Chapter 5 Study Guide
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
Biodiversity
The variety of life in the world or in a particular habitat or ecosystem.
Species richness
The number of species in a given area.
Species evenness
The relative proportion of individuals within the different species in a given area.
Phylogeny
The branching pattern of evolutionary relationships.
Evolution
A change in the genetic composition of a population over time.
Microevolution
Evolution below the species level.
Macroevolution
Evolution that gives rise to new species, genera, families, classes, or phyla.
Gene
A physical location on the chromosomes within each cell of an organism.
Genotype
The complete set of genes in an individual.
Phenotype
A set of traits expressed by an individual.
Mutation
A random change in the genetic code produced by a mistake in the copying process.
Speciation
The process by which new species arise.
Environmental scientists
Scientists who study the environment and the relationships between organisms and their environment.
Phylogenetic tree
A diagram that shows the evolutionary relationships among various biological species based on similarities and differences in their physical or genetic characteristics.
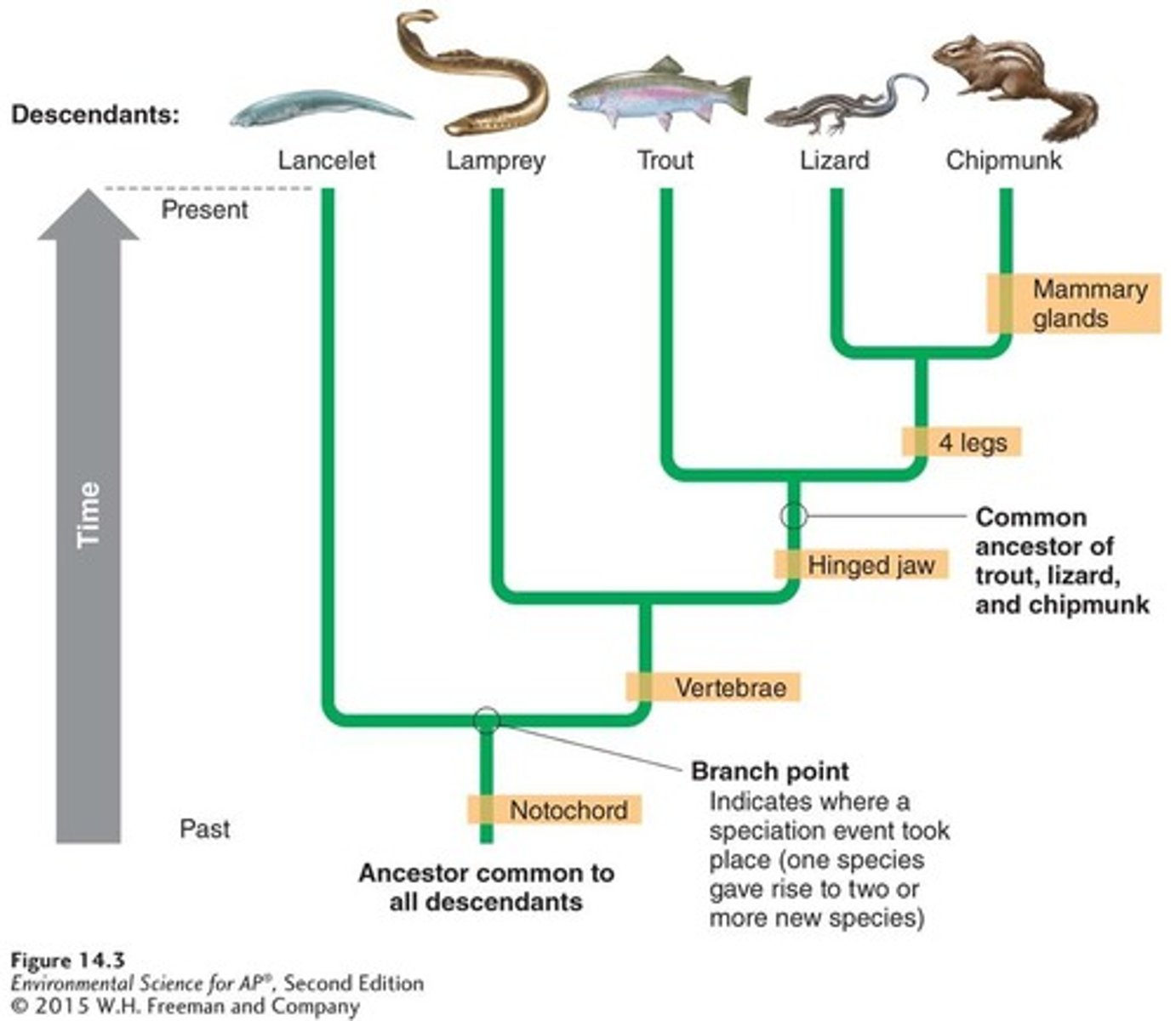
Genetic diversity
The total number of genetic characteristics in the genetic makeup of a species.
Artificial selection
The process by which humans breed other animals and plants for particular traits.
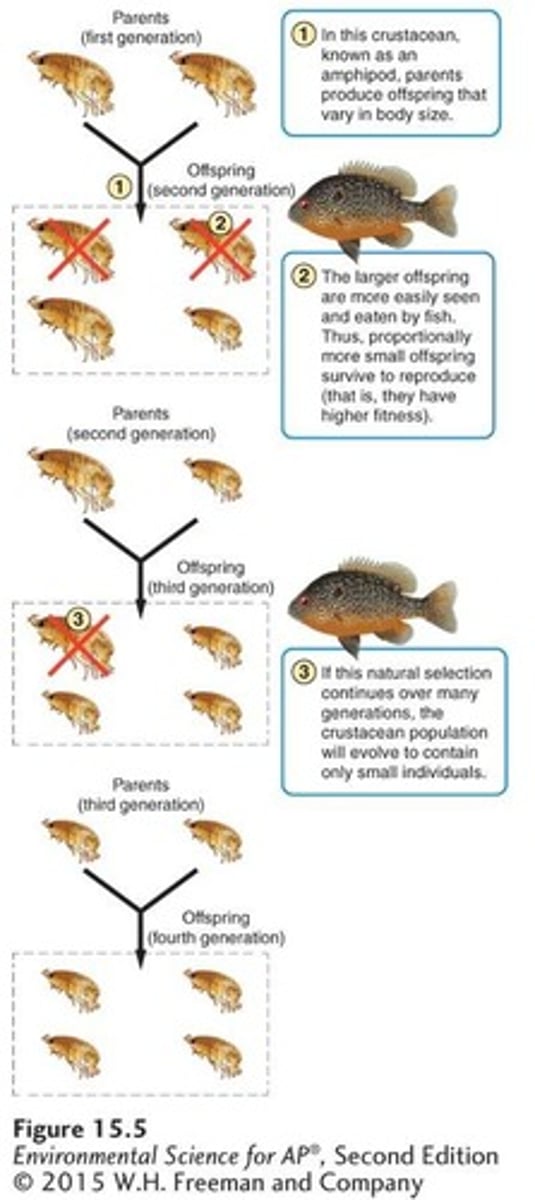
Natural selection
The process whereby organisms better adapted to their environment tend to survive and produce more offspring.
Random processes
Processes that occur without a predictable pattern or cause, influencing evolution.
Morphological changes
Changes in the form or structure of organisms over evolutionary time.
Species diversity
The variety and abundance of different species in a given area.
Baseline
A standard or reference point used for comparison.
Recombination
The process of combining different genes from parents to create genetic diversity in offspring.
Recombination
The genetic process by which one chromosome breaks off and attaches to another chromosome during reproductive cell division. This process does not create new genes, but brings together new combinations of alleles on a chromosome, producing new traits.
Evolution by artificial selection
The process in which humans determine which individuals breed, typically with a preconceived set of traits in mind.
Artificial selection
The diversity of domesticated dog breeds is the result of artificial selection on wolves.
Evolution by natural selection
The process in which the environment determines which individuals survive and reproduce.
Natural Selection
All species produce an excess number of offspring. Only those offspring with the fittest genotypes will pass on their genes to the next generation.
Natural selection
Natural selection favors any combination of traits that improves an individual's fitness.
Fitness
An individual's ability to survive and reproduce.
Adaptation
A trait that improves an individual's fitness.
Mutation
As the number of mutations accumulates in a population over time, evolution occurs.
Gene flow
The process by which individuals move from one population to another and thereby alter the genetic composition of both populations.
Genetic drift
A random process that can lead to changes in allele frequencies in a population.
Bottleneck effects
A sharp reduction in the size of a population due to environmental events or human activities, leading to a loss of genetic diversity.
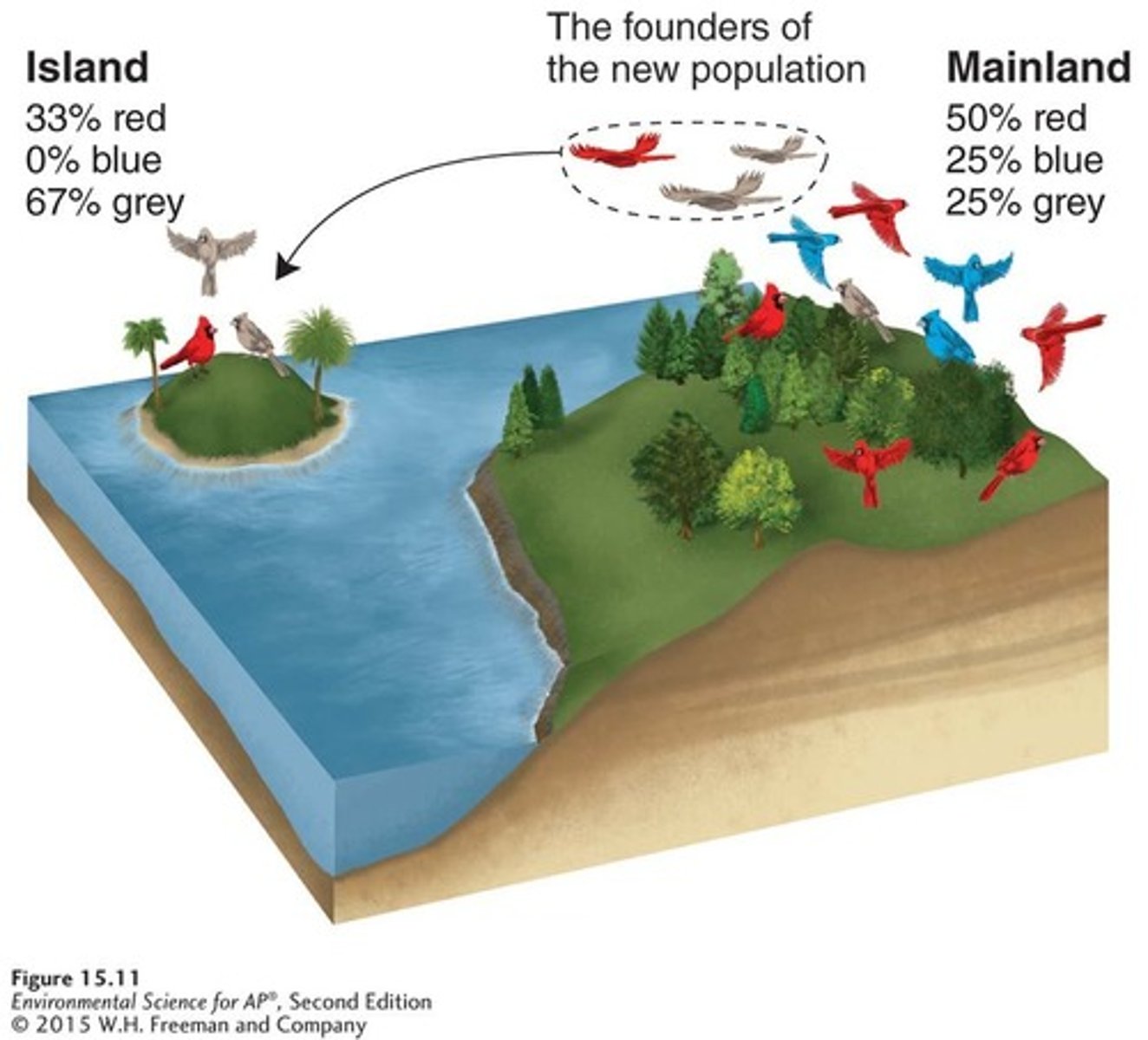
Founder effects
A loss of genetic variation that occurs when a new population is established by a very small number of individuals from a larger population.
Evolution by mutation
A mutation can arise in a population and if it is not lost it may increase in frequency over time.
Gene flow effects
The arrival of individuals from adjacent populations alters the frequency of alleles in the population.
Gene flow consequences
In a population that is experiencing natural or artificial selection, high gene flow from outside can prevent the population from responding to selection.
Gene flow benefits
Gene flow can be helpful in bringing in genetic variation to a population that lacks it.
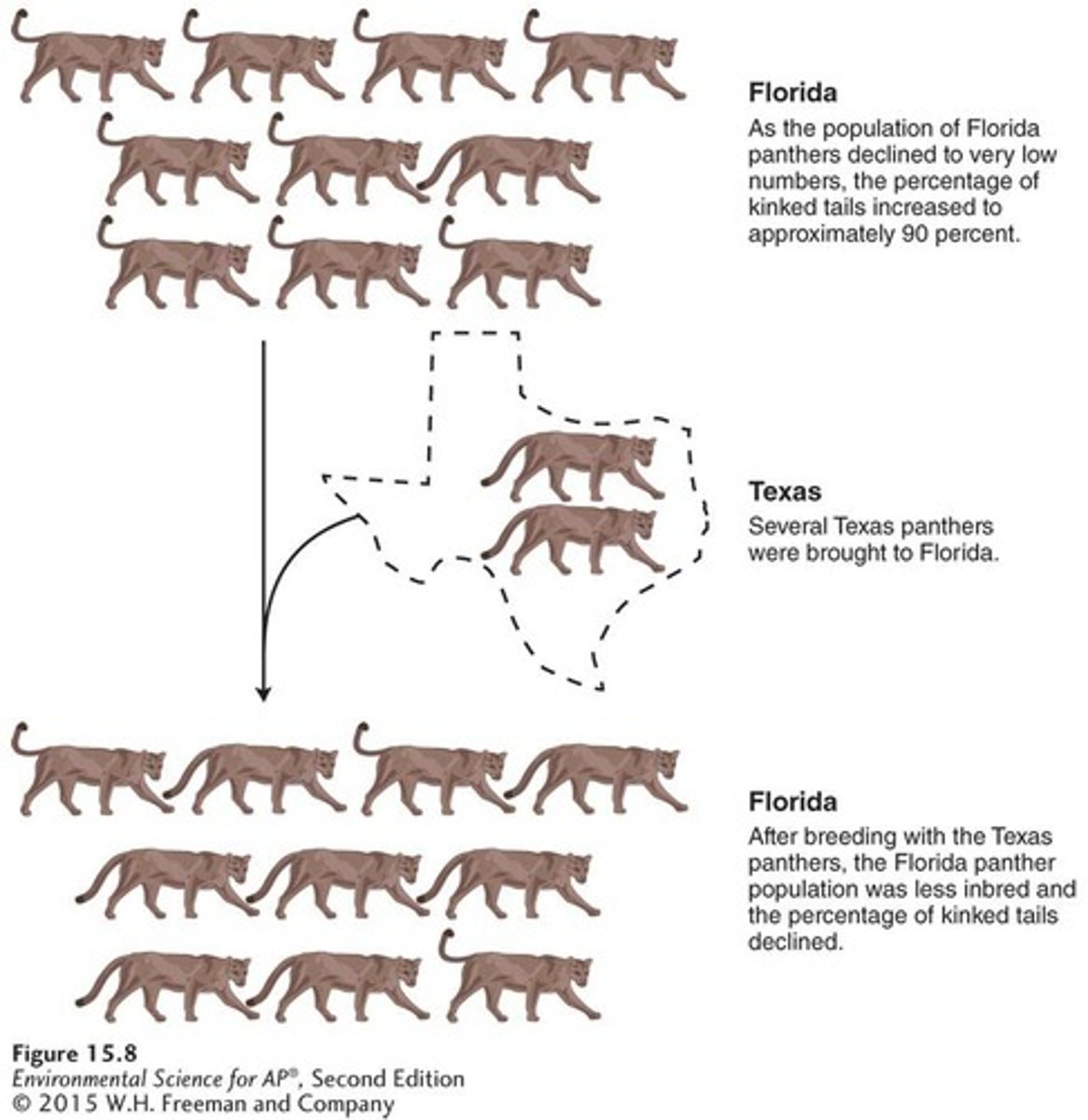
Florida panther example
As the Florida panther declined in population size, the animals experienced low genetic variation and showed signs of inbreeding, which lead to kinky tails, heart defects, and low sperm counts.
Genetic Drift
A change in the genetic composition of a population over time as a result of random mating.
Small Population Genetic Drift
In a small population, some less-common genotypes can be lost by chance as random mating among a small number of individuals can result in the less-common genotype not mating.
Large Population Genetic Drift
In a large population, it is more difficult for the less-common genotypes to be lost by chance because the absolute number of these individuals is large.
Bottleneck Effect
A reduction in the genetic diversity of a population caused by a reduction in its size.
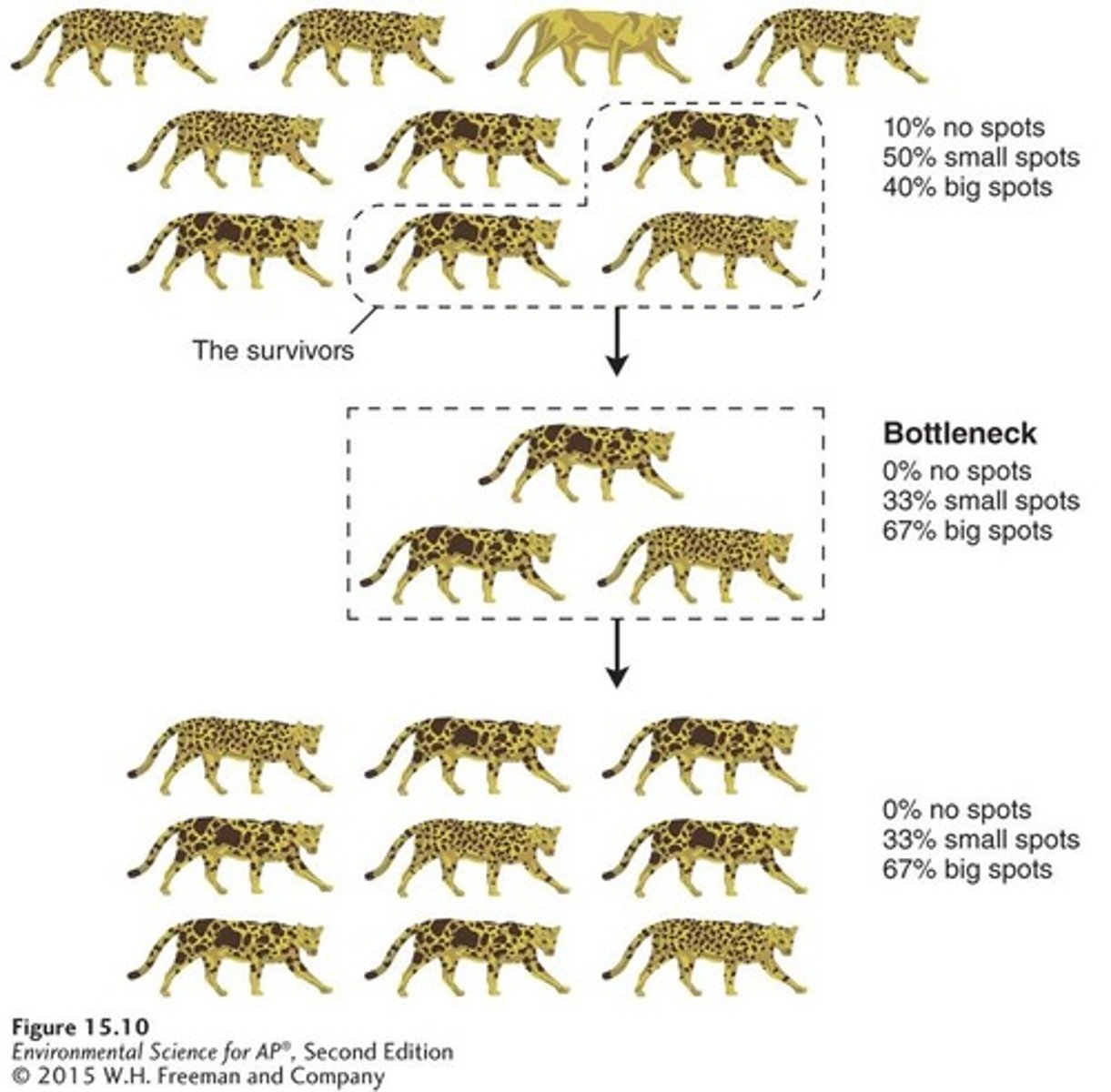
Consequences of Bottleneck Effect
Low genetic variation in a population can cause increased risk of disease and low fertility.
Extinction
The death of the last member of a species.
Founder Effect
A change in the genetic composition of a population as a result of descending from a small number of colonizing individuals.
Allopatric Speciation
The process of speciation that occurs with geographic isolation.
Sympatric Speciation
The evolution of one species into two, without geographic isolation.
Geographic Isolation
Physical separation of a group of individuals from others of the same species.
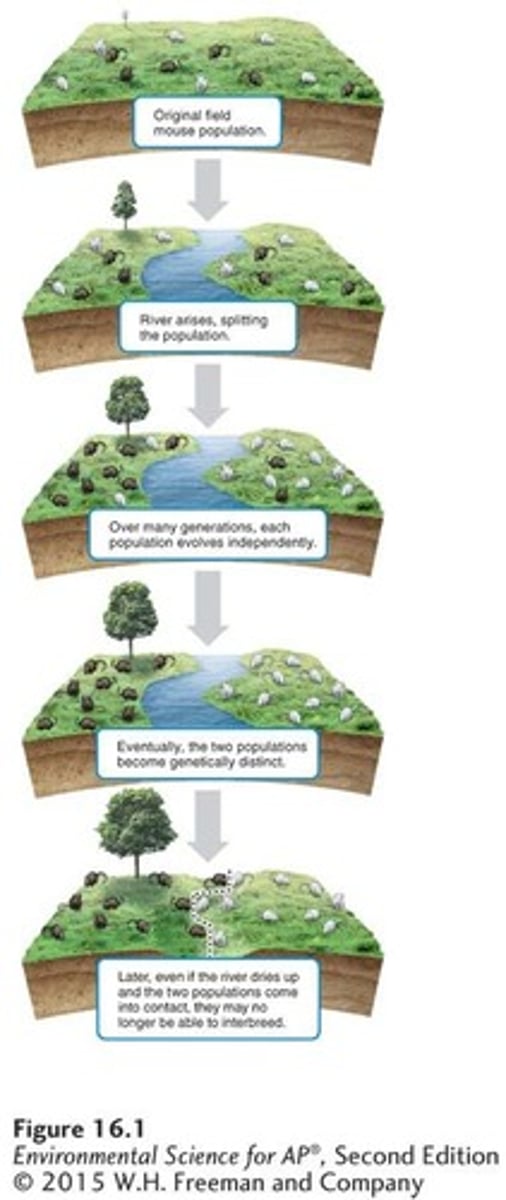
Reproductive Isolation
The result of two populations within a species evolving separately to the point that they can no longer interbreed and produce viable offspring.
Natural Selection in Allopatric Speciation
Natural selection may favor different traits in the environment of each isolated population, resulting in different adaptations.
Polyploidy in Sympatric Speciation
Usually happens through polyploidy.
Bottleneck Effect Consequences
The bottleneck effect means species are less able to adapt to future environmental changes.
Genetic Composition Change
The genetic composition can change over time due to random mating.
Survivor Genetic Composition
If a population experiences a drastic decrease in size, some genotypes will be lost, and the genetic composition of the survivors will differ from the composition of the original group.
Population Growth Example
The Florida population experienced a growth from 30 to 160 individuals after the introduction of eight panthers from Texas.
Genetic Variation Reduction
Reduced population numbers means reduced genetic variation.
Speciation Processes
New species commonly evolve through two processes: allopatric and sympatric speciation.
Genetic Distinction Over Time
Over time, the two populations may become so genetically distinct that they are no longer capable of interbreeding.
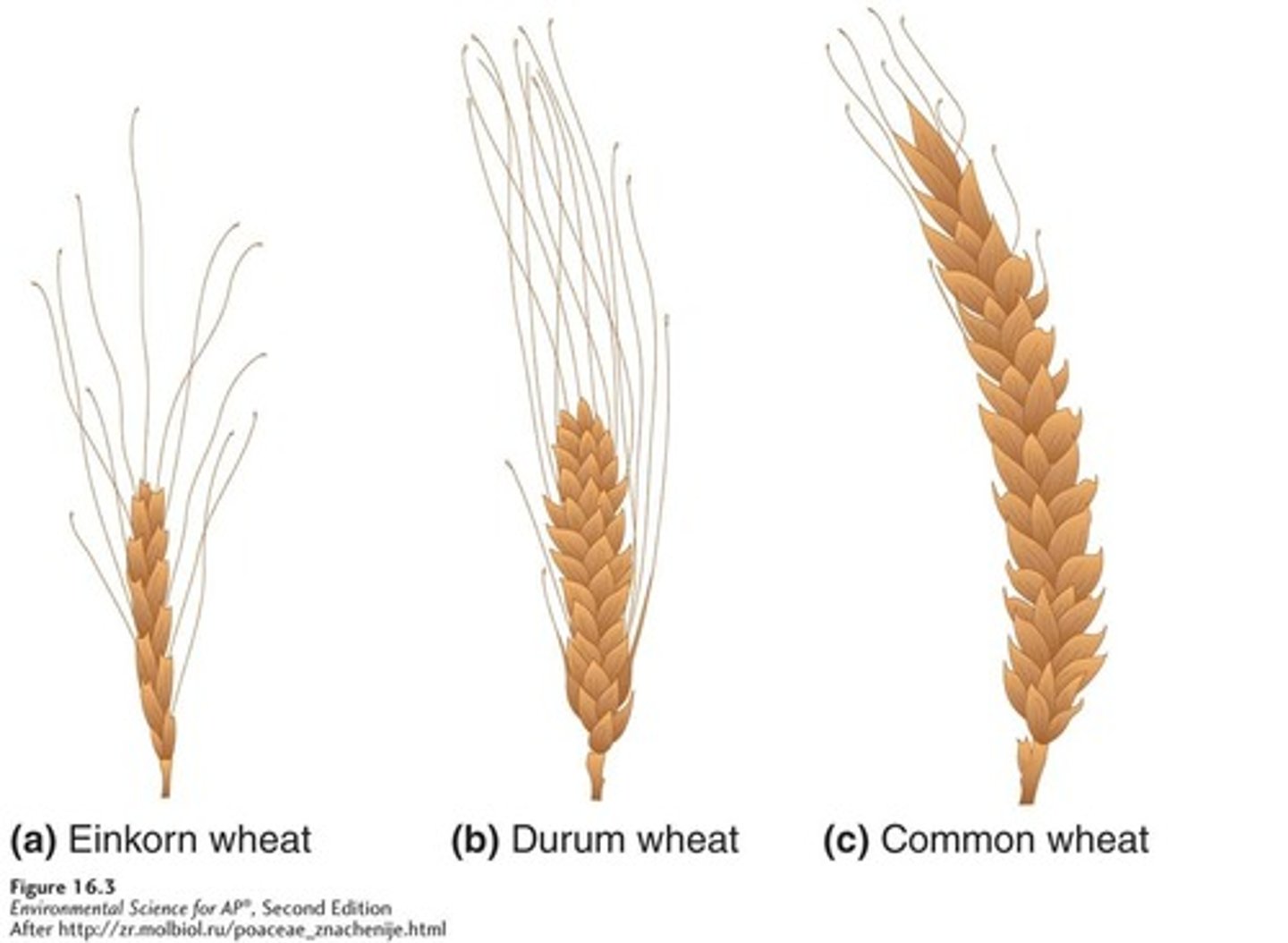
Polyploidy
An increase in the number of sets of chromosomes beyond the normal two sets.
Einkorn wheat (Triticum boeoticum)
Has two sets of chromosomes and produces small seeds.
Durum wheat (Triticum durum)
Bred to have four sets of chromosomes and produces medium-sized seeds.
Common wheat (Triticum aestivum)
Bred to have six sets of chromosomes and produces the largest seeds.

Pace of evolution
Depends on several factors including generation times and genetic variation.
Environmental change
Can alter species distributions and cause species extinctions.
Slow rates of evolution
Occur when a population has long generation times or contains low genetic variation.
Evolution by artificial selection
Can be very rapid.
Genetically modified organism (GMO)
An organism produced by copying genes from a species with a desirable trait and inserting them into another species.
Fundamental niche
The suite of abiotic conditions under which a species can survive, grow, and reproduce.
Realized niche
The range of abiotic and biotic conditions under which a species actually lives.
Distribution
Areas of the world in which a species lives.
Range of tolerance
The limits to the abiotic conditions that a species can tolerate.
Niche generalist
A species that can live under a wide range of abiotic or biotic conditions.
Niche specialist
A species that is specialized to live in a specific habitat or to feed on a small group of species.
Niche specialists
Do well when environmental conditions remain relatively constant.
Niche generalists
Fare better under changing conditions because they have a number of alternative habitats and food sources available.
Species extinctions
Occur when species cannot adapt to environmental changes or move to more favorable environments.
Average life span of a species
Appears to be only about 1 million to 10 million years.
Mass extinction
A large extinction of species in a relatively short period of time.
Five Global Mass Extinctions
Five global mass extinction events have occurred since the evolution of complex life roughly 500 million years ago.