Harvard Human Anatomy - Cells, Tissues and Systems
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Cell
The smallest independent unit of living tissue, composed of molecules and organized by membranes.
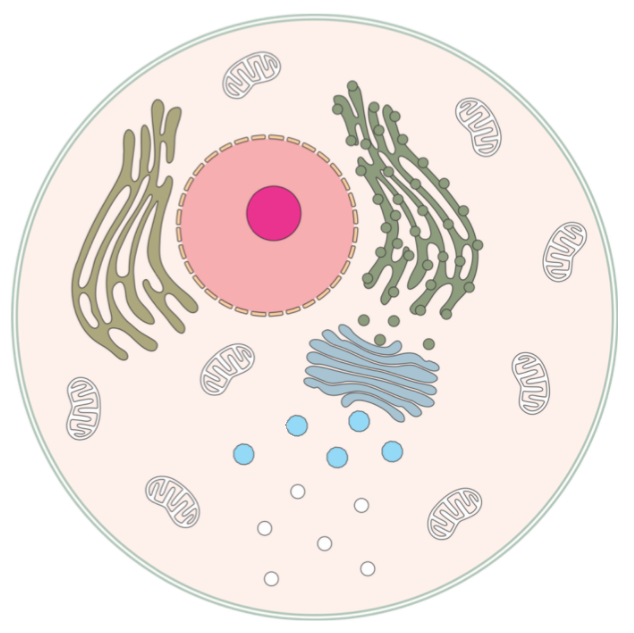
Cell membrane
A selective barrier between the interior and exterior of the cell.
Circulatory System
Distributes body fluids, enabling transport of oxygen and nutrients and removal of CO2 and waste.
Cytoplasm
Comprised of the cytoskeleton suspended in cytosol.
Digestive system
Chief functions include absorption of water and breakdown and absorption of food.
Endocrine system
Synthesizes and secretes hormones disseminated through the circulatory system.
Epithelial tissue
Forms a barrier covering external and internal body surfaces.
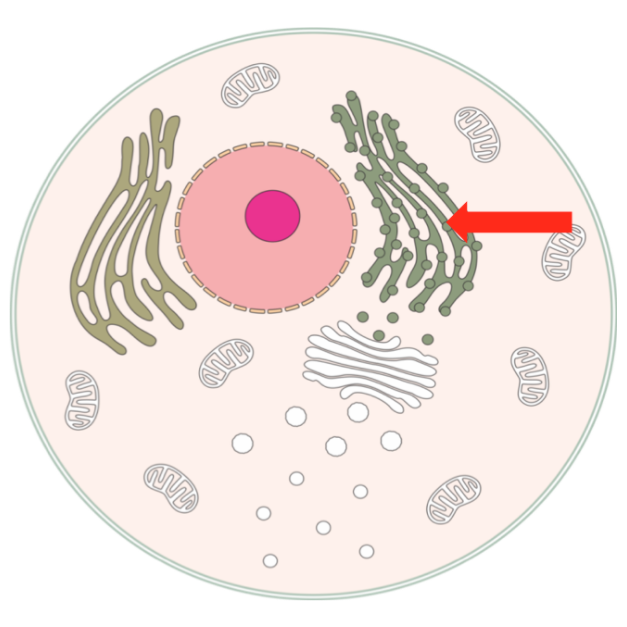
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
A system of membrane-bound tubules and cisternae within the cell.
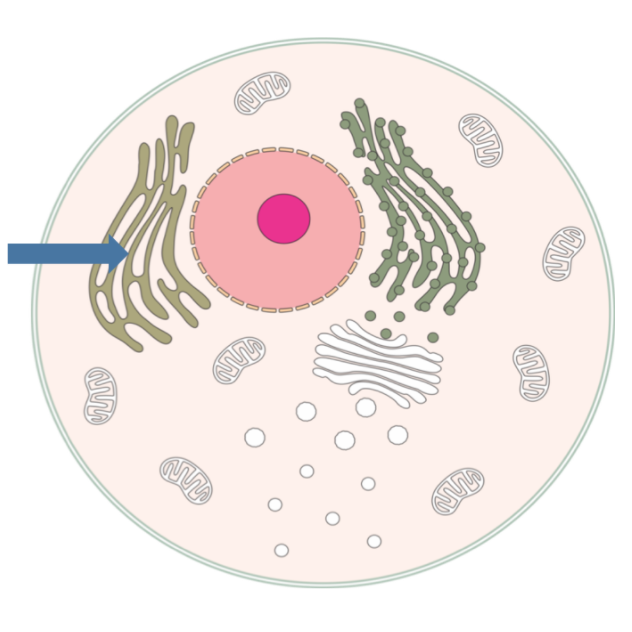
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
major site of protein and enzyme synthesis within the cell. membrane surface is covered with ribosomes.
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
found in cells specializing in hormone synthesis or detoxification
Golgi apparatus
Sorts and packages proteins produced in the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
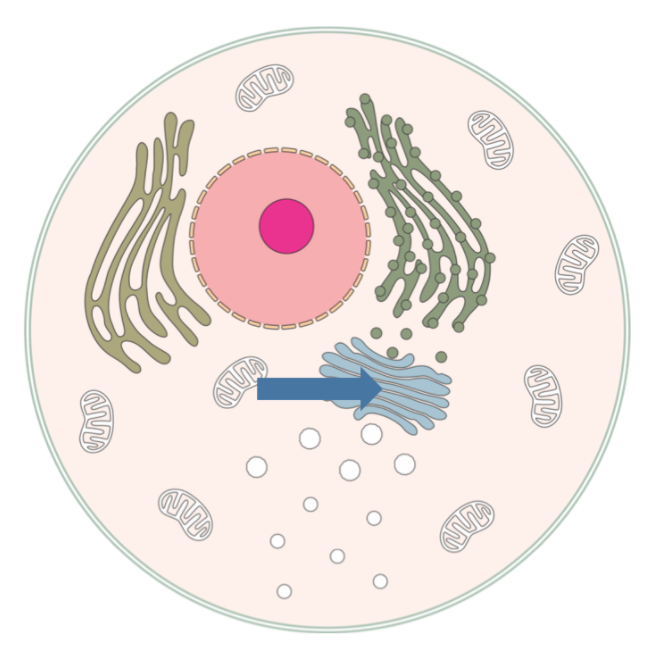
Histology
The study of the minute structure of cells, tissues, and organs in relation to their functions.
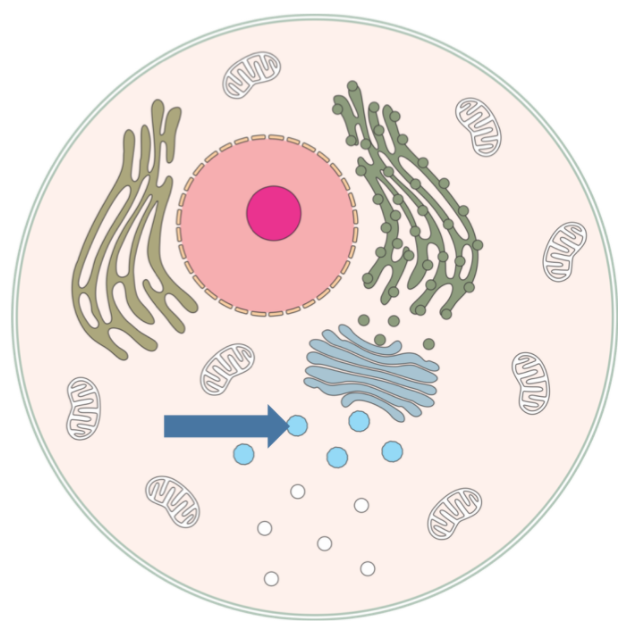
Lysosomes
Small membrane-bound packets of enzymes that digest microorganisms and cell debris.
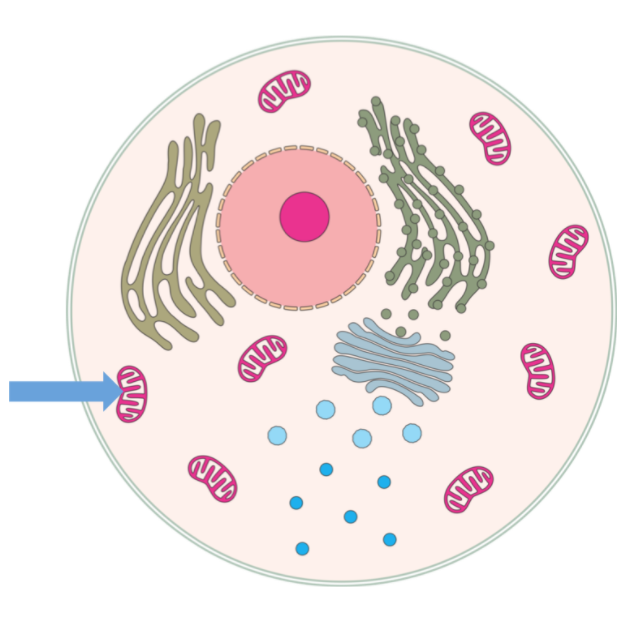
Mitochondria
Principal energy sources of cells, sites of oxidative phosphorylation and ATP formation. Numerous in cells that actively secrete protein,
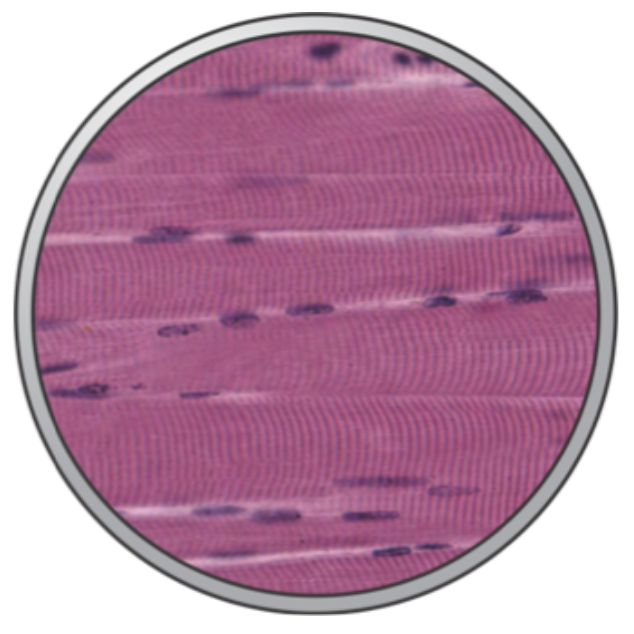
Muscle tissue
Basic function is motion achieved by contraction and sliding of filament arrays.
Musculoskeletal system
Achieves motion, comprising bones, joints, muscles, and fascia.
Nervous tissue
Basic function is sending and receiving information.
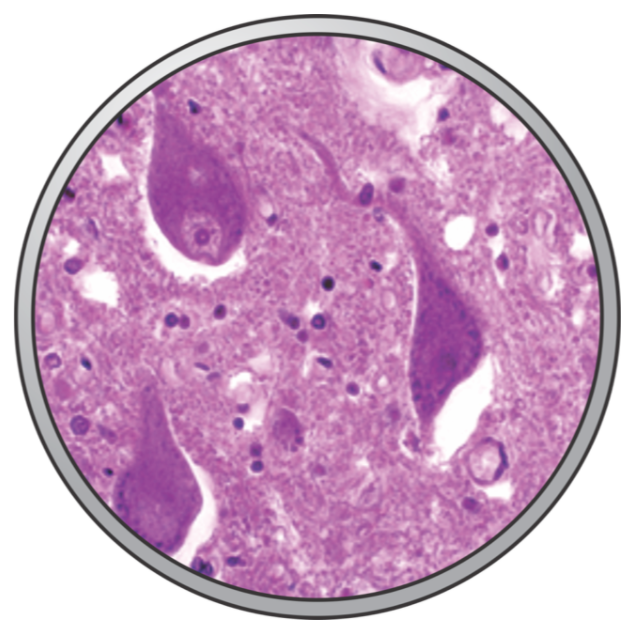
Nervous system
Enables communication between the central nervous system and other body regions.
Nucleus
Contains genetic material, serves as the cell control center.
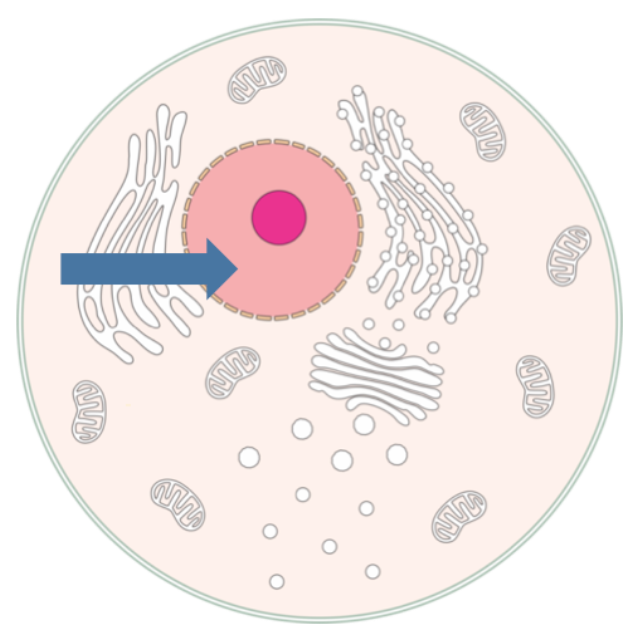
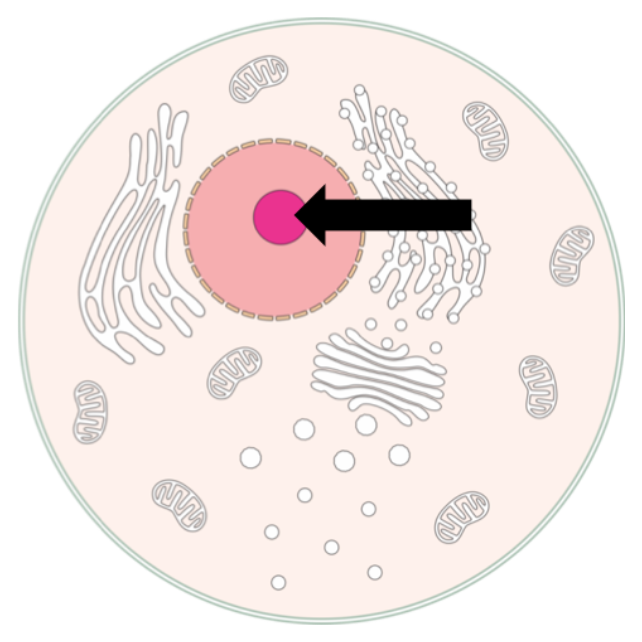
Nucleolus
Site of ribosomal RNA synthesis and ribosome assembly within the nucleus.
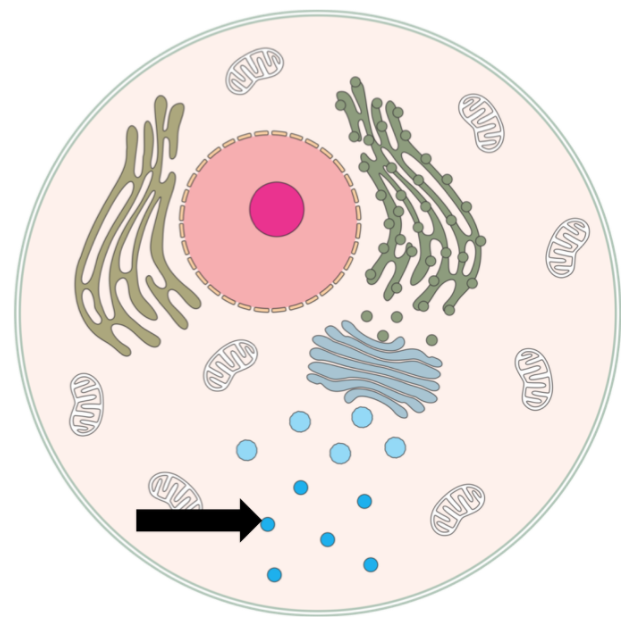
Organelle
Functional components of cells, including the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticula, etc.
Peroxisomes
Membrane-bound packets of enzymes that oxidize organic substances and form hydrogen peroxide.
Respiratory system
Consists of a conducting portion (the airway) and a gas exchange portion (the alveoli).
Skin
The largest organ of the body, consisting of an outer epidermis and an inner dermis.
Supportive / Connective Tissue
Includes building materials and structural supports like fat, tendons, bone, and cartilage.
Urogenital system
Includes the urinary system and the male and female reproductive systems.