L26 (Reed) - Pediatric Dermatology
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
describe neonatal skin (not preterm)
40-60% thinner than adult skin
less hairy
weaker attachment between epidermis and dermis —> higher risk for injury
body surface area-to-weight ratio is up to 5x larger in infants
lanugo
hair on preterm infants
not effective for thermal stability or trans epithelial water loss
describe premie skin
imature stratum corner (even at 32-34 weeks)
increased transpidermal water loss —> dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, thermal instability
increased percutaneous absorption
intact barrier function occurs by ______ weeks of life
3 weeks (can be up to 8 weeks if extremely low birthweight)
acrocyanosis
blush discoloration of hands and feet in response to vasomotor instability or cold (vasoconstriction of small arterioles)
spares lips/mucous membranes
perioral area may be affected
extremities may be cool to touch
resolves within first few months —> no further evaluation, just reassurance to parents
treatment for acrocyanosis
none
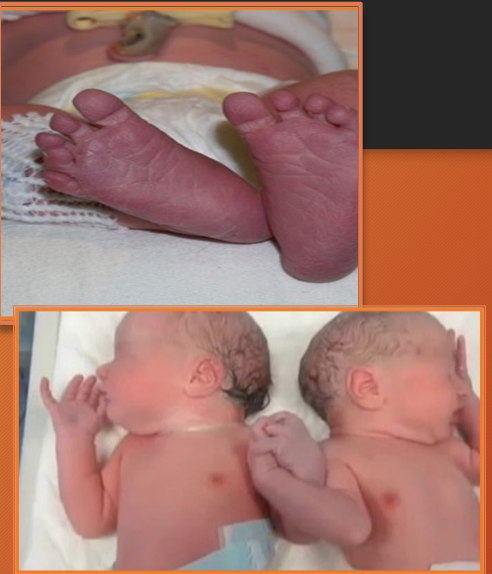
acrocyanosis
cutis marmorata
reticulated bluish mottling of skin
physiological response to chilling —> dilation of capillaries and small venues
net/lace-like appearance (“blue lines” in case presentation)
usually disappears as infant is rewarmed
may be seen up to several months
bears no medical significance
treatment for cutis mamorata
none
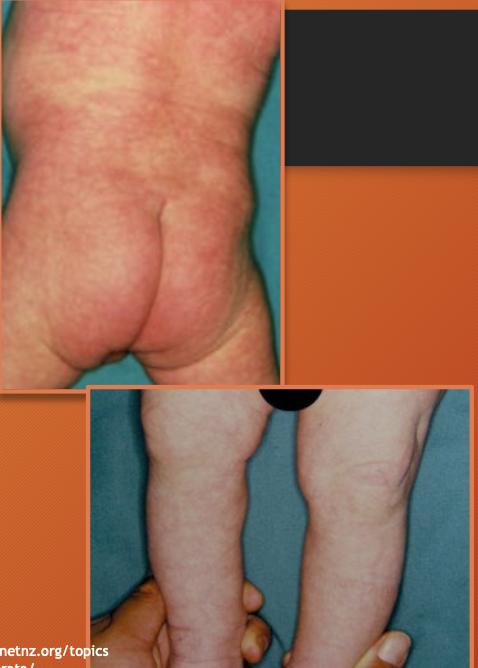
cutis marmorata
harlequin color change
transient, unilateral erythema on side that is laid on
macular
blanchable
sharp midline separation
unknown cause, involves cutaneous blood vessel tone
treatment for harlequin color change
none
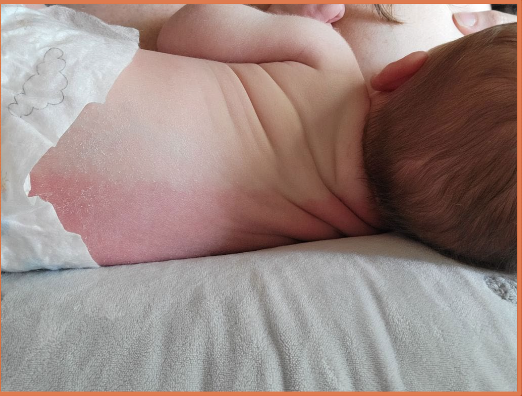
harlequin color change
caput succedaneum
localized edema of the scalp due to mechanical forces from parturition (esp if prolonged) and venous congestion
may see divot from where pressure was applied on sca
often crosses midline
halo scalp ring present
spontaneously resolves in 48 hours (days!)
treatment for caput succedaneum
none
caput succedaneum
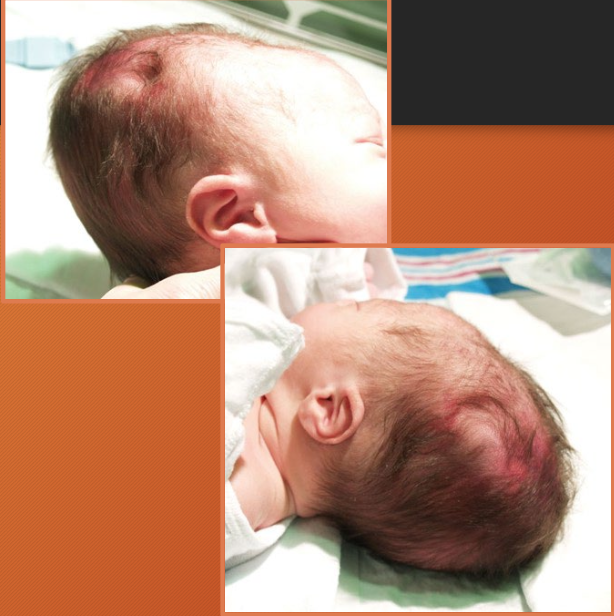
halo scalp ring
alopecia in circular pattern around the scalp - pressure necrosis phenomenon
usually transit —> resolves in months to years (but can become permanent)
occurs with caput succedaneum or prolonged labor
treatment for halo scalp ring
none
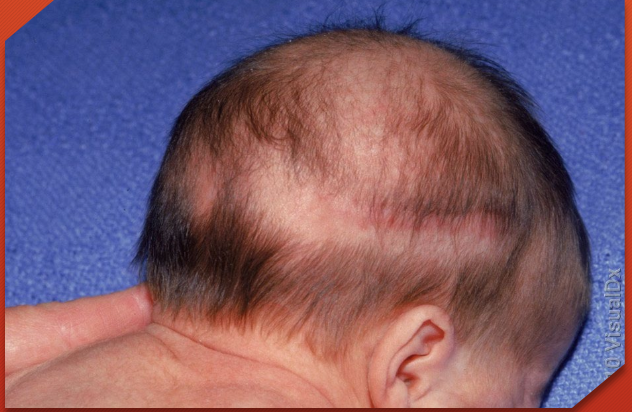
halo scalp ring (seen in caput succedaneum or prolonged labor)
cephalohematoma
SUBPERIOSTEAL hematoma overlying calvarium - due to prolonged labor, instrument-assisted delivers, abnormal presentations
does NOT cross midline
limited to one cranial bone
complications:
calcification - may persist for years
hyperbiliruinemia - MC issue
infection
resolution occurs spontaneously over several weeks to months
treatment for cephalohematoma
none
MC complication with cephalohematoma
hyperbilirubinemia
Cephalohematoma vs Caput succedaneum: which one crosses midline? Why?
Caput succedaneum - it is not subperiosteal, so it isn’t limited by suture lines!
cephalohematoma
miliaria
sweat-retention phenomena due to immature epidermis
maculopapular
maceration (thinning) and obstruction of eccrine ducts
keratinous plugging
occurs on neck and abdomen
two forms: rub, crystalline
prevalent in first few weeks of life
miliaria ruba
deeper level of sweat gland obstruction
small erythematous papule, vesicles, or papulovesicles
miliaria crystallina
clear superficial pinpoint vesicles
inflammatory surrounding
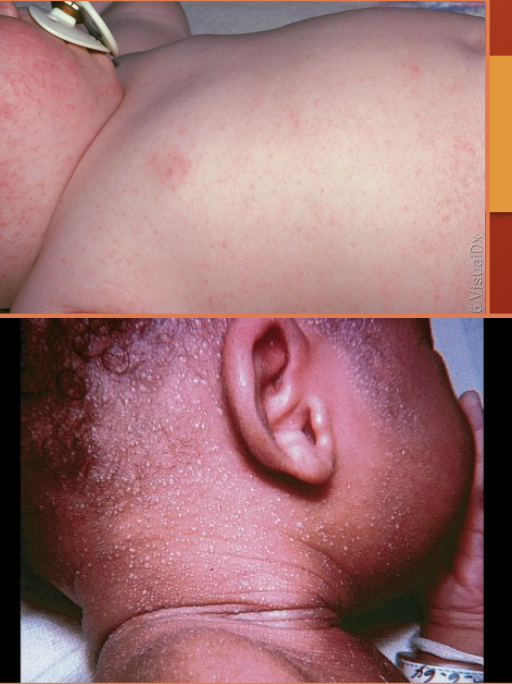
miliaria (ruba on top, crystalline on bottom)
treatment for miliaria
avoid excessive heat/humidity
cotton clothing
cool baths
air conditioning
don’t over-apply moisturizers
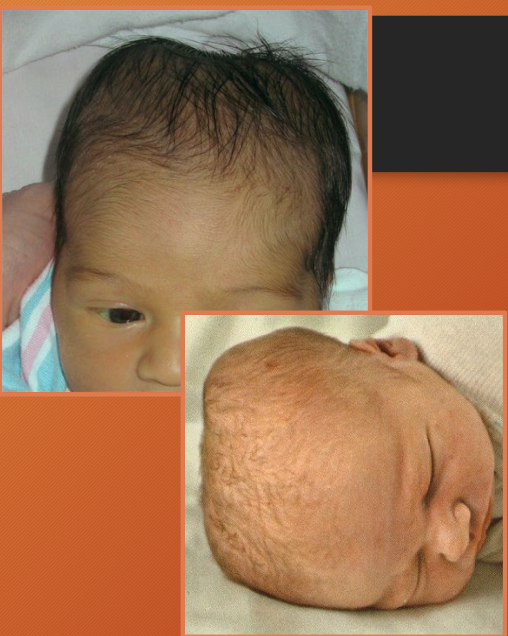
milia
retention cysts - due to keratin within the dermis
tiny 1mm pearly white papules
on cheeks, nose, chin, forehead
epstein perals = Bilia on hard palate
frequently clustered in groups
usually disappear spontaneously by 4 weeks
treatment for milia
none
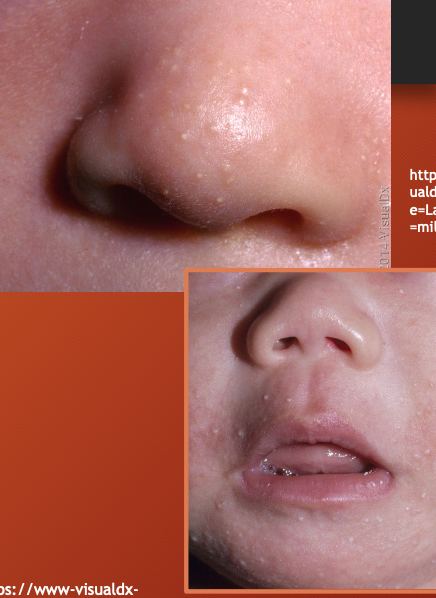
milia
epstein pearls
milia on hard palate
sebaceous gland hyperplasia
physiologic manifestation of maternal androgen stimulation
yellow/white pinpoint papules
occur on nose (can also be cheeks and upper lip)
resolves spontaneously by 3 weeks
treatment for sebaceous gland hyperplasia
none
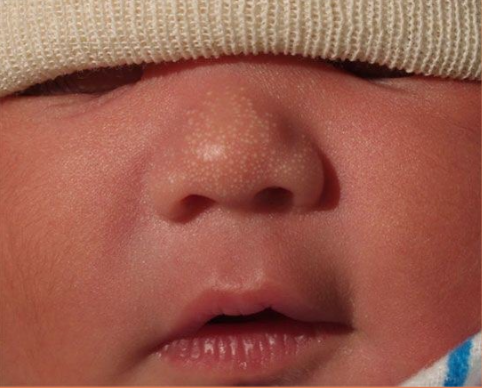
sebaceous gland hyperplasia
neonatal cephalic pustulosis
“neonatal acne” - inflammatory response to Malassezia spp.
erythematous papules on face (cheeks, chin, eyelids)
no comedones!!!
mean onset is 3 weeks
treatment for neonatal acne
reassurance
ketoconazole
infantile acne and it’s treatment
occurs around 9 months - due to hormonal imbalance (increased LH)
comedones!!!
treatment: retinoids, benzyl peroxide, antibiotics
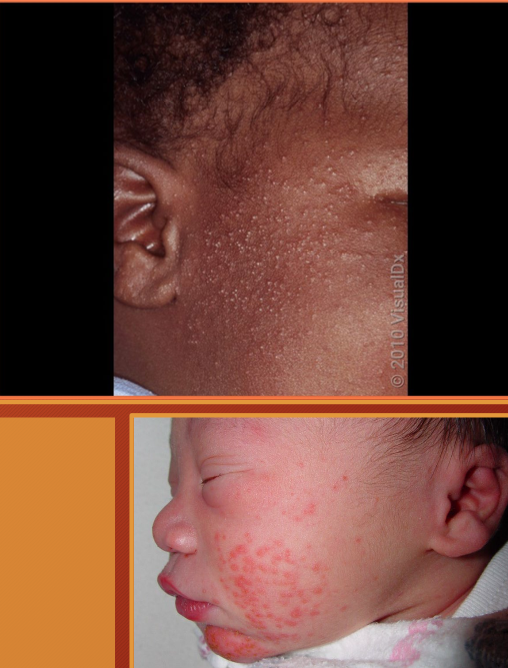
neonatal acne
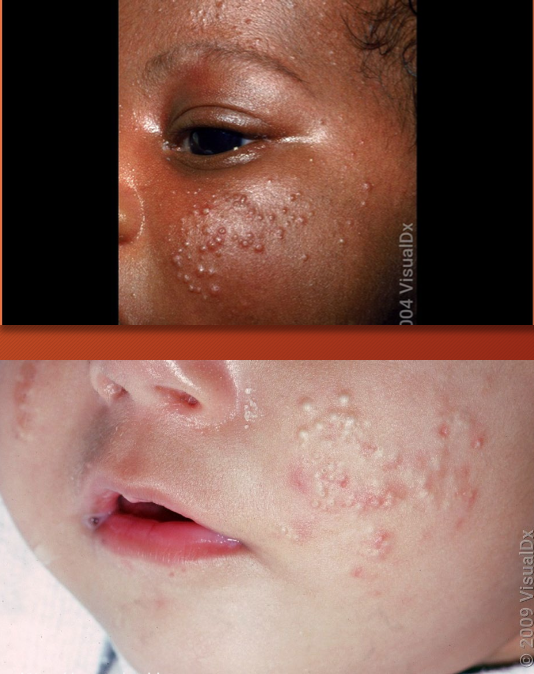
infantile acne
erythema toxicum neonatorum
red splotchy area on body - idiopathic
can be diffuse over body
spares palms and soles
appears in first 4 days —> tends to remit and recur during first two weeks after birth
no therapy necessary —> resolves spontaneously
treatment for erythema toxicum neonatorum
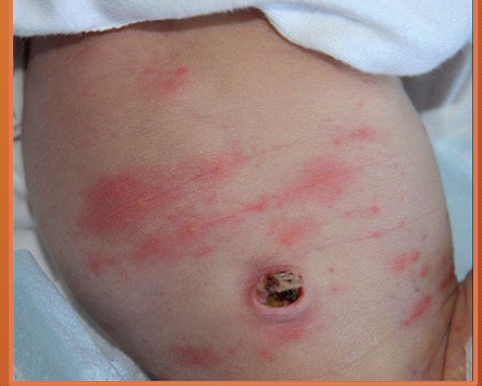
erythema toxicum neonatorum
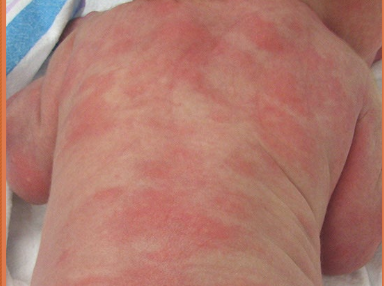
erythema toxicum neonatorum
What will a Wright or Giemsa stain show for erythema toxicum neonatorum?
predominance of eosinophils
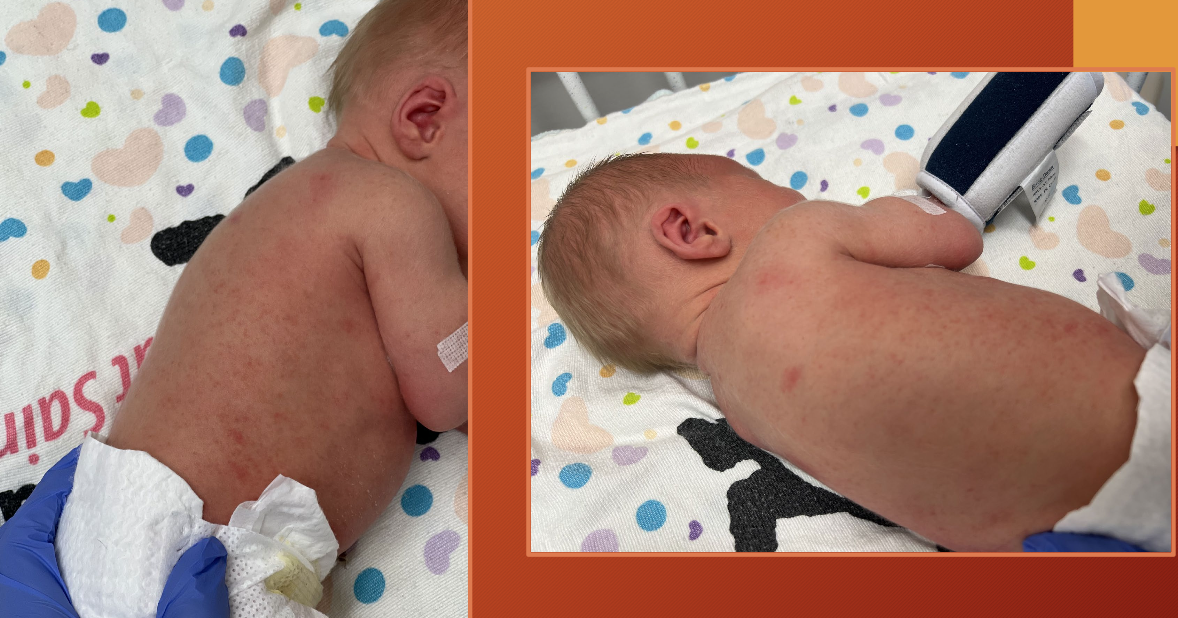
erythema toxicum neonatorum
transient neonatal pustular melanosis
idiopathic - presents AT BIRTH
sterile superficial pustules
rupture easily —> leave hyper pigmented macule surrounded by fine white “collarette” of scale
three phases = pustules, rupture, hyper-pigmented papules
diffuse distribution
therapy unnecessary —> disappear in 2 days (hyperpigmentation fades over three months)
treatment for transient neonatal pustular melanosis
none
what does a Giemsa stain of transient neonatal pustular melanosis show?
neutrophils and acellular debris
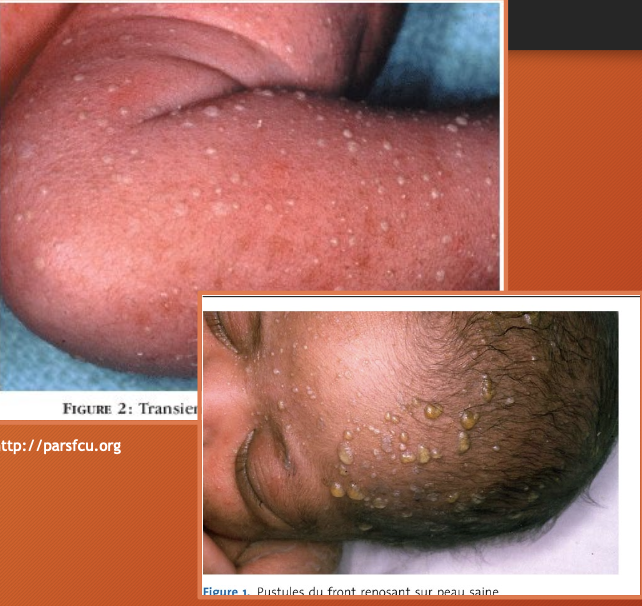
transient neonatal pustular melanosis
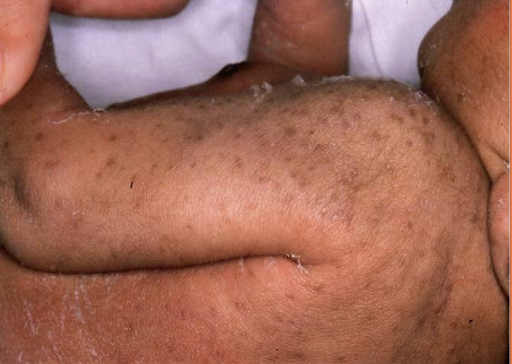
transient neonatal pustular melanosis
hemangioma
MC benign soft tissue tumor of child
vascular
superficial or deep (or mix)
MC in head and neck regions
MC in females
appear 2-3 weeks of life
etiology unknown, but maybe related GLUT-1 in placenta tissue??
superficial hemangioma
bright red
protuberant
sharply demarcated
noncompressible
deep hemangioma
blueish
firm
cystic
less likely to regress
compressible
hemangioma phases of growth
proliferative phase
growth period
greatest growth by 5 months
Plateau phase
period of stability
Involution phase
spontaneous regression
10% every year
treatment for hemangioma
monitoring
topical or oral beta blockers
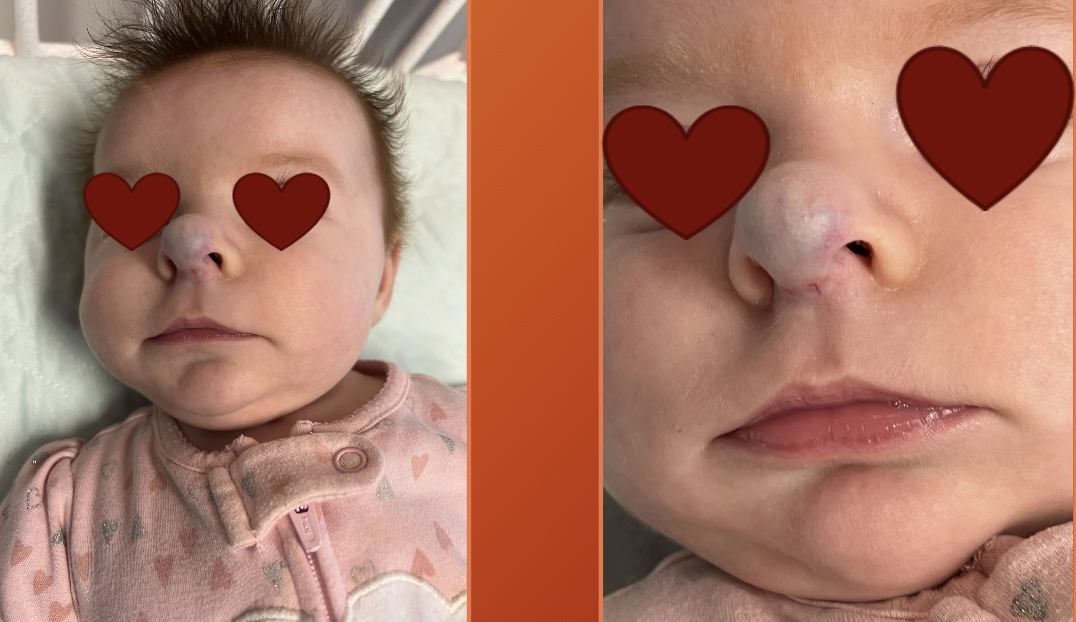
hemangioma
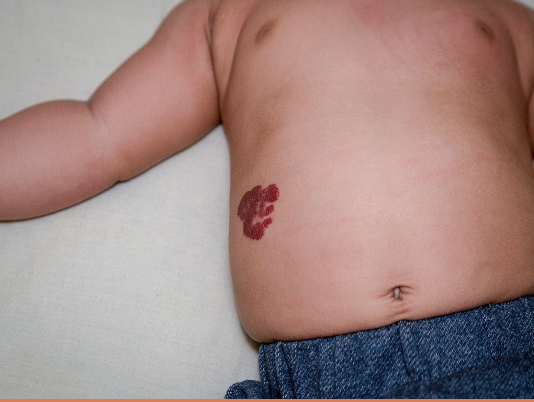
hemangioma
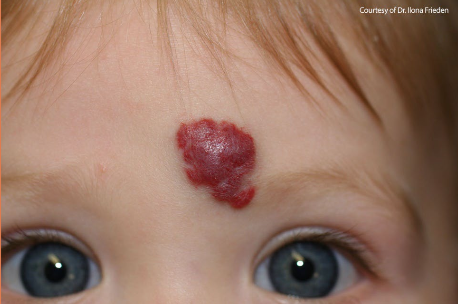
hemangioma
nevus simplex
“salmon patch” “stork patch”
vascular lesion - due to capillary malformation
pale pink vascular patch
occurs in nuchal area, glabella, eyelids
can “flare” with heat or stress
usually disappears by school age
treatment for nevus simplex
none
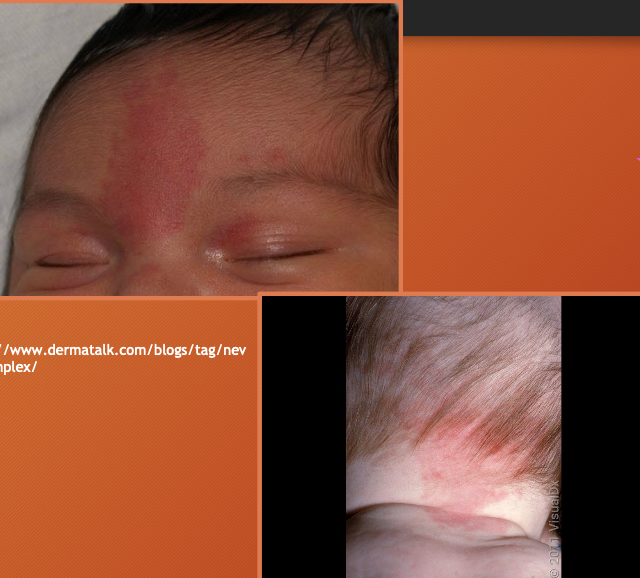
nevus simplex
congenital dermal melanocytosis
“slate nevus”
collections of spindle shaped melanocytes deep in dermis
deep brown/slate grey/ blue-black patches in lumbosacral region
black>hispanic>white
may raise abuse suspicion (looks like bruising)
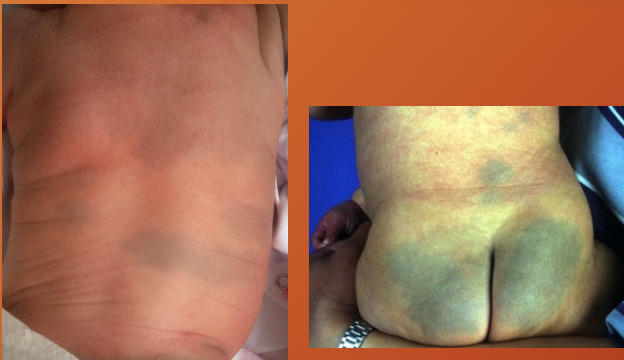
congenital dermal melanocytosis
irritant diaper dermatitis
skin reaction to diaper friction - due to proteolytic enzymes in stool, soaps, excessive heat, moisture
occurs on convex surfaces of buttocks, vulva, perineal area, lower abdomen, proximal thighs
spares intertriginous creases
treatment of irritant diaper dermatitis
GOAL: keep dry, protected, infection-free
frequent diaper changes (when stool is present)
gentle cleansing with moist cloth or fragrance free wipe (do NOT over wash)
exposure to air when possible
lots of topical therapy (zinc oxide, petrolatum)
educate parents
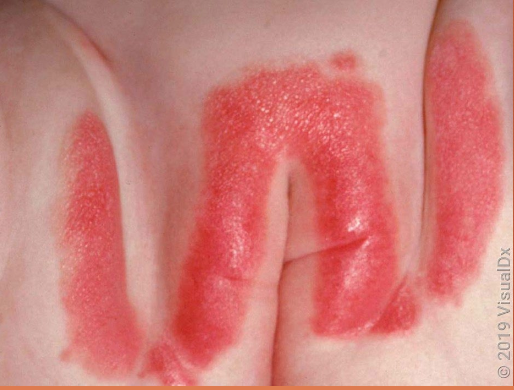
diaper candidiasis
Candida albicans is in lower intestine of infants —> feces leads to skin infection
widespread beefy red erythema
occurs on buttocks, lower abdomen, inner thighs
raised edge with sharp marginization
white scales at border
DIAGNOSTIC HALLMARK = pinpoint satellite lesions
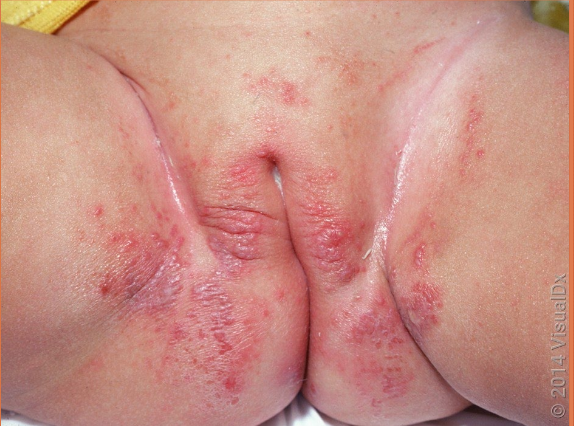
irritant diaper dermatitis
irritant diaper dermatitis
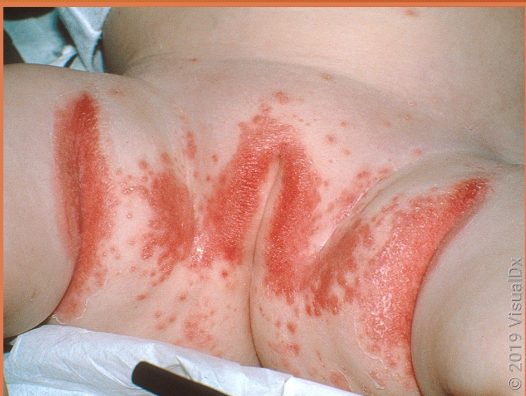
diaper candidiasis
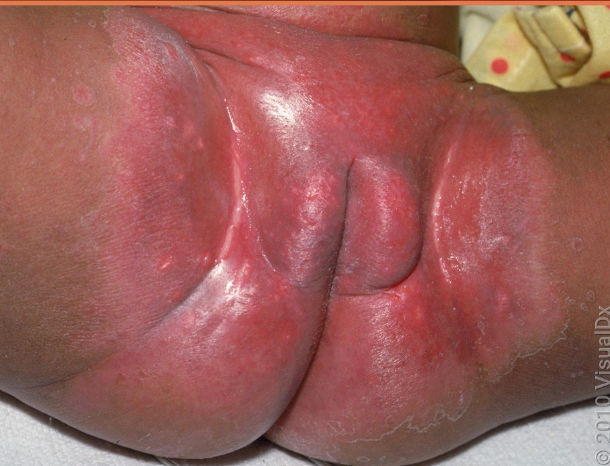
diaper candidiasis
treatment for diaper candidiasis
topical nystatin (or clotrimazole or ketoconazole)
oral antifungul treatment is best when thrush is also present (or just a very severe case)
what does a potassium hydroxide smear show with diaper candidiasis?
budding yeast or pseudohyphae
seborrheic dermatitis
chronic and relapsing inflammatory disorder - due to high sebaceous gland concentration and increased hormone levels
erythematous macule or patches with greasy scale
seen on eyebrows, alar folds, posterior auricular region, pre-sternal region, maybe scalp
treatment for seborrheic dermatitis
vigorous scrubbing during baths —> desensitizes and reduces scaling
olive or coconut oil
low-potency topical corticosteroid or anti-fungal twice daily
anti-seborrheic shampoo with pyrithione zinc, selenium sulfide, or ketoconazole
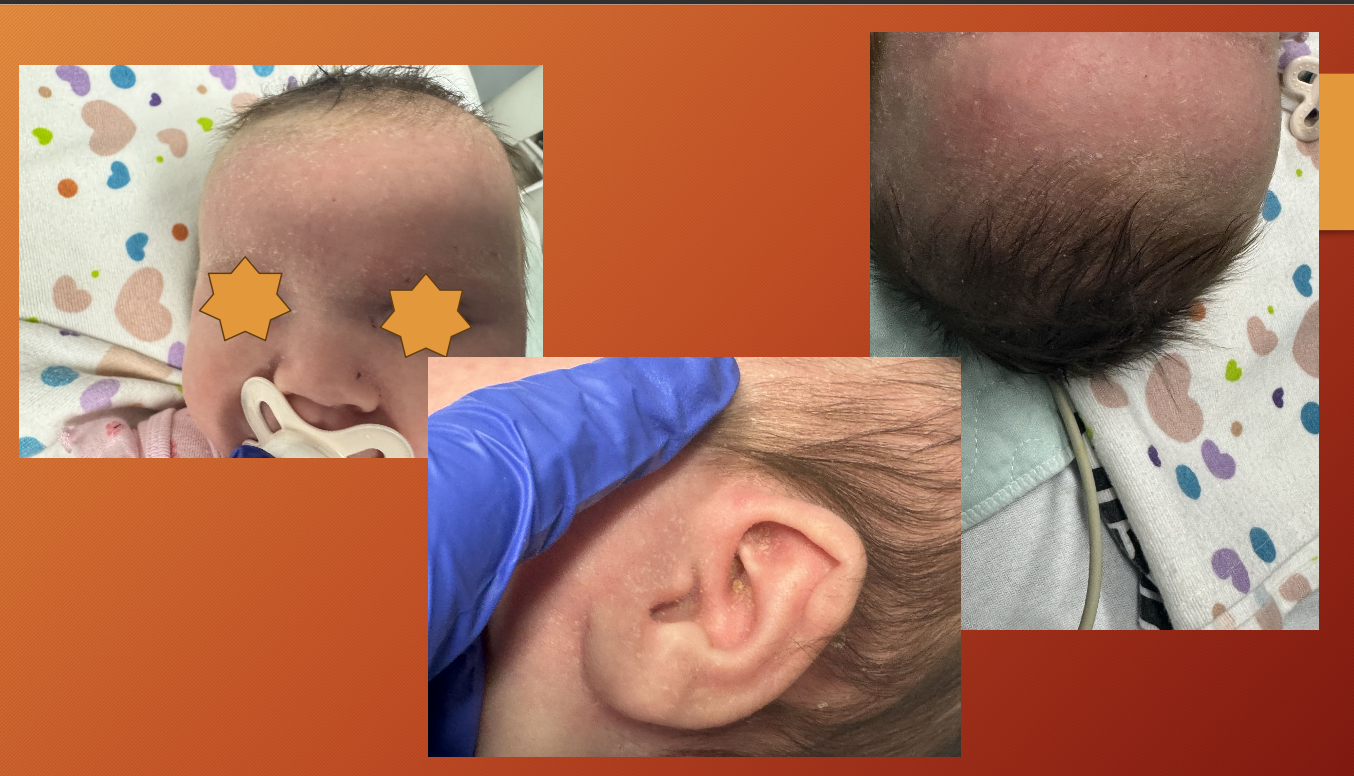
seborrheic dermatitis
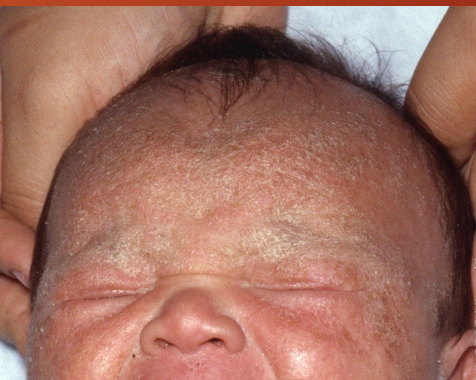
seborrheic dermatitis
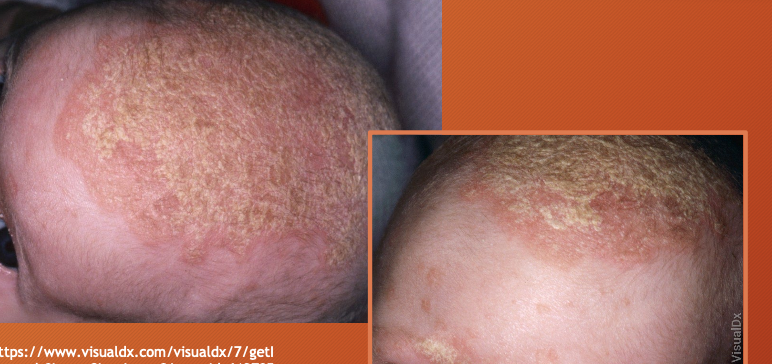
seborrheic dermatitis