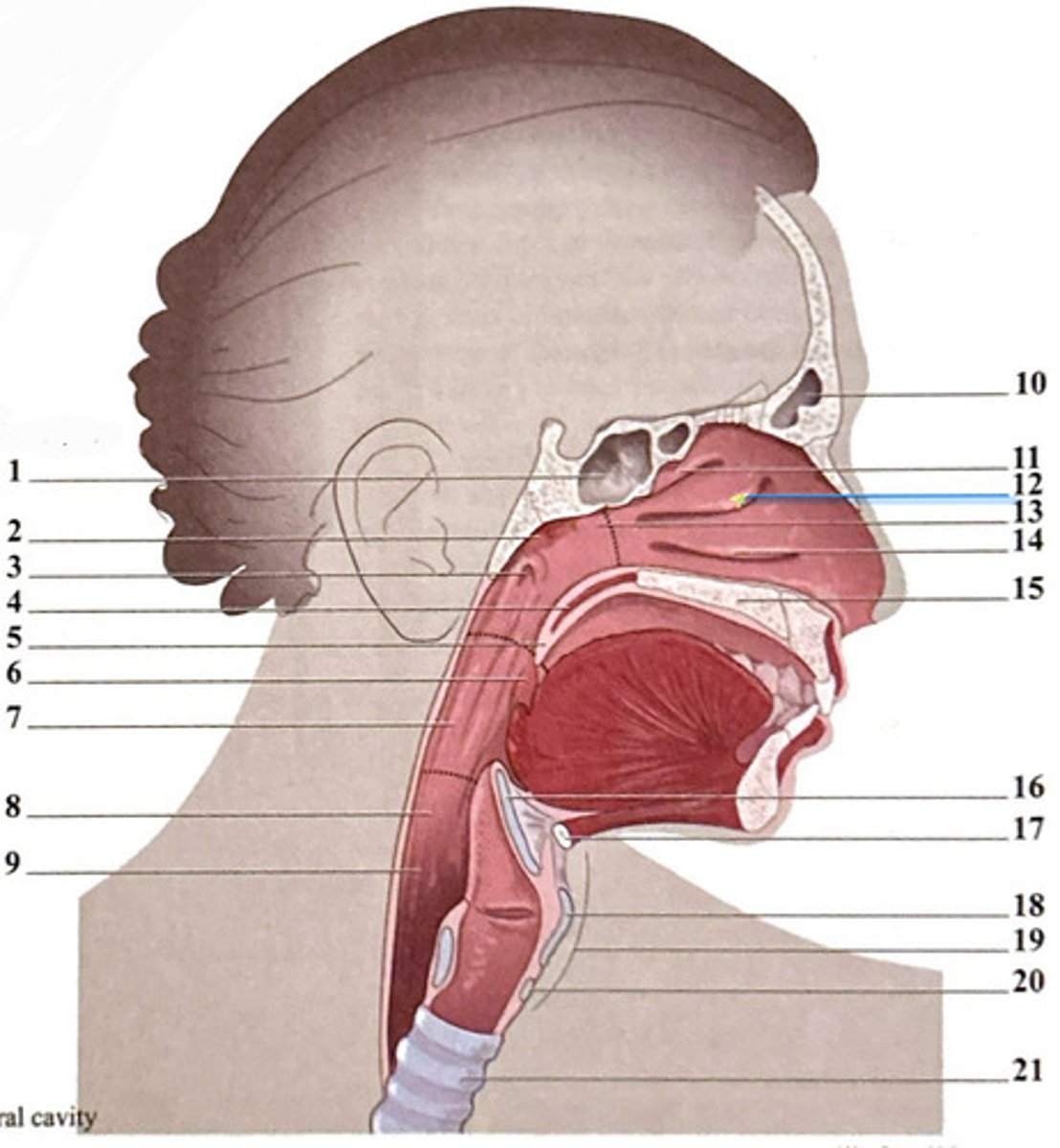
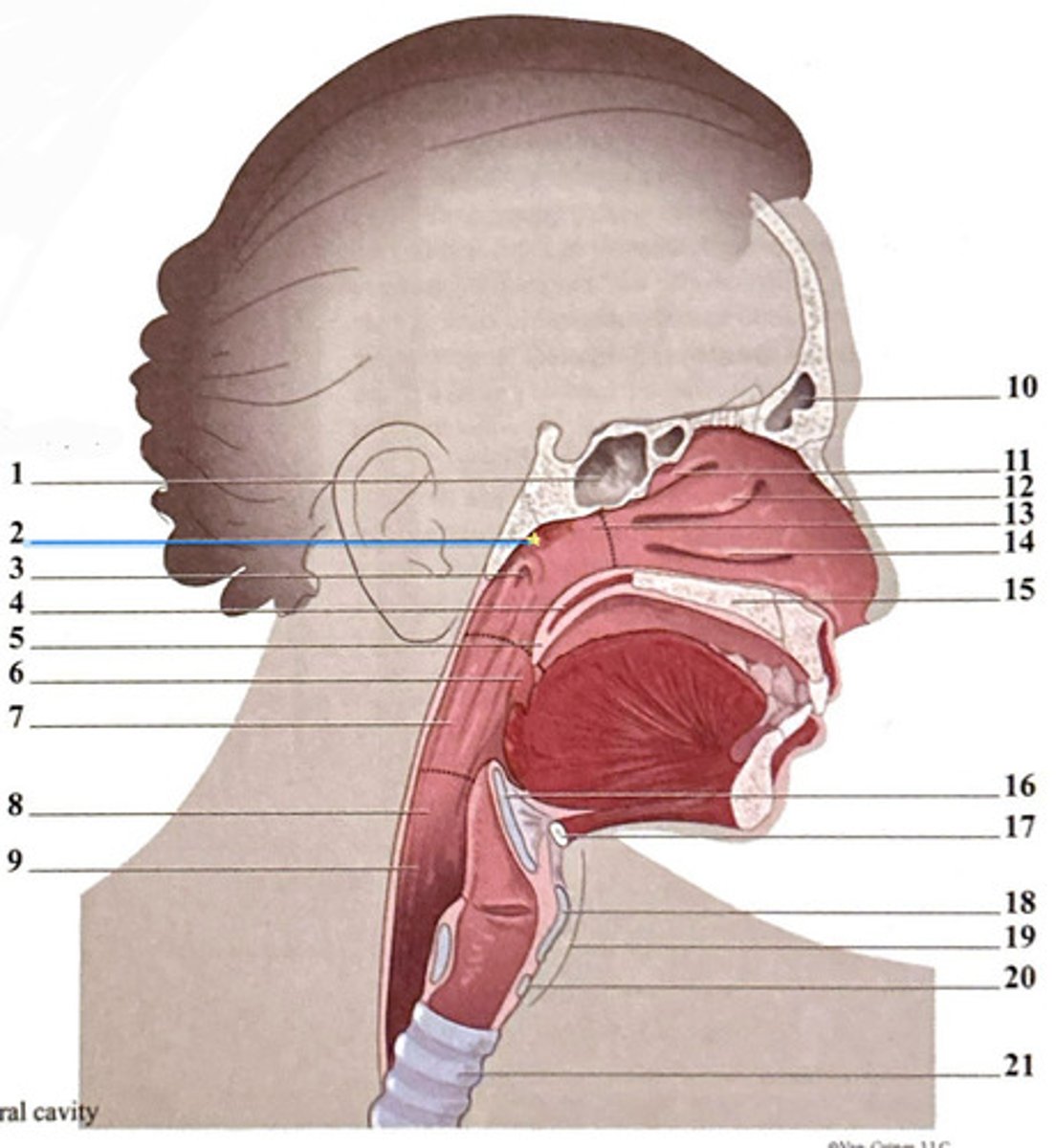
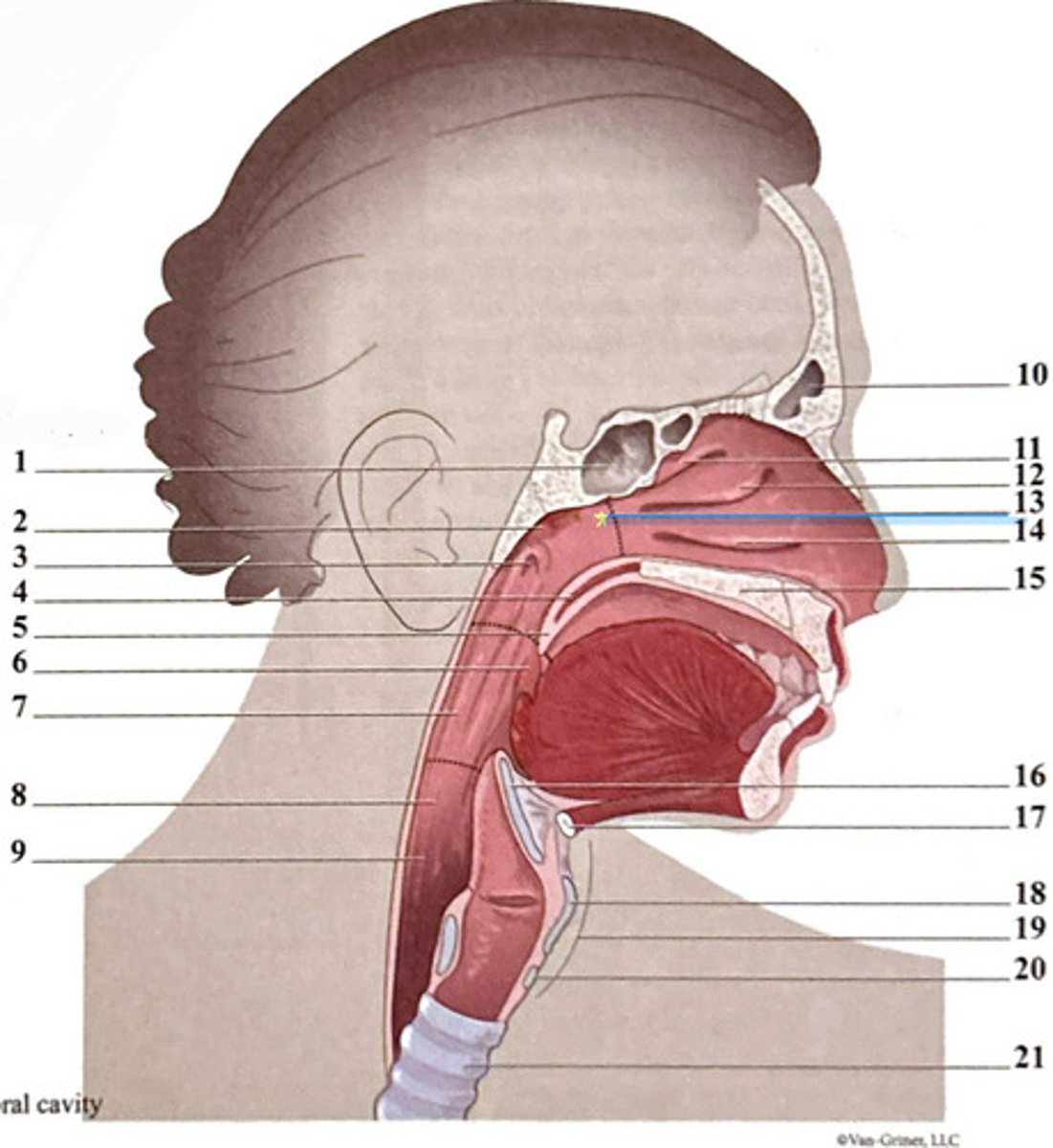
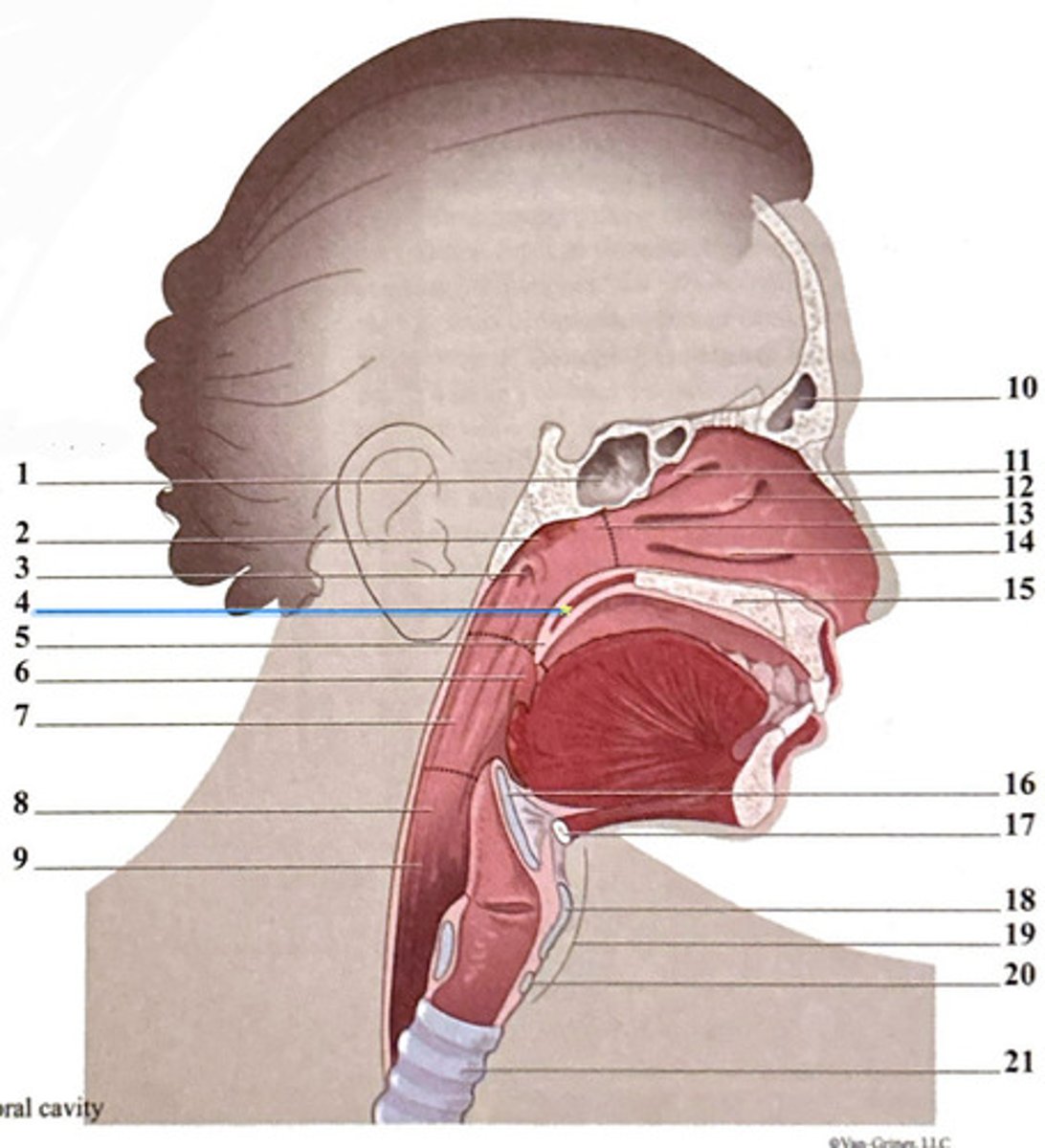
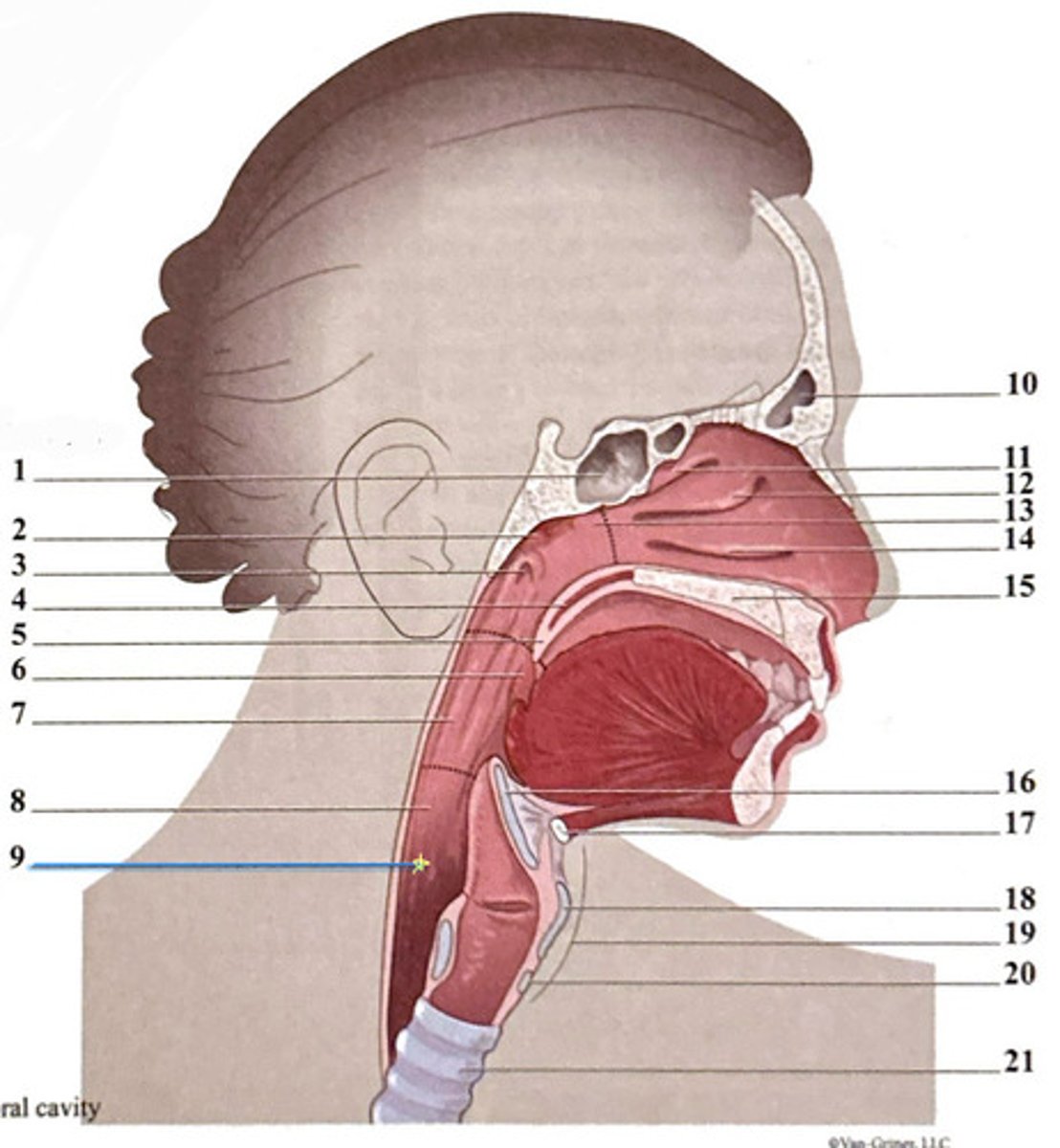
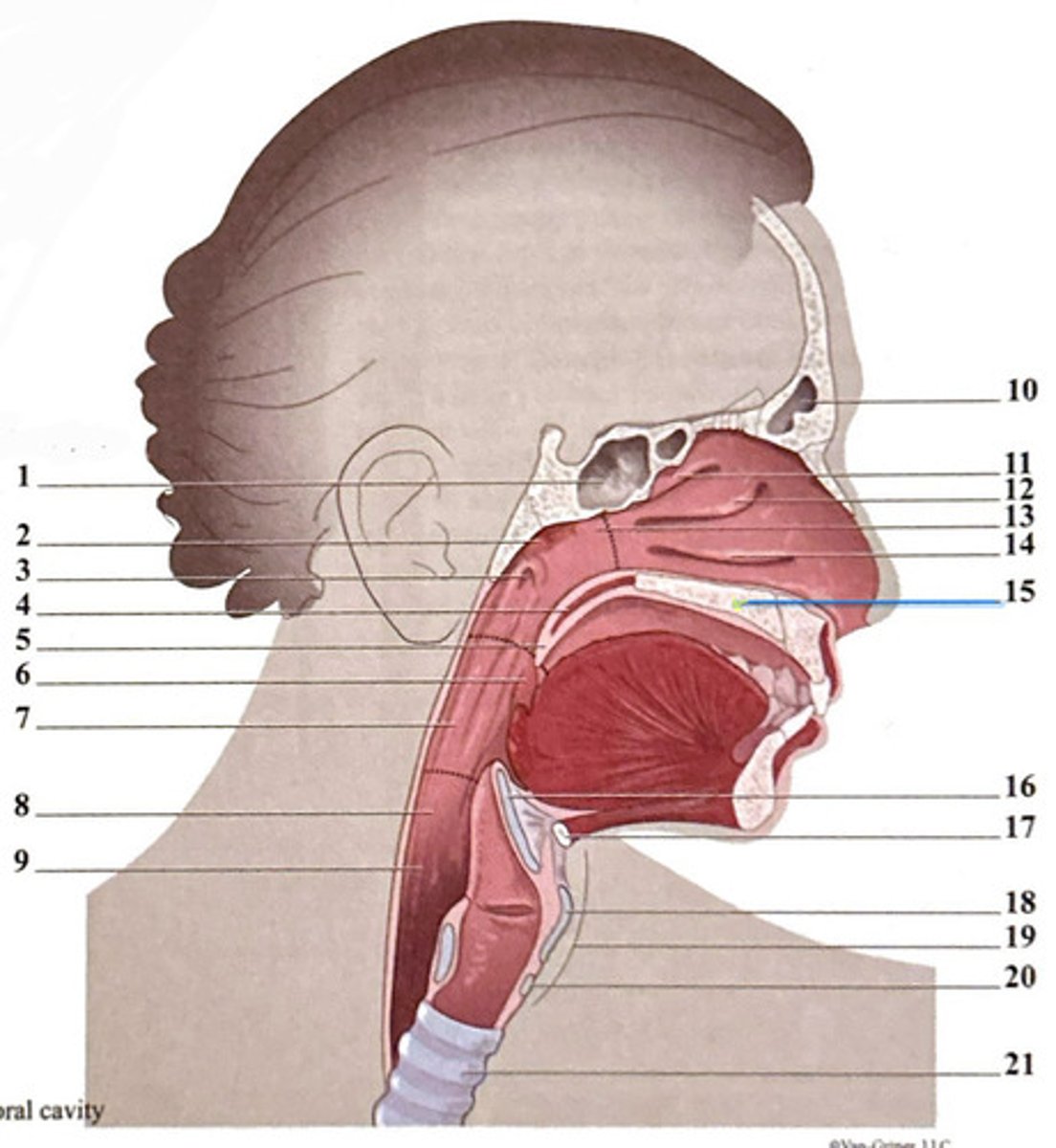
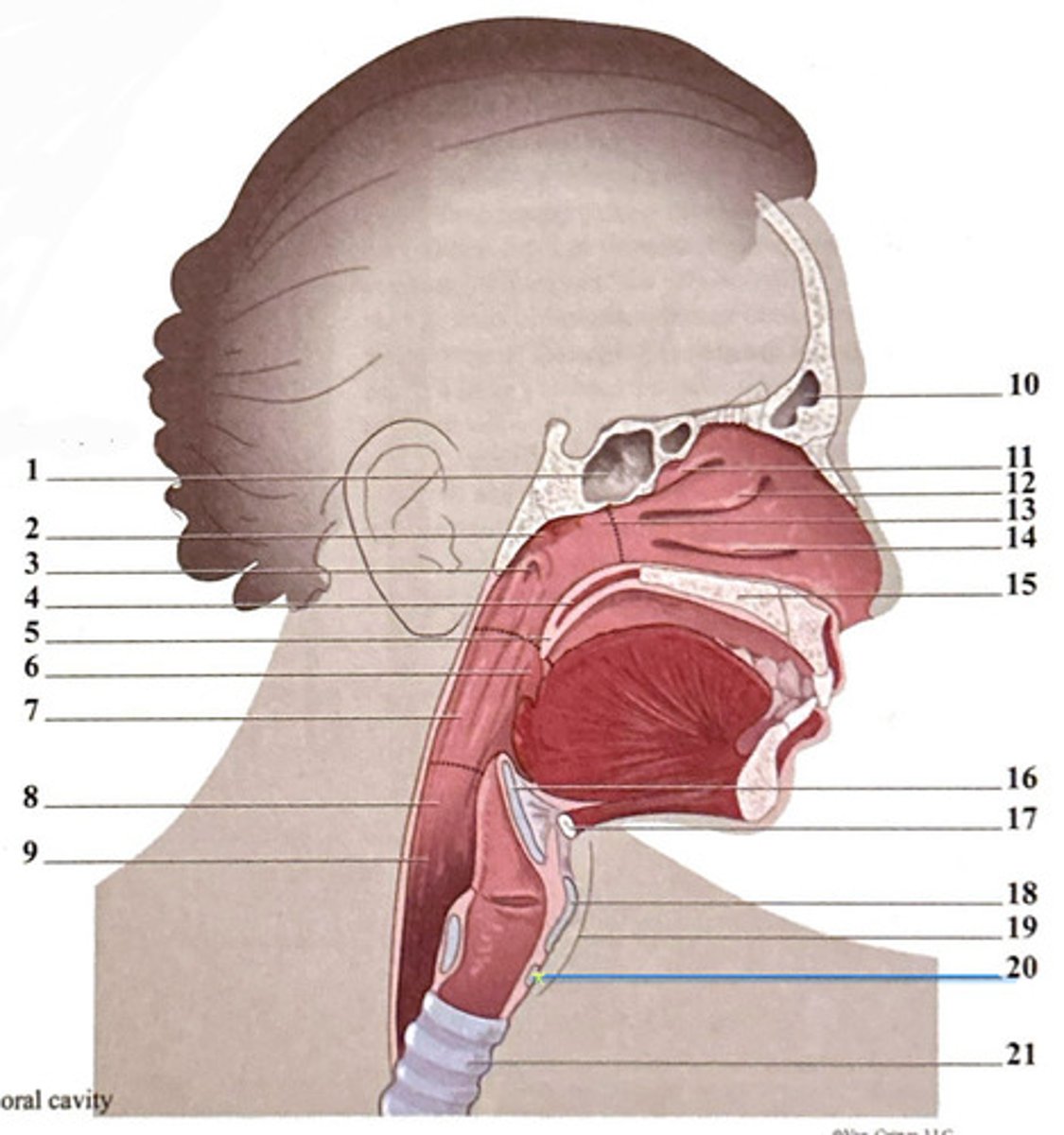
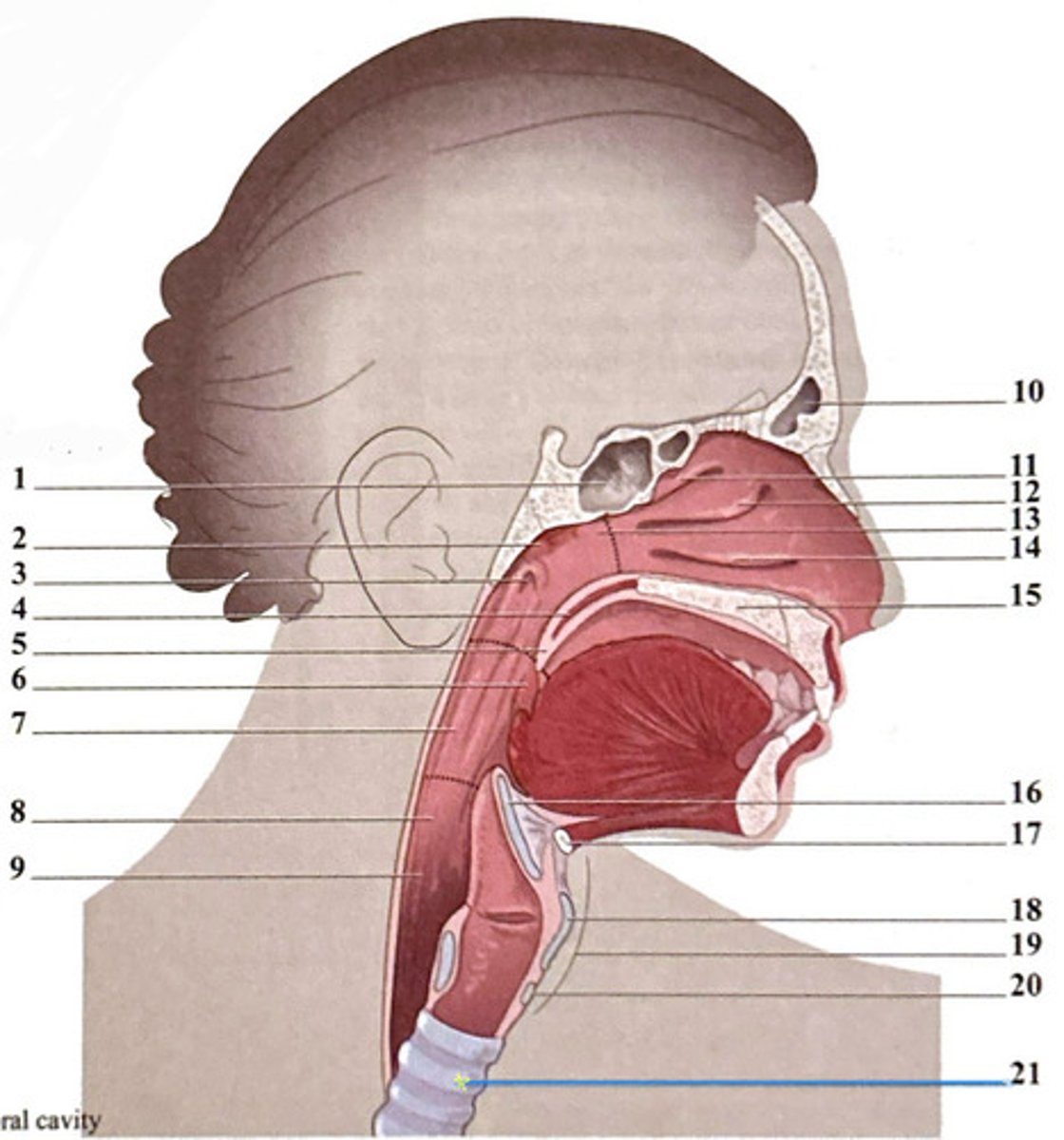
uvula
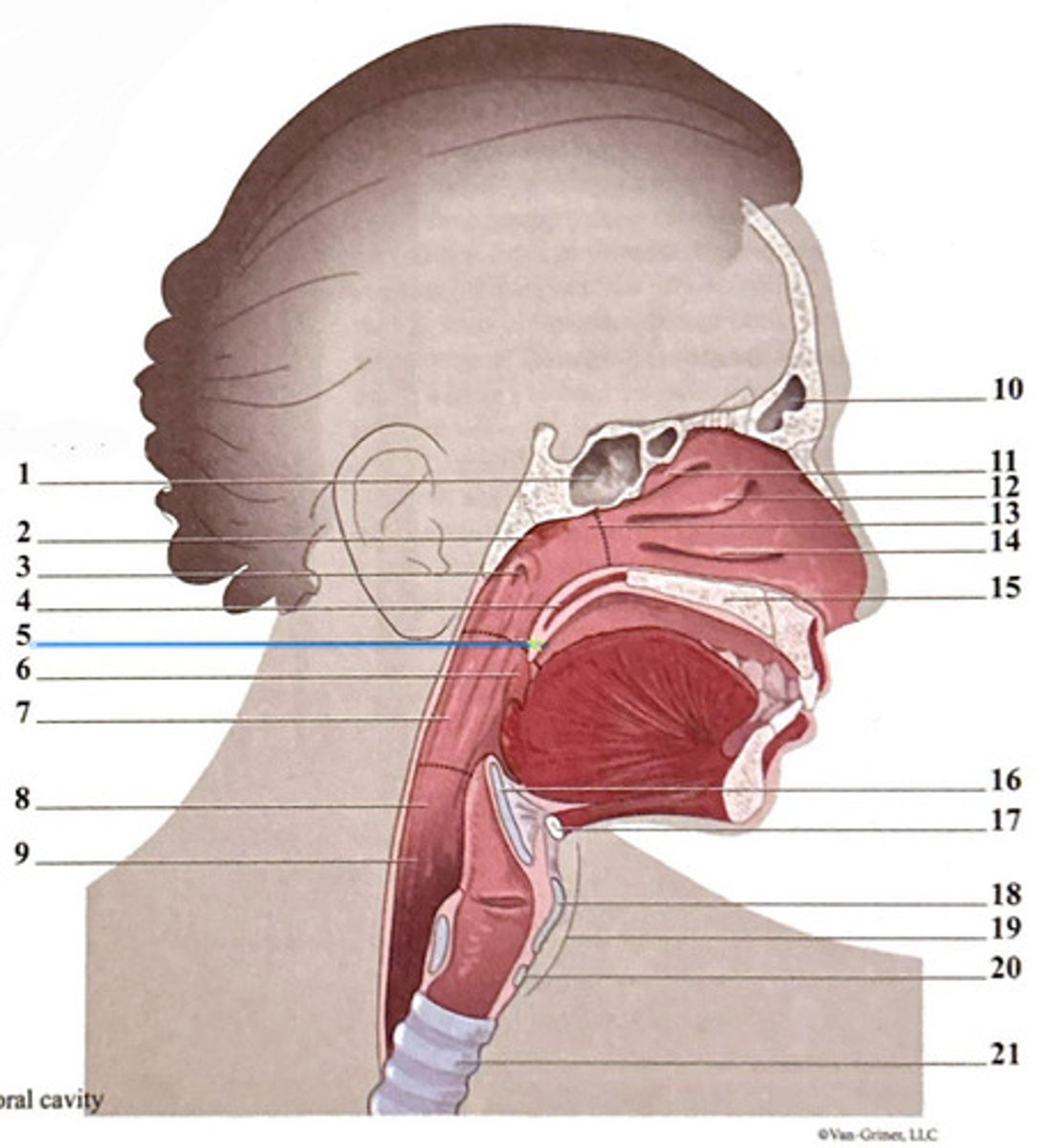
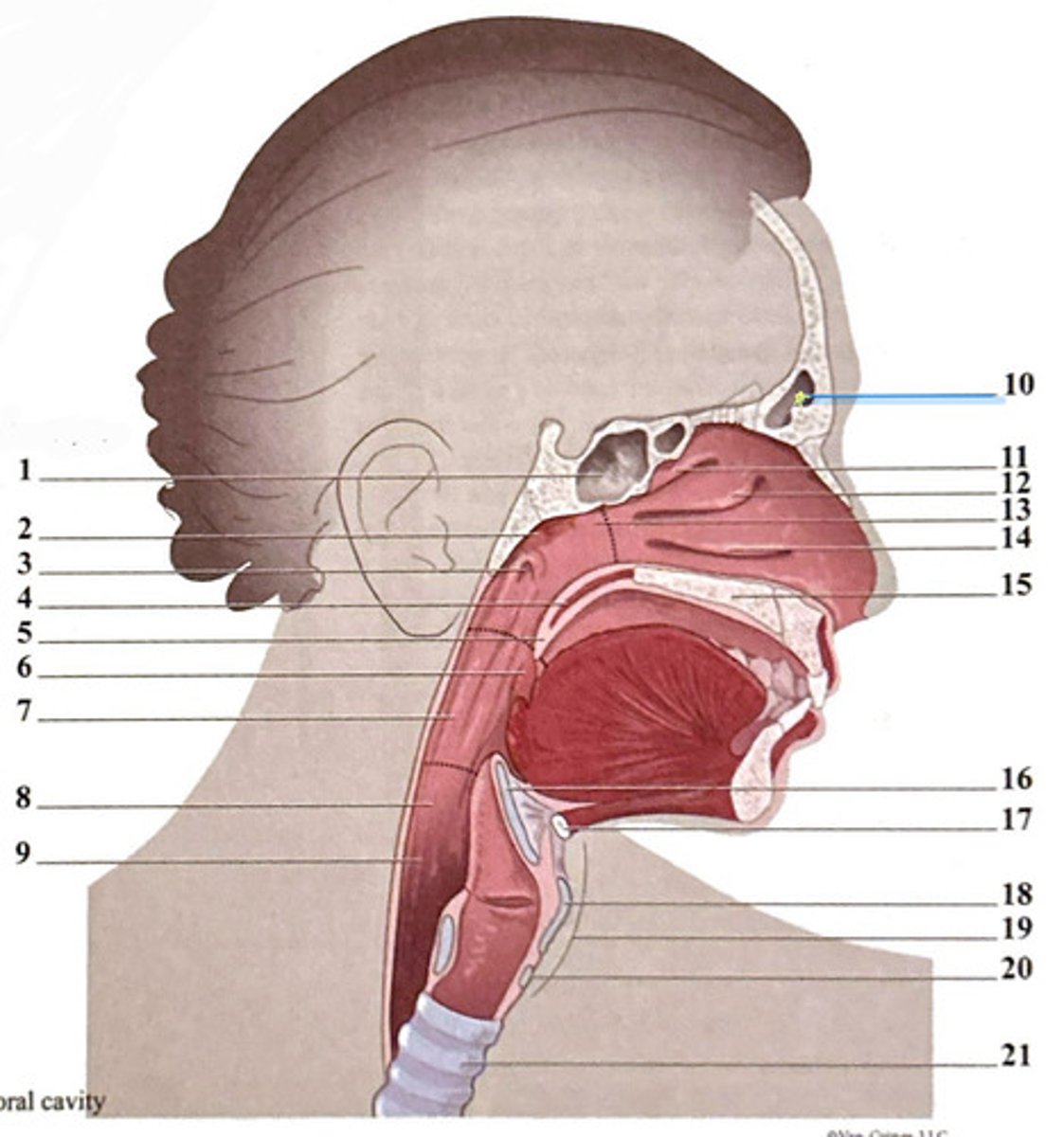
frontal sinus
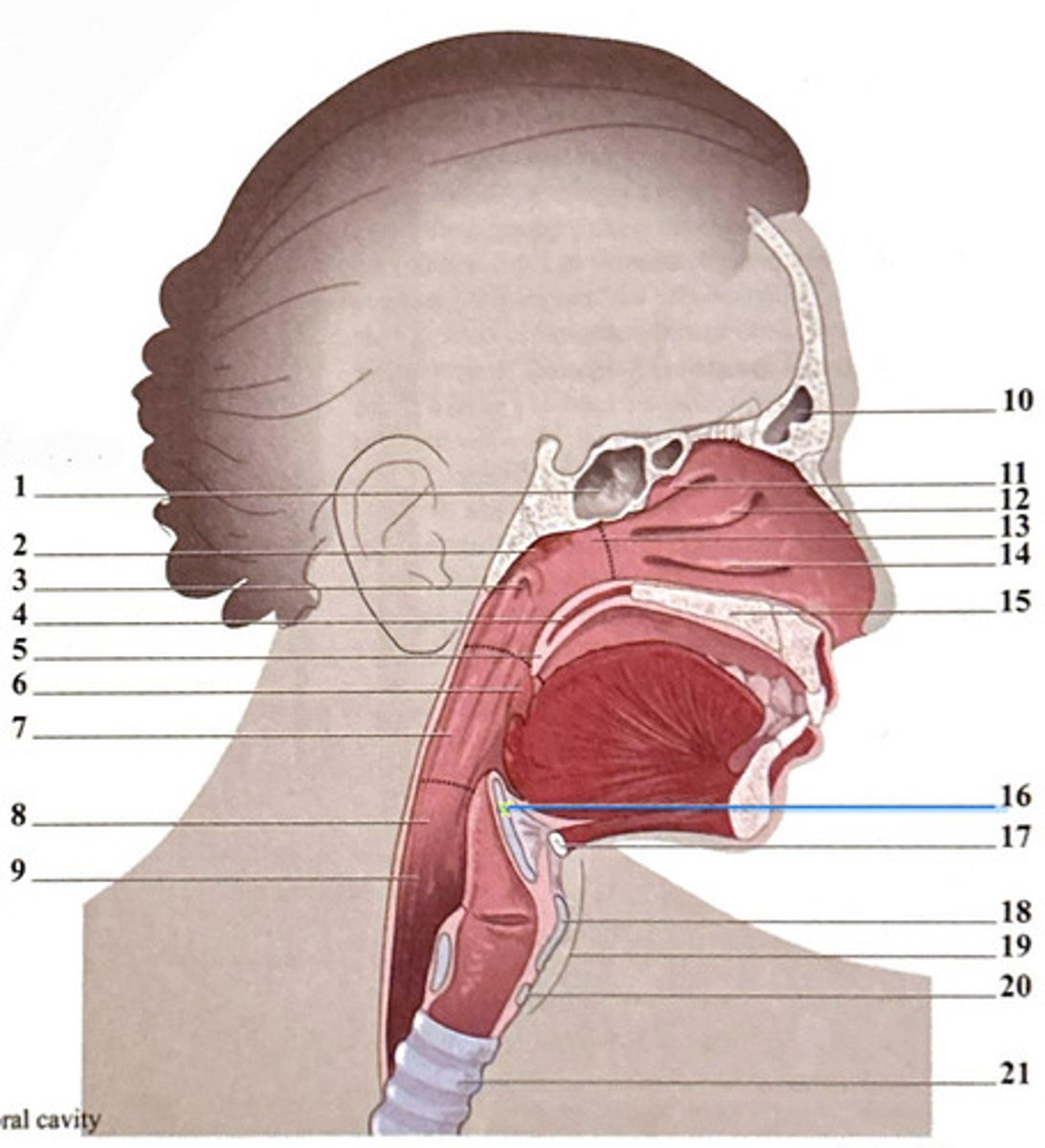
epiglottis
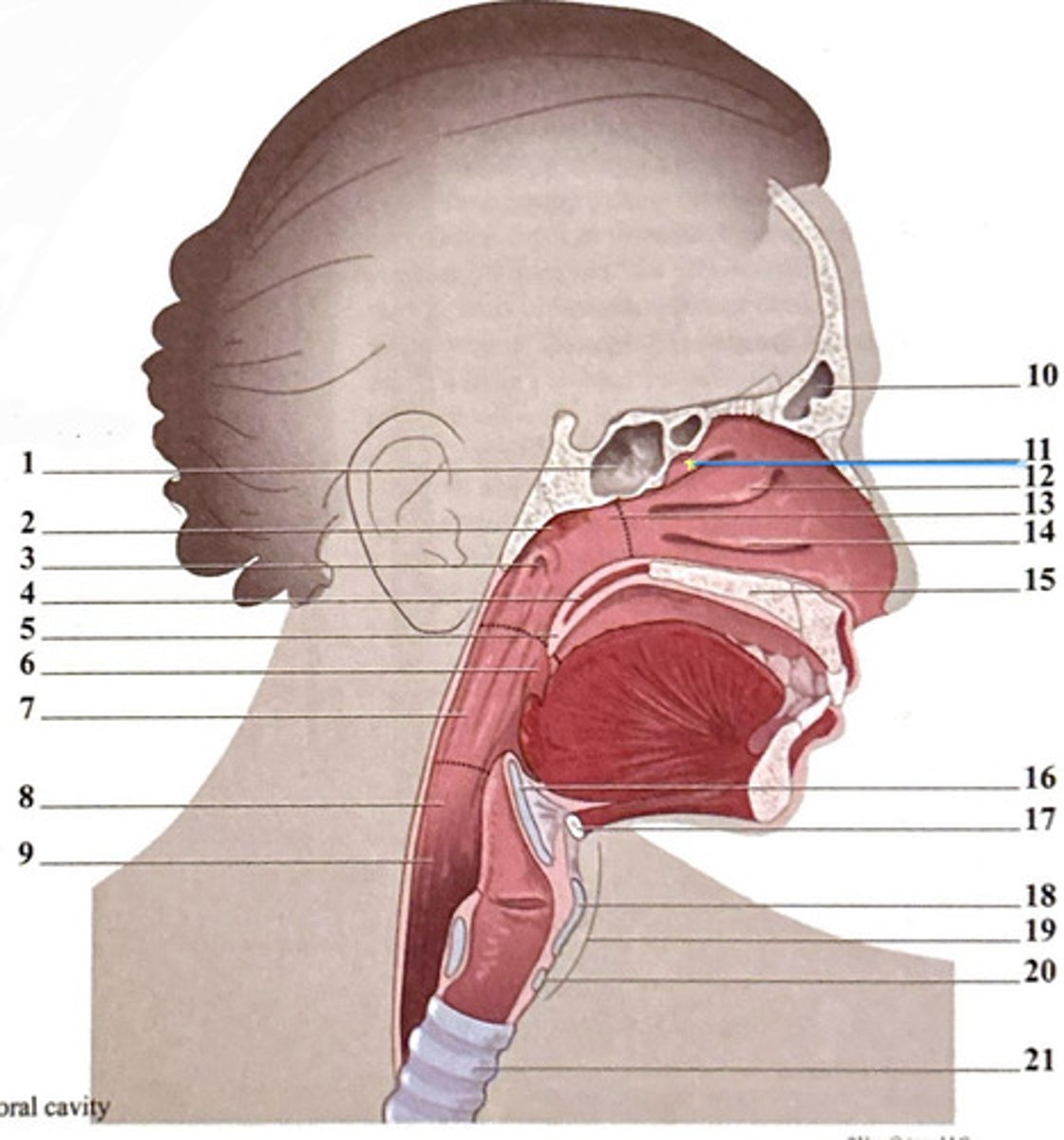
superior nasal concha
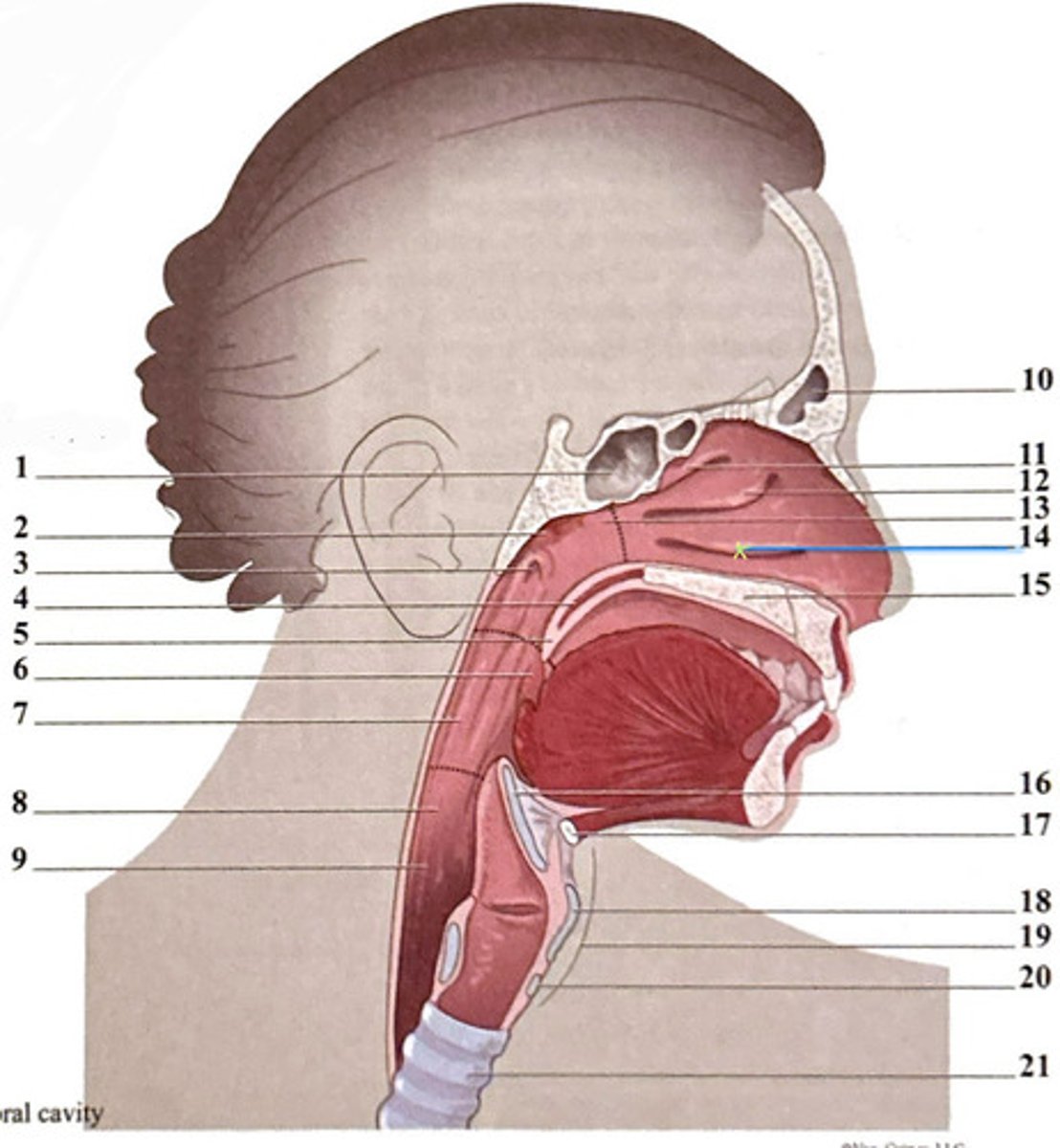
hyoid bone
sphenoidal sinus
palatine tonsil
middle nasal concha
thyroid carilage
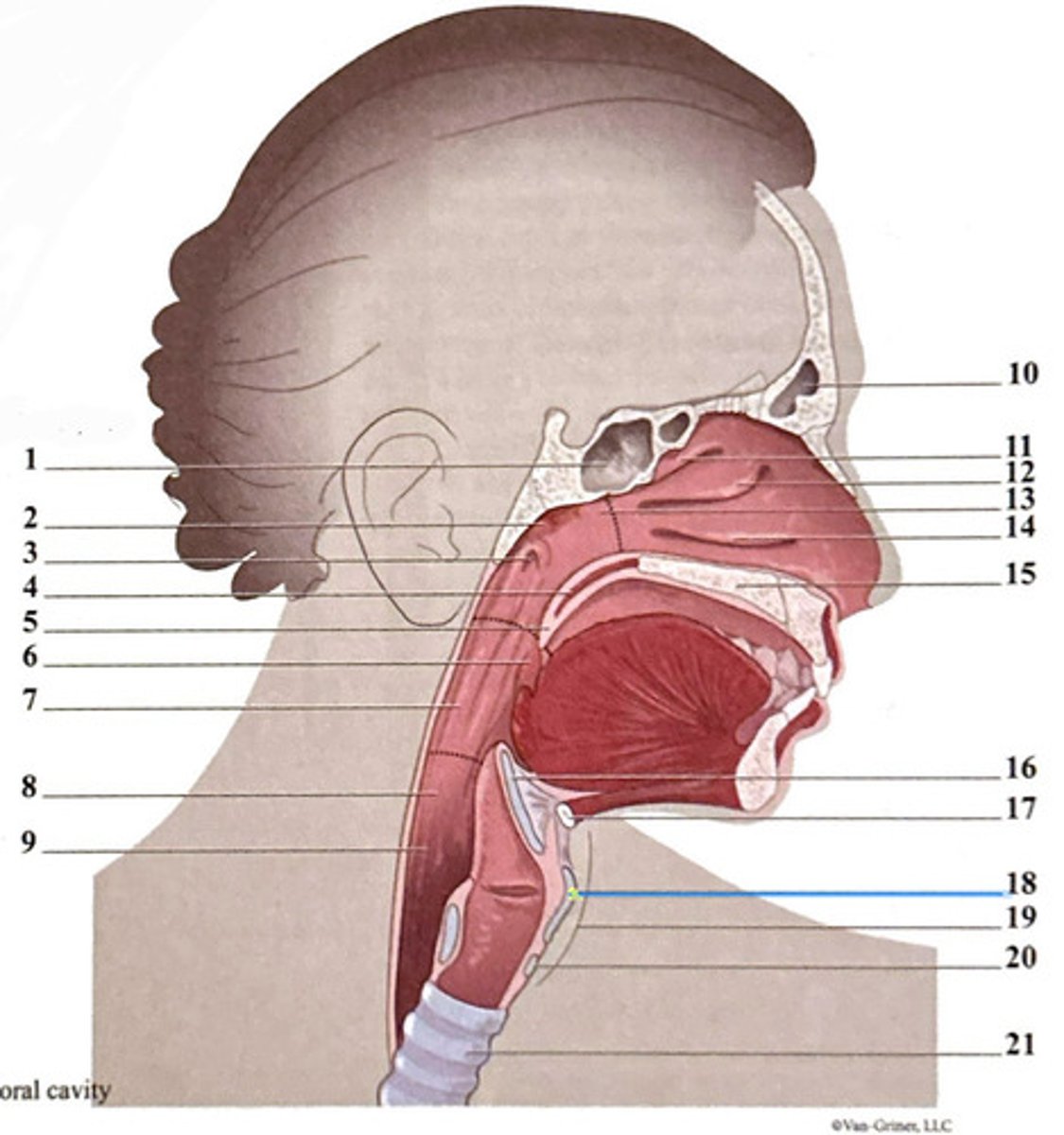
adenoid tonsil
oropharynx
nasopharynx
laryngeal cartilages
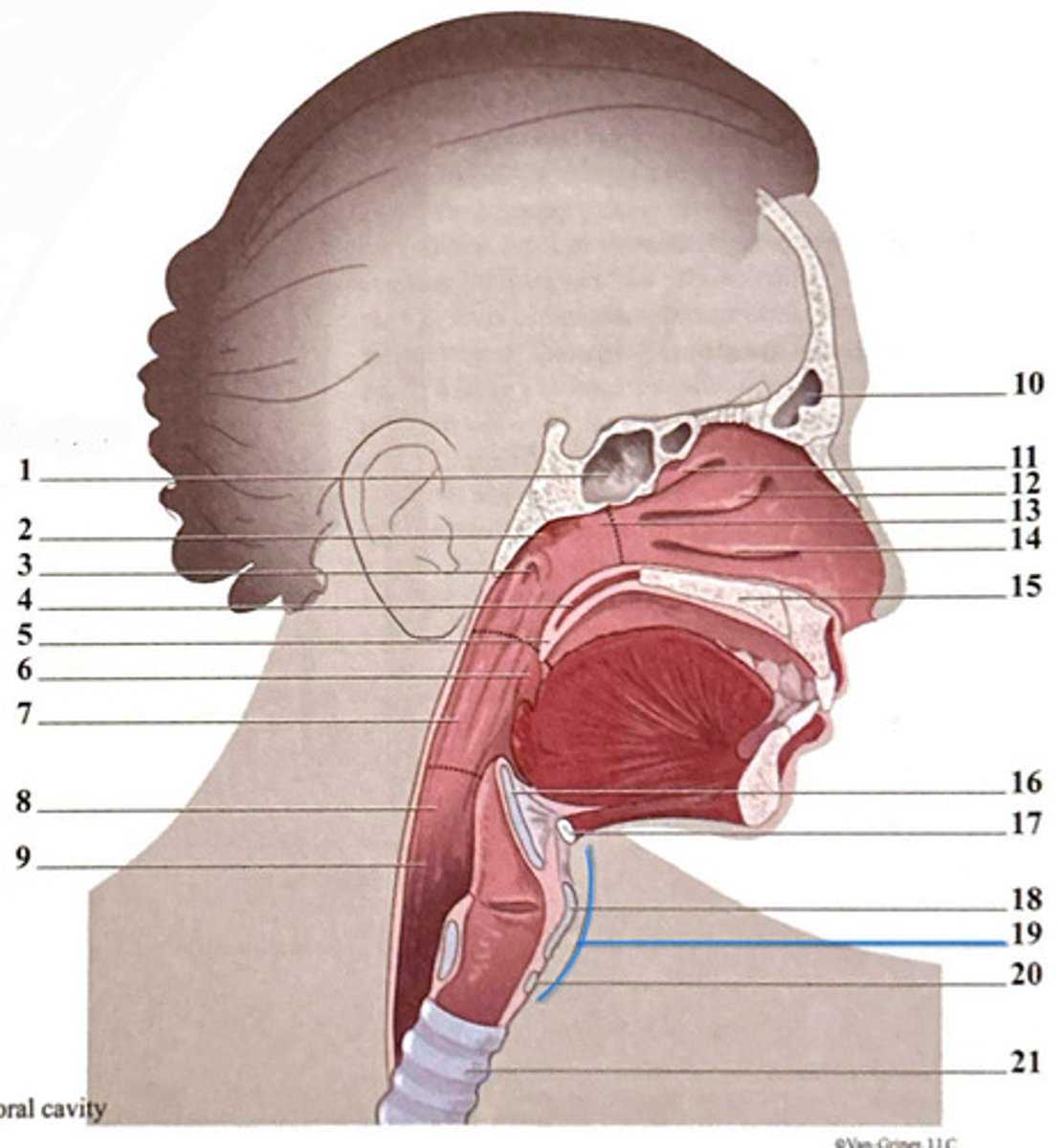
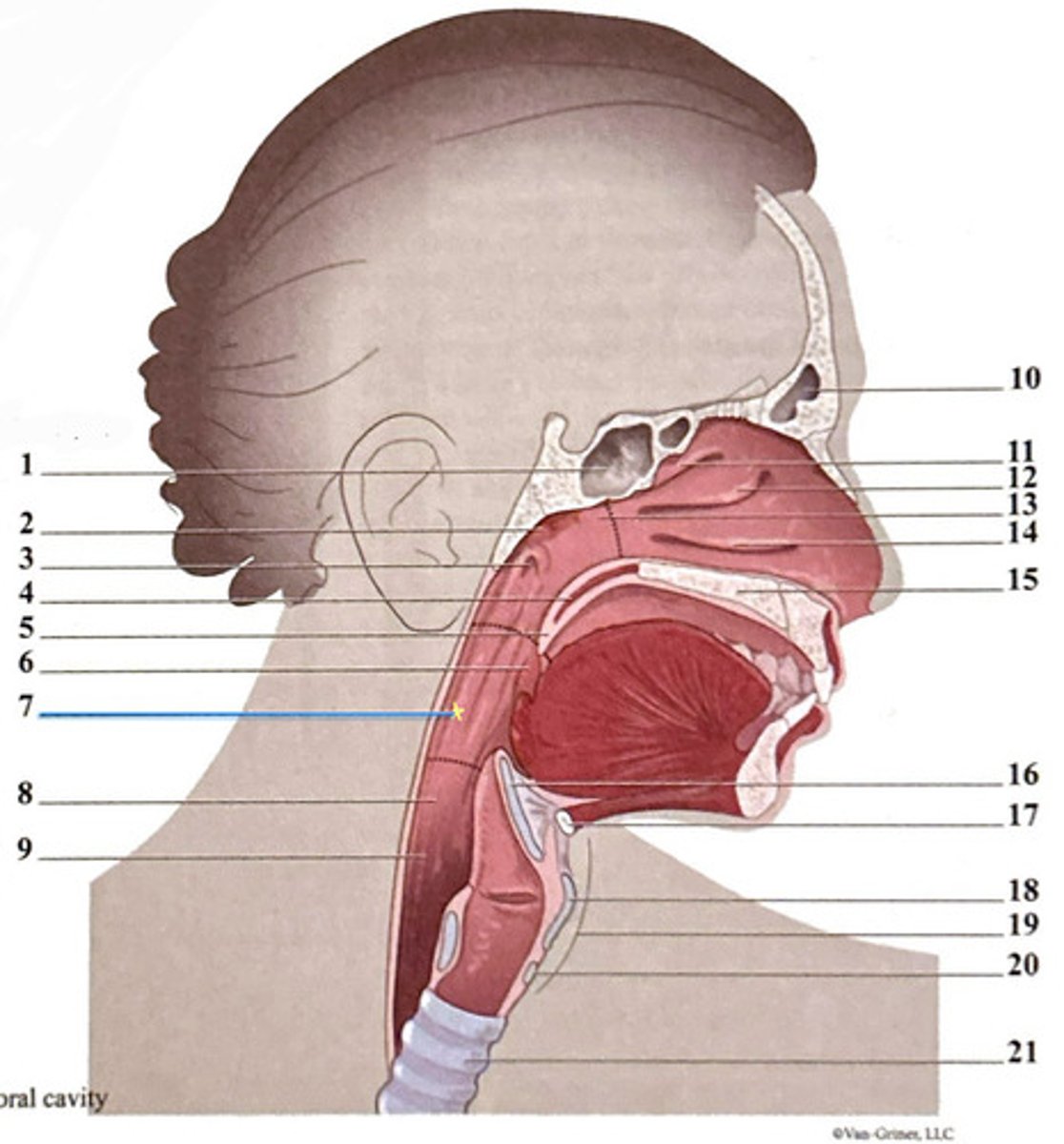
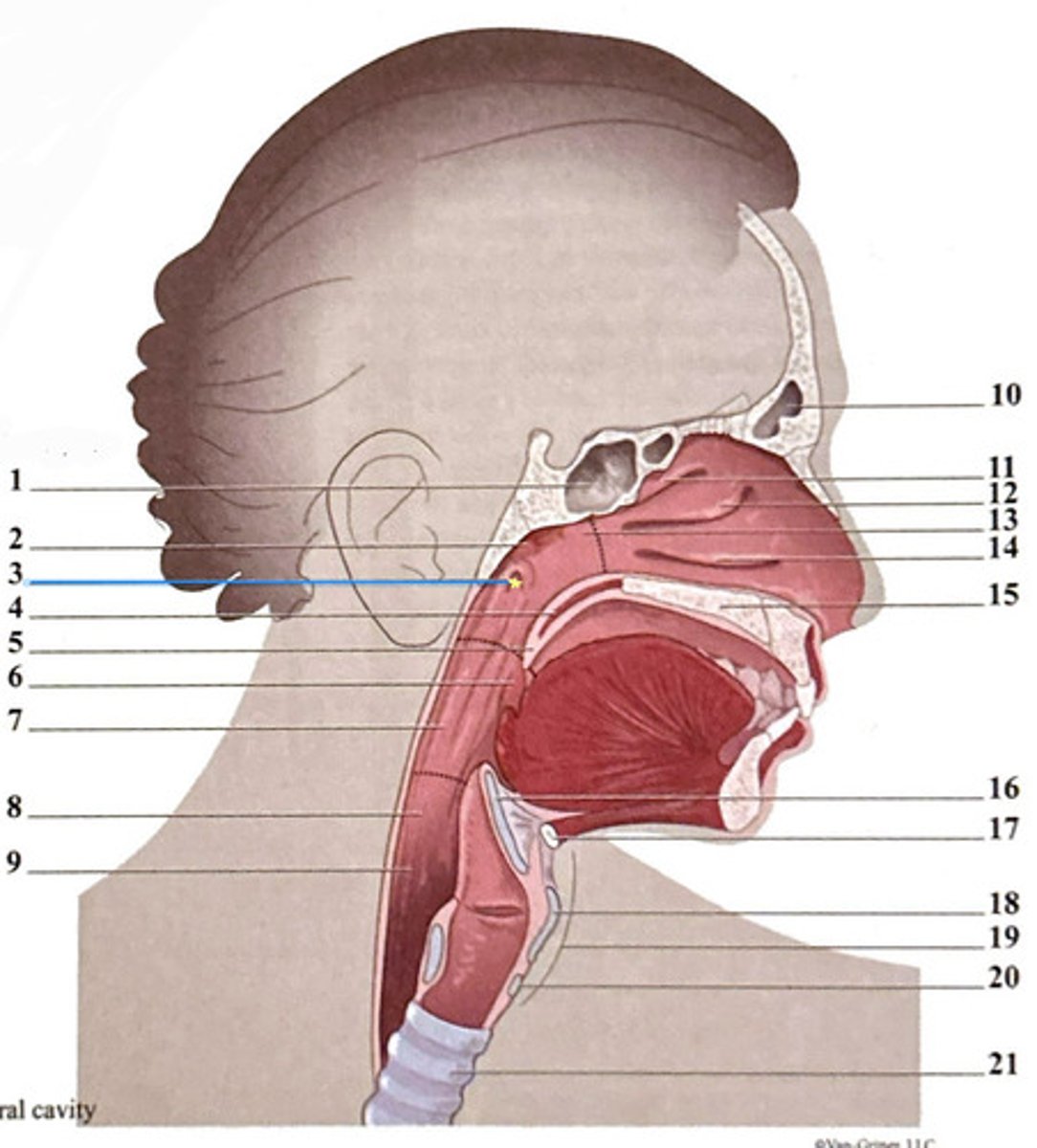
pharyngeal opening of the Eustachian tube
hypopharynx (laryngopharynx)
inferior nasal concha
soft palate
esophagus
horizontal plate of palatine bone
cricoid cartilage
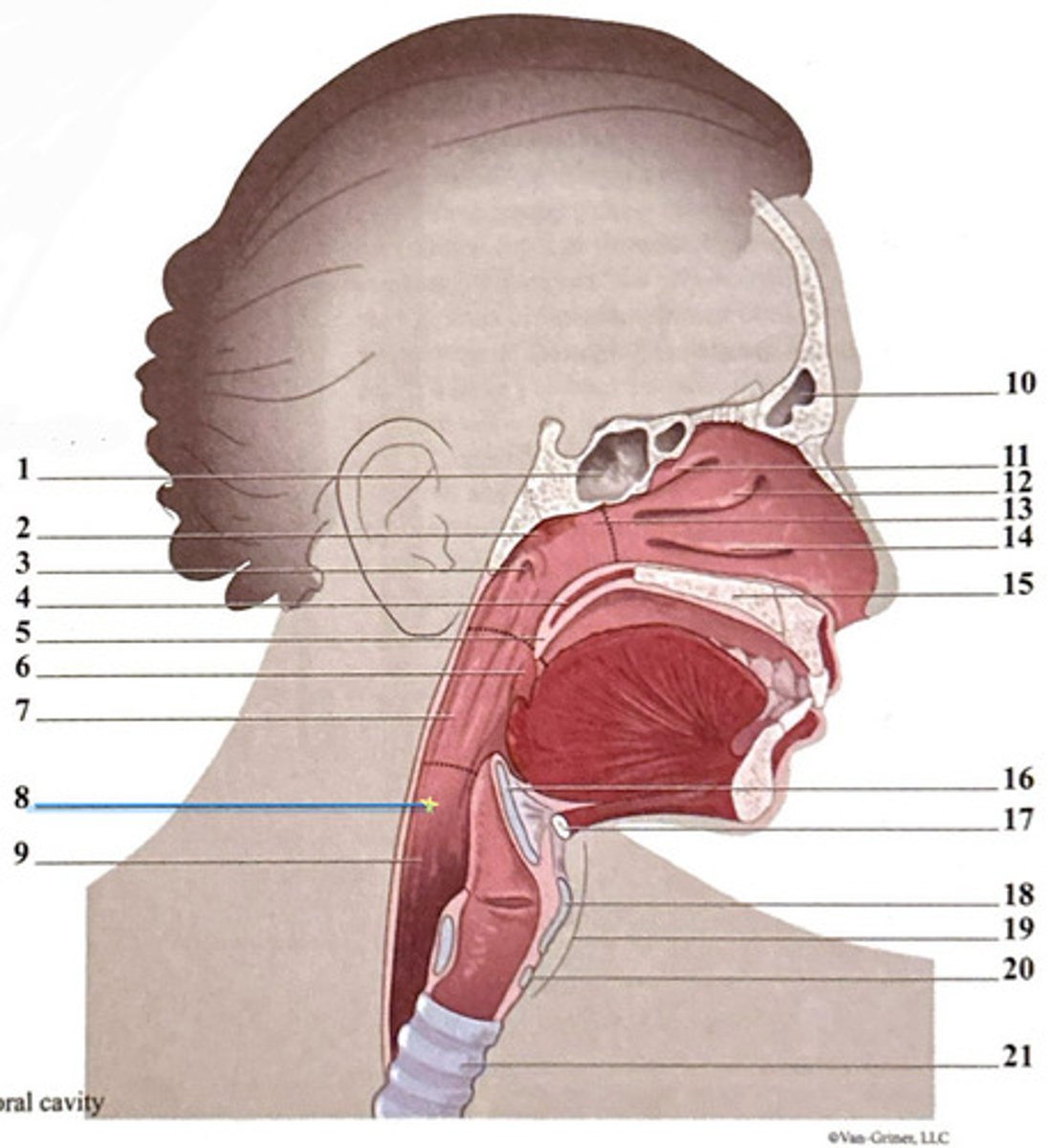
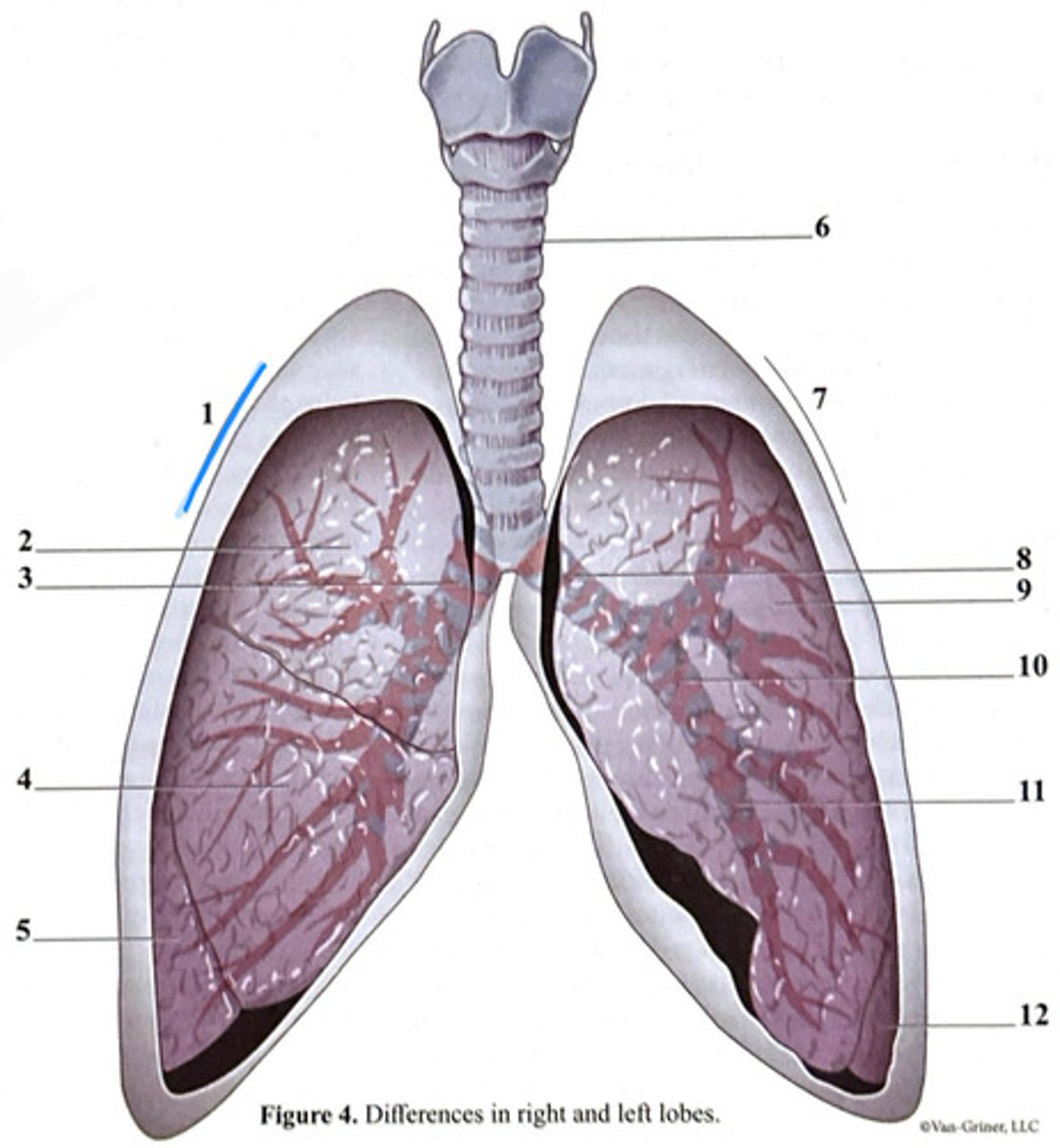
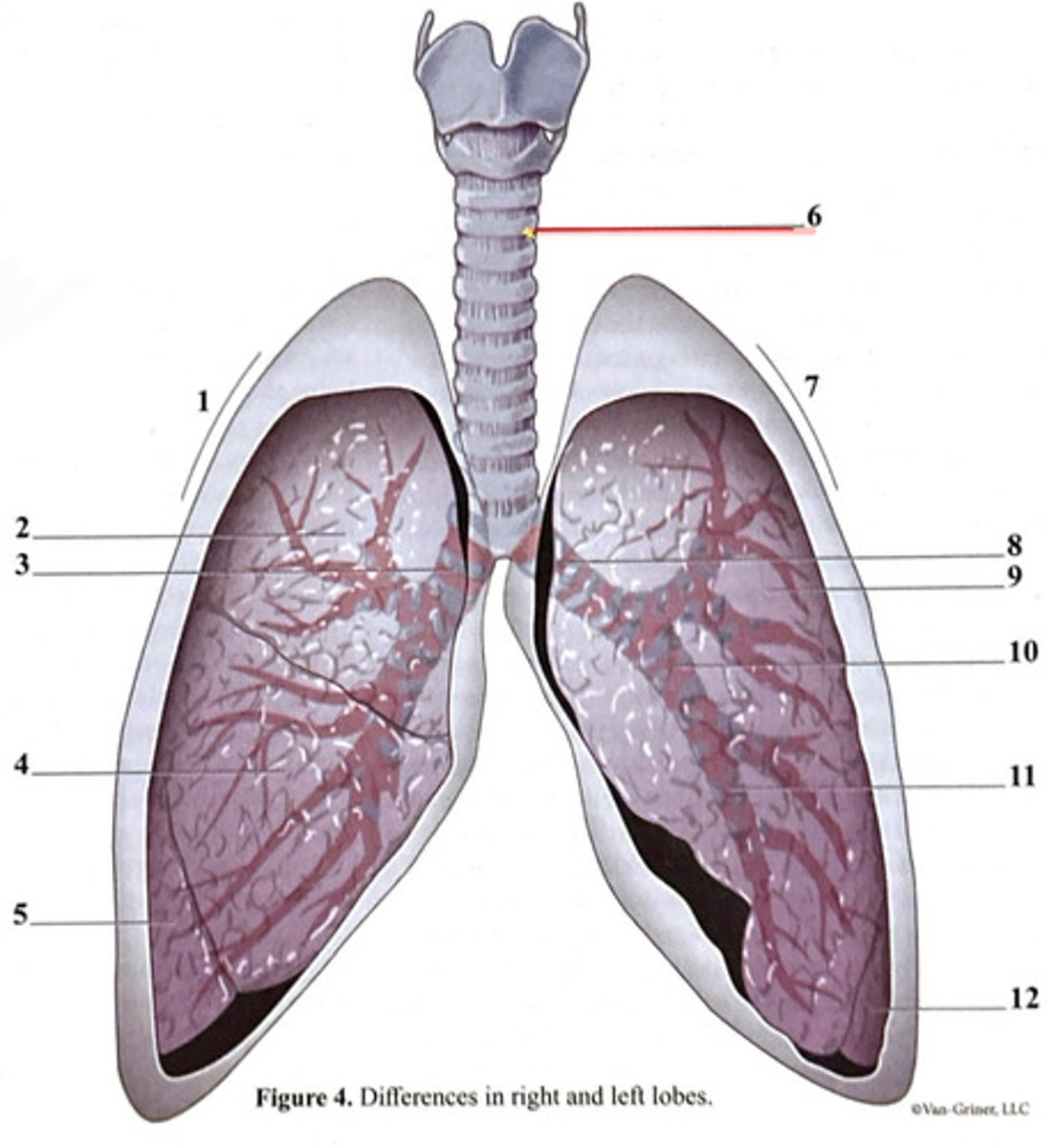
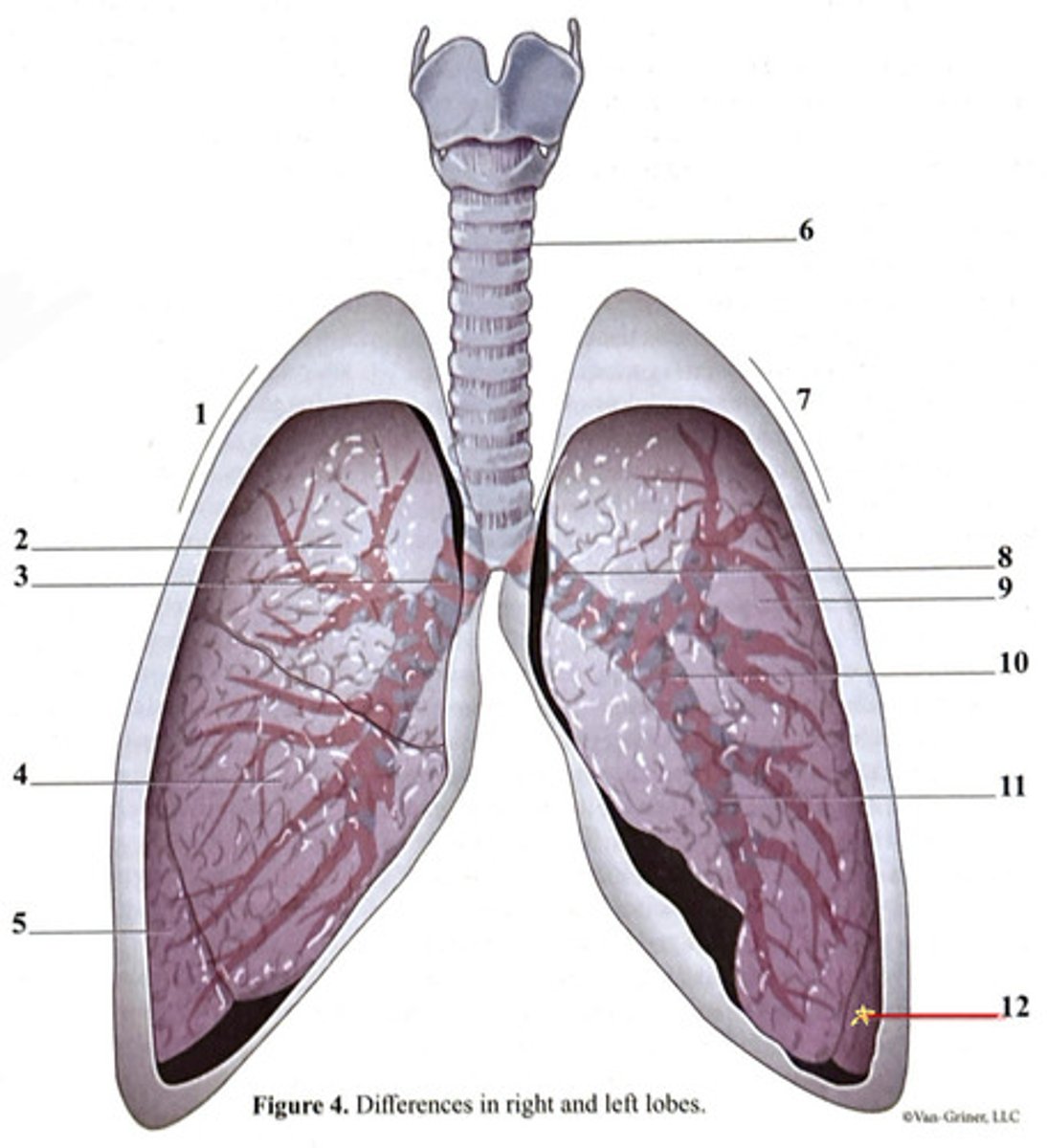
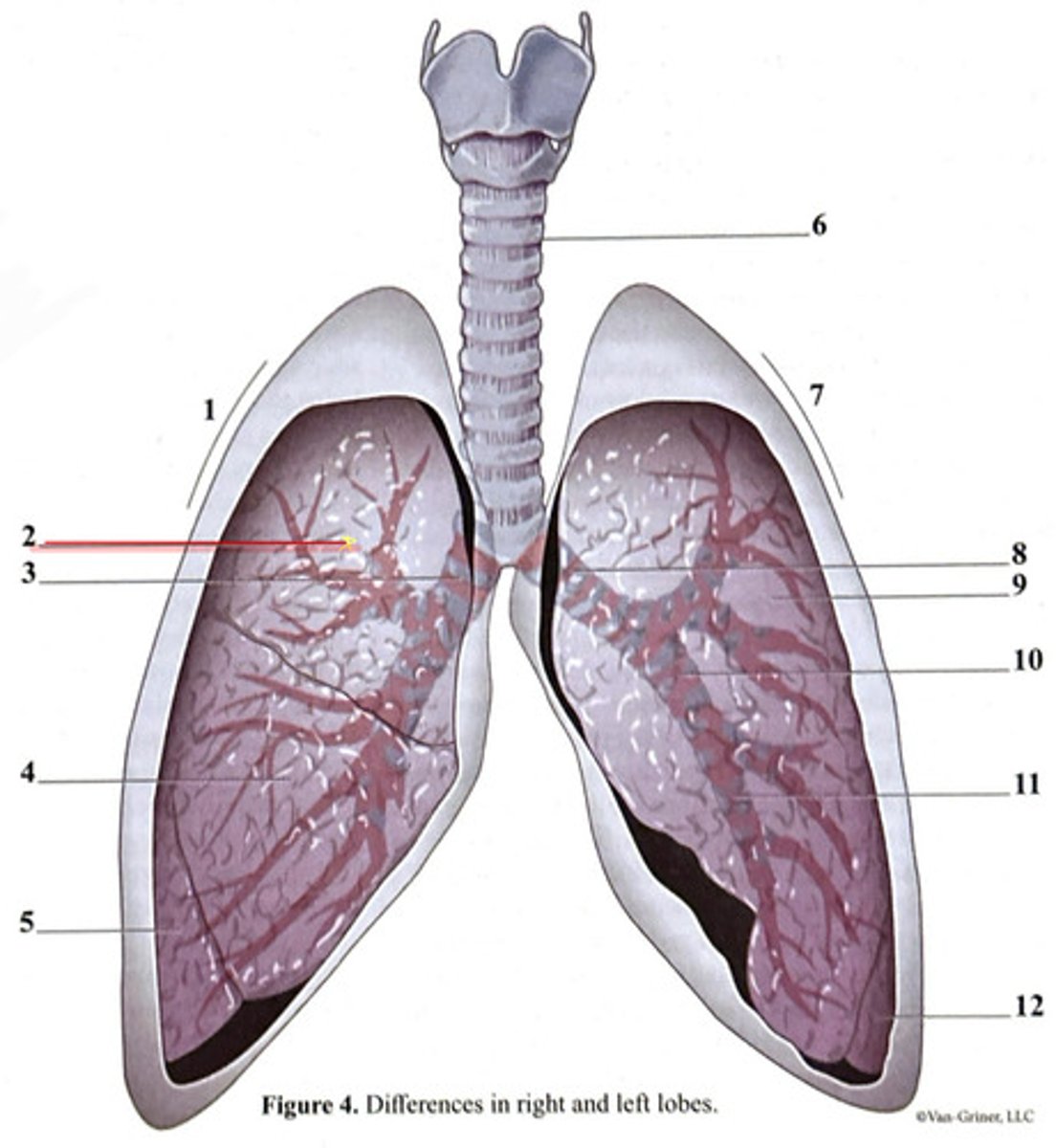
trachea
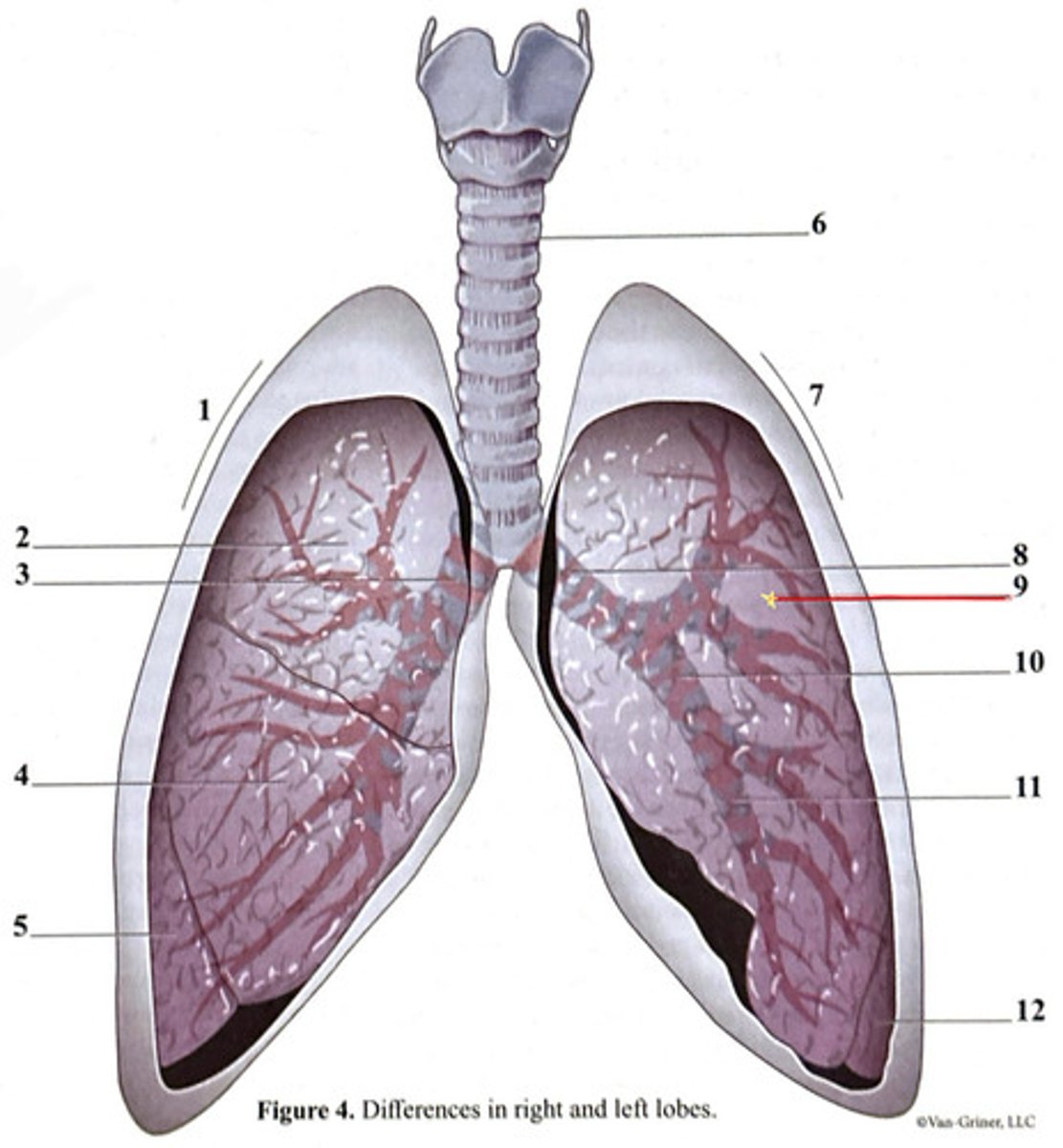
inferior lobe
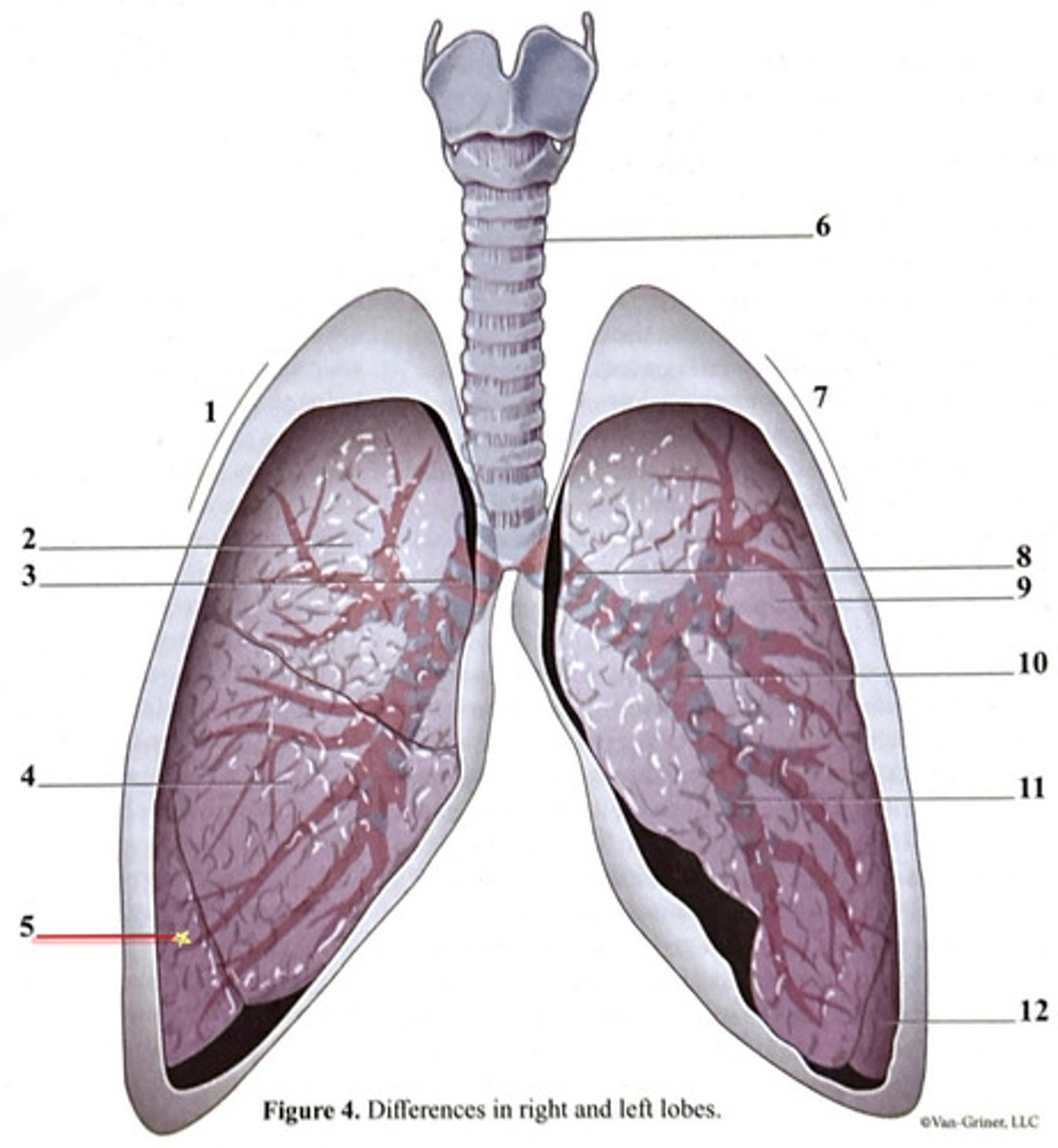
secondary bronchus
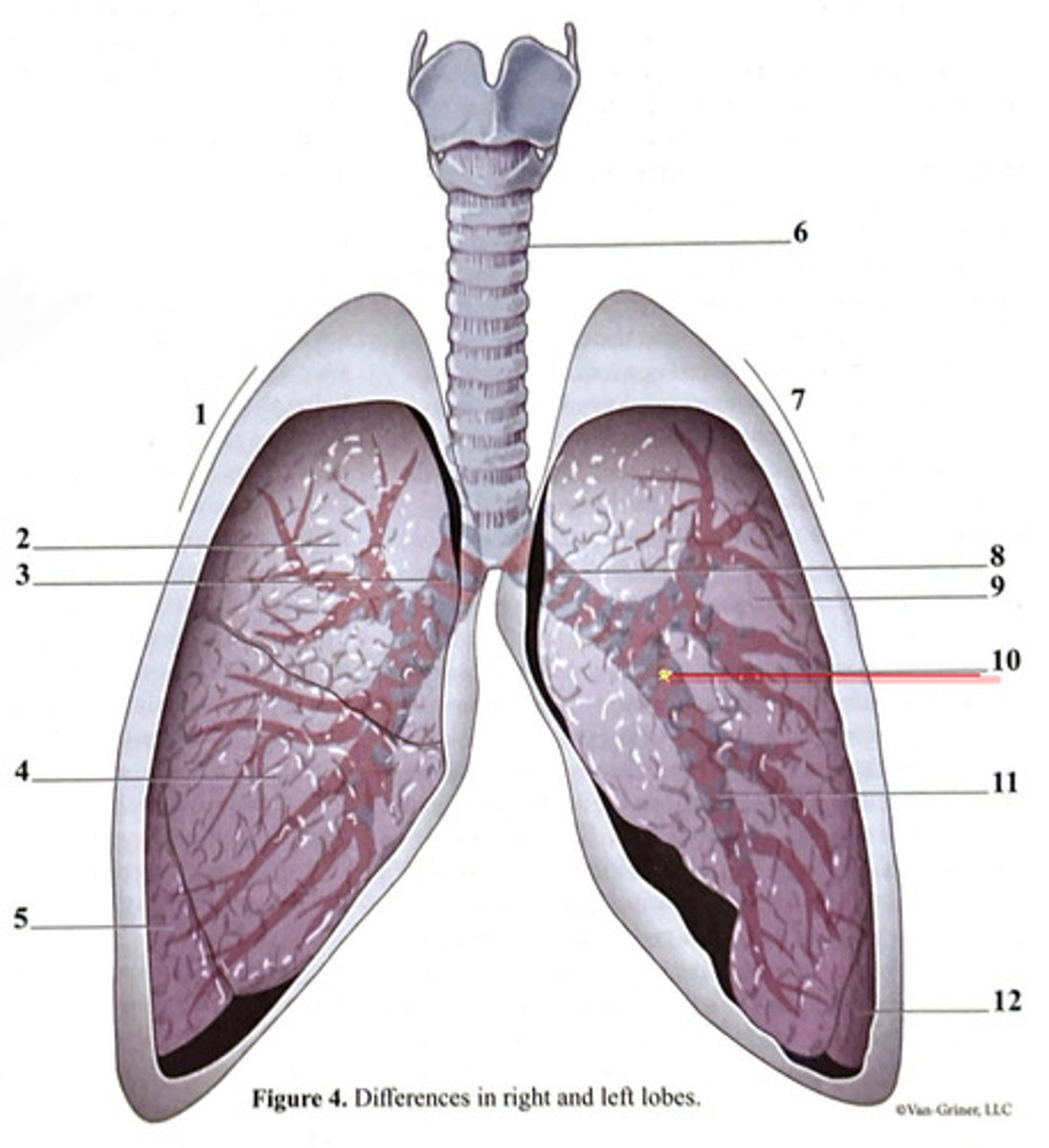
tertiary bronchus
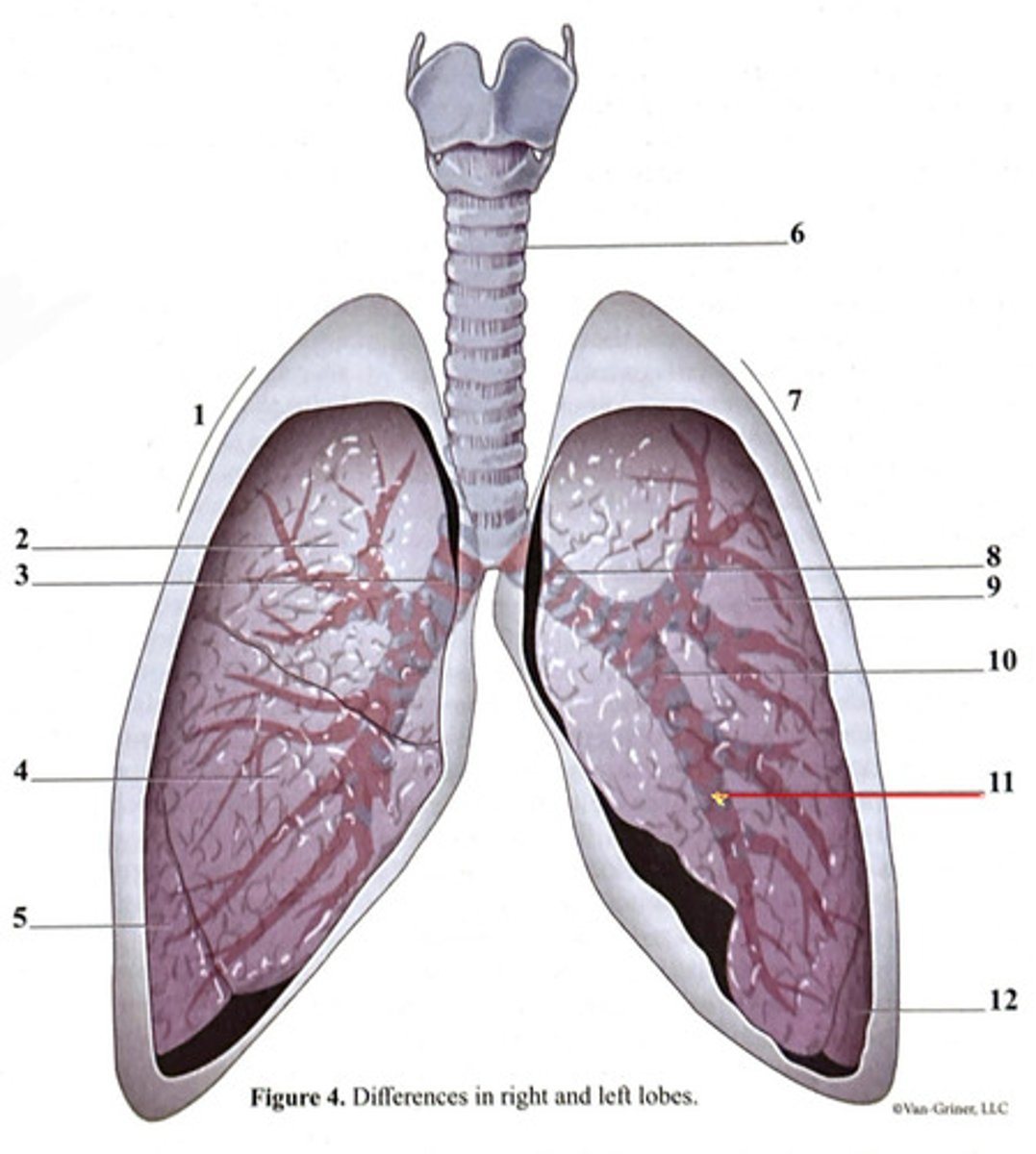
right lung
trachea
inferior lobe
superior lobe
left lung
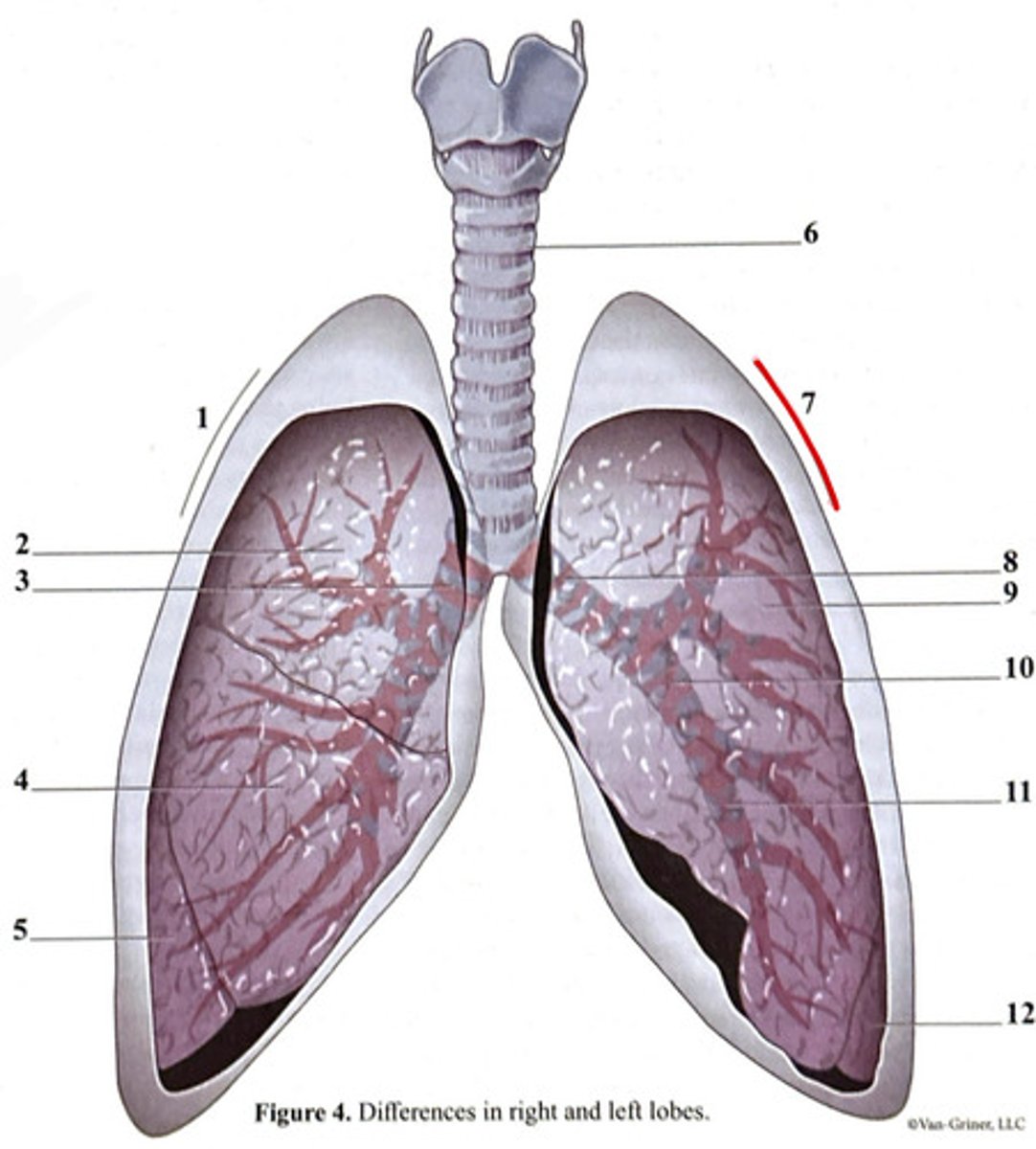
cartilage ring
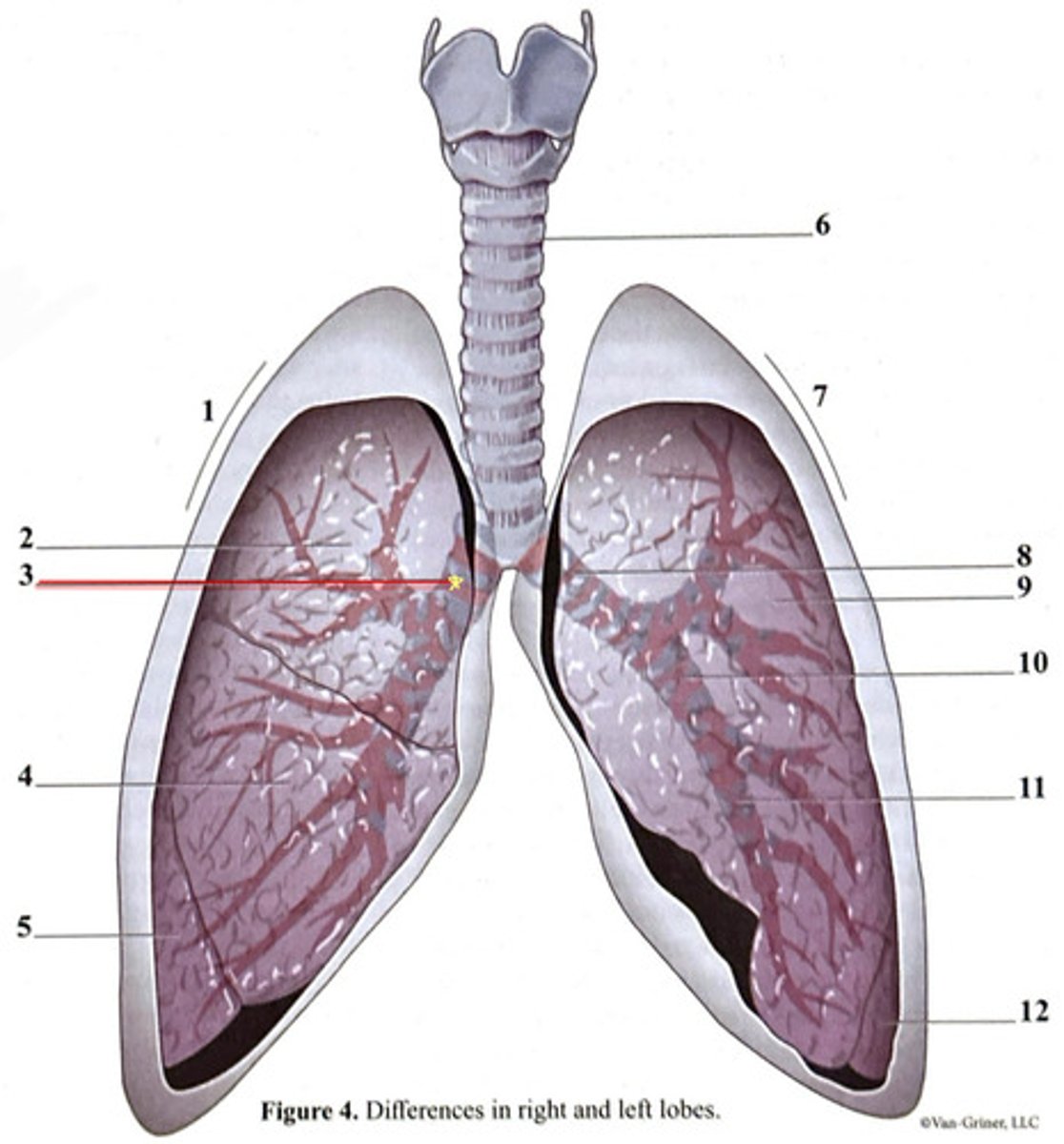
primary bronchus
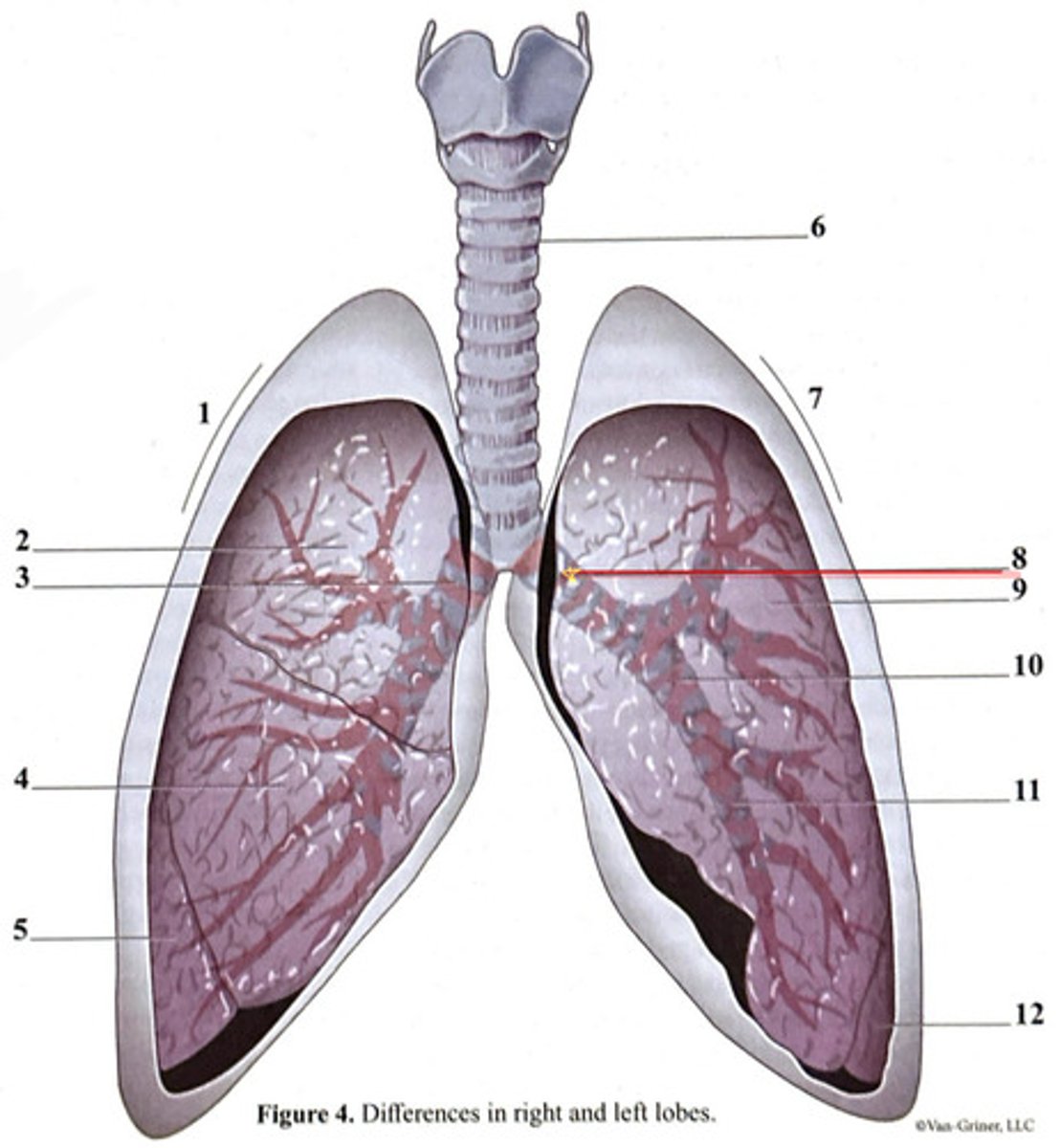
middle lobe
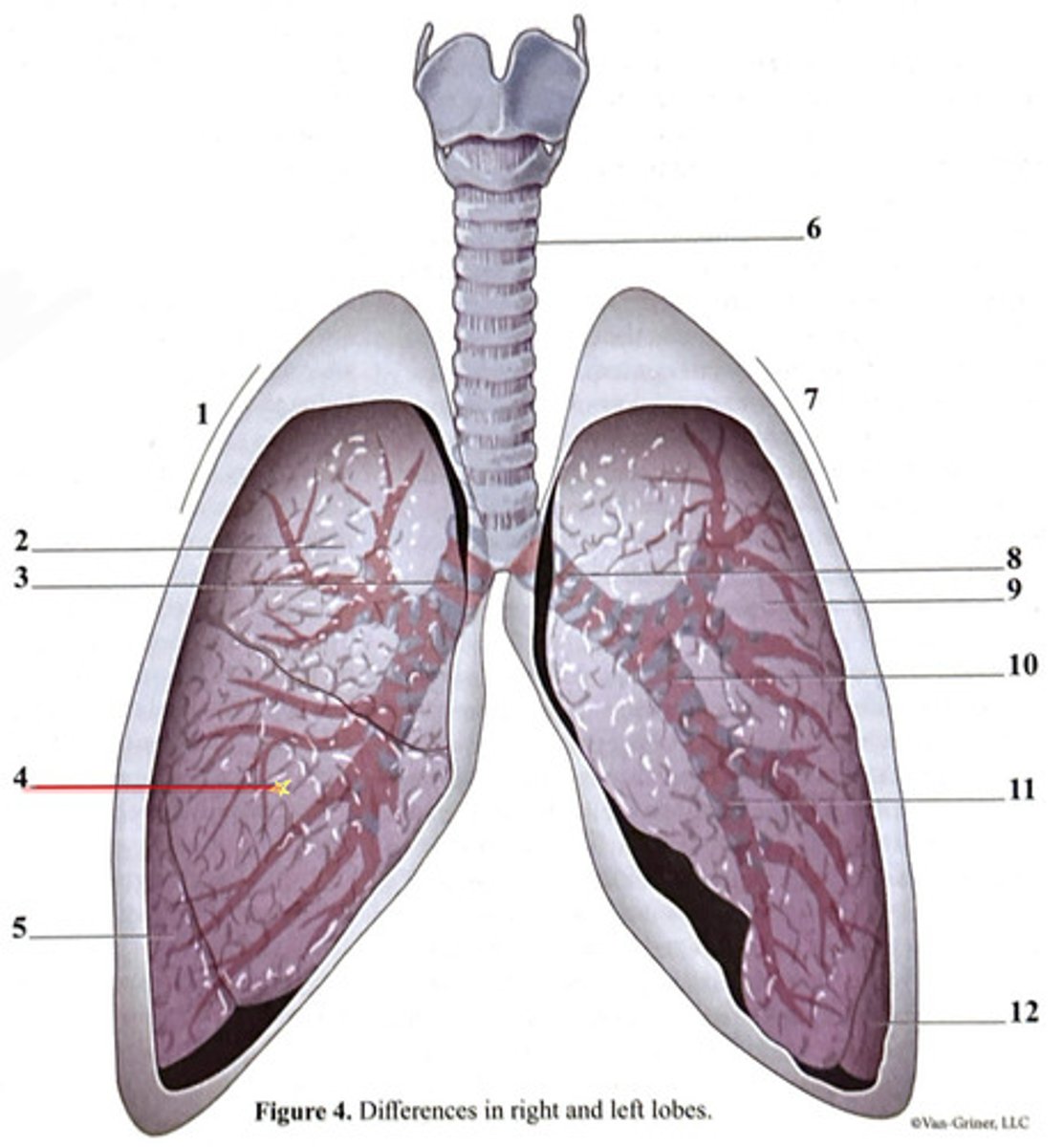
superior lobe
Primary function of the respiratory system
release CO2 from body and acquire O2 for use by body
4 steps of respiration
1. pulmonary ventilation
2. external respiration
3. transport of respiratory gases
4. internal respiration
pulmonary ventilation
movement of air into (inspiration) and out of (expiration) the lungs so that gases in lungs are constantly refreshed w/ infusions of fresh air and effusions of old air
external respiration
CO2 diffuses to lungs from blood
O2 diffuses to blood from lungs
transport of respiratory gases
-uses blood of cardiovascular system
-CO2 transported from cells of body tissues to lungs
-O2 transported from lungs to cells of body tissues
internal respiration
O2 diffuses from blood to cells of body
CO2 diffuses from cells of body to blood
cellular respiration
-CO2 is produced
-O2 is used
upper respiratory system
structures from nose to larynx
lower respiratory system
structures inferior to larynx
nose
warms and moistens entering air
-provides resonating chamber for vocalizations
-cleans and filters entering air
-houses olfactory receptors
difference in nose shape
difference in nose cartilage
olfactory mucosa epithelium
lines small portion of superior nasal cavity
-contains receptors for smell
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
-lines rest of nasal cavity
-goblet cells & seromucous nasal glands
seromucous nasal glands
composed of cells that secrete mucous & cells that secrete watery, enzyme-rich fluid to humidify incoming air (lysozyme = antibacterial)
function of mucous
traps bacteria, dust, and debris
antibiotic defensins
secreted by respiratory mucosa epithelial cells to assist in killing microbial invaders
cilia in nasal cavity
sweep contaminated mucous towards the throat to be swallowed/digested
_____ air slows cilia
cold
sneeze reflex
triggered when irritants (dust, pollen) contact rich supply of sensory nerve endings in nasal cavity
-sneeze forces irritants out to protect body from them
thin walled veins and capillary plexuses
-beneath the nasal epithelium
-warms air as it is inspired
-cold air reflexively stimulates plexuses to engorge blood = greater heat transfer
-superficial location
nose bleeds caused by
superficial location of veins/plexuses making them easily damaged
nasal conchae
increases surface area
-helps create turbulence that deflects non-gaseous particles onto mucous coatings
-cooled conchae causes moisture to precipitate out & heat to be exchanged into conchae to warm them (heat/moisture gradient constantly flipped each time we breathe in/out)
paranasal sinuses
located in frontal, sphenoid, maxillary, and ethmoid bones
-lighten skull
-prone to inflammation (i.e., allergies, infection)
sinusitis
inflamed sinuses
-additional mucous/inflammatory products are produced, blocking openings between sinuses and nasal cavity
-air in sinus is absorbed = partial vacuum
sinus headache
inflamed sinuses become swollen and filled with mucous leading to buildup of pressure from air being absorbed and a partial vacuum being created
inflammation of nasal mucosa
-excessive mucous production
-leads to congestion & postnasal drip
-due to viral/bacterial infection or allergic reactions
function of epiglottis
flaps over larynx to keep food out of the nasal cavity and lungs
function of cilia
propels mucous toward the stomach
when swallowing food...
-muscular soft palate & uvula move superiorly to block off nasopharynx
-epiglottis flaps over larynx
pharyngeal tonsil (adenoid)
contains lymphatic tissue that traps/destroys pathogens
swollen pharyngeal tonsils
can block air passage & force patient to breathe through mouth
-painful
breathing through mouth
greatly decreases warming, filtering, and humidifying effect on air compared to air through nose
pharyngotympanic tubes
connect middle ear to nasopharynx so that air in middle ear can match pressure w/ atmospheric air (important for sound conduction & proper hearing)
oropharynx and laryngopharynx
receives both food and air
-have more protective stratified squamous epithelium
respiratory system divided into
respiratory zone and conducting zone
respiratory zone
site of external respiration
-made up of microscopic alveoli, alveolar ducts, respiratory bronchioles
microscopic alveoli
main site of gas exchange
conducting zone
consists of all tubes transporting air from nose to respiratory bronchioles
-air is humidified, warmed, filtered/cleansed
vocal folds housed in
larynx
vocal folds/vocal cords
voice production
laryngeal prominence of thyroid cartilage
Adam's apple
-more prominent in males bc thyroid cartilage is stimulated by androgens during male puberty to grow larger
-estrogen stimulates fat deposition in necks of females = smaller prominence
arytenoid cartilages
anchor vocal folds
help move the vocal folds allowing tension & relaxation
glottis
vocal folds and opening between them
-opens/closes during intermittent expiration to produce speech
laryngeal muscles
moves cartilage of larynx to change length of vocal folds and size of glottis to change pitch & produce vocalization
tense vocal folds
vibrate more
-produces higher pitch
male puberty's effect on respiratory tract
-thyroid cartilage enlargens
-larynx and vocal folds enlarge and become longer and thicker to produce deeper voice
loudness determined by
force with which air is expired across vocal folds
-more force = louder sound
pharynx, nasal, oral, and sinus cavities
resonate sounds to enhance/amplify them
enunciation
muscles in lips, soft palate, tongue, pharynx
laryngitis
inflammation of the vocal folds which causes them to swell and vibrate incorrectly
-hoarse tone
-commonly caused by viral infection
straining to defecate
vocal folds completely close over glottis to stop air passage
-abdominal muscles contract & glottis closes to increase intra-abdominal pressure to help empty rectum = Valsalva maneuver
valsava maneuver
holding the breath and straining against a closed glottis.
-increases pressure in thorax = decreases venous return to heart by squeezing major blood vessels & presses on Vagus nerve to increase vagal tone
inhalation
-thoracic pressure decreases
-venous return increases
-vagal tone decreases
-HR increases
exhalation
-thoracic pressure increases
-venous return decreases
-vagal tone increases
-HR decreases
Boyle's law
A principle that describes the relationship between the pressure and volume of a gas at constant temperature
expiration
diaphragm relaxes, ribs and sternum depress: chest cavity and lungs contract
inspiration
diaphragm contracts, ribs and sternum expand: chest cavity and lungs expand
heart rate increases when we
breathe in
heart rate decreases when we
breathe out
trachea
composed of mucosa, submucosa, and adventitia
-elasticity allows it to move during breathing
-cartilage rings hold trachea open for air to move continuousl
cartilage rings of trachea
C-shaped
-allows for esophagus behind to expand during swallowing
mucosa of trachea
pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium containing goblet cells
-produces/moves mucus up out of lungs
submucosa of trachea
seromucous glands
adventitia of trachea
outermost connective tissue sheath
trachealis
between esophagus and trachea
-contraction aids in rapid movement of air & mucus out of lungs/trachea during coughing
right side
3 bronchi
left side
2 bronchi