CH 22:Darwin's Evolution Theory: Key Concepts and Evidence
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What is the essence of Darwin's reflection on life's diversity?
Darwin suggests that life, originally created by a Creator, has evolved into endless forms through natural processes.
What are the three key observations about life according to Darwin?
1. Organisms are well suited for their environments. 2. Unity of life through shared characteristics. 3. Diversity of life with numerous species.
What does Darwin mean by 'evolution = descent with modification'?
Evolution refers to the process by which species change over time, leading to new species through gradual adaptations.
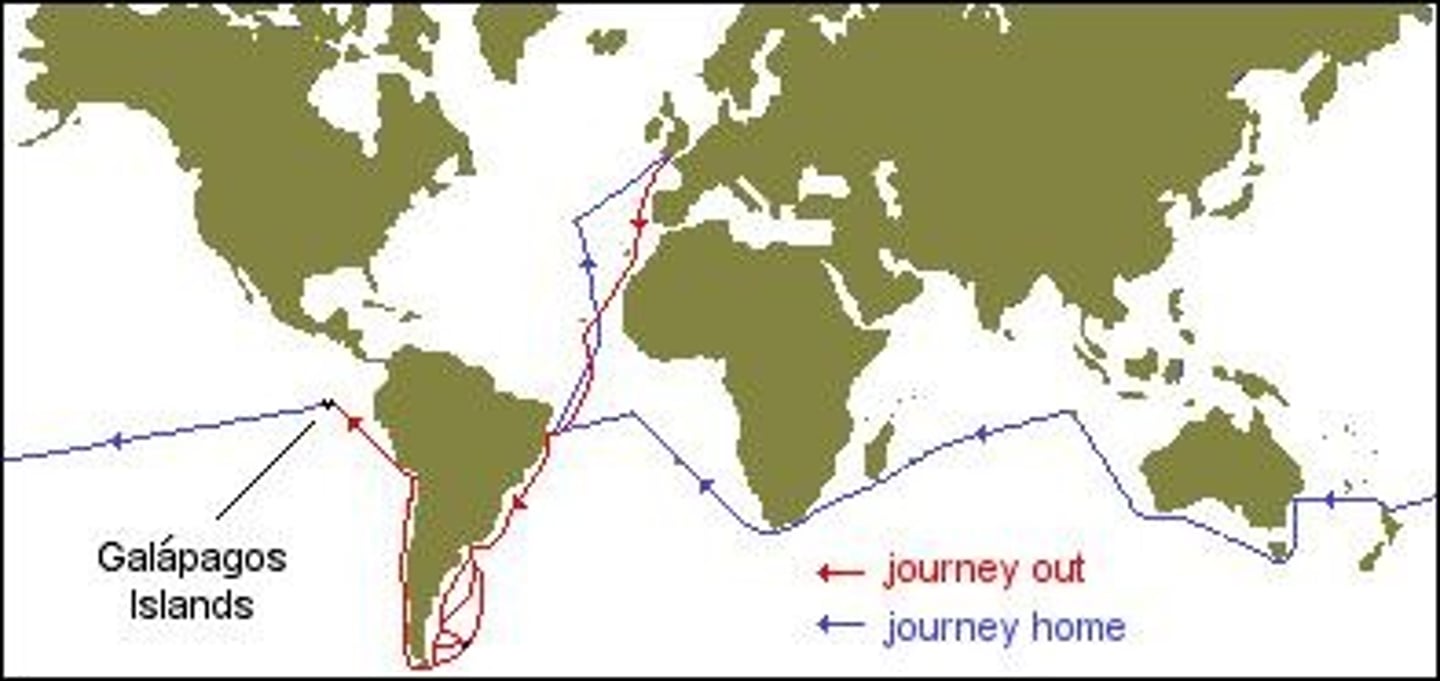
What was the significance of Darwin's trip on the HMS Beagle?
Darwin observed unique species in the Galapagos Islands, which influenced his ideas on evolution and natural selection.
What is the role of natural selection in evolution?
Natural selection is the chief mechanism of evolution, where individuals with advantageous traits are more likely to survive and reproduce.
How did Darwin view the history of life?
He viewed it as a tree with multiple branches, representing the descent from common ancestors and the extinction of some species.
What is artificial selection and how does it relate to natural selection?
Artificial selection is the human practice of breeding for desired traits, similar to natural selection, which occurs in nature.
What are the two inferences Darwin drew from his observations?
1. Individuals with advantageous traits tend to produce more offspring. 2. Unequal survival and reproduction lead to the accumulation of favorable traits.
What types of evidence support the theory of evolution?
Fossils, taxonomy, comparative anatomy, comparative embryology, and biogeography.
How do fossils provide evidence for evolution?
Fossils are remains or imprints of past life preserved in sedimentary layers, showing changes over time.
What is the hierarchical classification system developed by Linnaeus?
It classifies organisms into groups: Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species.
What are homologous structures?
Similar anatomical structures in different species that indicate a common ancestor, though they may serve different functions.
What is the difference between homologous and analogous structures?
Homologous structures share a common evolutionary origin, while analogous structures have similar functions but different origins.
What does comparative embryology reveal about evolution?
It shows that vertebrate embryos share similar features, indicating a common ancestry.
What is biogeography?
The study of the geographic distribution of species, showing how related species are found in different areas.
What is microevolution?
Evolutionary changes in allele frequencies within a population, influenced by natural selection, genetic drift, and gene flow.
What is macroevolution?
Evolutionary change on a grand scale, including the origins of new structures, trends, and mass extinctions.
What did Darwin's observations of Galapagos finches reveal?
They showed that different beak types evolved in response to different environmental pressures.

What is the significance of the concept of 'survival of the fittest'?
It refers to the idea that individuals best adapted to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce.
How does the concept of descent with modification explain biodiversity?
It explains how species evolve and diversify from common ancestors through gradual changes over time.
What is the importance of the fossil record in understanding evolution?
It provides a historical record of life on Earth, showing how species have changed and evolved over time.
How does taxonomy imply relatedness among species?
It groups species based on shared characteristics, suggesting evolutionary relationships among them.
What is the significance of adaptations in evolution?
Inherited traits that enhance an organism's survival and reproduction in specific environments.
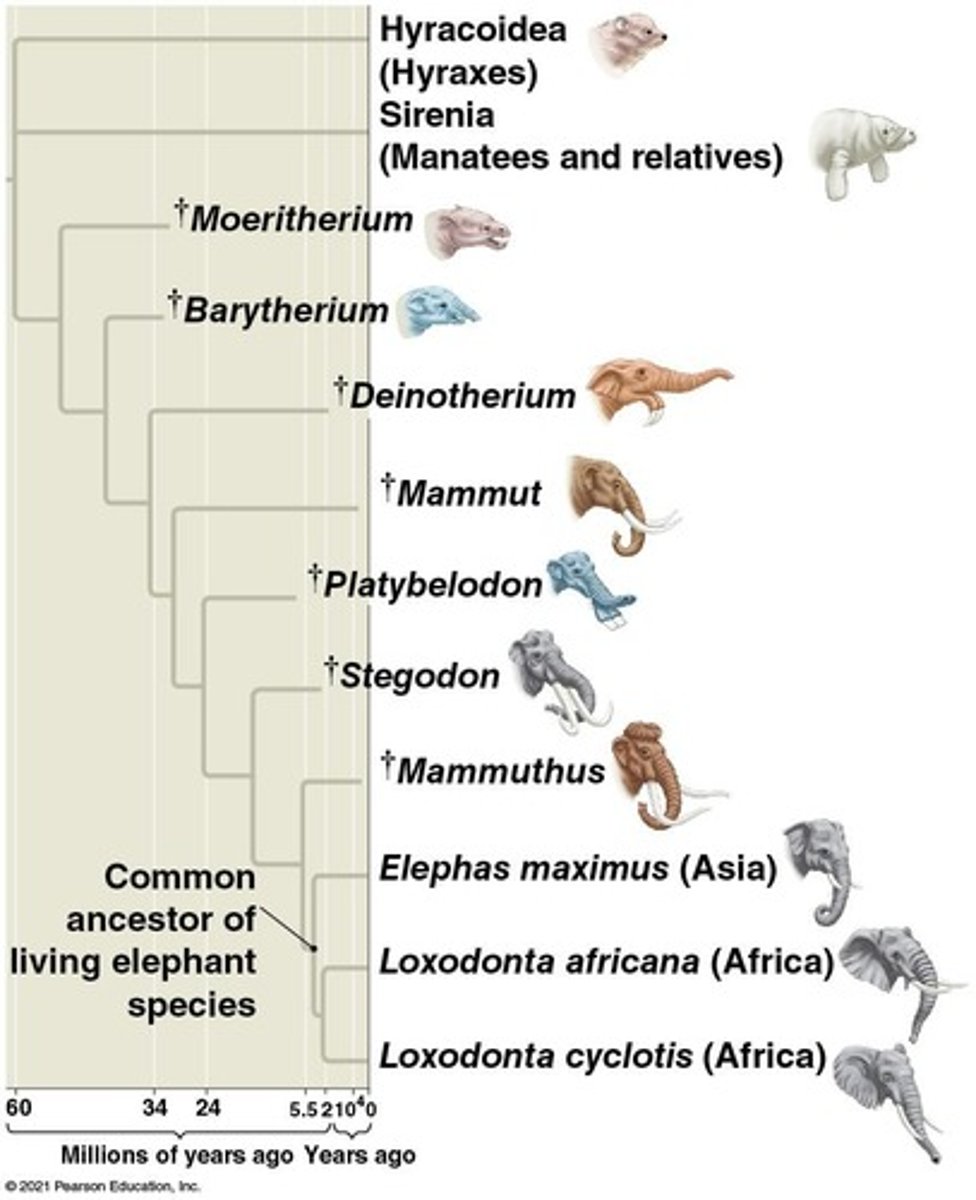
How does the concept of a phylogenetic tree relate to evolution?
It visually represents the evolutionary relationships and descent among species, showing common ancestors.
What is the role of genetic drift in evolution?
A mechanism of evolution that causes random changes in allele frequencies in a population.
What are some examples of artificial selection?
Breeding of domesticated plants and animals, such as fruits, vegetables, and dog breeds.
Who was James Hutton?
He proposed the theory of gradualism, stating that Earth changed slowly over time.
Who was Jean Baptiste Lamarck, and what did he contribute to the theory of evolution.
Proposed his theory of evolution by transformation. He believed the environment affected an organism’s traits that would then get passed onto their offspring if used. This was referenced as “Inheritance of acquired characteristics.”
Who was Erasmus Darwin?
Proposed that all living organisms evolved from one common ancestor and that species could transform into a new species
Who was Charles Lyell?
Proposed that geological evidence (fossils found in sedimentary rocks) showed that the earth has been around for millions of years and had changed over time.