Genetics Quiz
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
review notes, mitosis/meiosis, worksheets
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
gene
sequence of DNA that codes for a specific protein/trait
allele
version of a gene
genotype
allele combination inherited from the parents
phenotype
physical trait expressed based on the genotype
homozygous
possessing two of the same alleles
homozygous dominant
2 dominant alleles
homozygous recessive
2 recessive alleles
heterozygous
possessing two different alleles
Mendel’s laws
law of segregation, law of independent assortment, law of dominance
law of segregation
during the formation of gametes, the two alleles will segregate, ensuring each gamete carries one allele for each gene
when does law of segregation occur?
anaphase I of meiosis
law of independent assortment
alleles for different genes segregate independently from one another during gamete formation, so the inheritance of one trait does not influence the inheritance of another; only occurs with unlinked genes
when does independent assortment occur?
during metaphase I of meiosis
law of dominance
dominant traits will mask the presence of recessive traits when an individual has a heterozygous genotype
punnett squares
tools used in genetics to predict possible genetic outcomes; helps determine the probability of an offspring inheriting a specific trait
monohybrid
examines one trait
dihybrid
examines the inheritance of two different traits simultaneously
test cross
figures out the unknown genotype (of a trait following simple dominance) of an individual by crossing it with a homozygous recessive individual
how to interpret the results of a test cross
if some of the offspring show the recessive phenotype, the unknown parent is heterozygous; if none of the offspring show the recessive phenotype, the unknown parent is homozygous dominant
multiplication rule
calculates the probability of multiple independent events occurring together/at the same time
addition rule
chance that an event can occur in 2 or more different ways
how to immediately tell if its addition or multiplication?
if its AND, it’s multiplication, and if its OR, it’s addition
incomplete dominance
neither allele is completely dominant over the other, instead, the heterozygous phenotype is a blend
codominance
both alleles are expressed equally in heterozygous phenotypes
multiple alleles
2+ alleles involved in determining phenotype
epistasis
relationship between two different genes; one gene will mask the expression of the other
polygenic inheritance
additive influence of multiple genes on a single trait
sex-linked traits
traits associated with genes found on sex chromosomes
x inactivation
in females, one of the two x chromosomes will become inactivated during embryonic development
non-nuclear DNA
mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own genomes; mom passes them on to her kids
phenotypic plasticity
environmental factors can affect which genes are being expressed, when they are expressed, and how much they are expressed
pedigrees
traces family history for a particular trait
autosomal recessive
requires 2 alleles to appear in phenotype
autosomal dominant
requires 1 allele to appear in phenotype
x-linked recessive
females require 2 alleles, males require 1 allele to appear in phenotype
x-linked dominant
requires at least 1 to appear in phenotype
y-linked (holandric)
only males affected
what does a square represent
males
what does a circle represent
female
what does a shaded in individual mean
that individual expresses the studied trait
what does a half shade mean (will not always be pictured)
carriers
what does a horizontal line connecting 2 individuals represent
marriage
what does a vertical line represent
children
what do the roman numerals represent
generation numbers
what do the numbers under each individual represent
helps identify specific individuals (generation + number)
how are individuals ordered on a pedigree
oldest on the left, youngest on the right
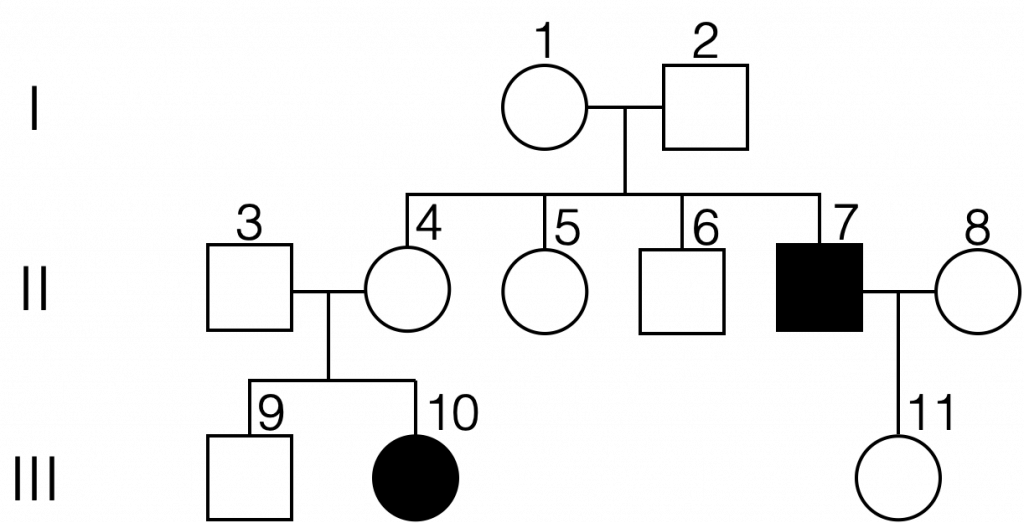
what type of inheritance?
autosomal recessive
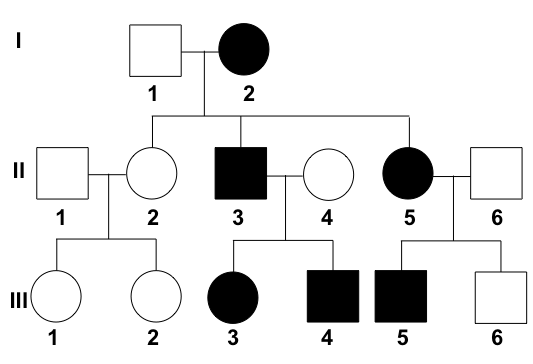
what type of inheritance?
autosomal dominant
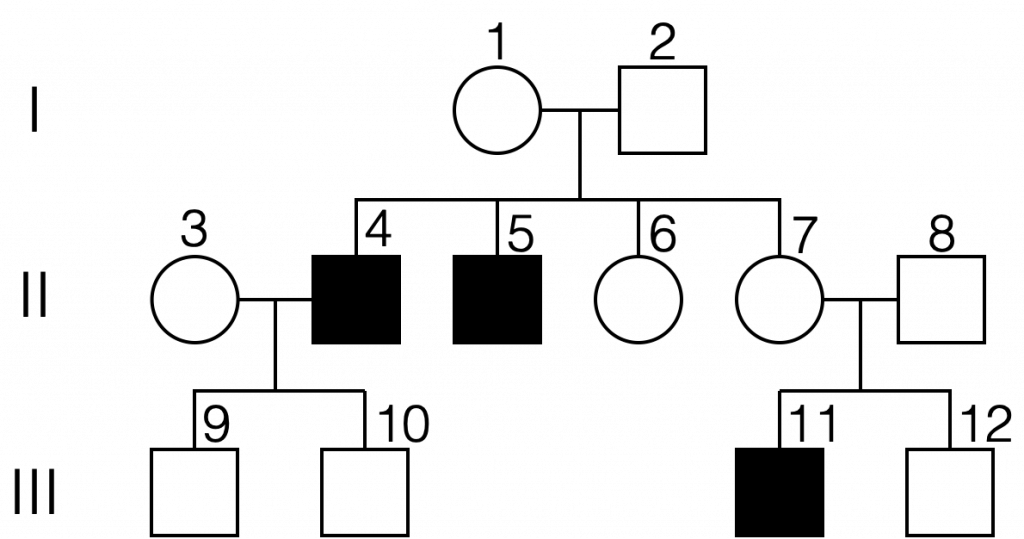
what type of inheritance?
x-linked recessive
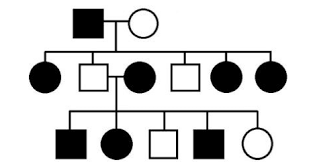
what type of inheritance?
x-linked dominant
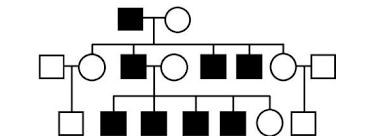
what type of inheritance?
y-linked