Ch. 13 Spinal Cord and Reflexes
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
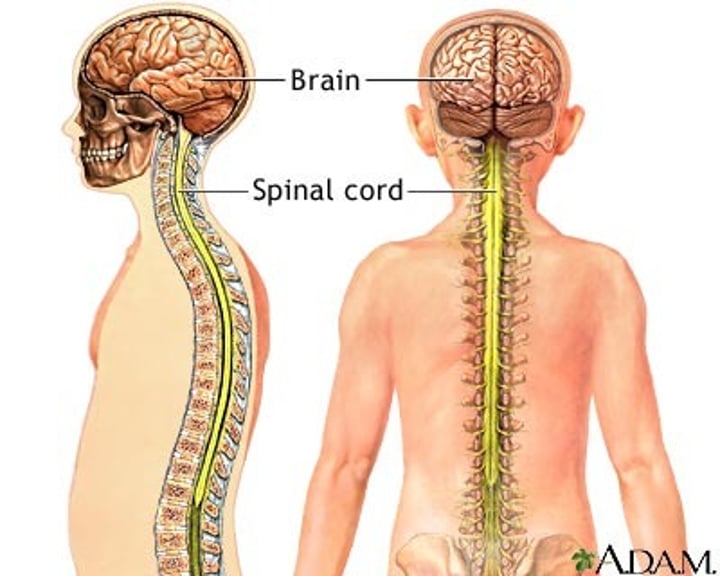
What is the primary function of the spinal cord?
to integrate and process information
spinal meninges
specialized membranes that provide protection, stability, and shock absorption; continuous with cranial meninges
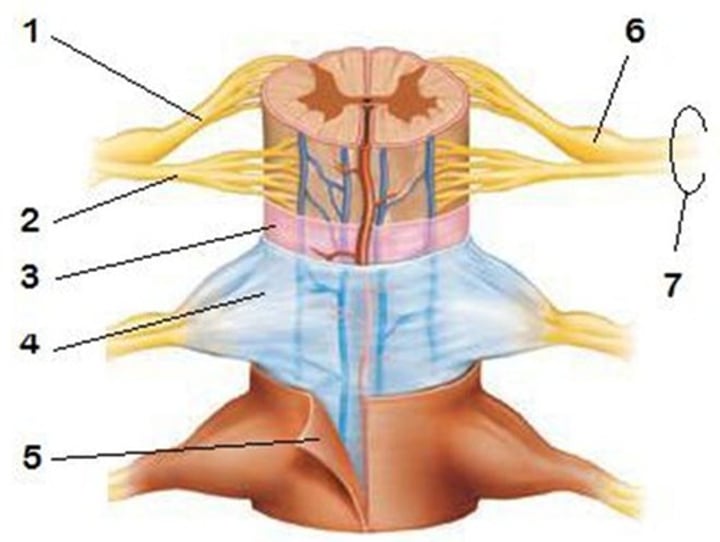
Name the spinal meninges from exterior to interior:
-dura mater
-arachnoid mater
-pia mater
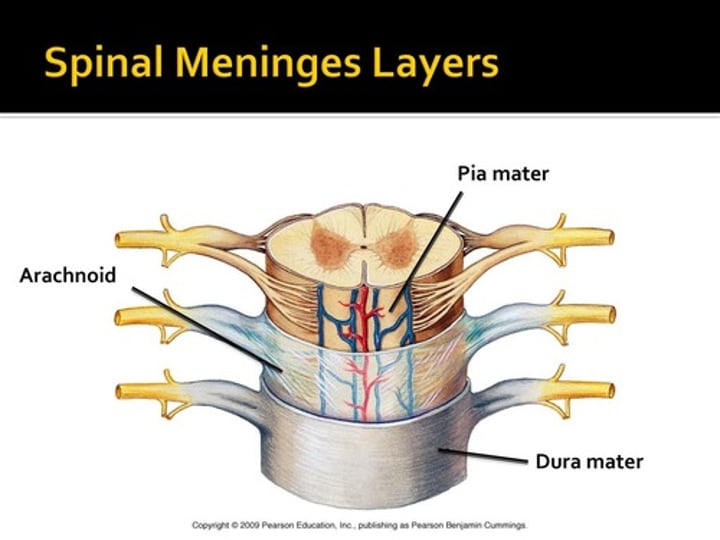
Dura mater
Tough, fibrous outermost layer of meninges that stabilizes the spinal cord within vertebral canal ("tough mother")
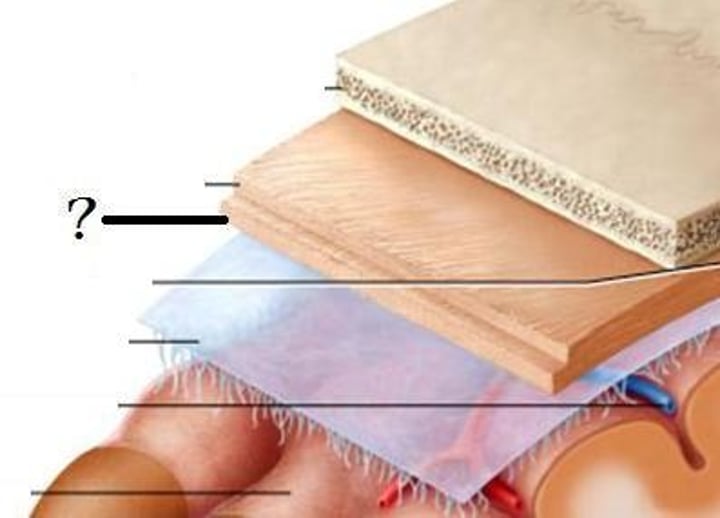
Arachnoid mater
"Spidery" middle layer of the meninges ("spider mother")
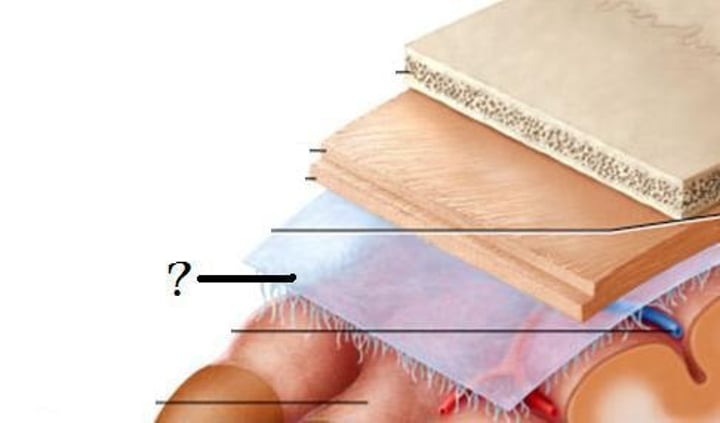
Pia mater
The deepest meningeal layer; blood vessels are found in this layer. This tissue is firmly bound to brain tissue and spinal cord tissue ("delicate mother")
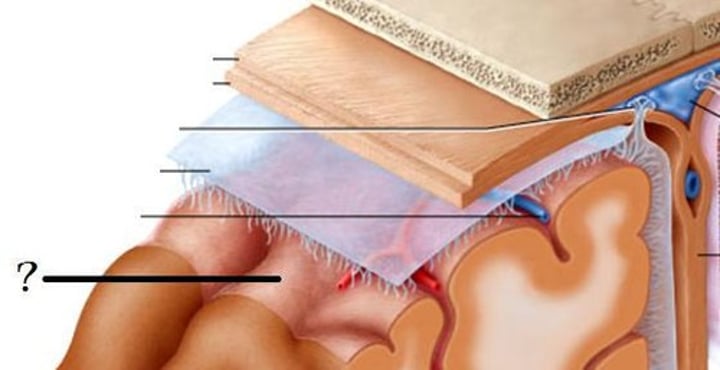
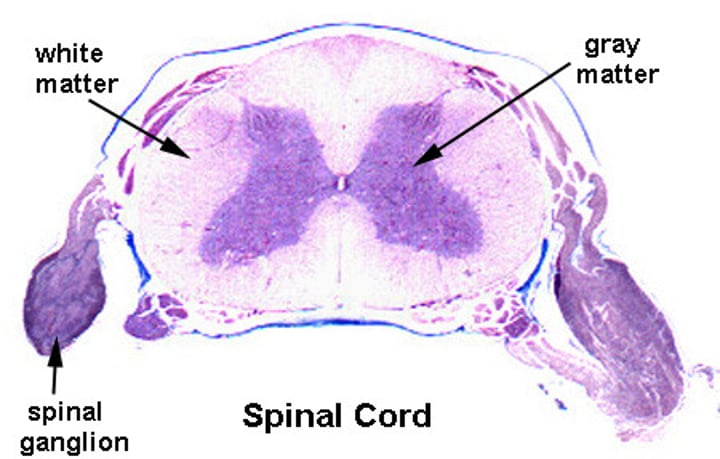
What does gray matter consist of?
neuron cell bodies and glial ("glue"; supporting) cells that are mostly unmyelinated
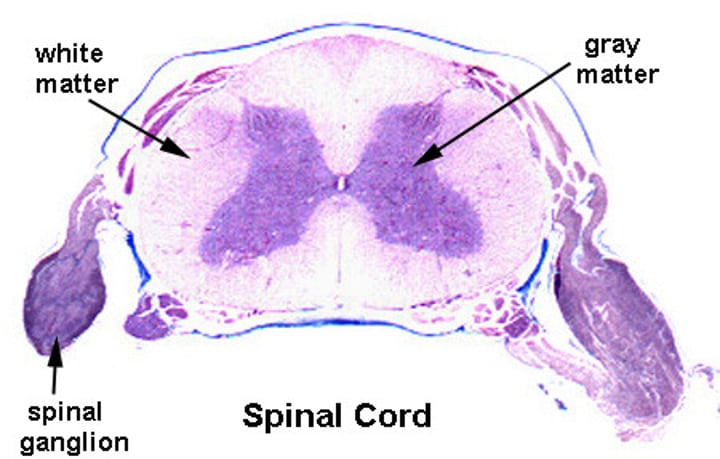
What does white matter consist of?
consists of axons (mostly myelinated); located outside gray matter area
31
Number of pairs of spinal nerves in the human body
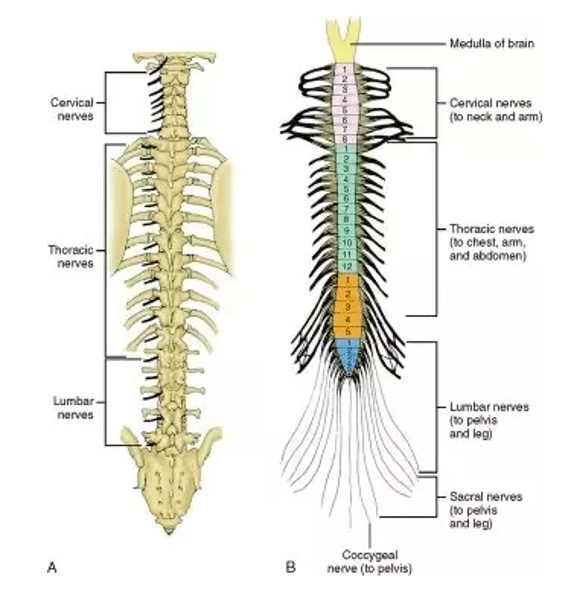
Order of spinal nerves from superior to inferior, with the number of spinal nerves in each division
-8 cervial nerves
-12 thoracic nerves
-5 lumbar nerves
-5 sacral nerves
-1 coccygeal nerve
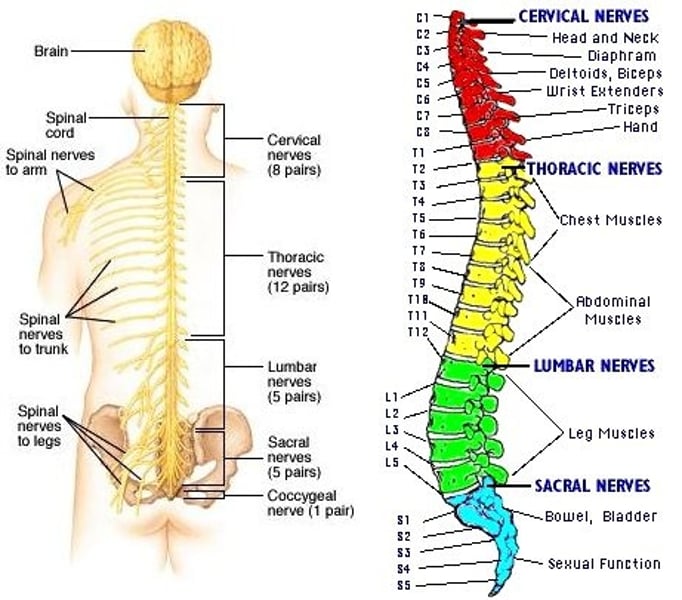
cauda equina
"horse's tail," a fan of nerve fibers at the inferior end of the spinal cord
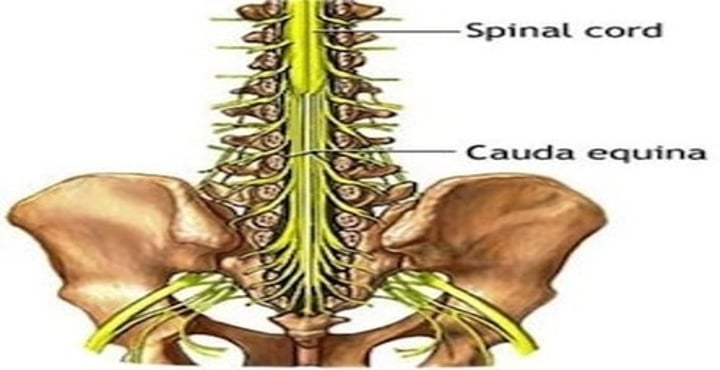
reflex
a rapid, automatic response to a stimulus
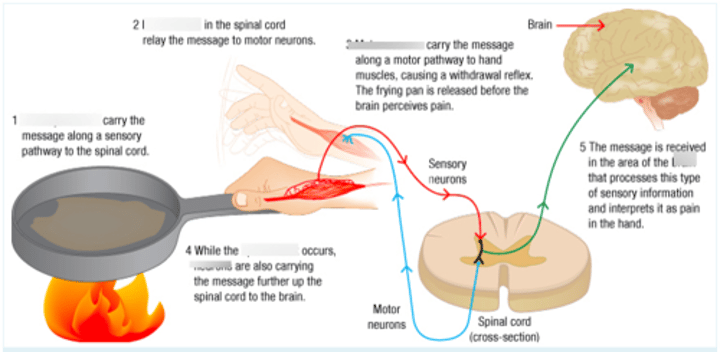
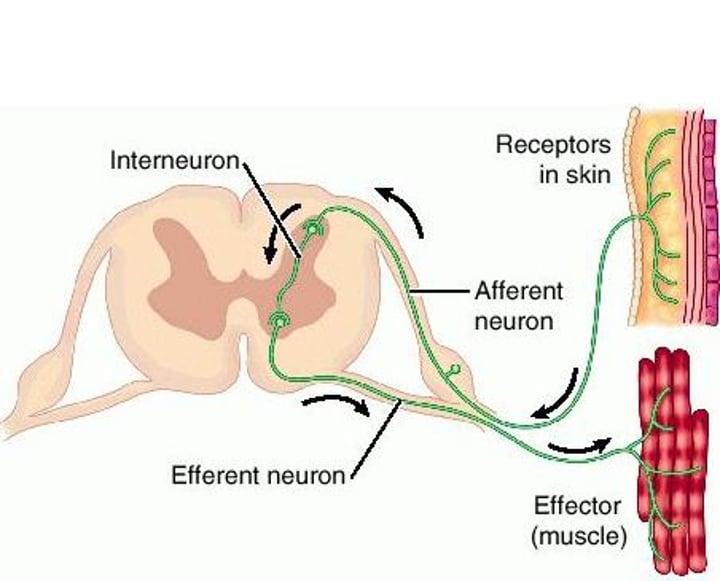
reflex arc
The nerve pathway involved in a reflex action, from receptor to effector. In vertebrates, most sensory neurons do not pass directly into the brain, but synapse in the spinal cord.
innate reflex
an inborn reflex
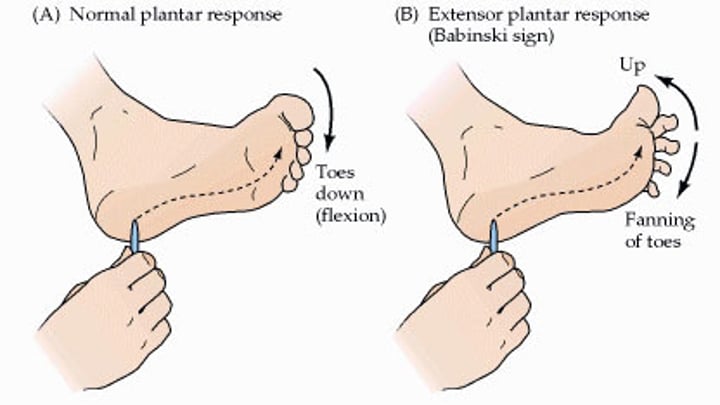
learned reflex
an acquired response to a stimulus; these are learned over time, and typically more complex (reactions that 'evolve' into reflexes)

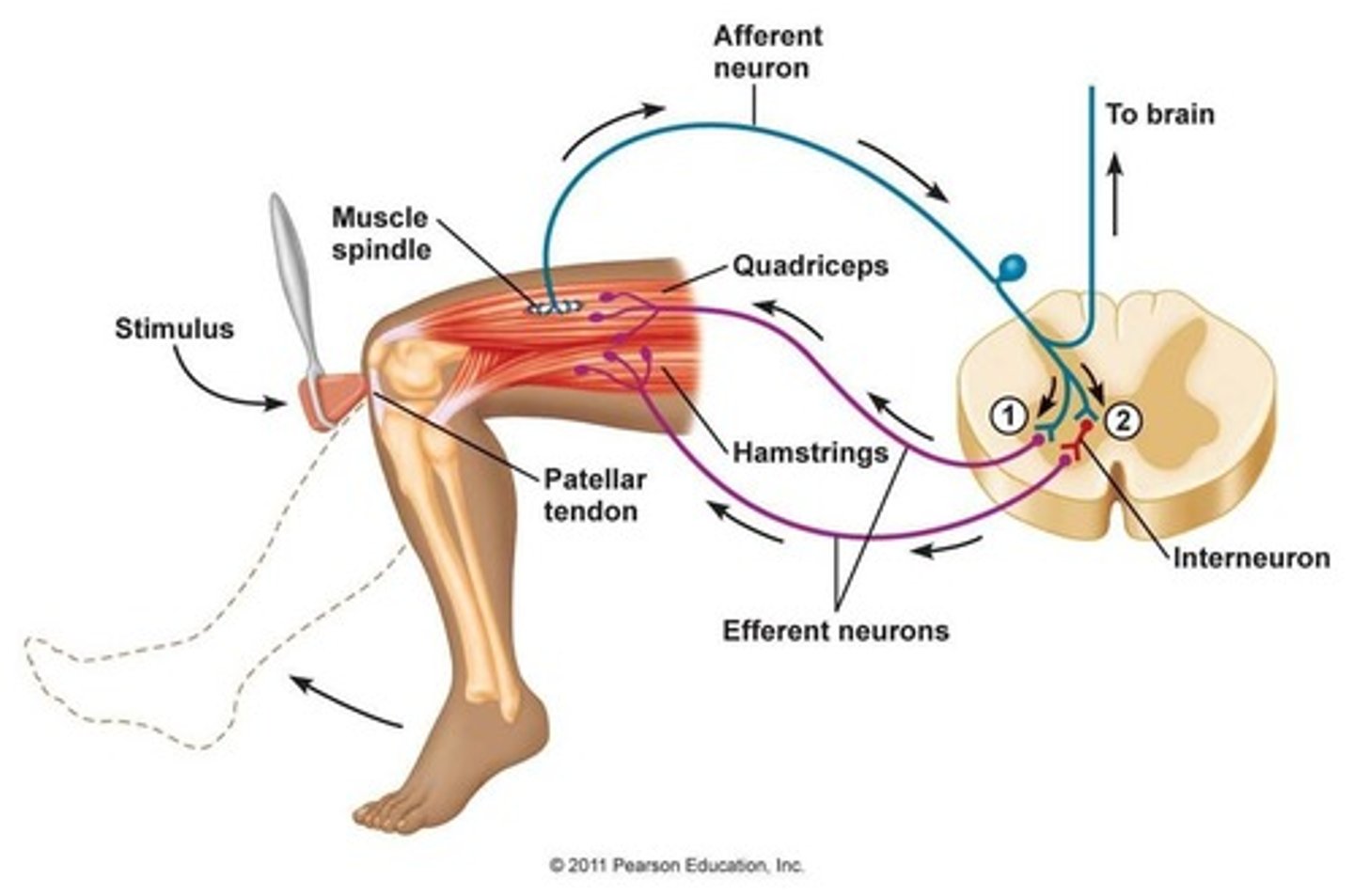
Name in order the 5 stages of a stretch reflex:
-1) stimulus stretches a muscle
-2) stretch receptors activated
-3) information is processed in spinal cord
-4) motor neurons are activated
-5) muscle (effector) contracts
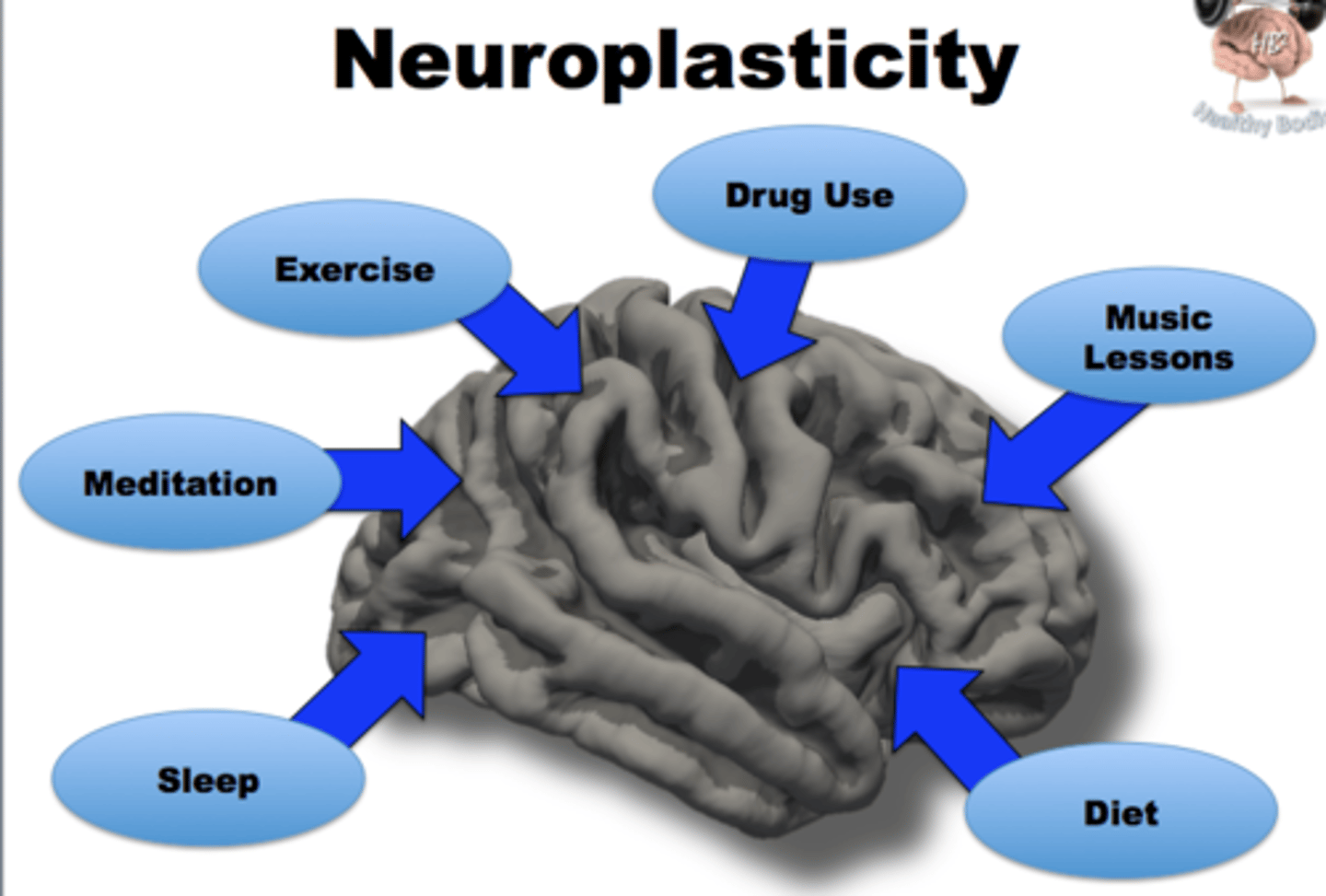
Neural plasticity
The brain's ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections throughout life. The brain can grow and change!
synaptic plasticity
the ability of synapses to strengthen or weaken over time, in response to increases or decreases in their activity (so "use it or lose it!")
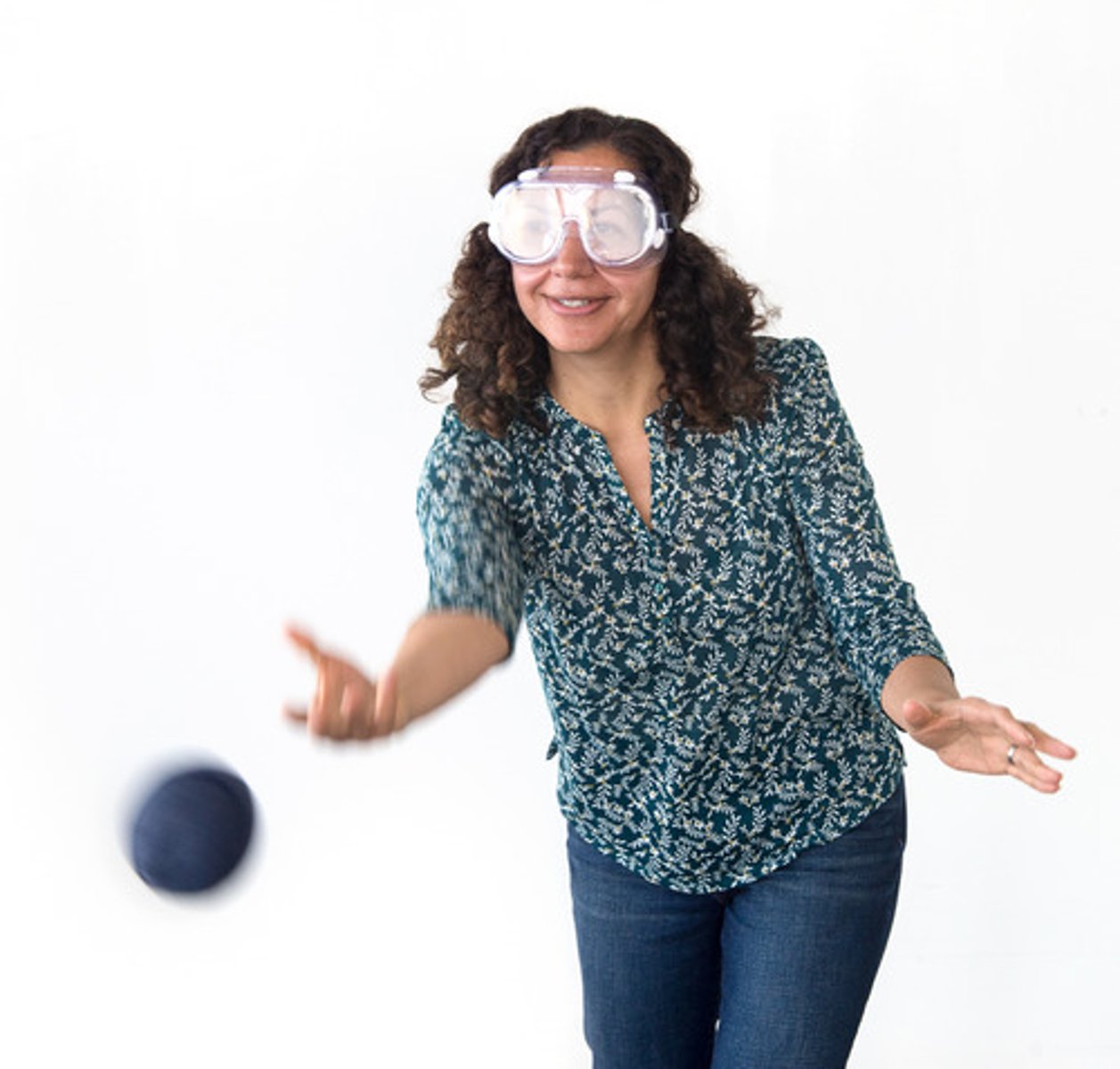
altered reality goggles
goggles that bend the light reaching your retina, distorting your vision and aim

reinforcement
voluntary muscle tension (pulling apart clasped hands, gritting teeth) to trigger weak or apparently missing reflexes; not just a diversion of the patient's attention