Reactions at sp2 centres - non-aromatic compounds as electrophiles
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
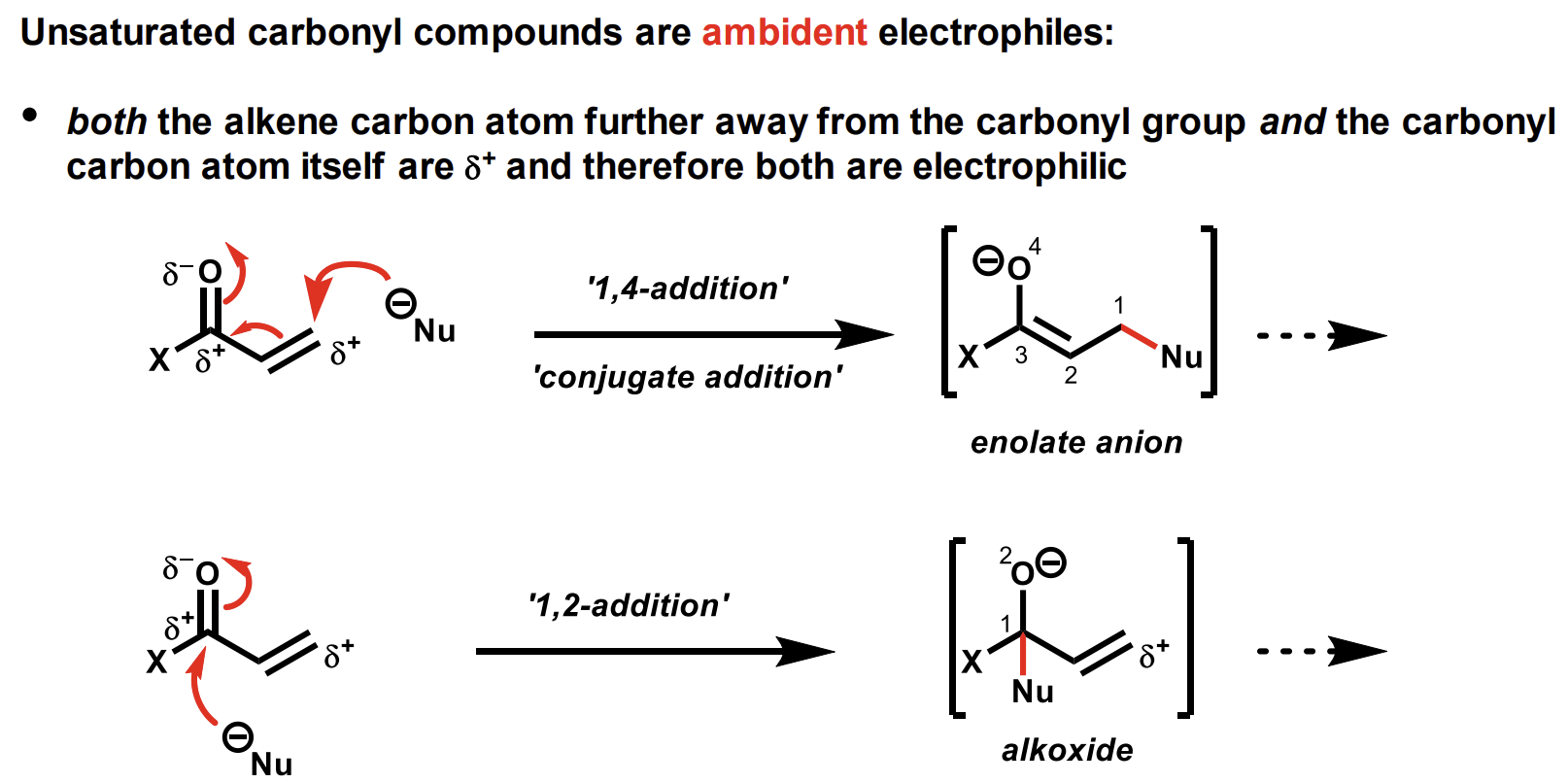
What are ambident electrophiles
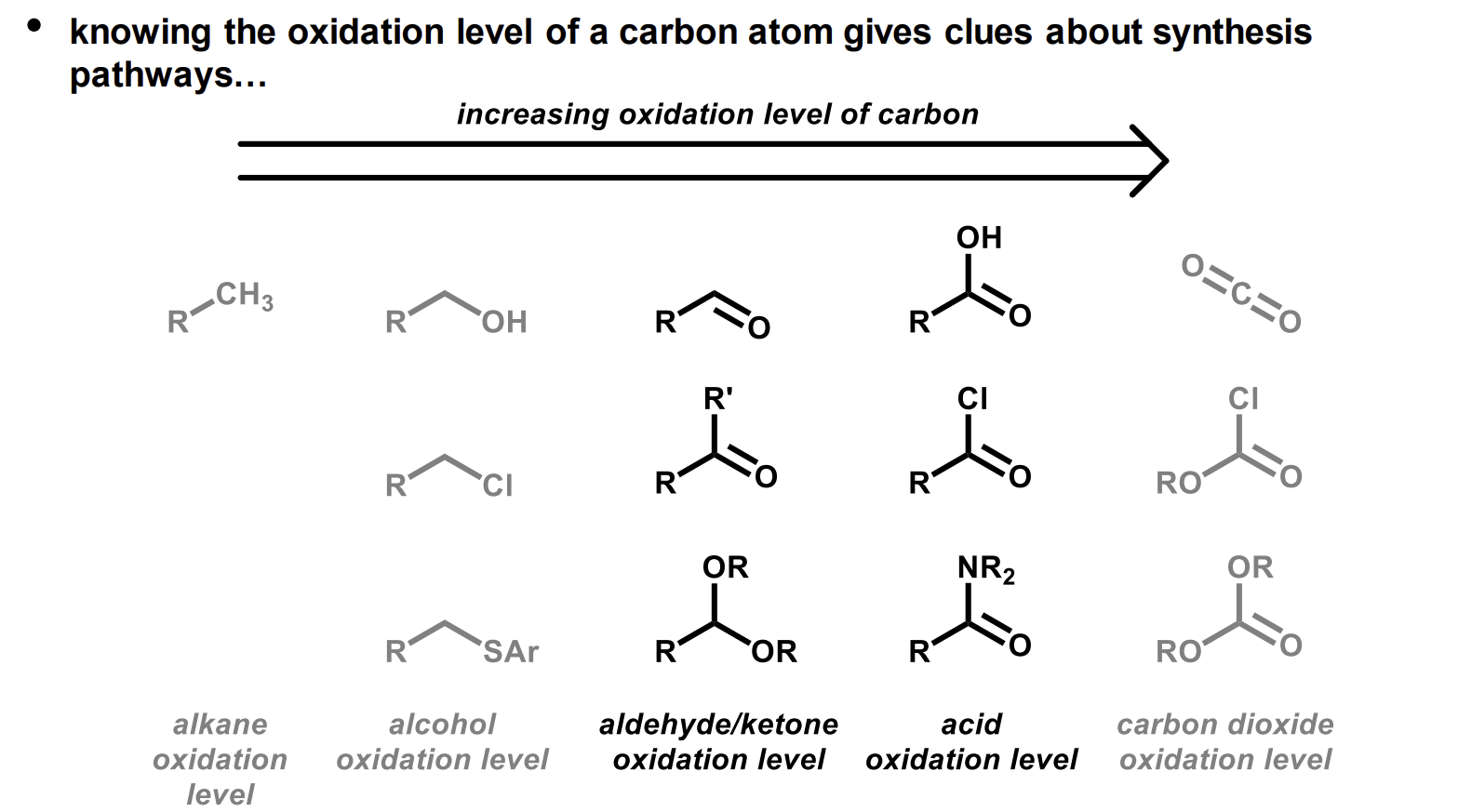
What are the different oxidation levels of alkyl groups and carbonyls
It tends to be the case that interconversion between same oxidation levels is easier.
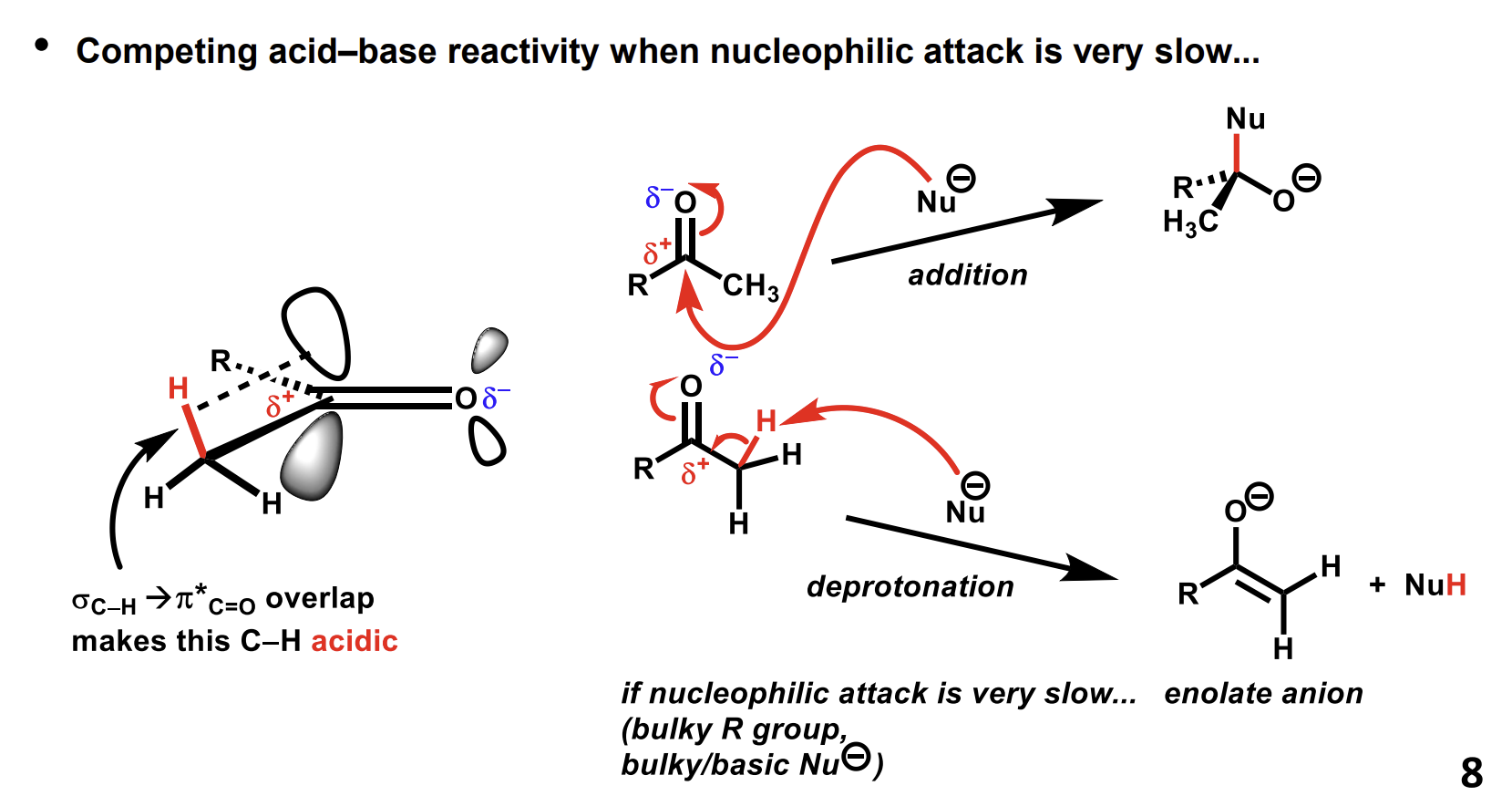
speed of reaction of aldehydes vs ketones
Aldehydes tend to react faster as there is less steric hindrance and less donation of electrons towards the electrophilic carbon.
The H on the Me is acidic and can result in a nucleophile acting as a base, forming an enolate product.
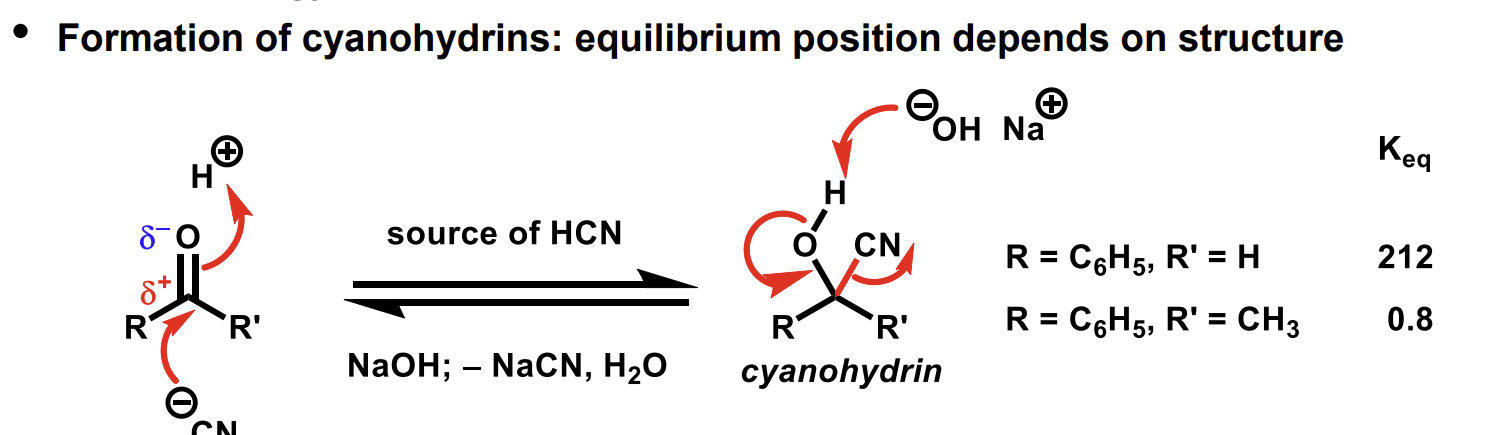
What is a way to form cyanohydrins and how can the equilibrium position be moved
The ketone equilibrium position is shifted not due to rates (energetics determine K) but due to increased steric clash on the sp3 centre compared to the relatively less hindered sp2 centre.
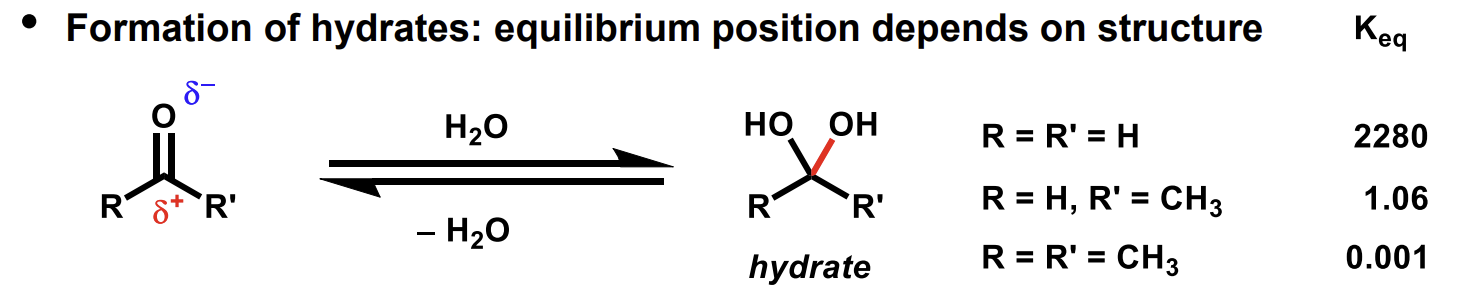
Impact of R groups on hydrate formation from carbonyls
Same idea as previous
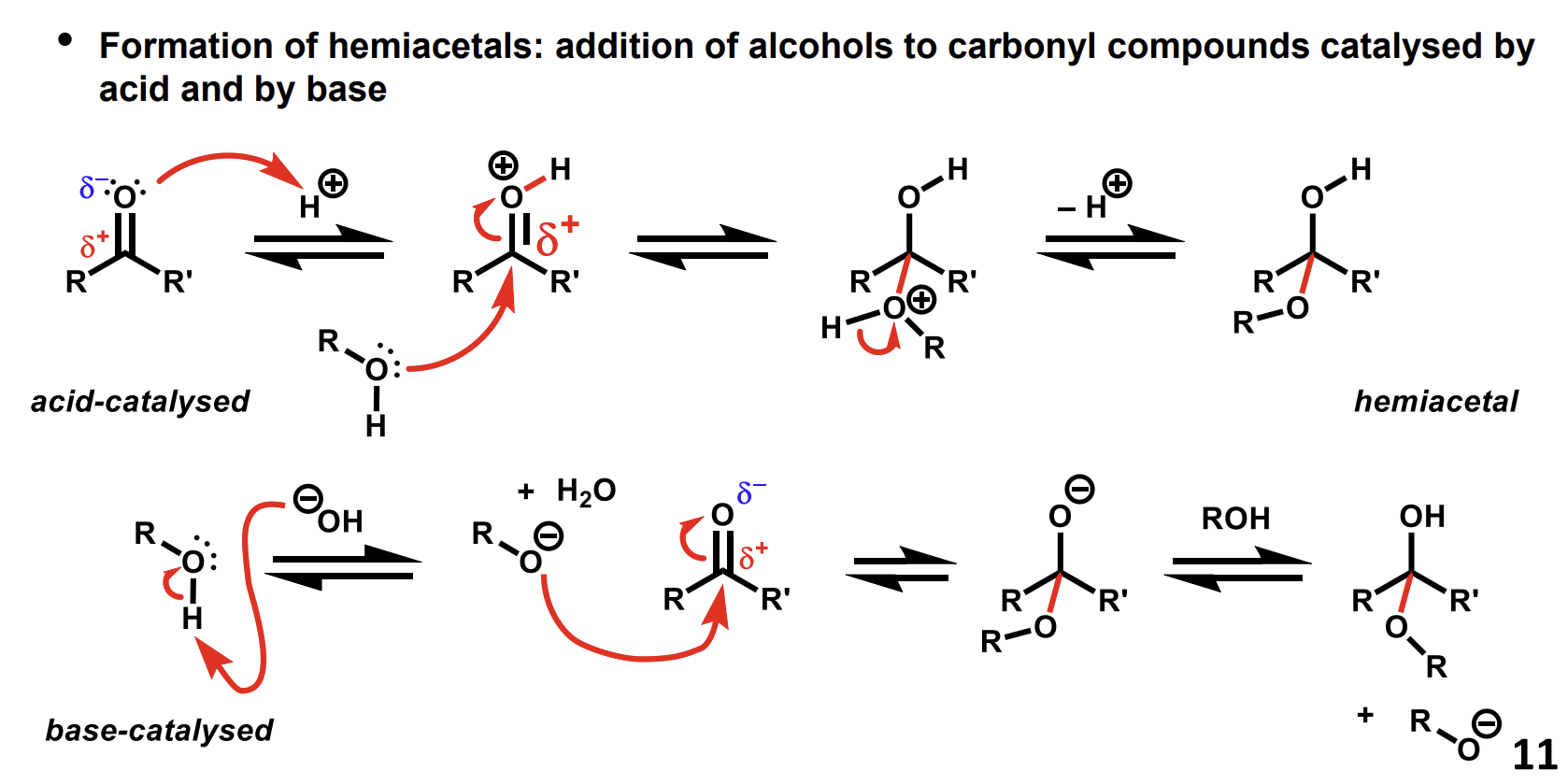
Mechanism for formation of hemiacetals using carbonyls
The acid makes the carbon more electrophilic
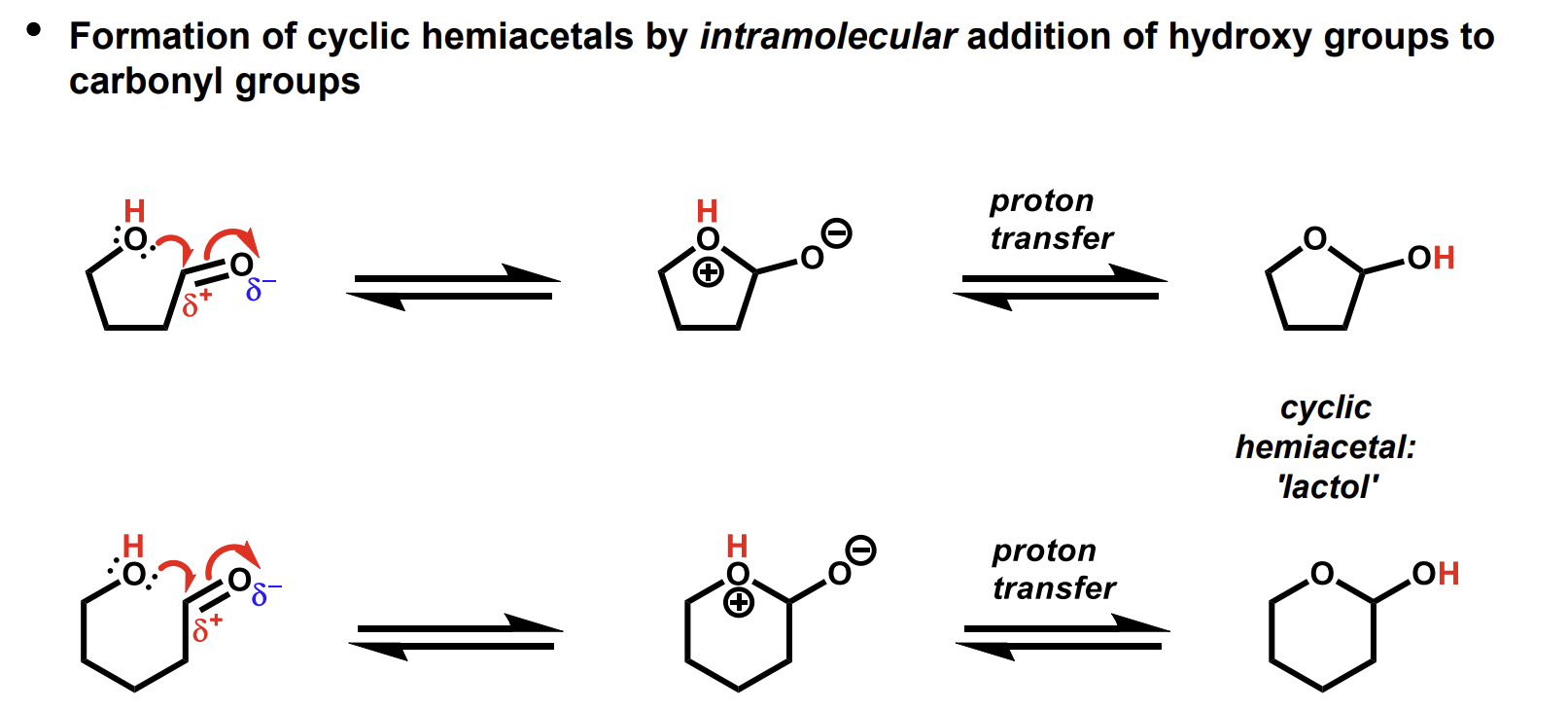
Formation of hemiacetals using intramolecular addition
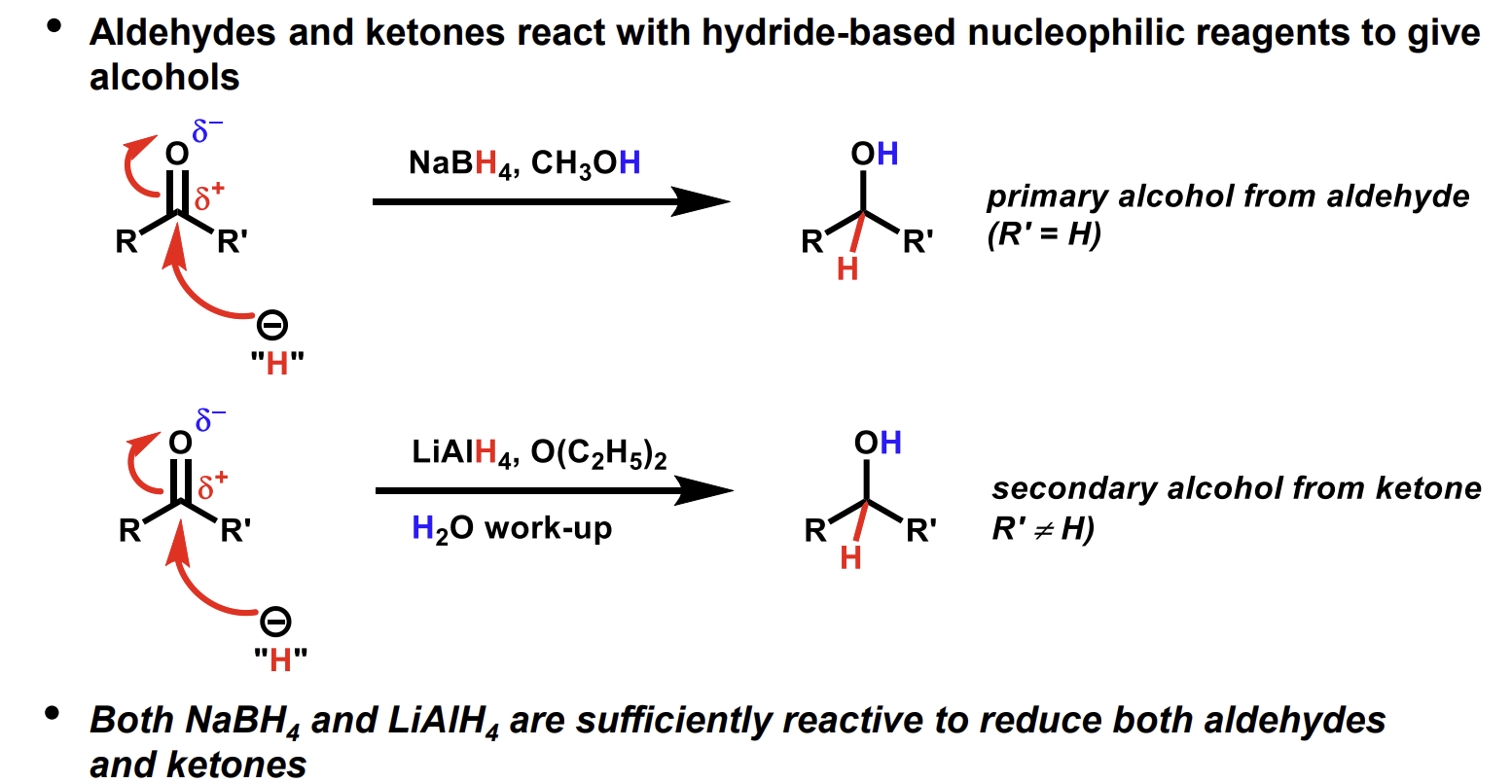
Considerations when producing alcohols from carbonyls
If using LiAlH4 an aprotic solvent should be used as stuff like methanol will be reduced to an alkoxide as it is a VERY powerful reducing agent
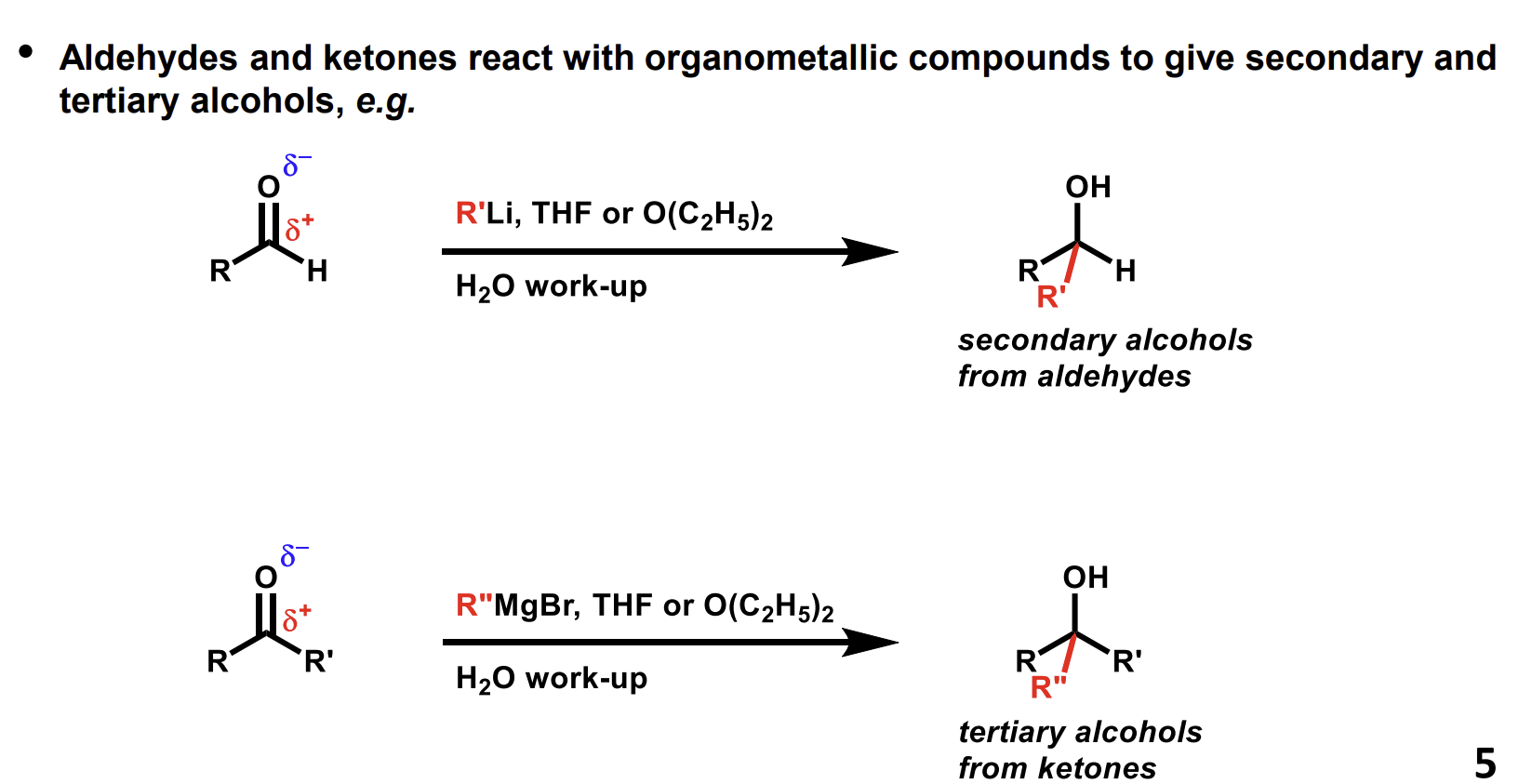
How do you produce secondary/ tertiary alcohols from carbonyls
Organometallic compounds
When drawing the mechanism the R group functions as a carbanion nucleophile.
Bottom one uses a Grignard reagent
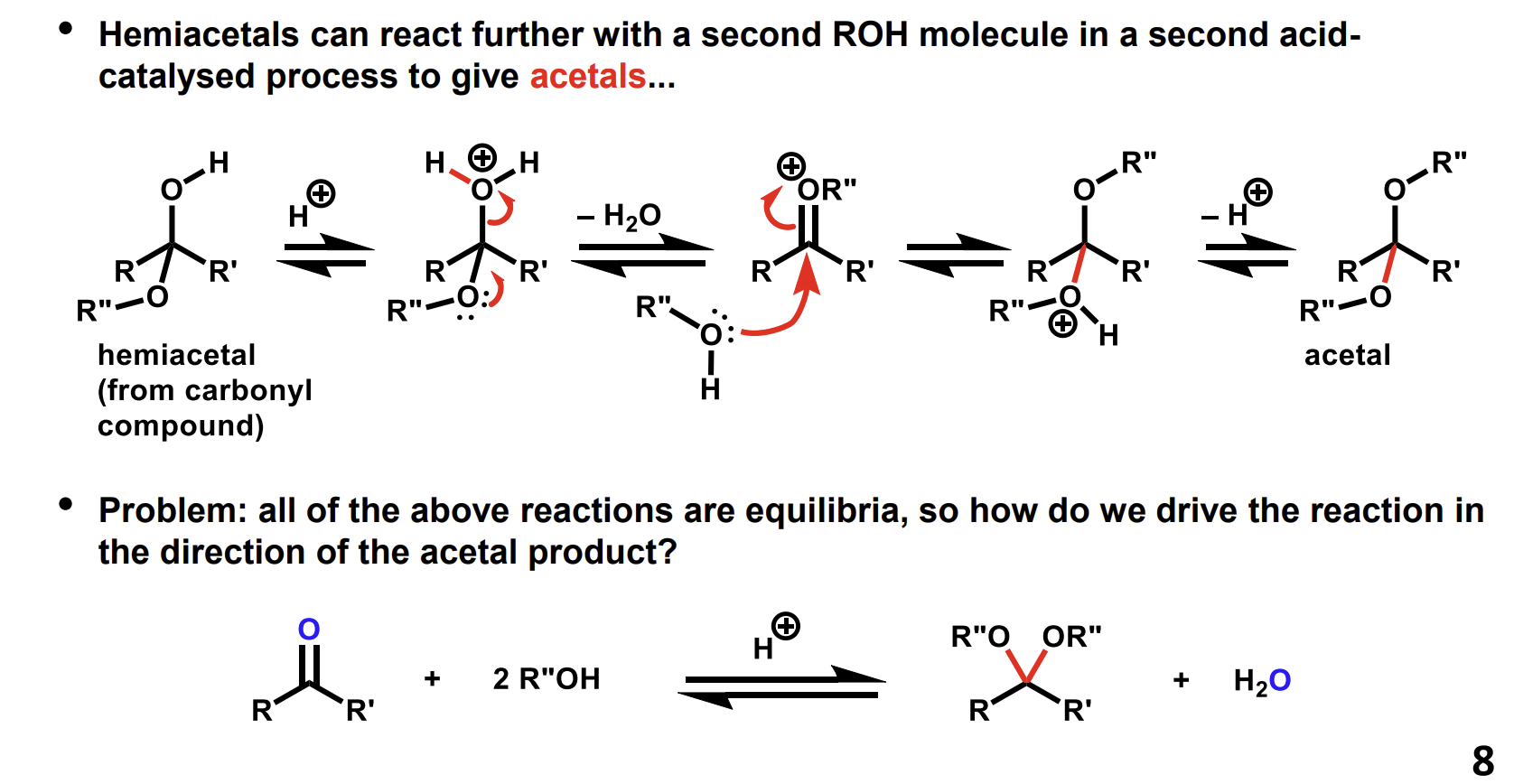
How can a hemiacetal react to form an acetal
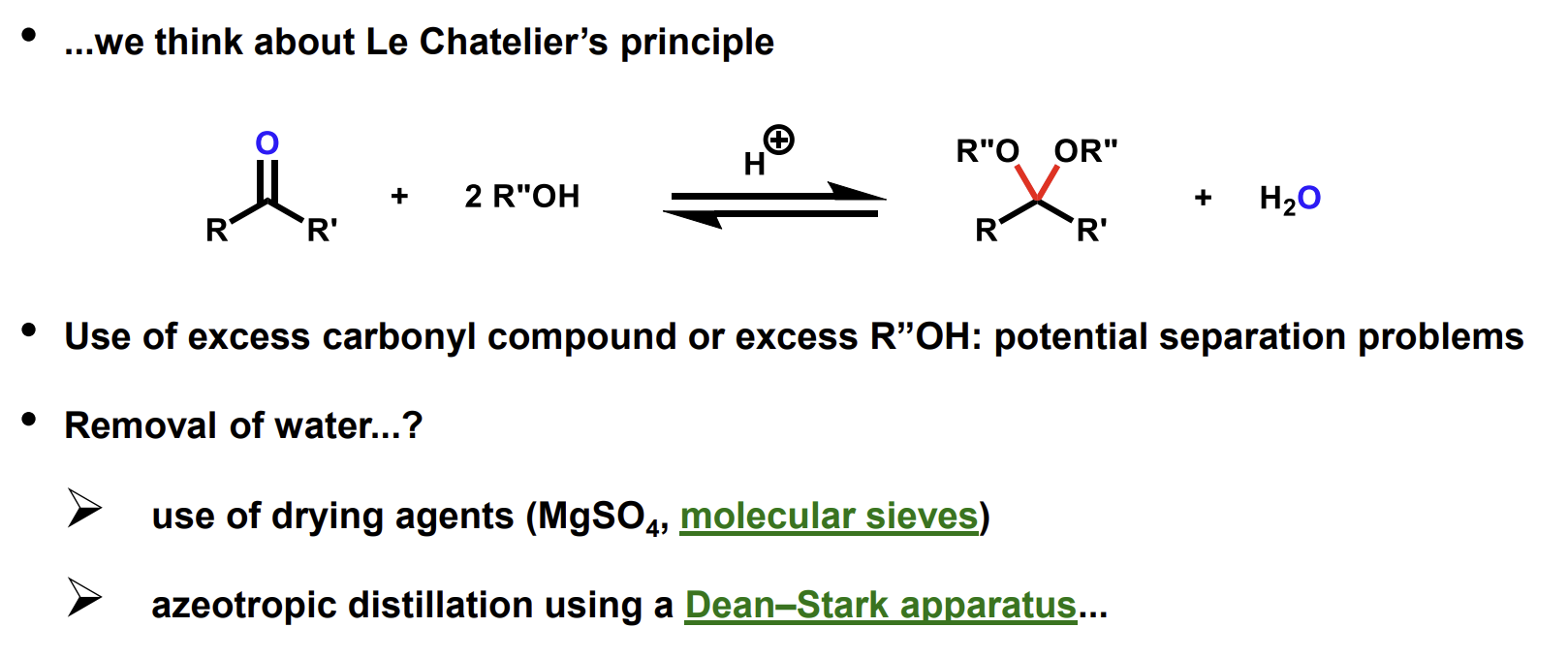
How do we drive the reaction to favour the acetal product
Using a large excess of reactant poses problems when separating stuff.
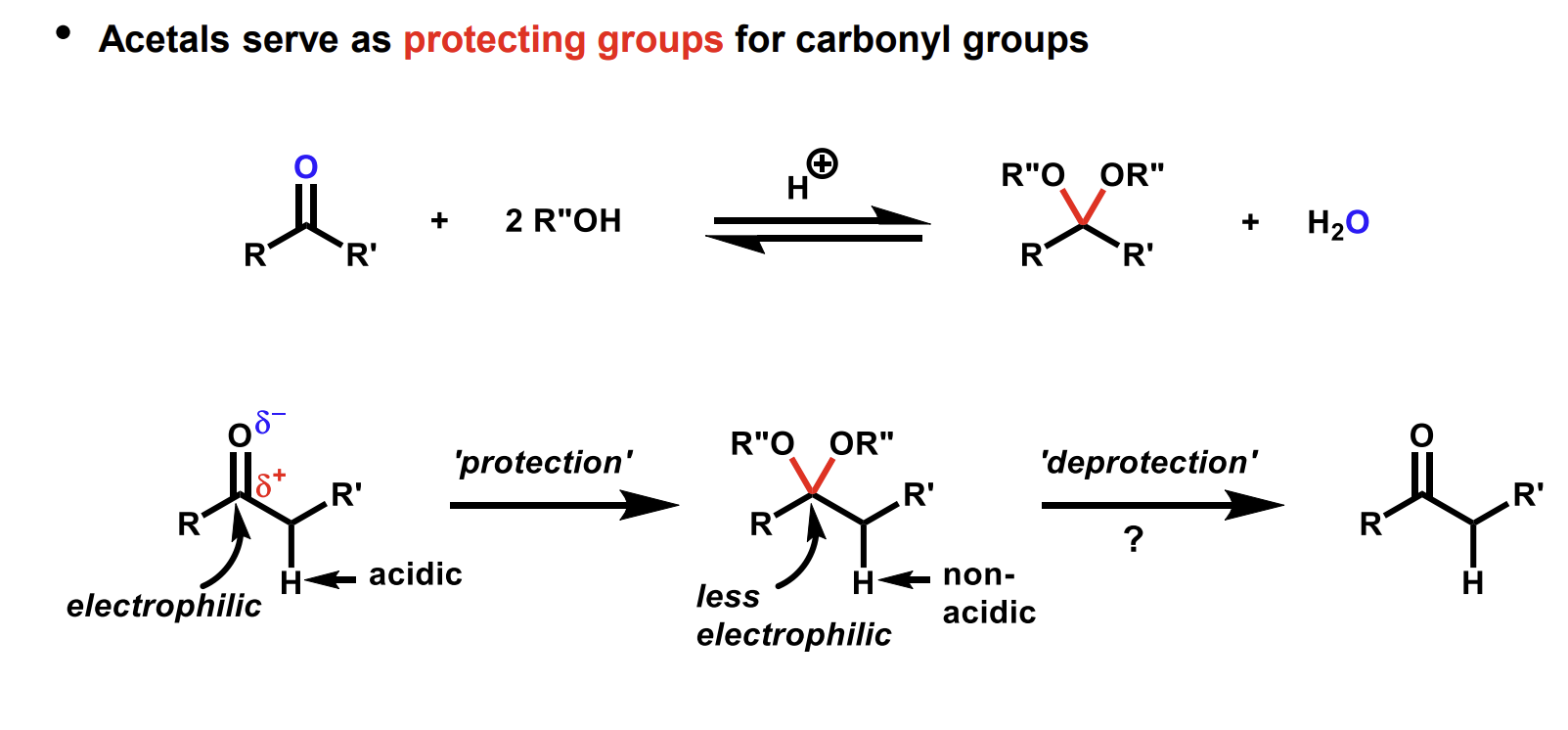
How does acetal work as a protecting group
We can protect the carbonyl by turning it into an acetal during a reaction elsewhere in the molecule.
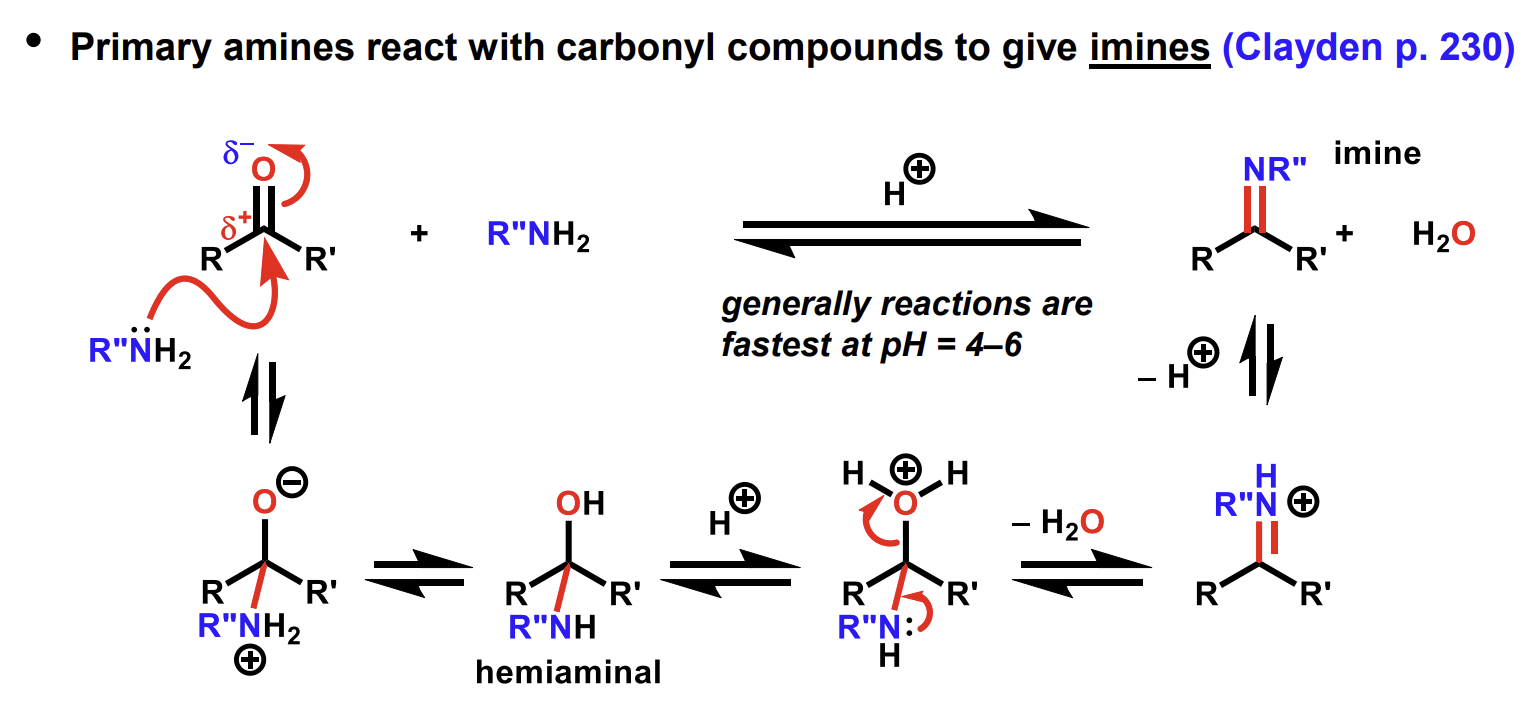
Reaction of carbonyls to form imines and the pH condition
We use pH 4-6 as too low pH will protonate the amine reactant
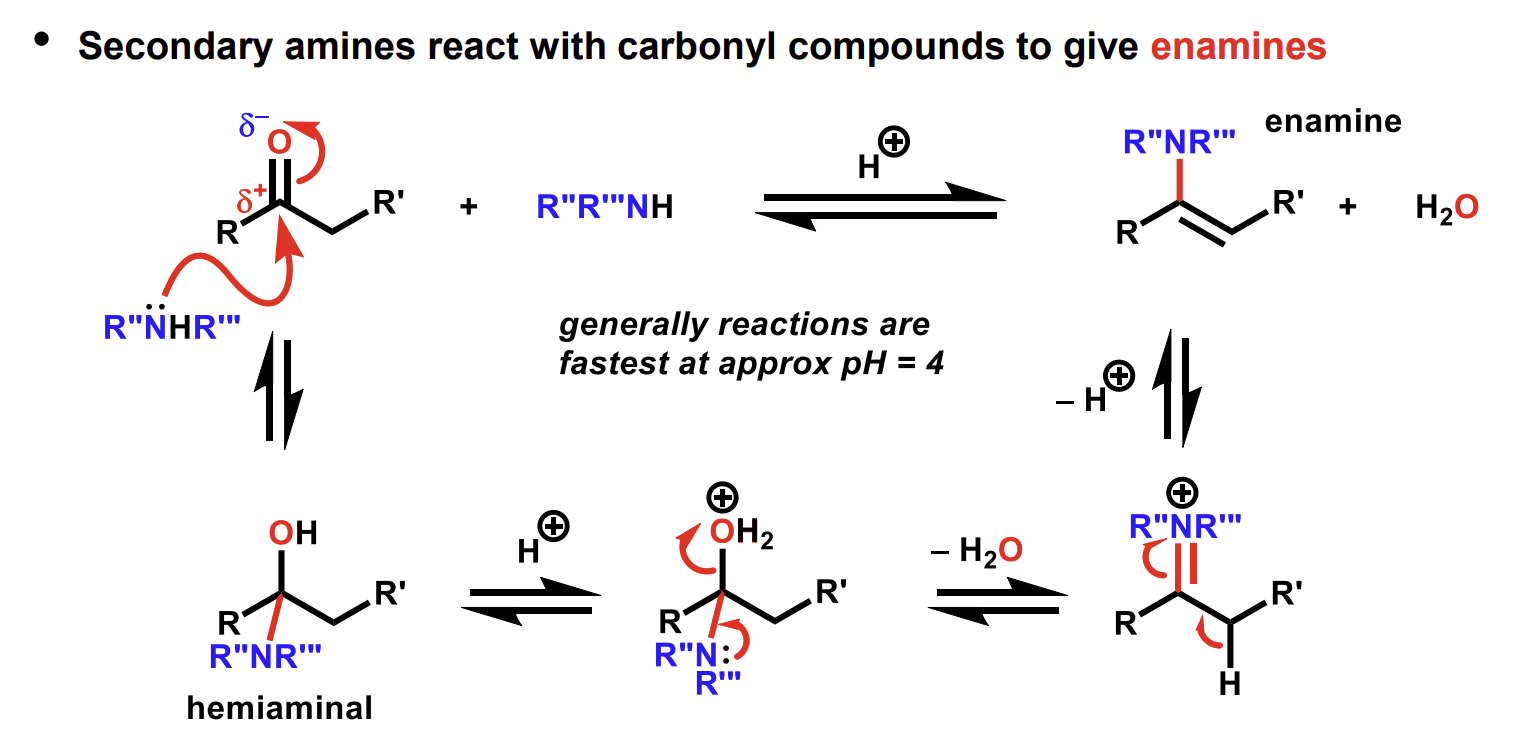
Reaction of carbonyls to form enamines
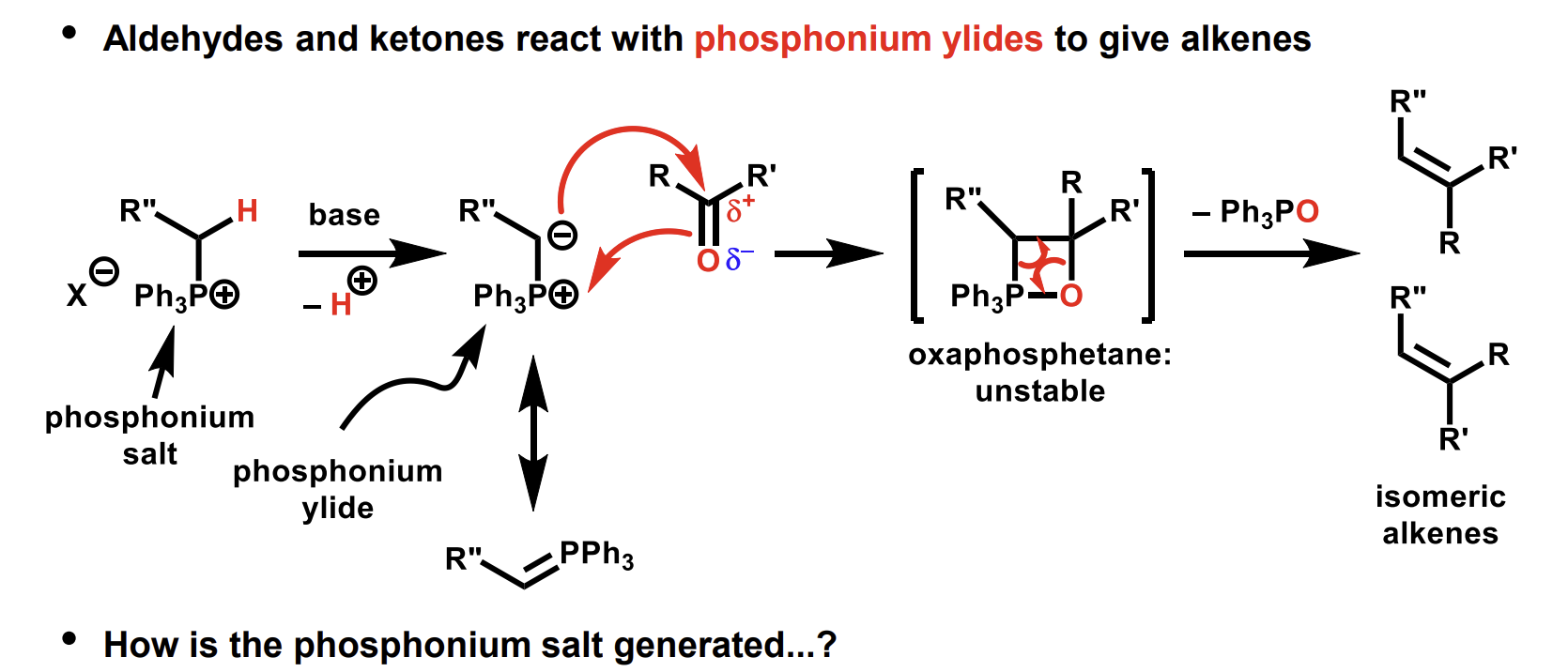
Aldehydes and ketones reaction to give alkenes
(Wittig reaction)
What is the benefit of this process over elimination
Elimination produces a mixture of products if the double bond can form in multiple positions.
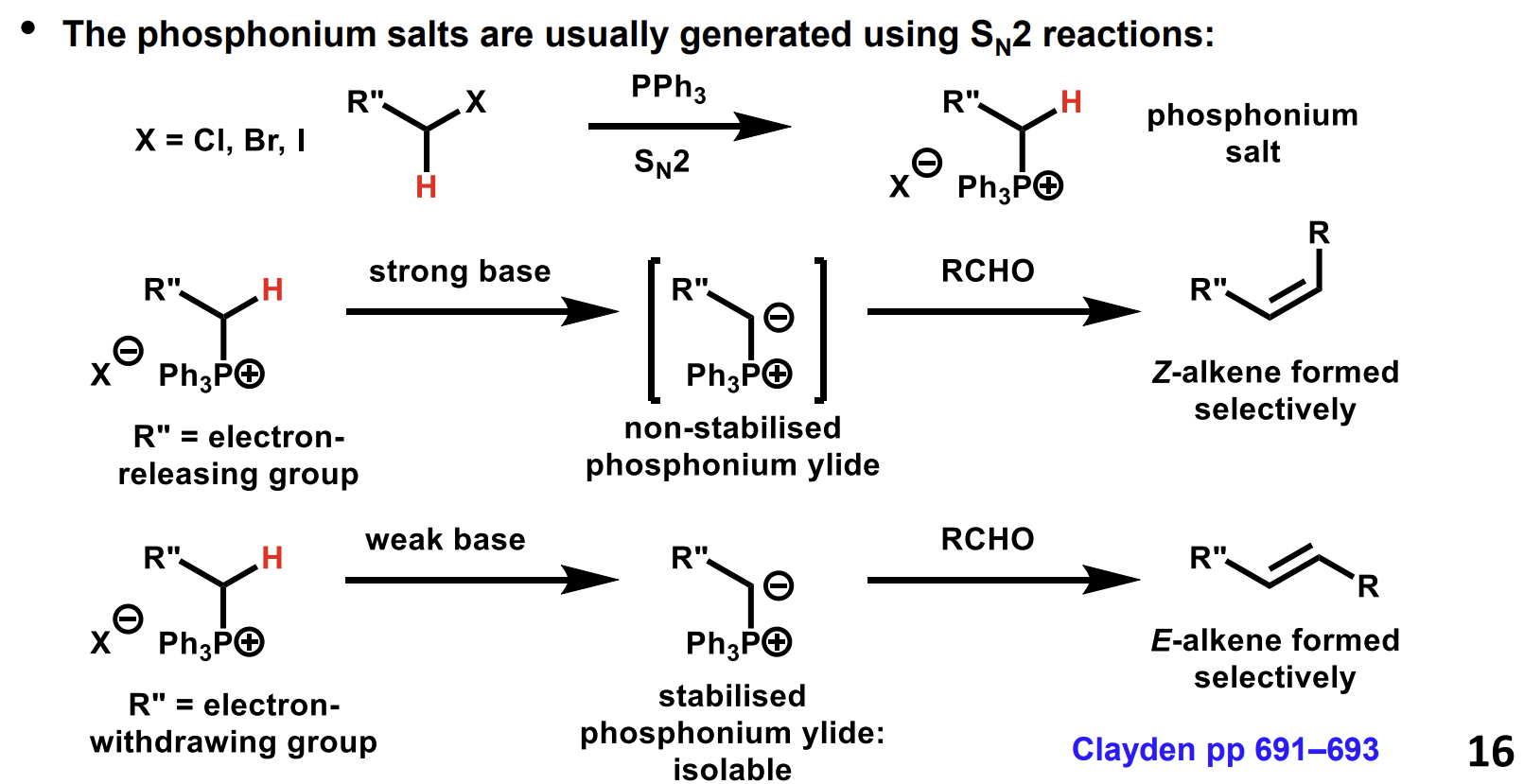
How is the phosphonium salt generated
The strength of the base used depends on whether the R group is electron donating or withdrawing.
Issues with the Wittig reaction
Ketones are not very reactive due to reasons discussed earlier and they give mixtures of geometric isomers
Triphenylphosphine oxide is awkward to remove