Chapter 23: Gross and Microscopic Anatomy of the Urinary System
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
fibrous capsule (kidney)
outermost layer of the kidney. It provides a covering of collagenous connective tissue that strengthen and protects the kidney tissue
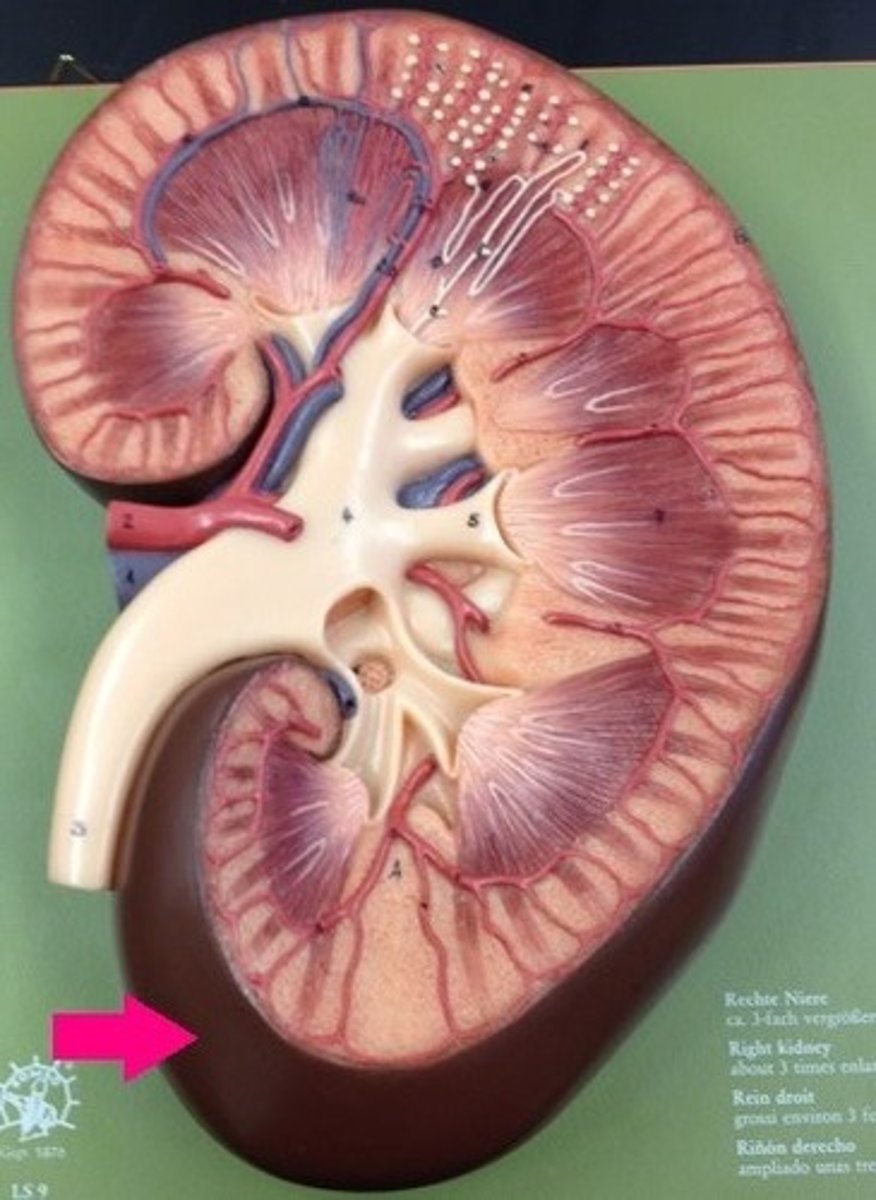
renal cortex (kidney)
outer layer of the kidney. Urine is continuously produced within this before it travels to the renal pyramids. (They have a striated appearance due to collecting ducts)
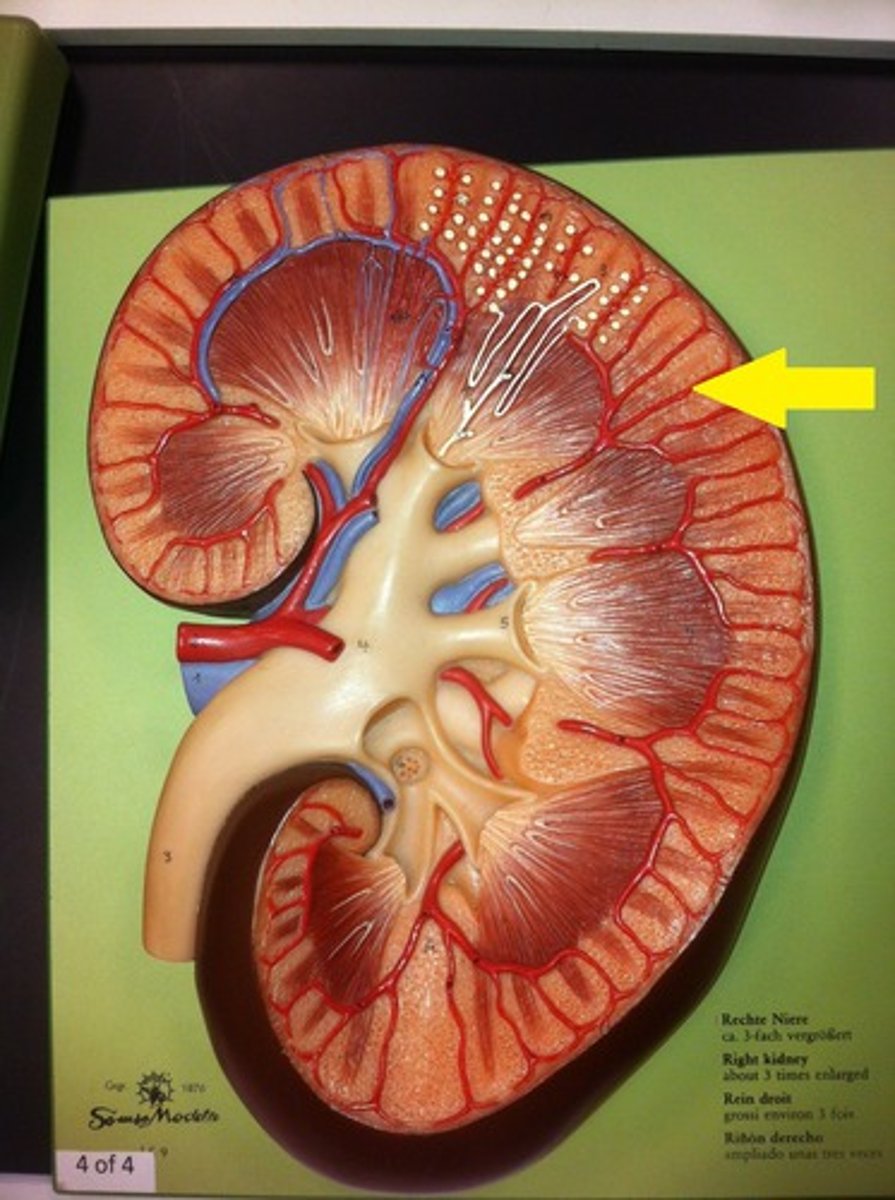
renal hilum (kidney)
A medial indentation where several structures enter or exit the kidney (ureters, renal blood vessels, and nerves)
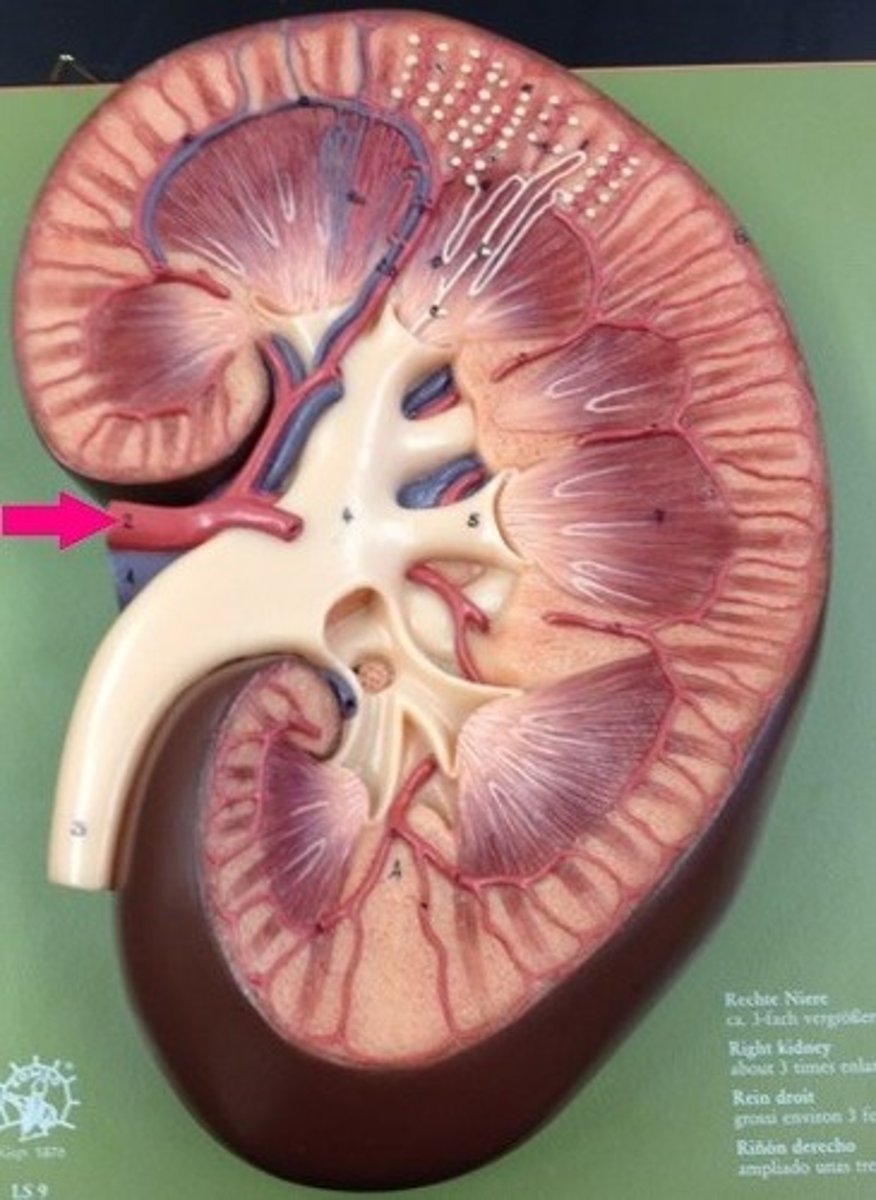
Renal artery (kidney)
carries blood into the kidney
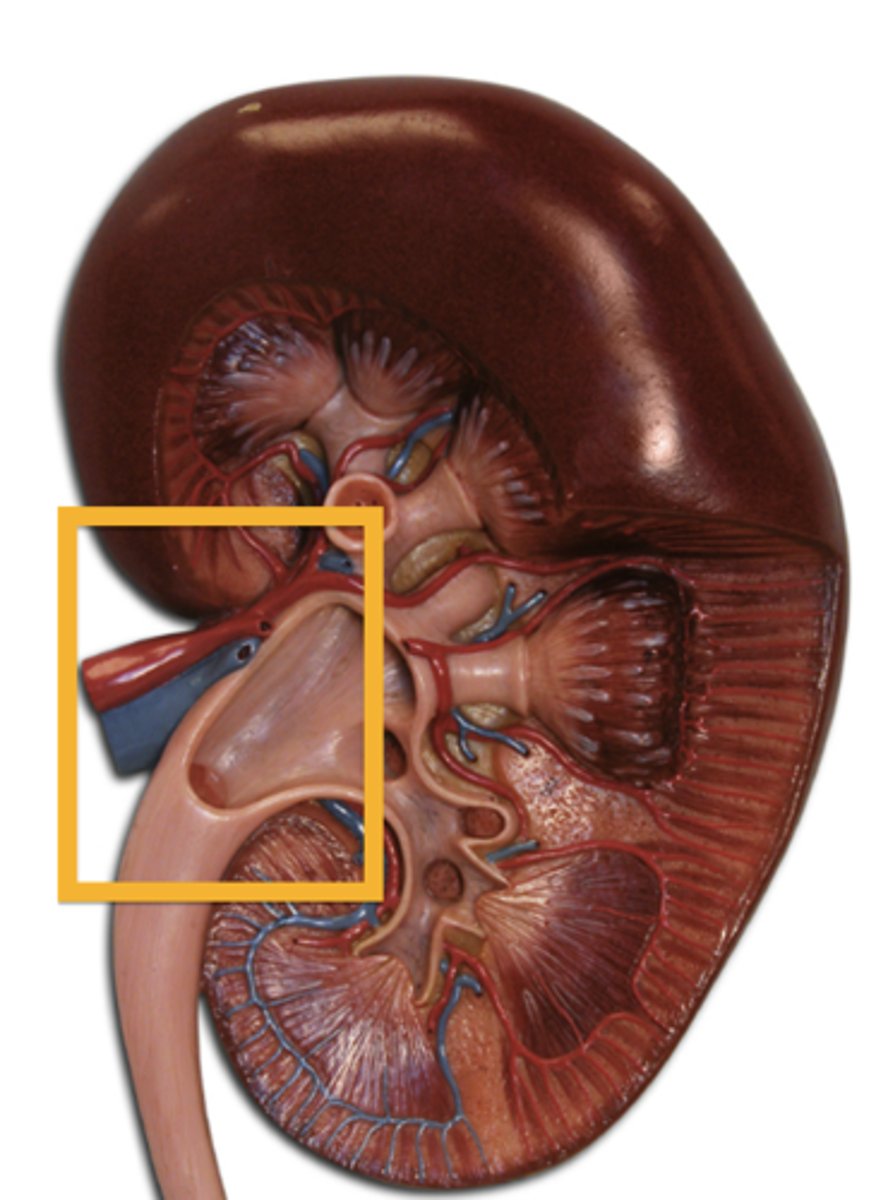
renal nerves
innervate kidneys and ureters
renal vein
blood vessel that carries blood away from the kidney
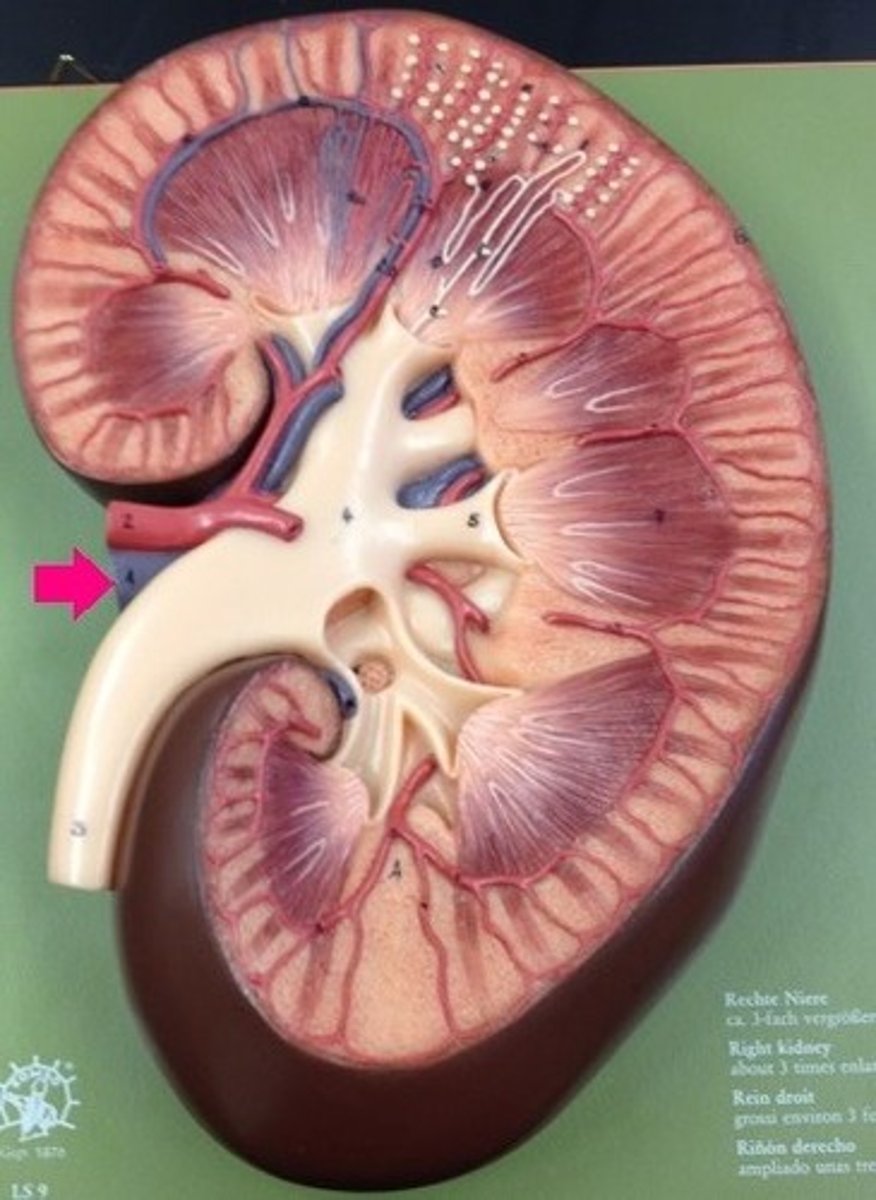
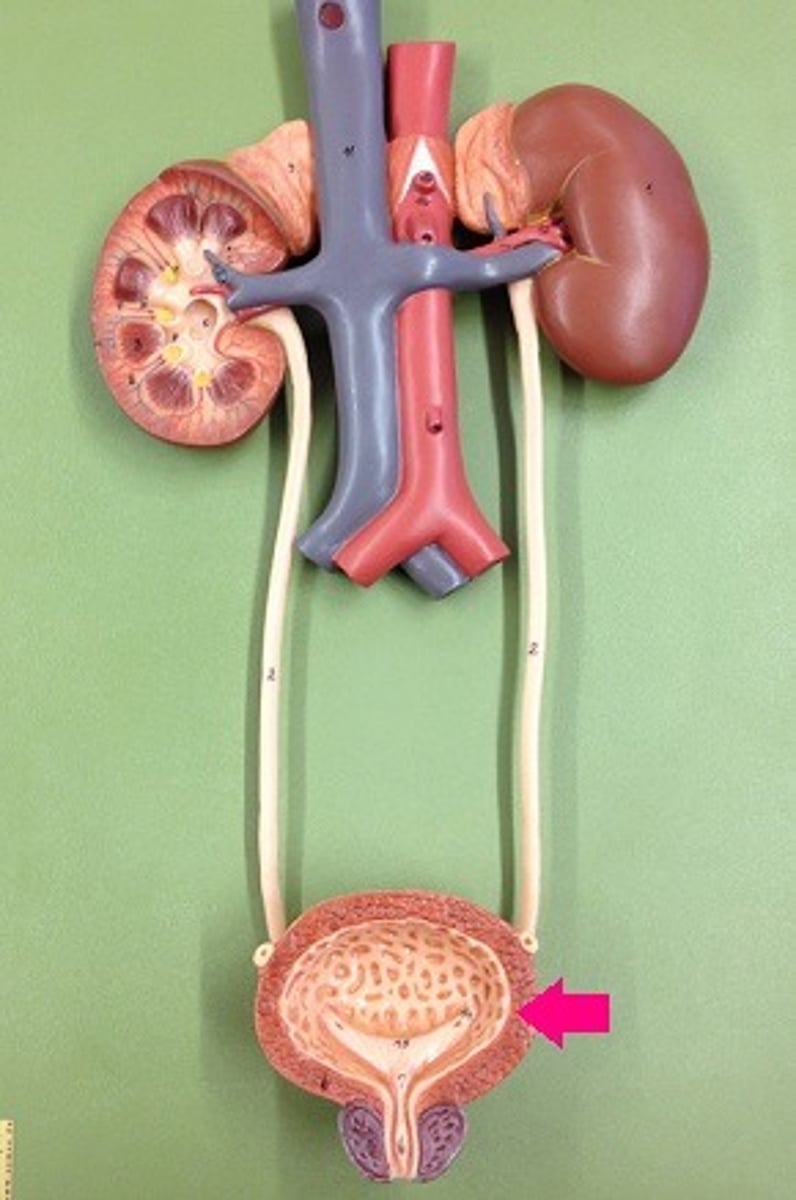
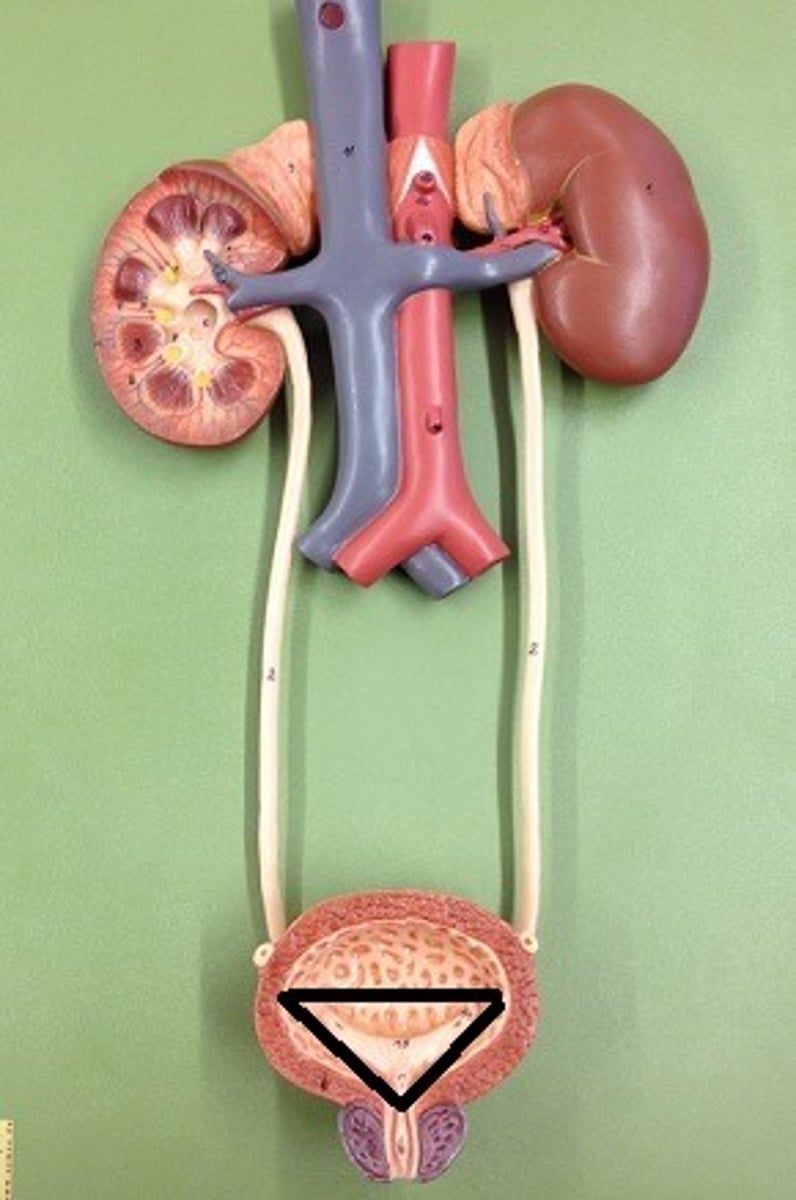
ureter
tube that carries urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder
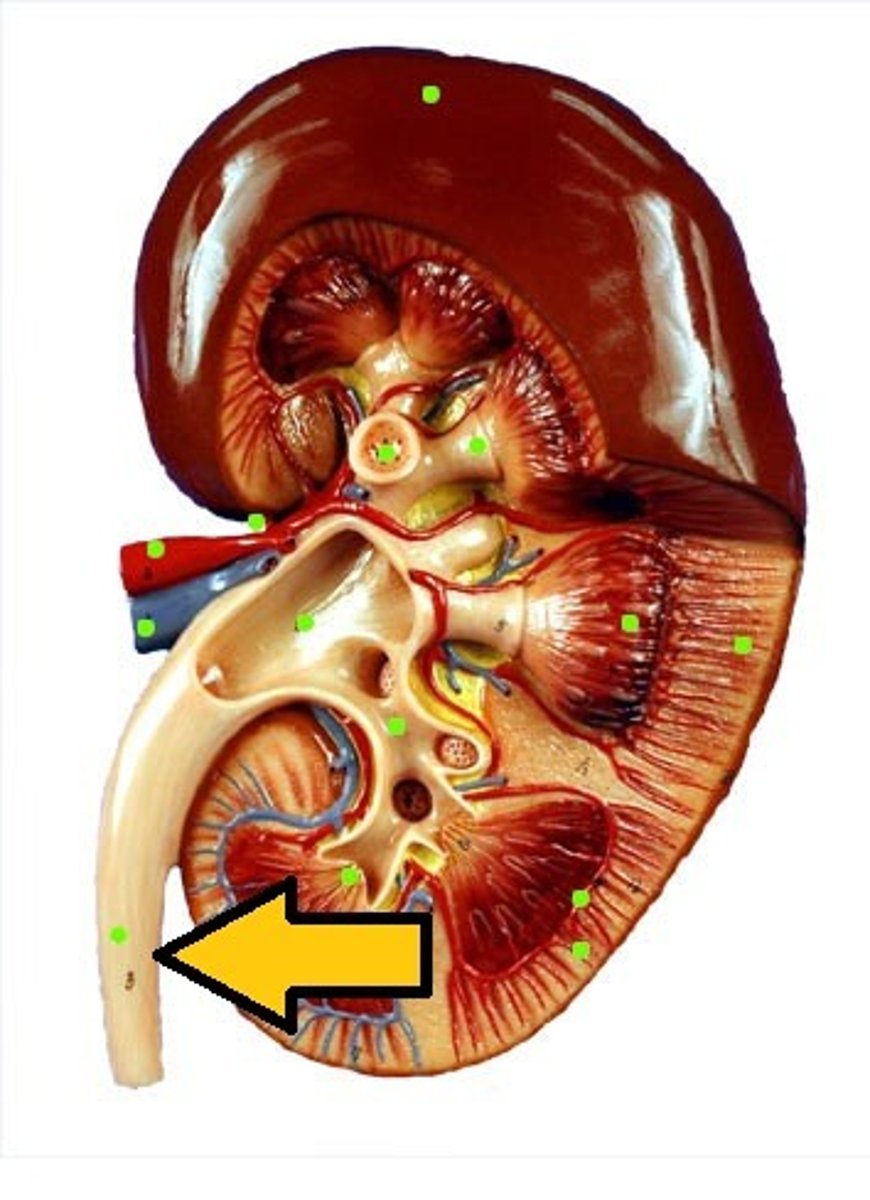
adrenal (suprarenal) glands
paired organs atop the kidneys.
cortex: secretes hormones such as including cortisone, aldosterone, sex hormones, ex.
medulla: secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine
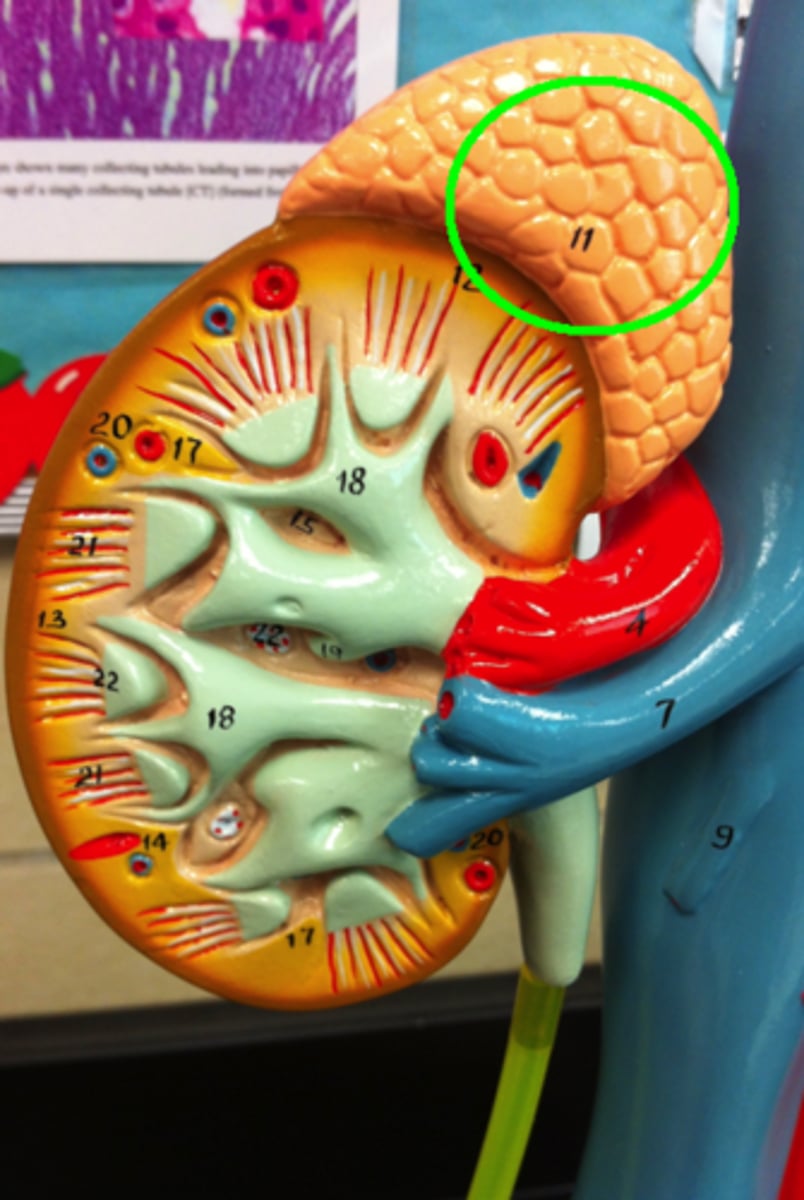
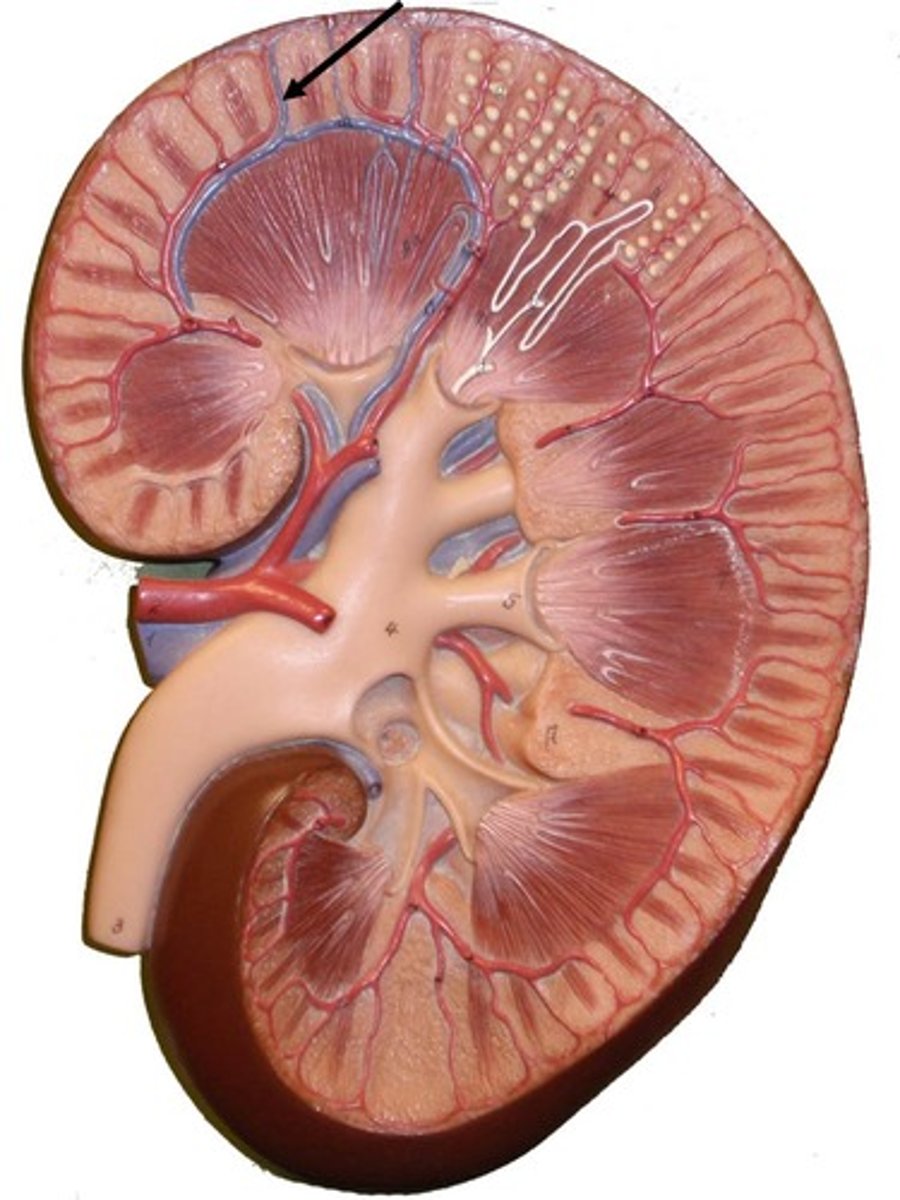
Medulla of kindey
primarily composed of triangular masses known as renal pyramids.
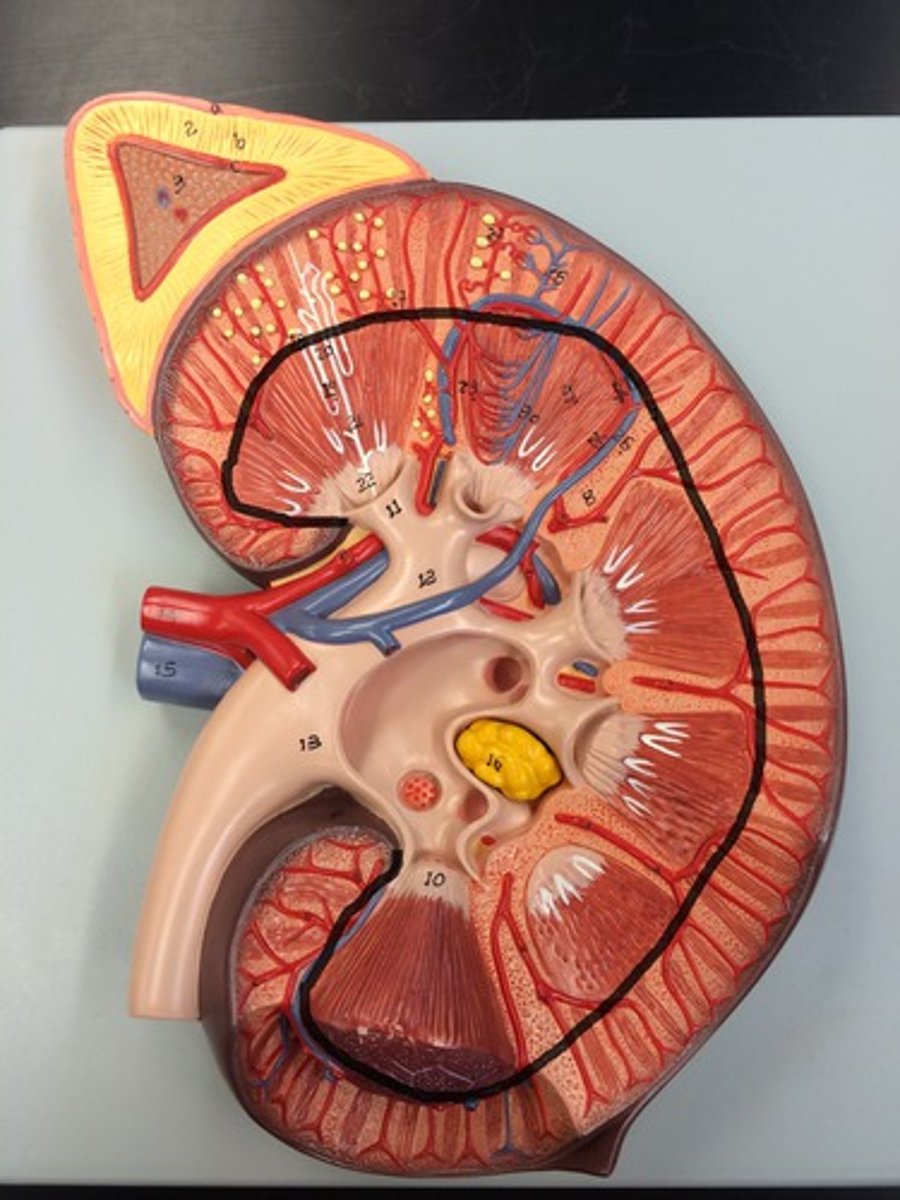
renal pyramids
triangular-shaped areas of tissue in the medulla of the kidney. The apex (renal columns) of the pyramids points towards the interior of the kidney.
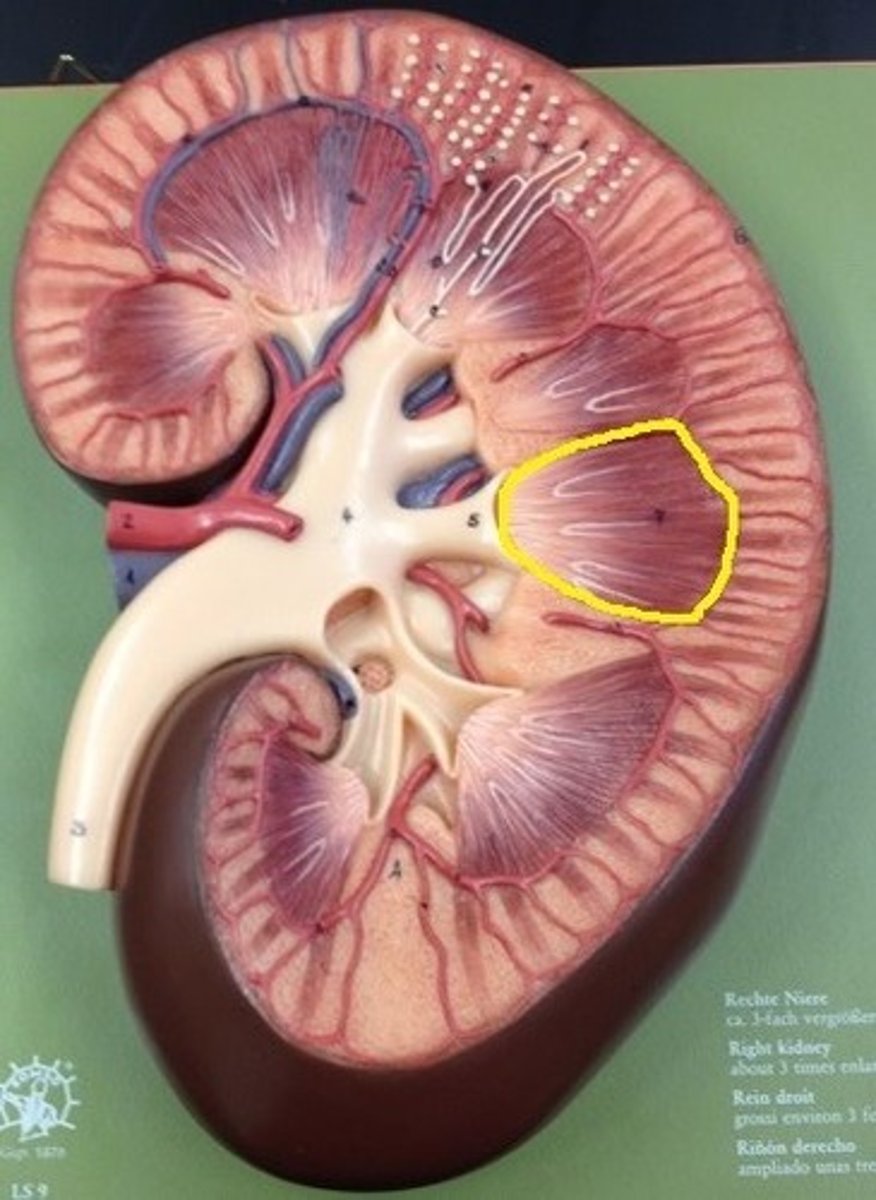
renal columns
Inward extensions of the cortex tissue separating the renal pyramids.
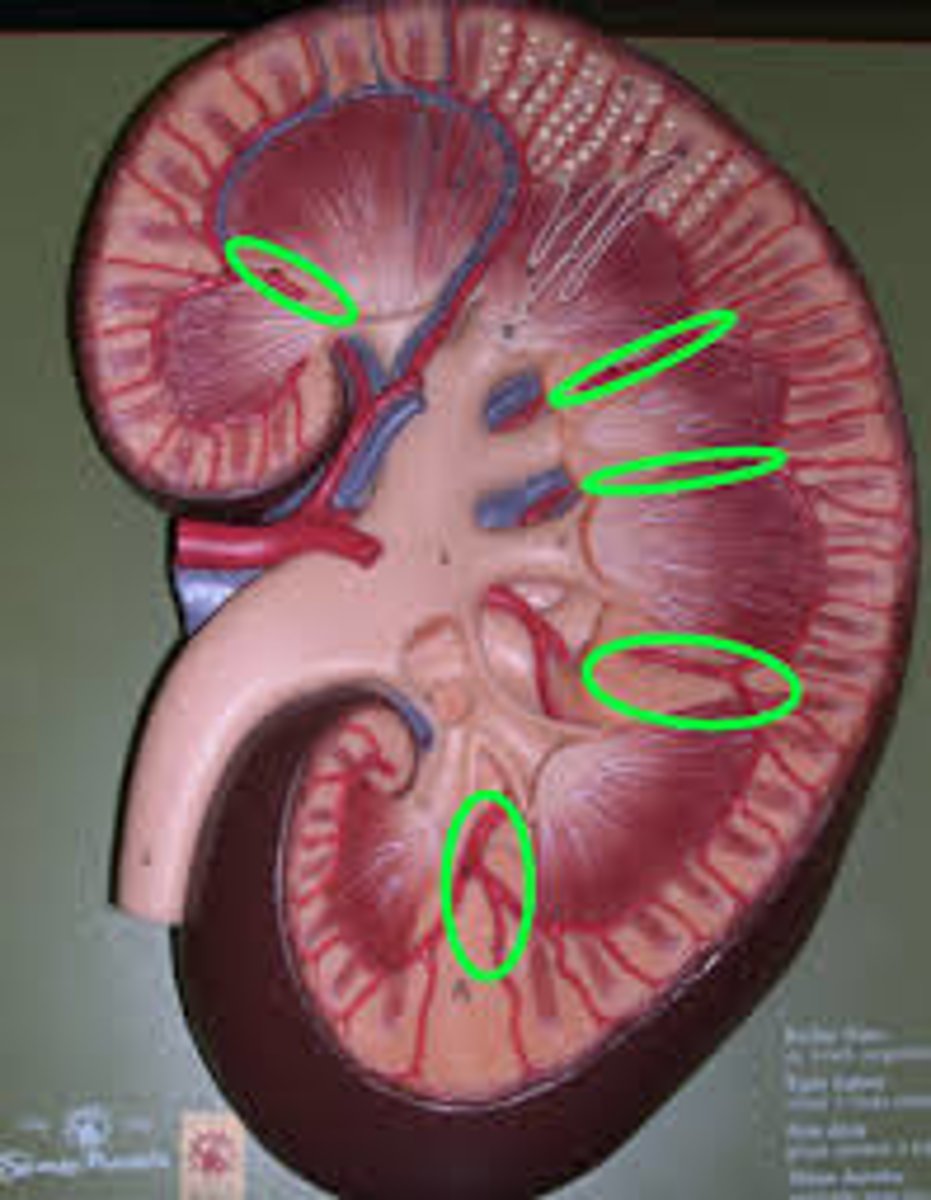
collecting ducts model
tubes in the kidney that collect urine from multiple nephrons and drain it into the renal pelvis

minor calyx
a cup-shaped structure that collects dripping urine from the renal papilla.
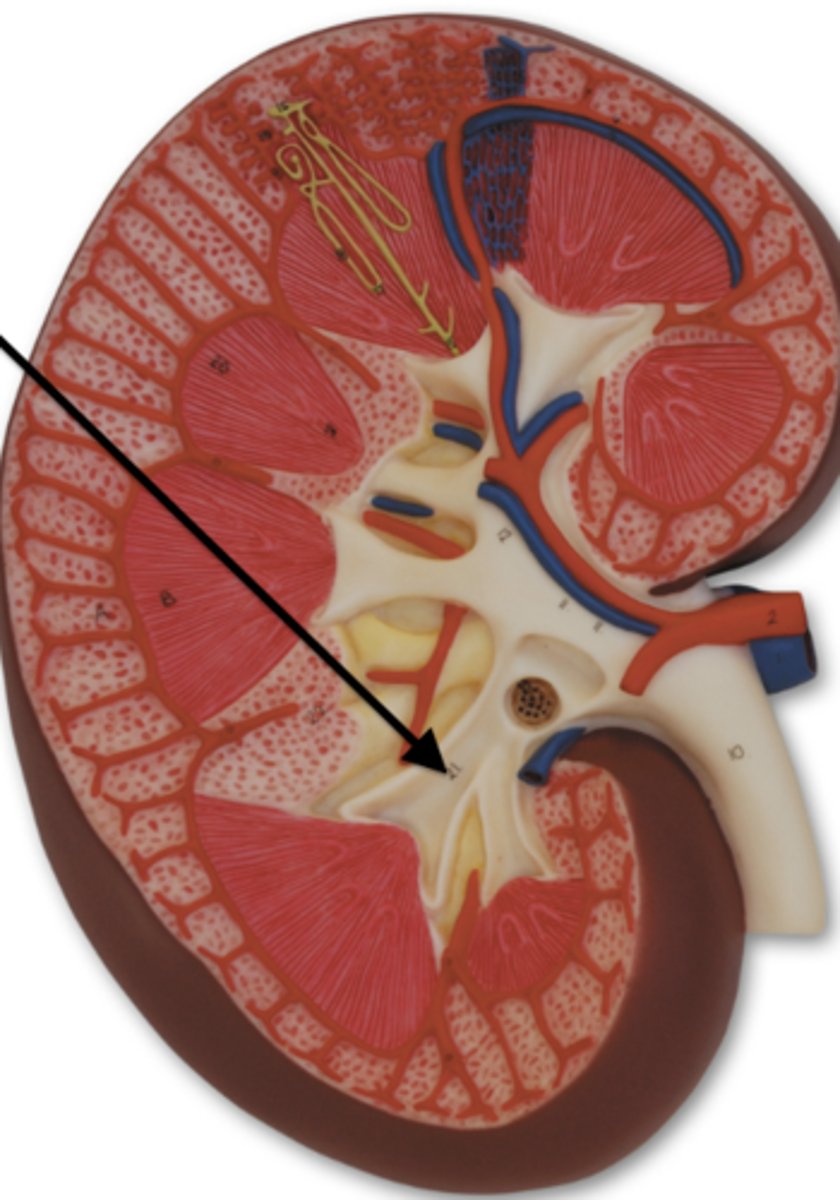
major calyces
cup-shaped structures that collect urine from minor calyces, and channel it into the renal pelvis.
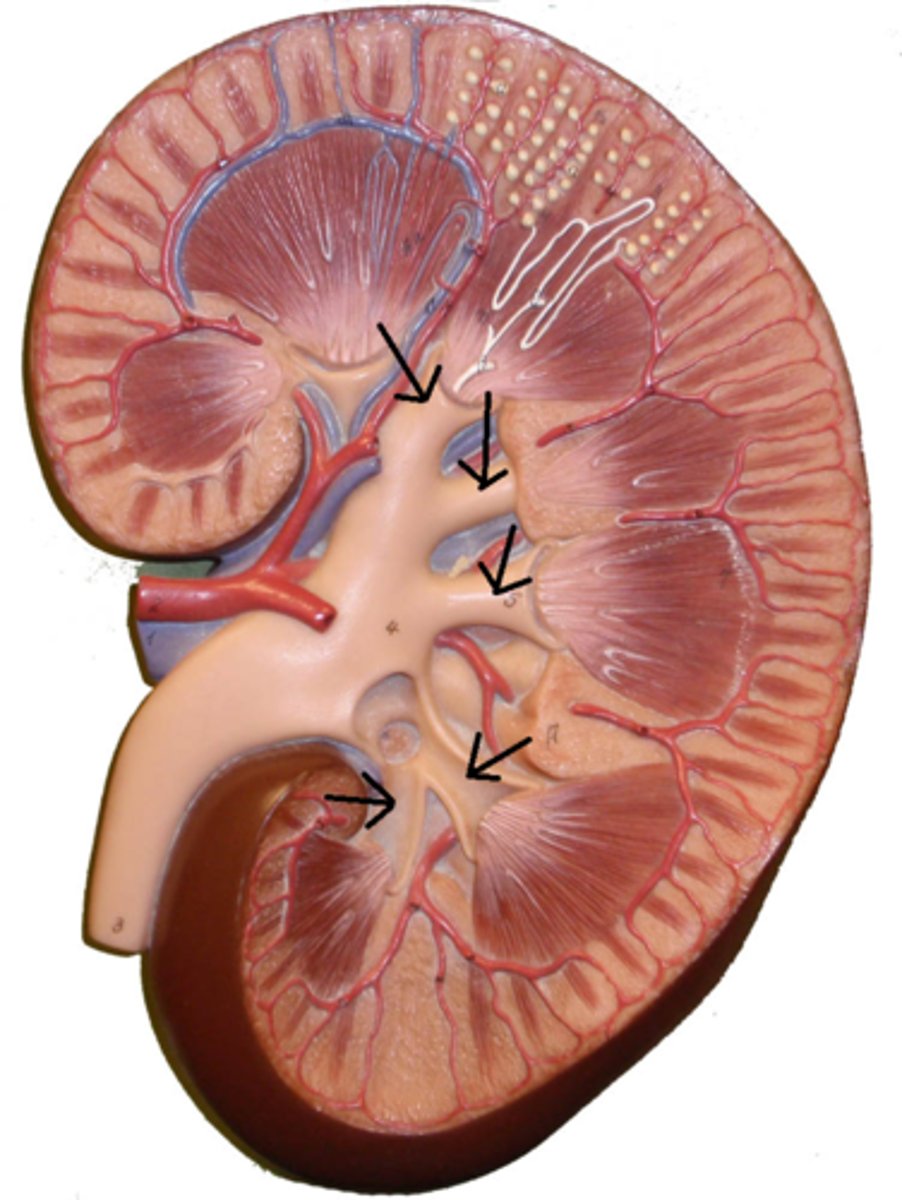
renal pelvis
structure near the renal hilum that exits the kidney and narrows to become the ureter.
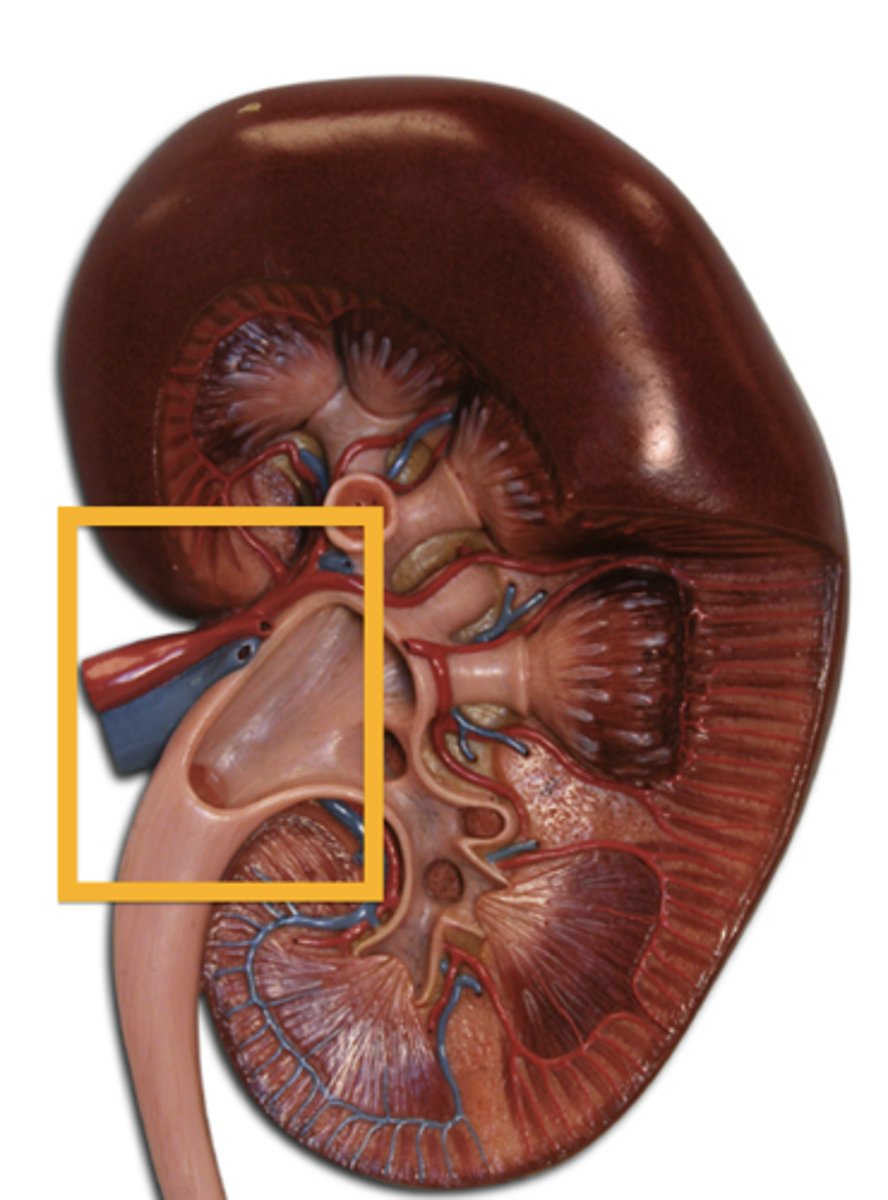
What is the pathway of urine flow in the kidney?
Renal cortex → Renal pyramid → Renal papilla → Minor calyx → Major calyx → Renal pelvis → Ureter
urinary bladder
collapsible storage sac for urine. It allows urine expulsion to occur infrequently despite the fact that urine is always being produced.
mucosa (kidney)
lined with transitional epithelium and is thrown into folds called rugae.
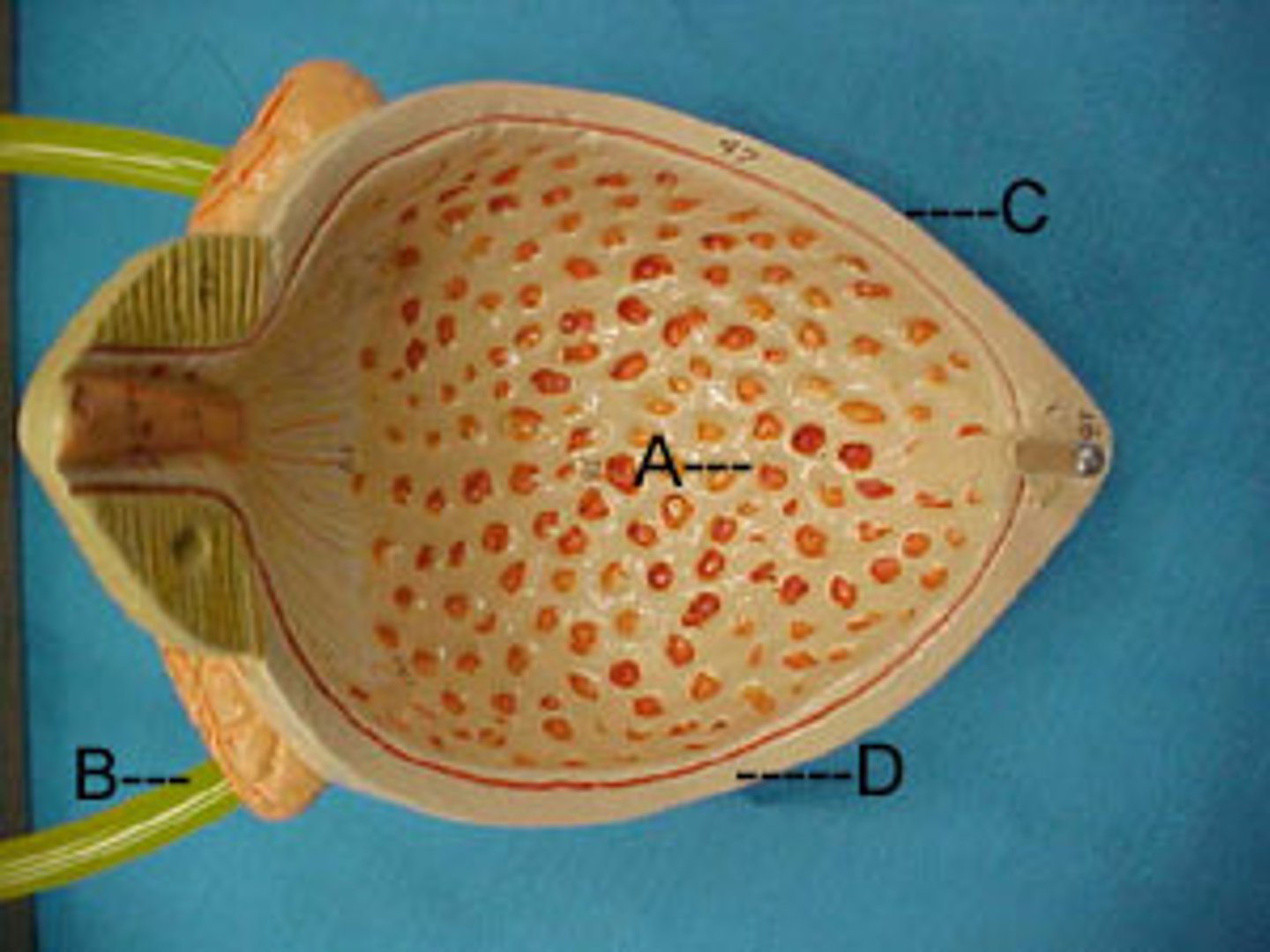
transitional epithelium
function: stretches readily and permits distension of urinary organ by contained urine
Location: lines the ureters, urinary bladder, and part of the urethra
Rugae
the folds in the lining the stomach. Allows the bladder to expand.
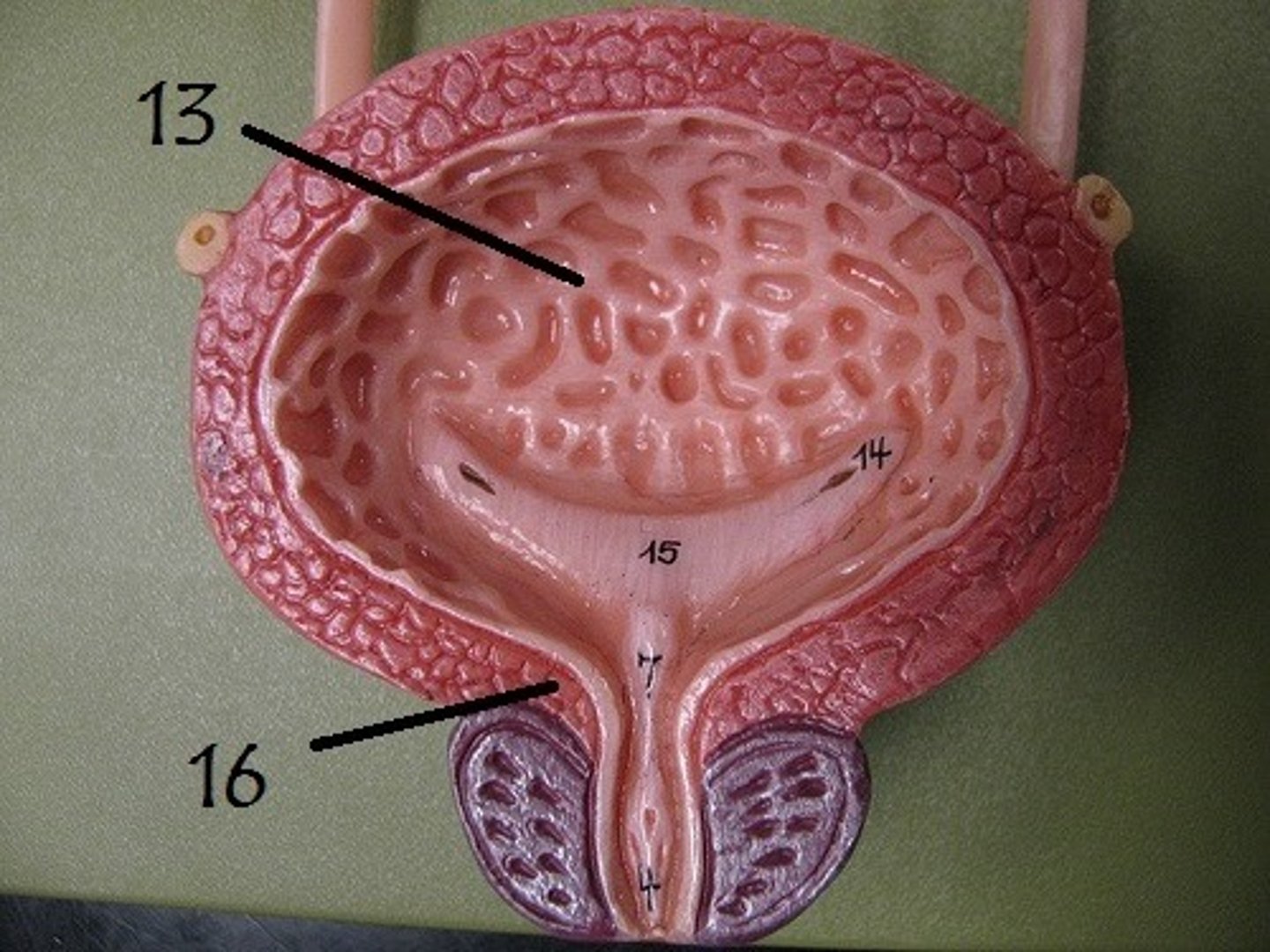
detrusor muscle
the smooth muscle layers of the urinary bladder
What lines the inside of the urinary bladder?
Is lined by parietal peritoneum on its superior surface and fibrous adventitia on all other sides.
urethra
tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body
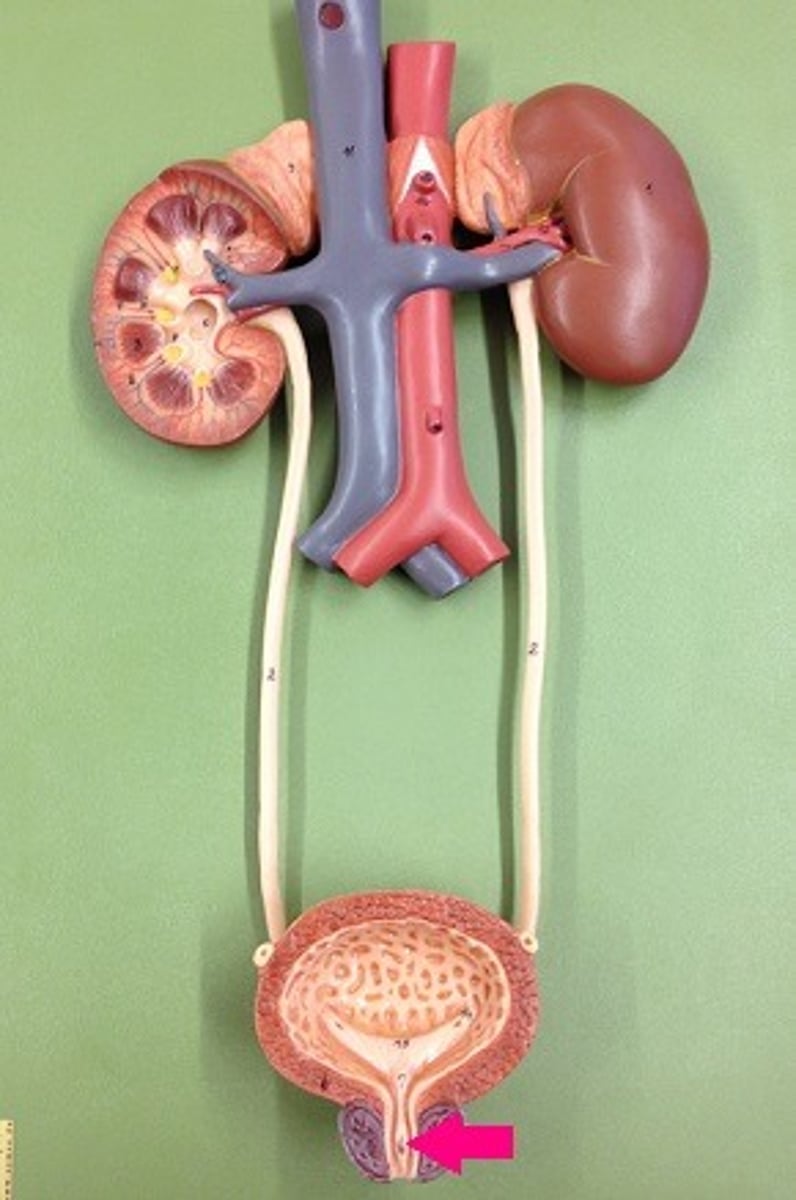
internal urethral orifice
opening in urinary bladder that leads into urethra
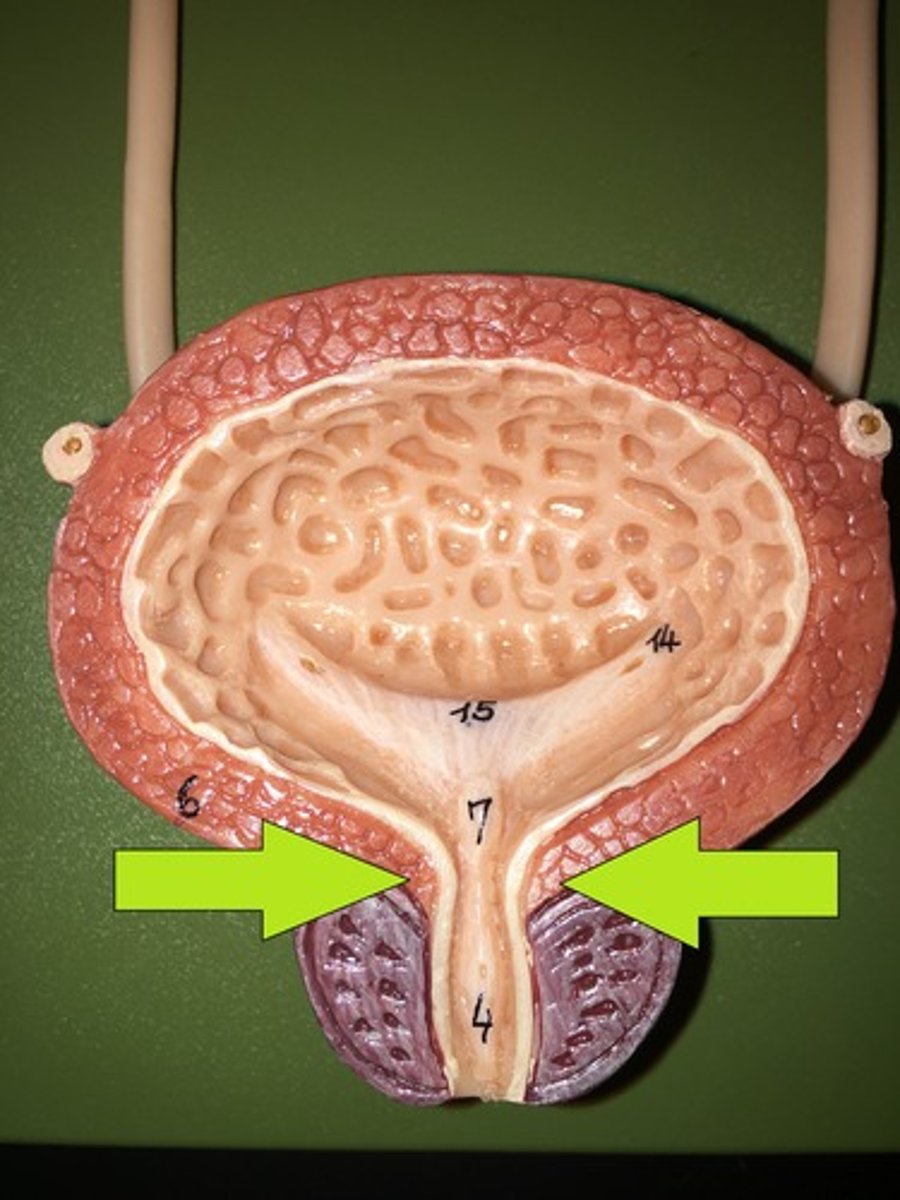
internal urethral sphincter
It opens during urination. Involuntary smooth muscle
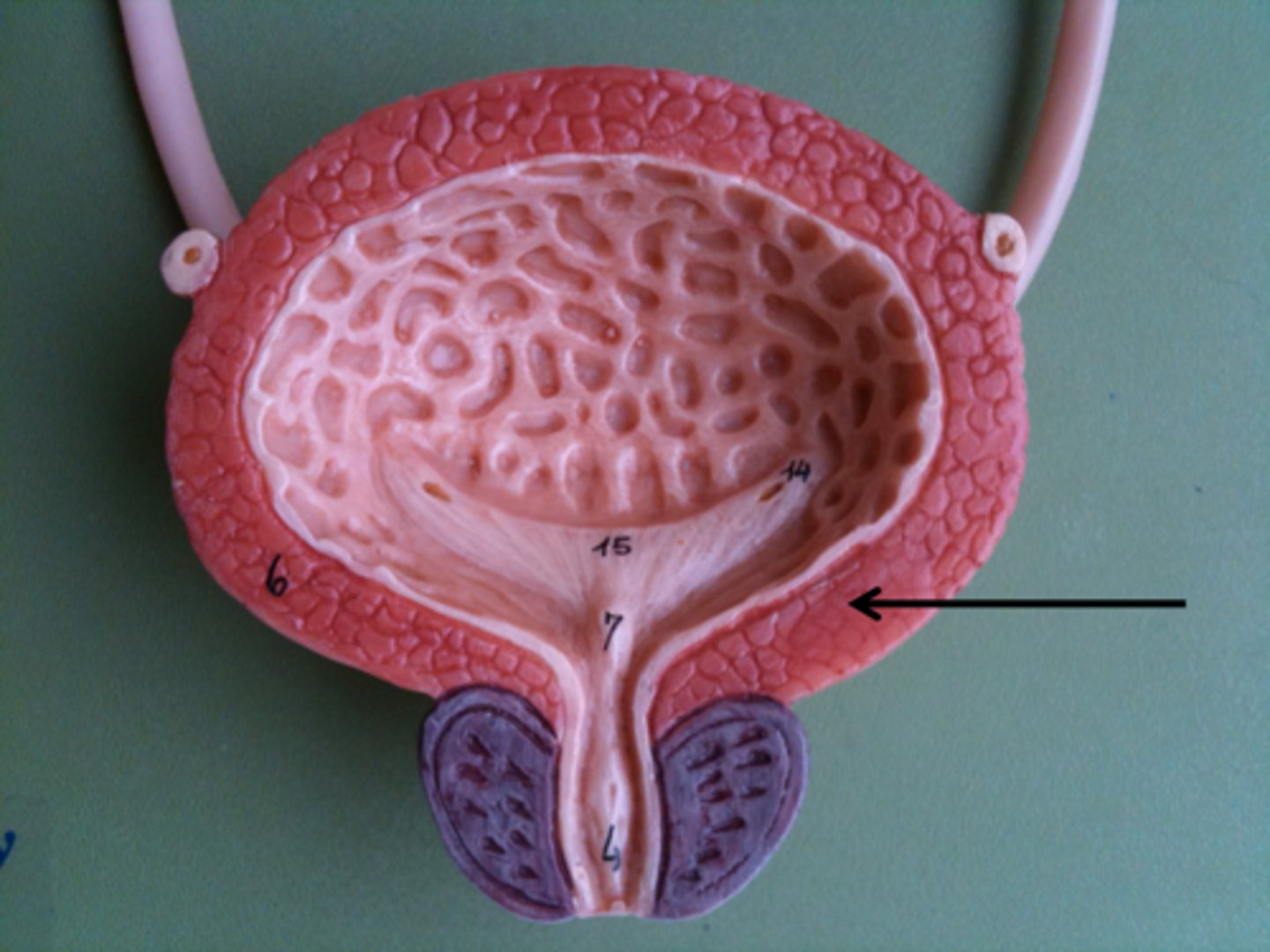
trigone
A smooth triangular region in the bladder, defined by two ureteric openings and the urethral orifice, that funnels urine into the urethra during urination.
Which organ receives the most blood per minute per weight, and why?
The kidney receives the most blood per minute per weight because its primary function is to maintain blood homeostasis.
segmental arteries
the first branches off the renal artery after it passes through hilum
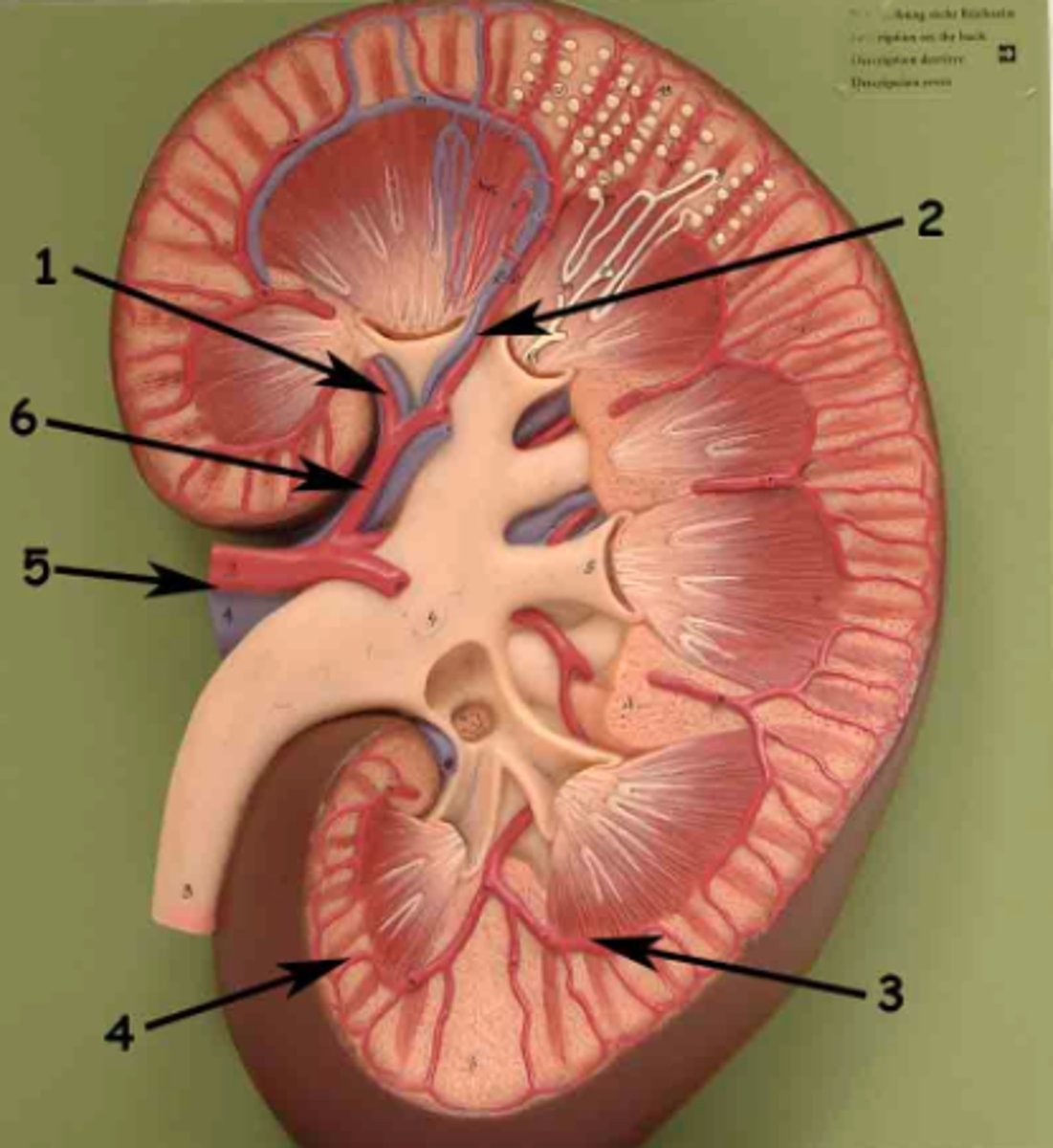
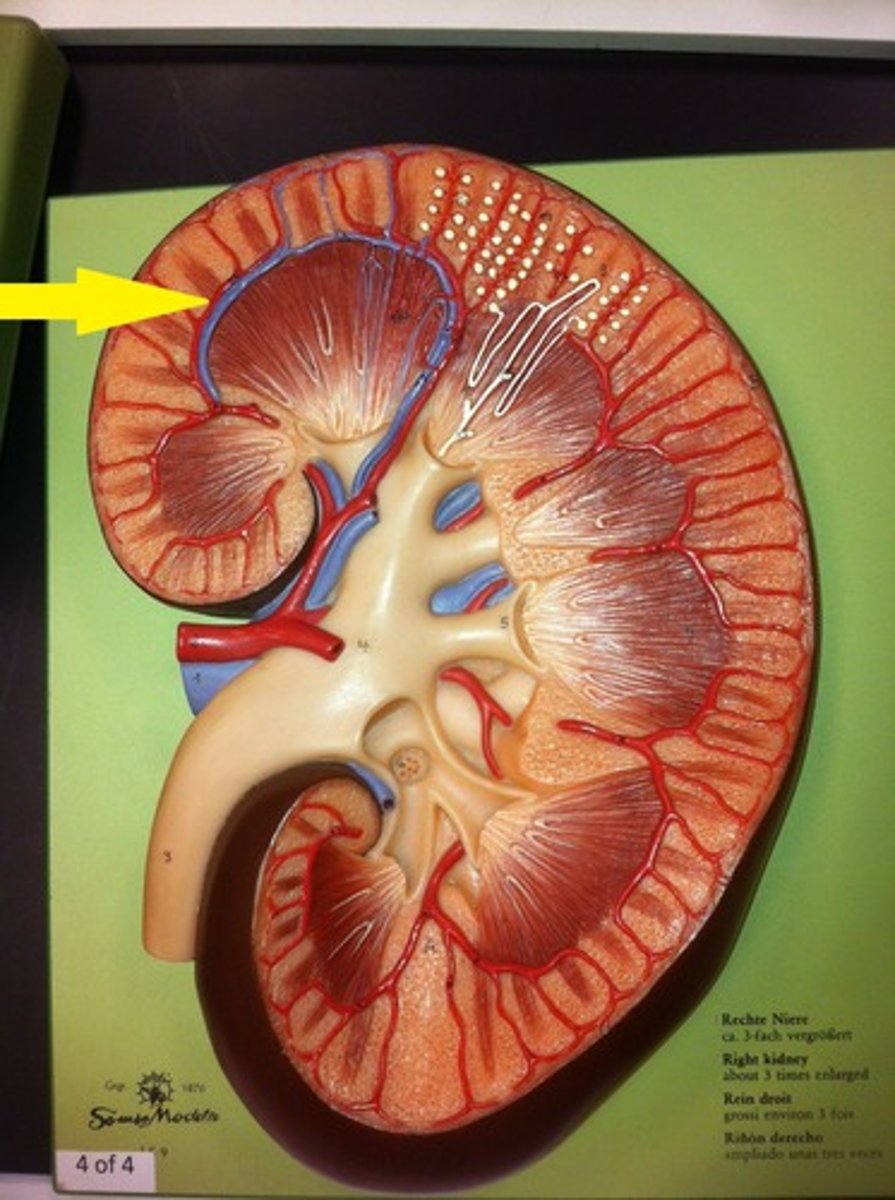
interlobar arteries
segmental arteries further divide into these arteries, which are located within the renal columns between the renal pyramids. supply blood to the arcuate arteries
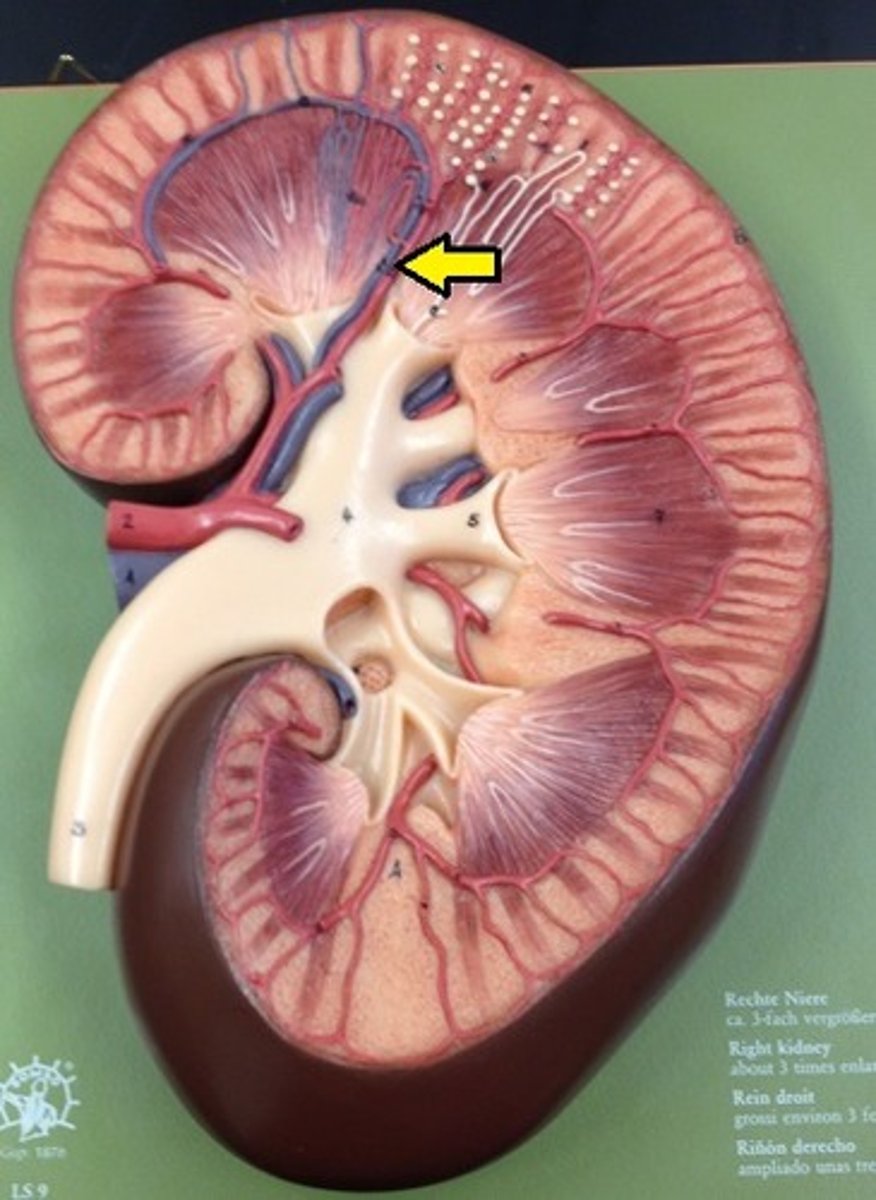
arcuate arteries
small vessels found at the base of the renal pyramids branched off from the interlobar arteries
glomerulus
tiny ball of capillaries in the kidney that collects blood from the afferent arterioles and filters it to, start the processing of making urine.
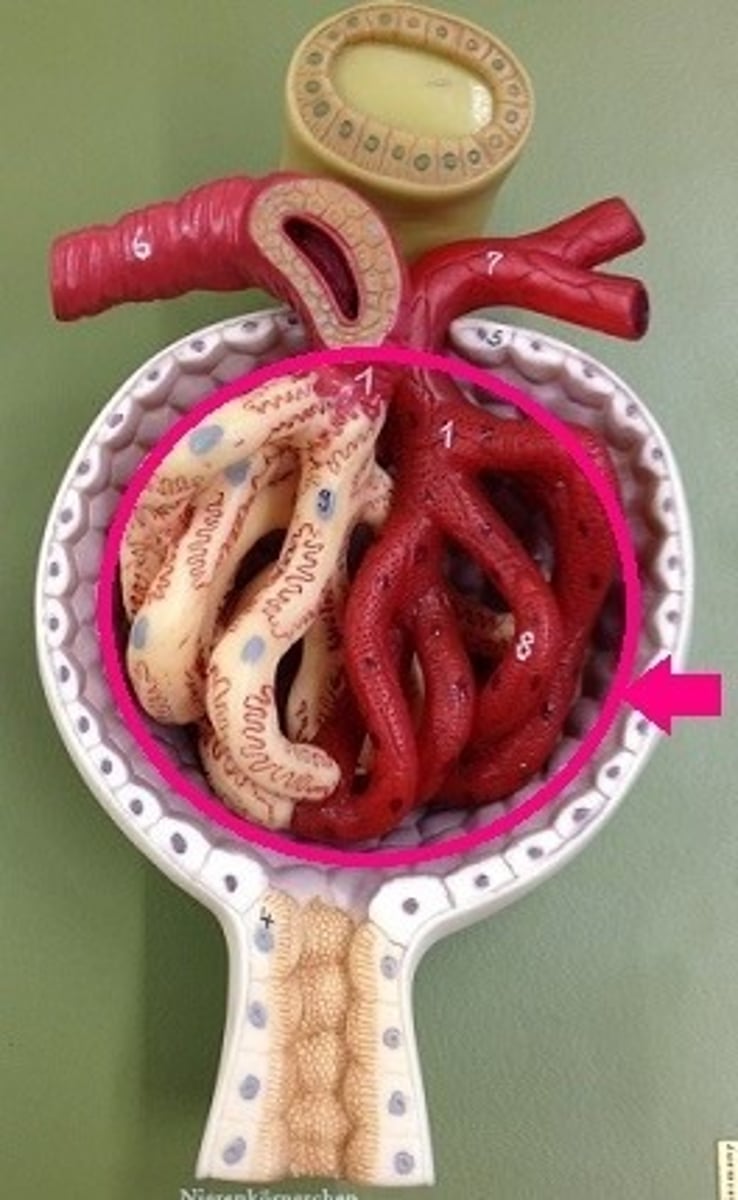
Filtration
first step in urine formation. filtrate of blood leaves kidney capillaries
efferent arteriole
Vessels exiting the glomerulus. Contains only 80% of the volume of the afferent arteriole since a fraction of blood plasma is filtered in the glomerulus.
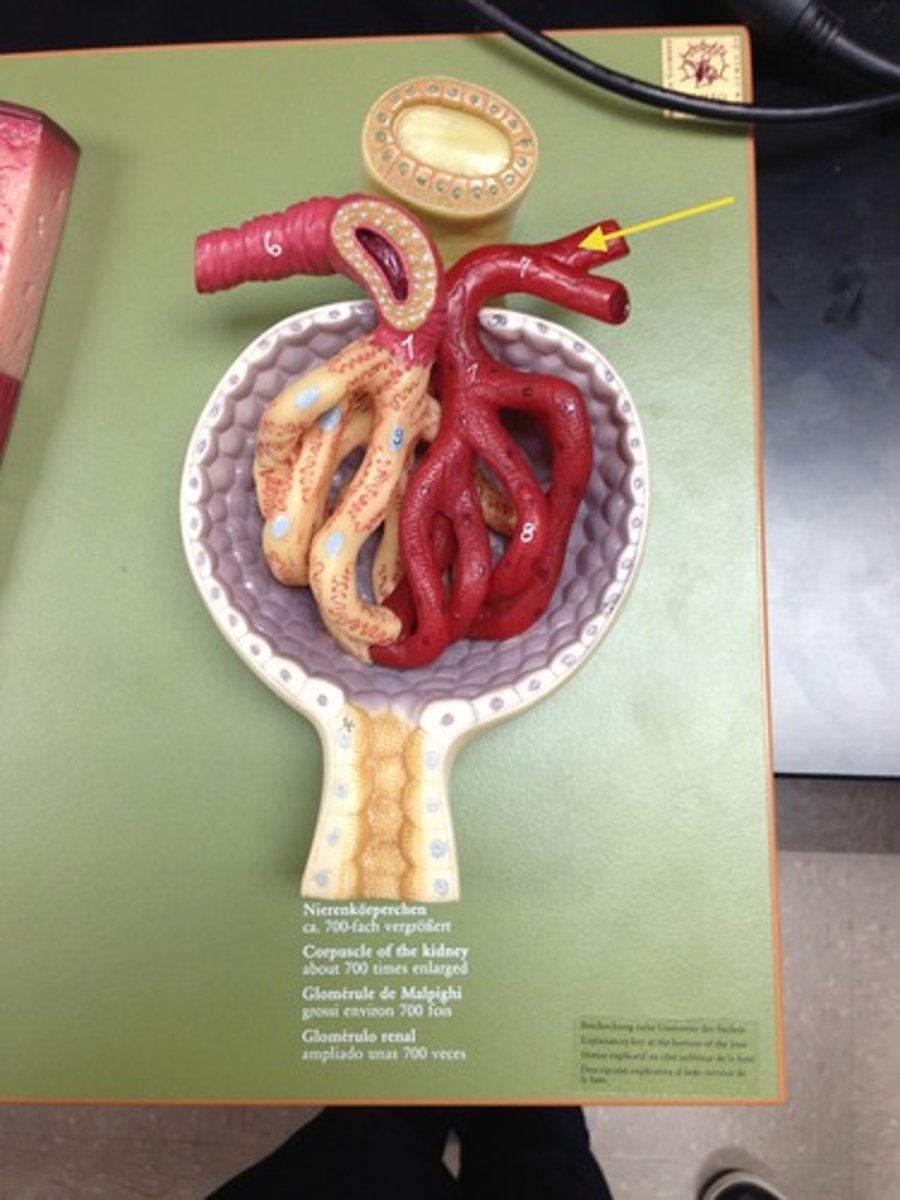
peritubular capillaries
collects blood from the efferent arterioles. The vast majority of fluid filtered at the glomerulus is reclaimed.
vasa recta
thin, straight vessels that some efferent arterioles empty into.
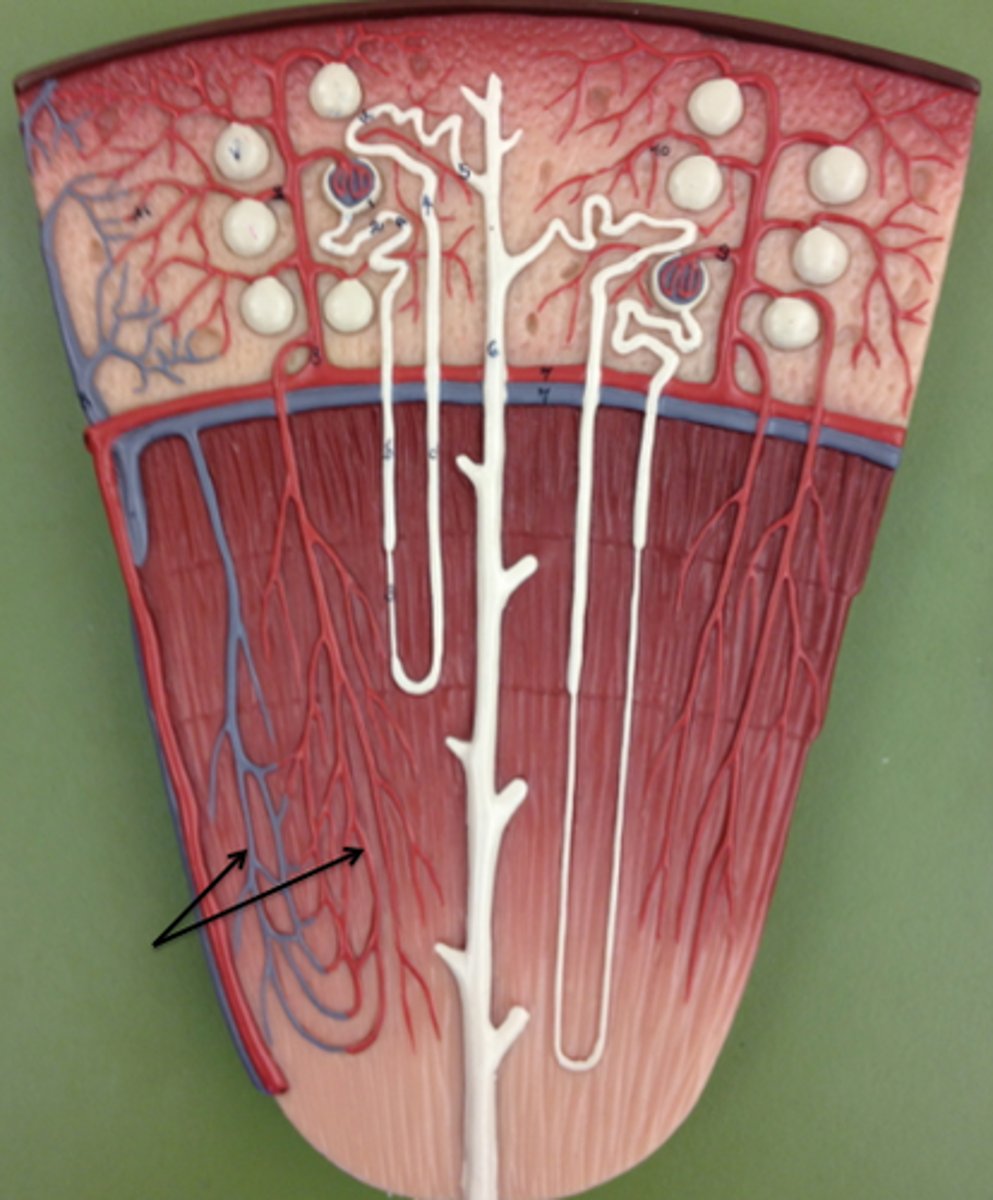

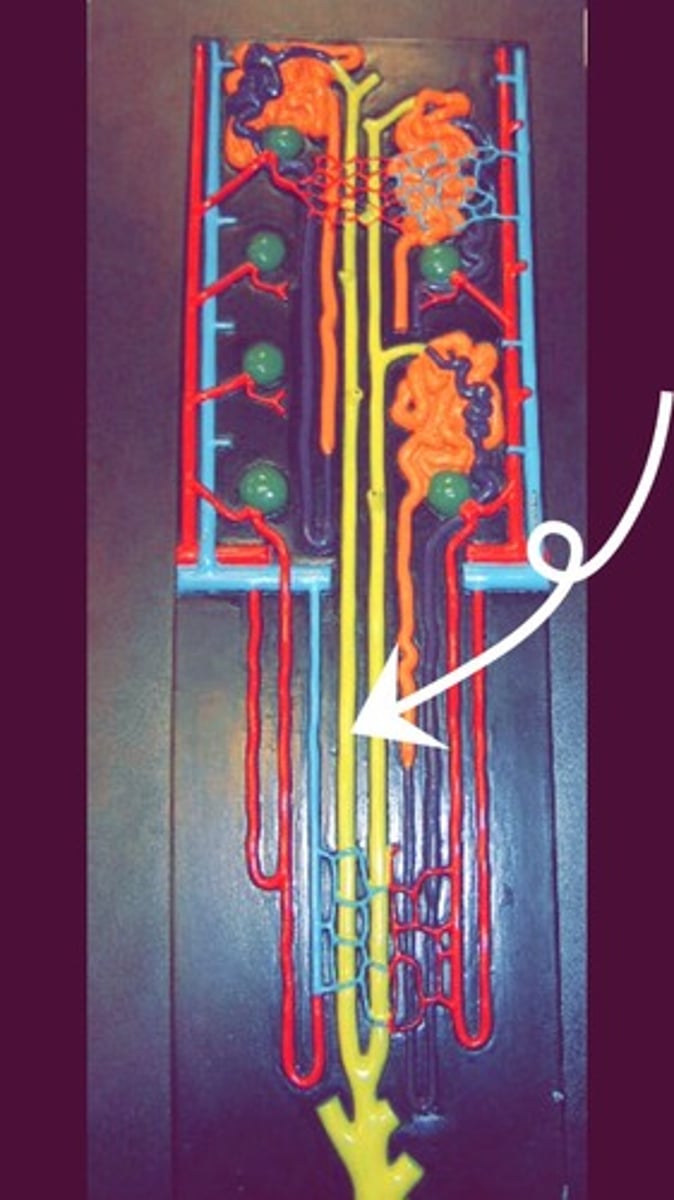
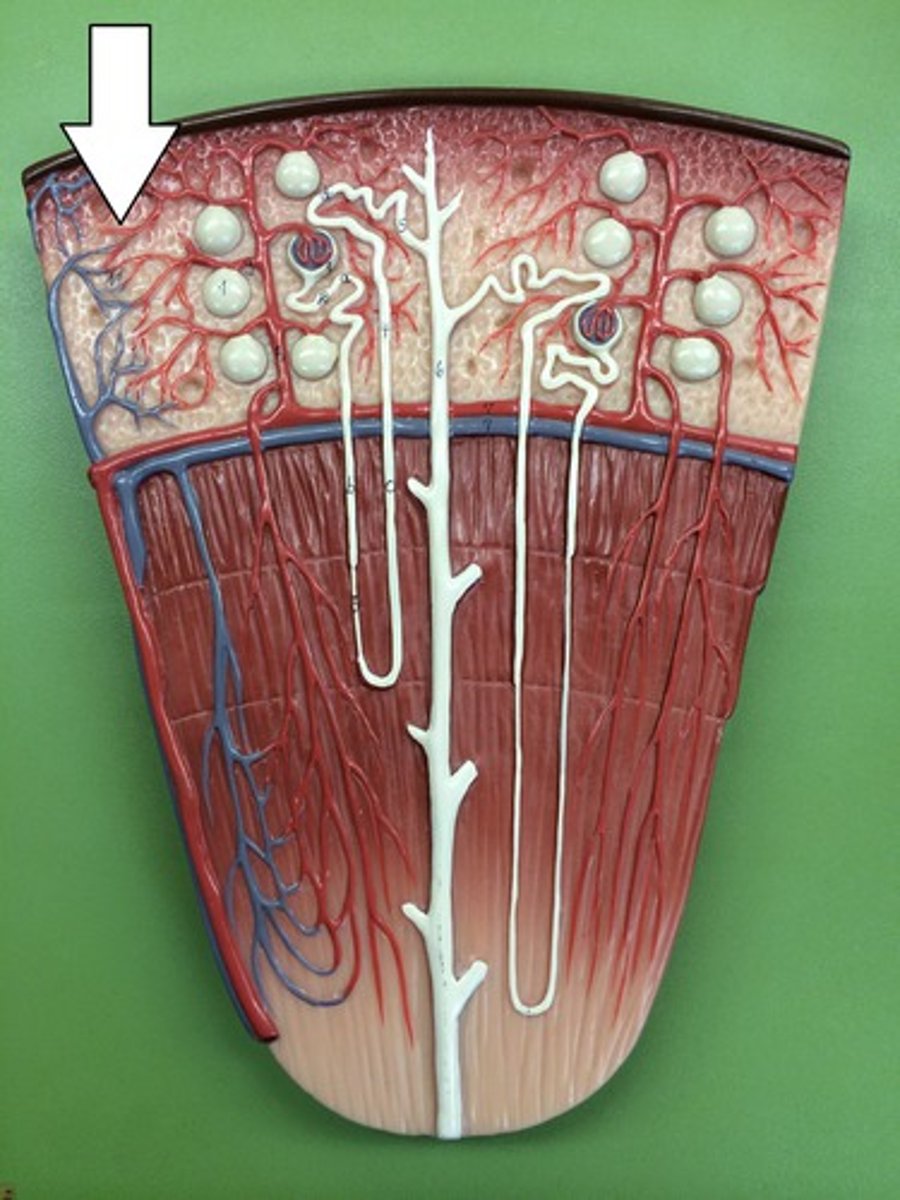
interlobular veins
Adjacent to the interlobular arteries. collects blood from the peritubular capillaries and vasa recta.
arcuate veins
receives blood from the interlobular veins, and drains into the interlobar veins.
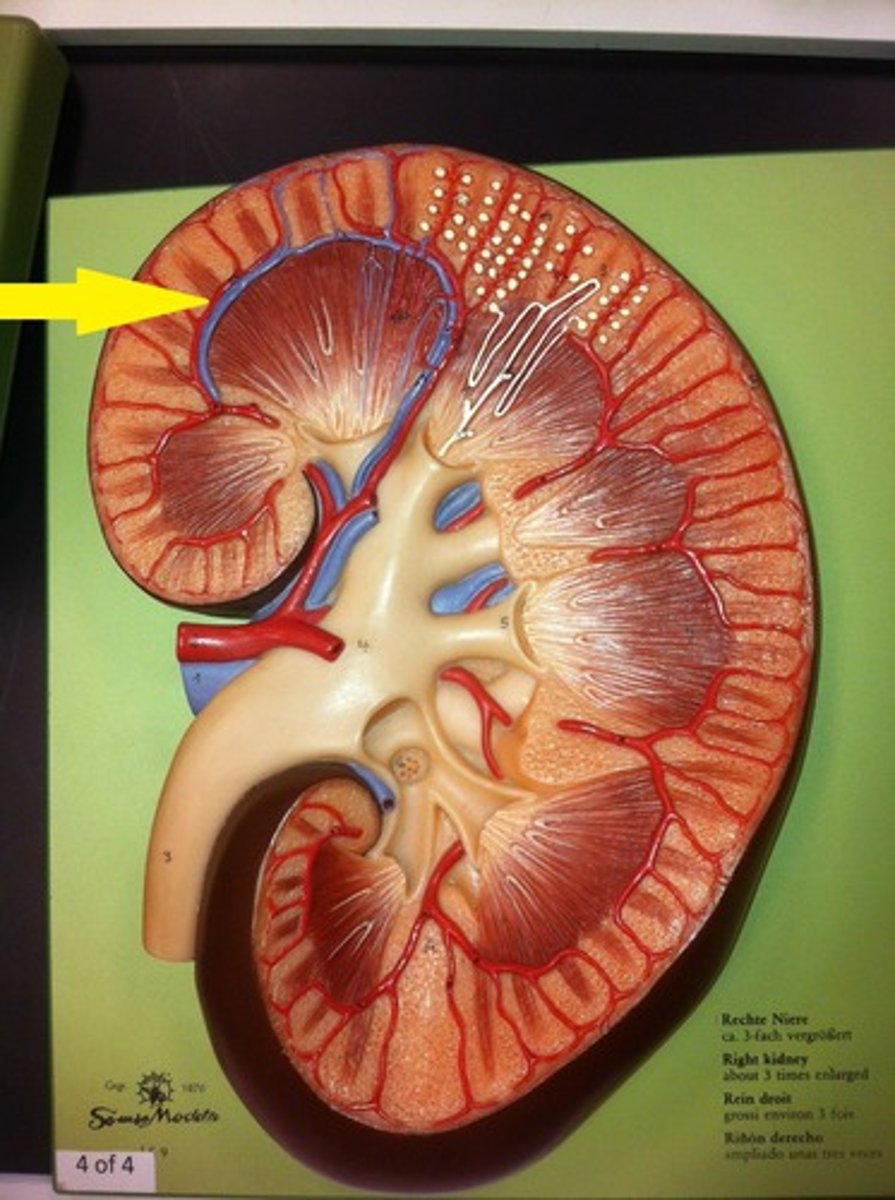
interlobar veins
receives blood from the arcuate veins before draining it into the renal veins.
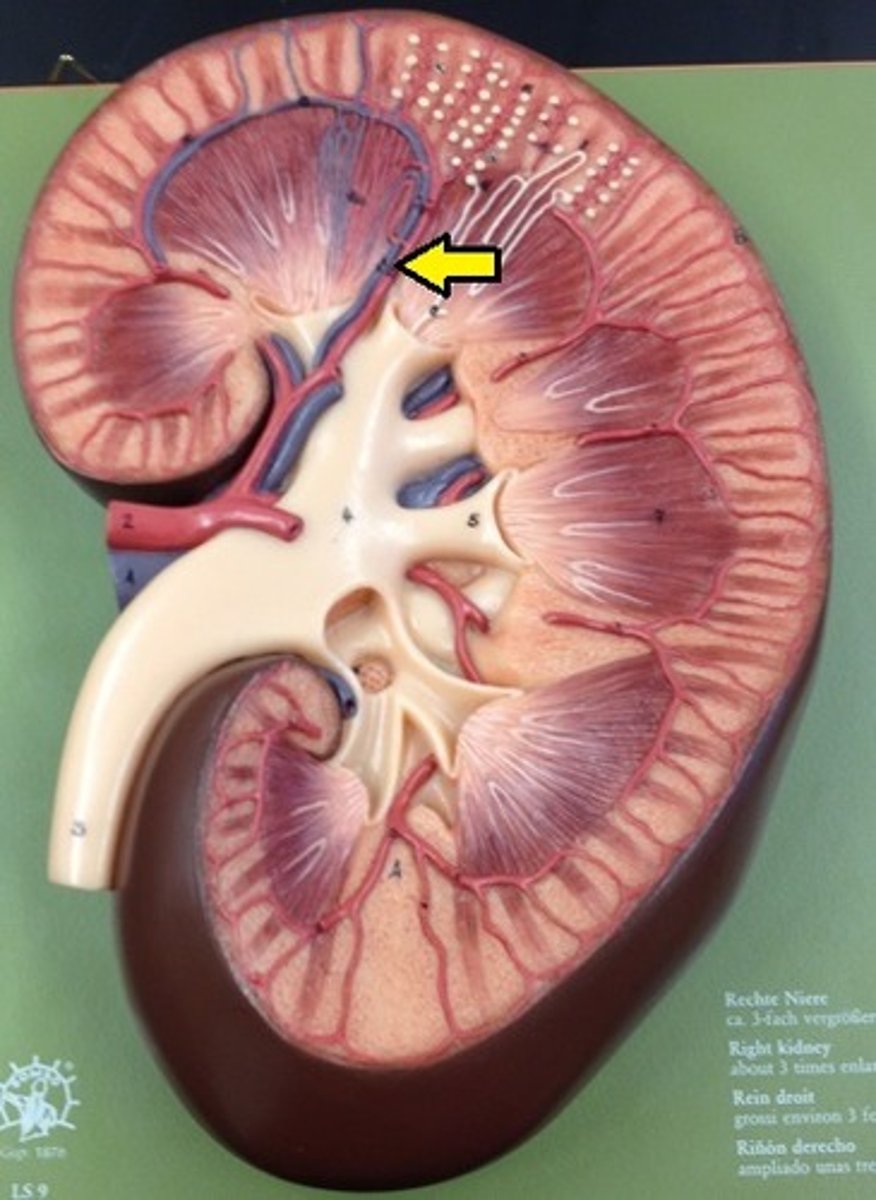
what is the pathway for renal blood flow?
Abdominal aorta → Renal artery → segmental artery → interlobar artery → arcuate artery → interlobular artery → afferent arteriole → Glomerulus → Efferent arteriole → Peritubular capillaries/ Vasa recta → interlobular vein → Arcuate vein → Interlobar vein → Renal vein → Inferior vena cava
glomerular capsule
an enclosing structure surrounding each spherical glomerulus.
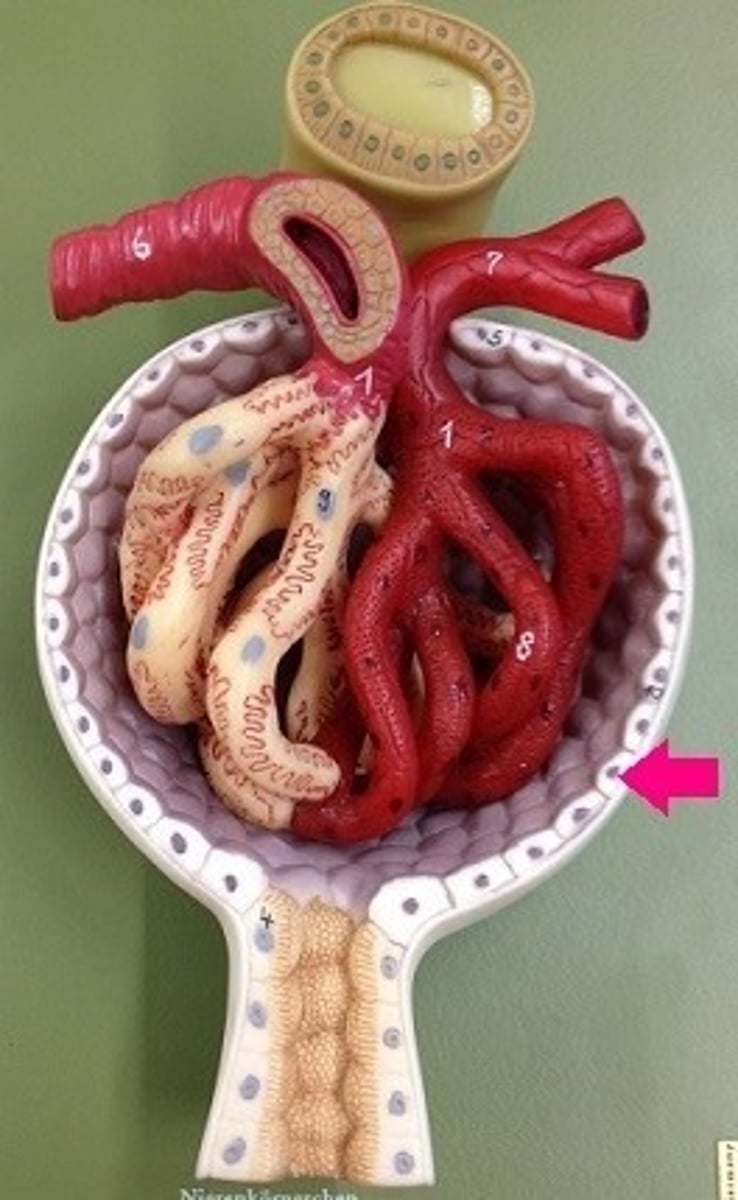
visceral layer
The portion of the capsule lying directly upon the glomerulus and is composed of cells known podocytes.
podocytes
cells in the kidneys that wrap around the capillaries of the glomerulus. They help filter the blood and stop large things like proteins from leaving the bloodstream.
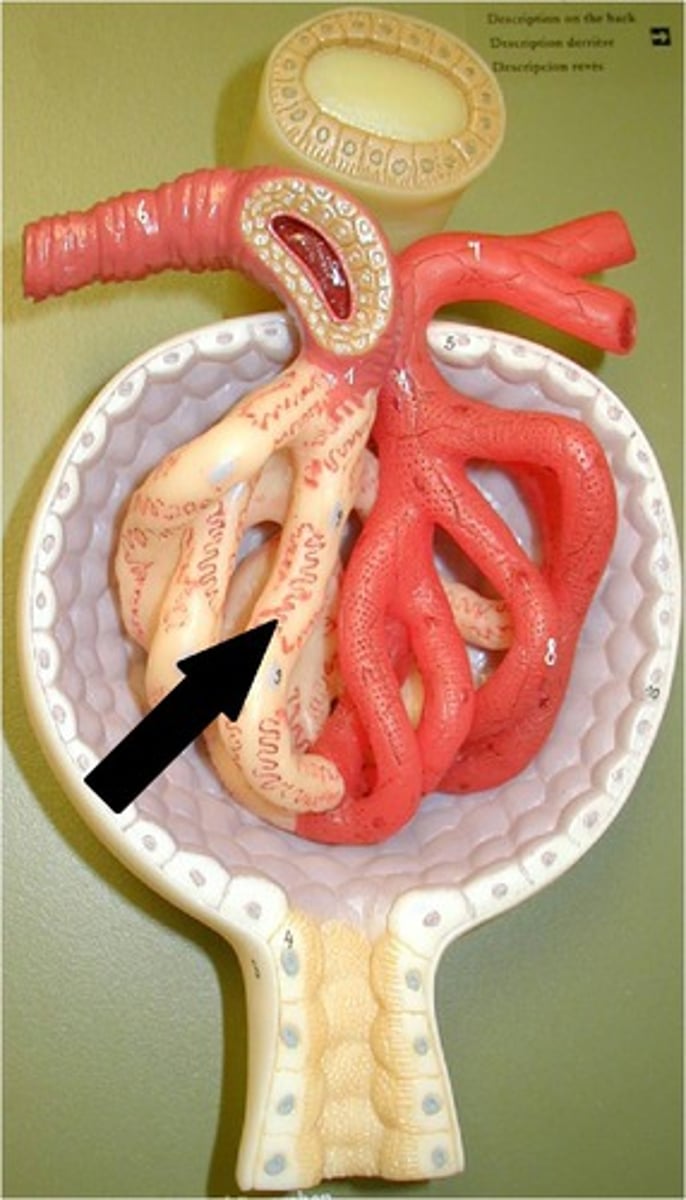
parietal layer
Outer layer of the glomerular capsule. Composed of simple squamous epithelium
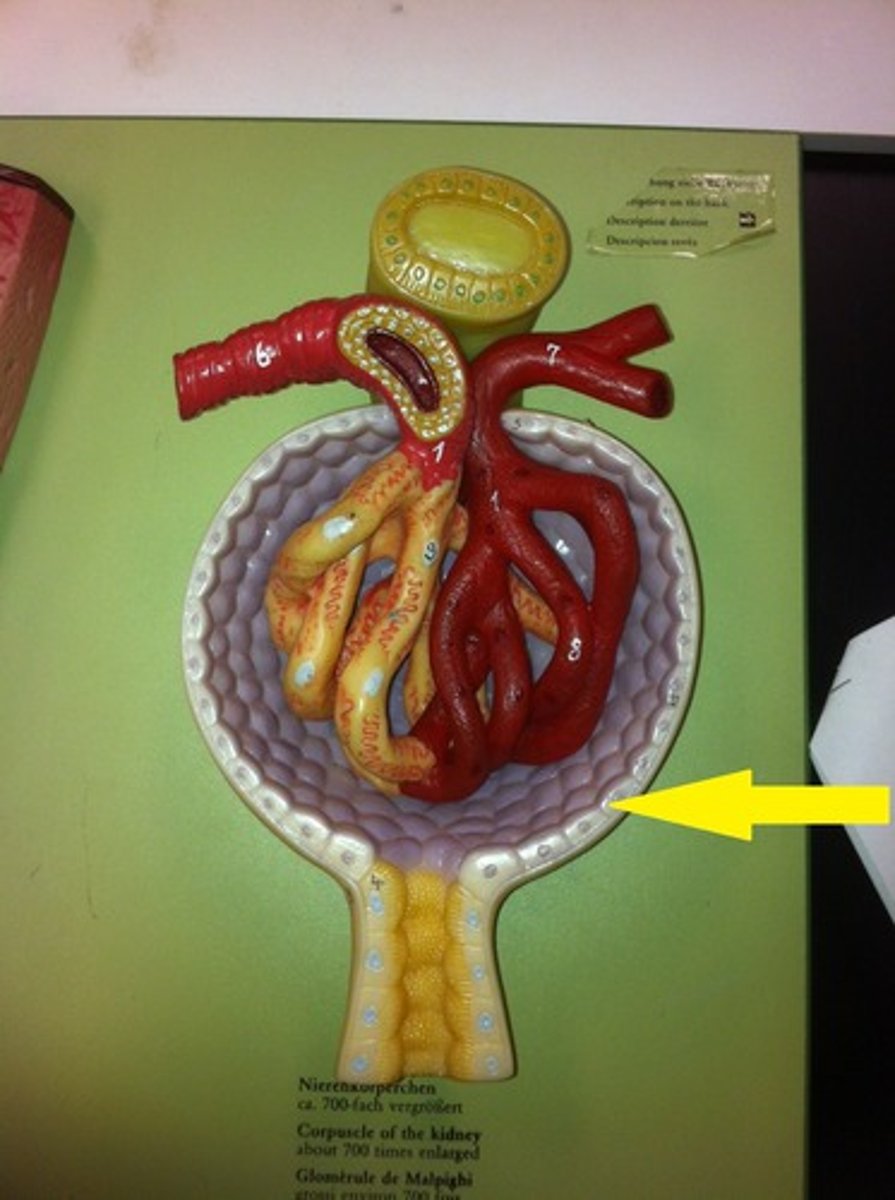
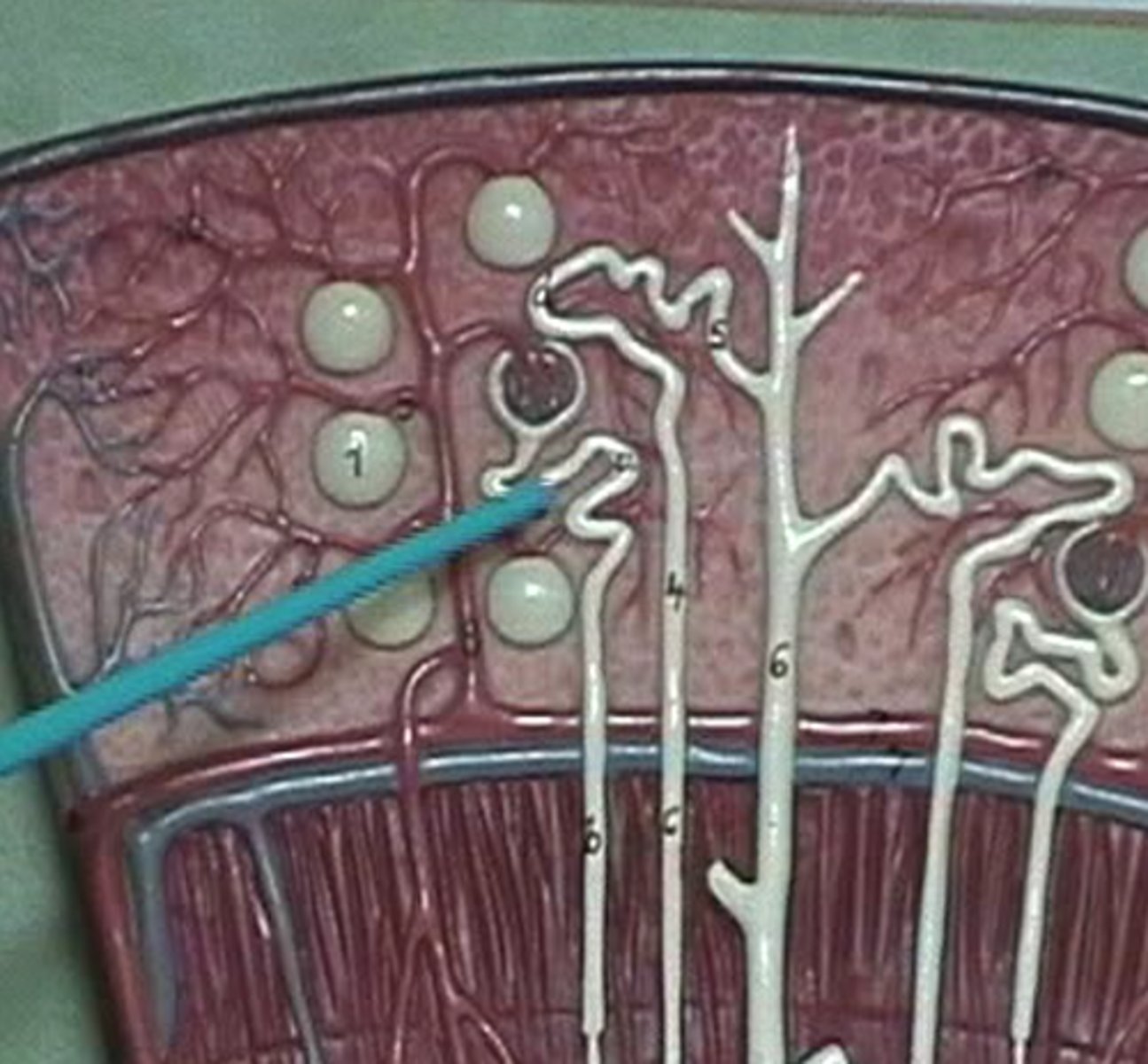
renal corpuscle
glomerulus and glomerular capsule
filtrate
fluid that enters the lumen of the capsule. It contains solutes of two varieties; things that we'd like to keep (ex. nutrients) and things that we'd like to excrete (ex. waste)
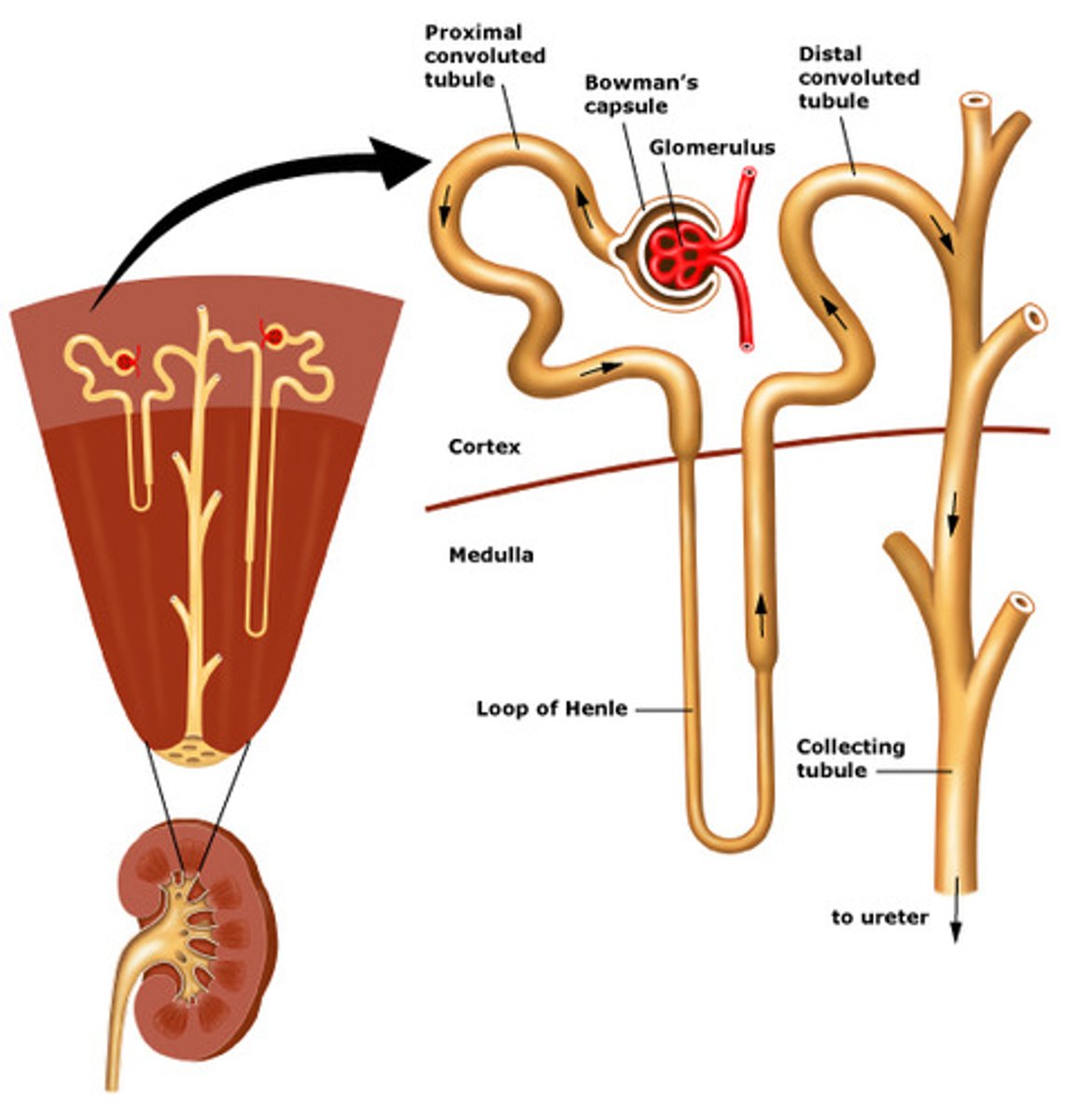
proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)
a tortuous tube that filtrate exits out of and is lined by simple cuboidal epithelial cells laden with microvilli. This gives the PCT significant surface area.
reabsorption and secretion
Reabsorption: The process of transporting solutes, such as glucose, that were filtered at the glomerulus but should not be excreted in urine from the lumen of the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) to the lumen of the neighboring peritubular capillary.
Secretion: The process of transporting solutes that were not filtered at the glomerulus but should be excreted in urine from the lumen of the peritubular capillary to the lumen of the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT).
Which type of vessels performs reabsorption and secretion?
proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) and peritubular capillaries.
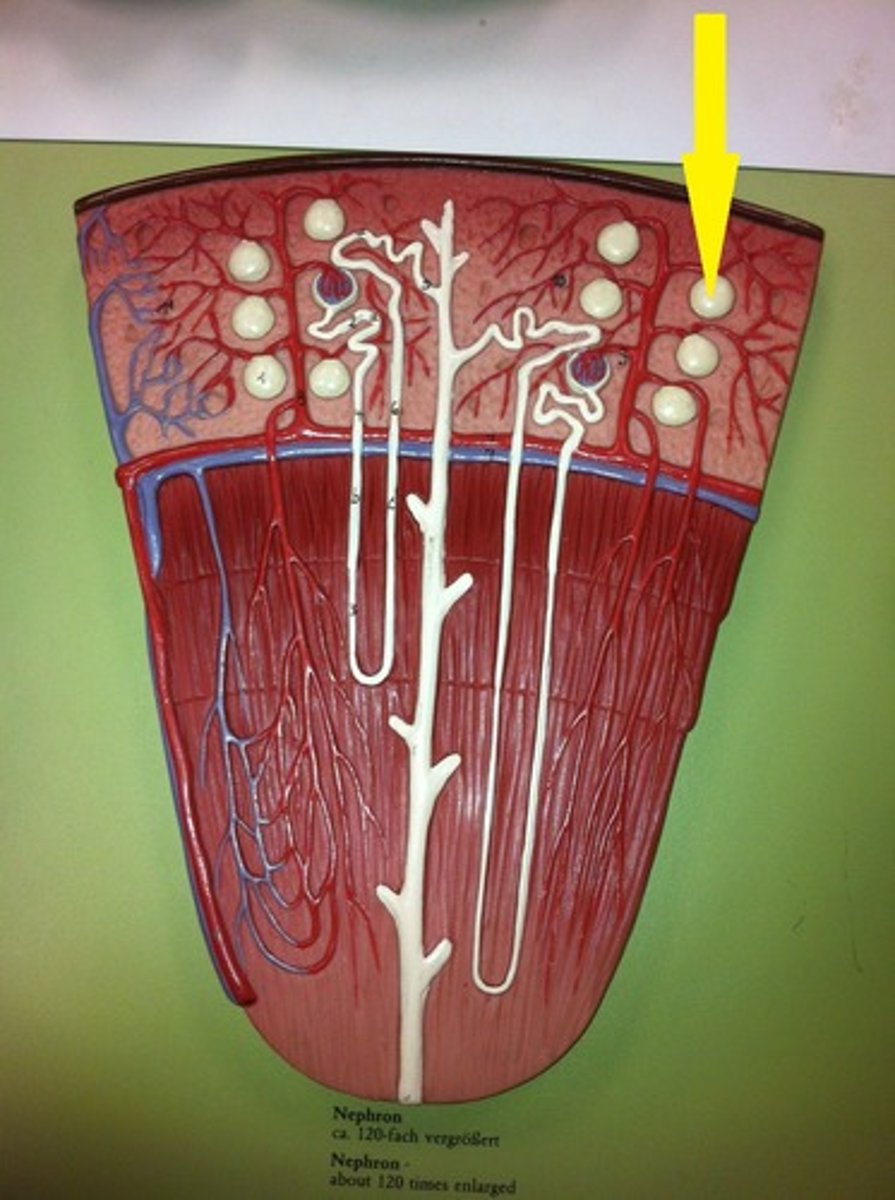
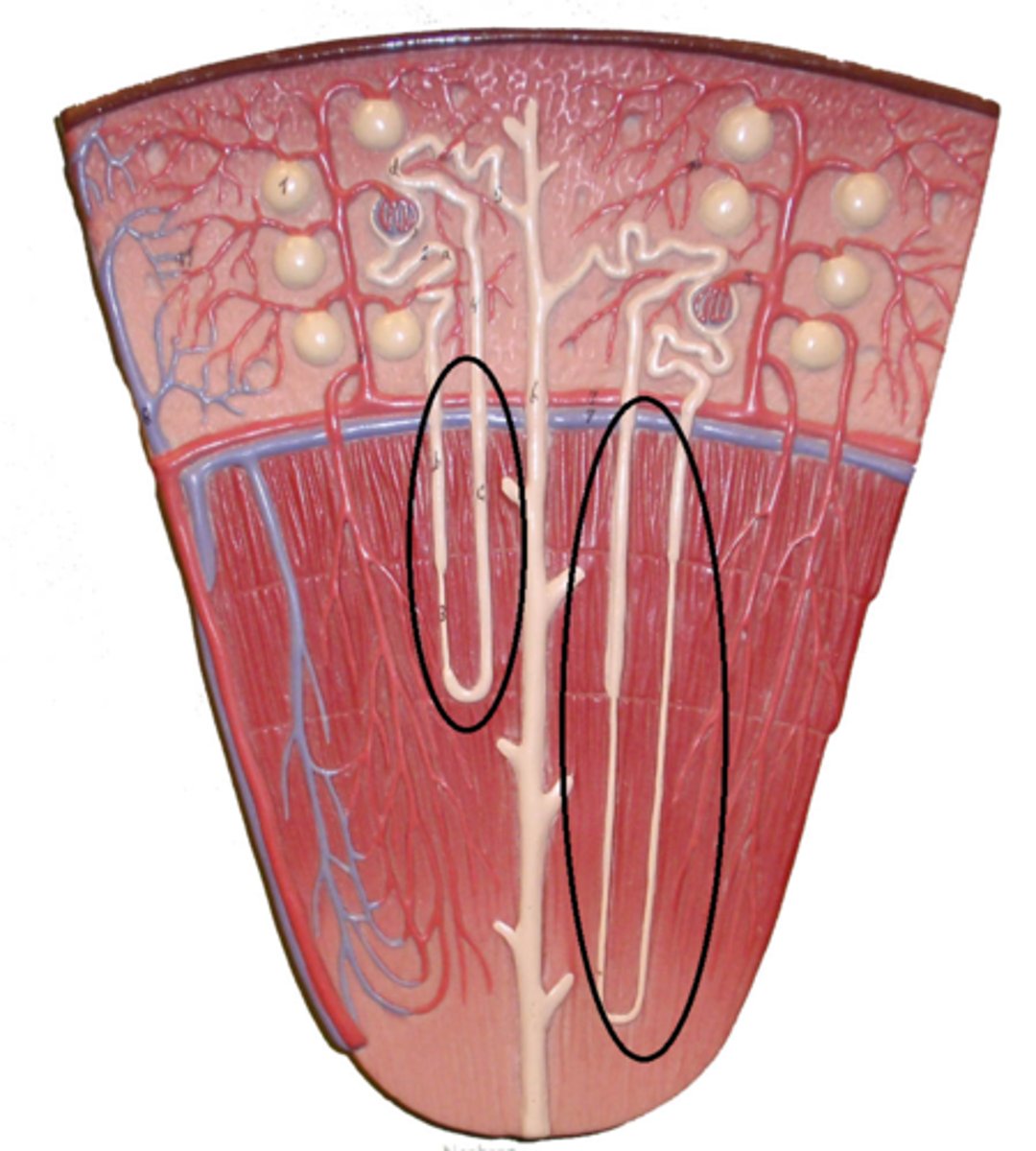
Loop of Henle
Is a long straight tube with a single characteristic hairpin turn. It functions primarily augmenting the kidney's ability to concentrate.
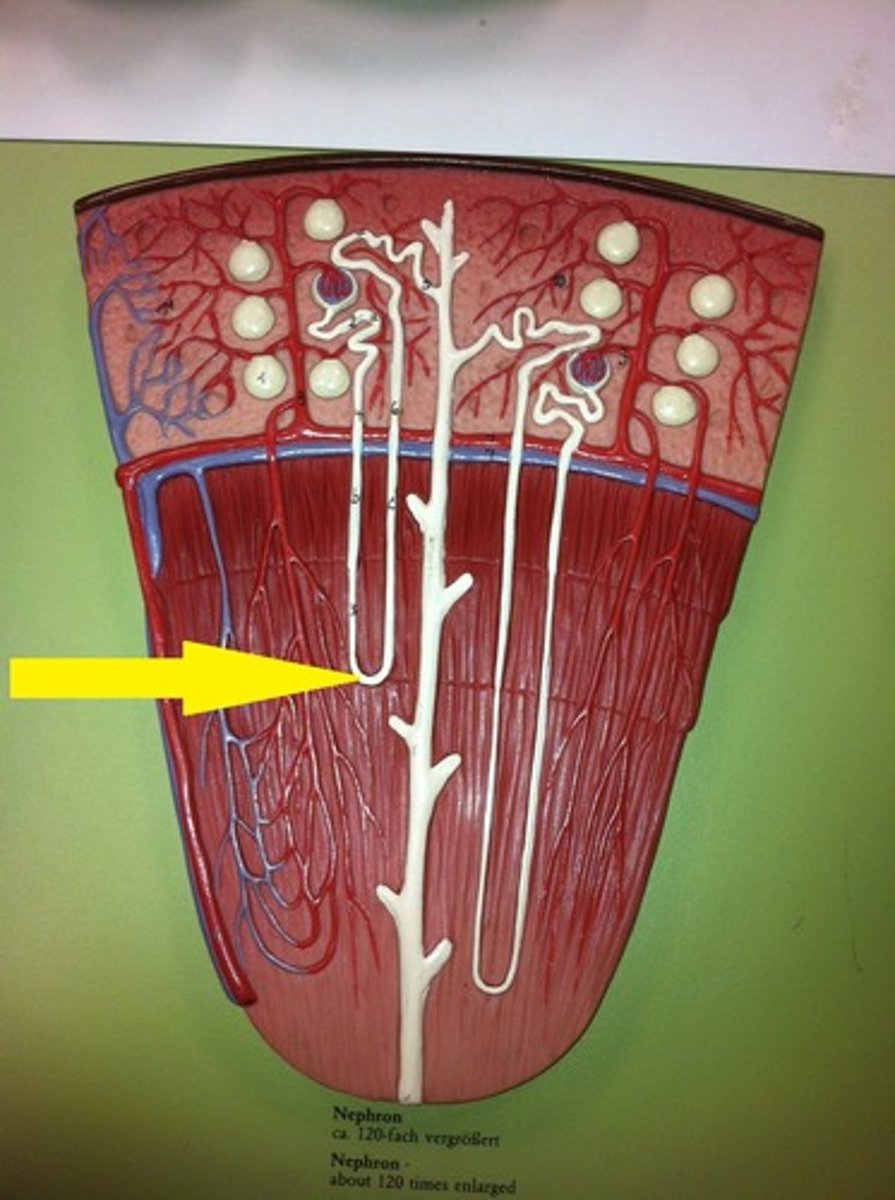
distal convoluted tubule (DCT)
A twisty tube adjacent to the loop of Henle that the filtrate will enter to get its ionic content modified.
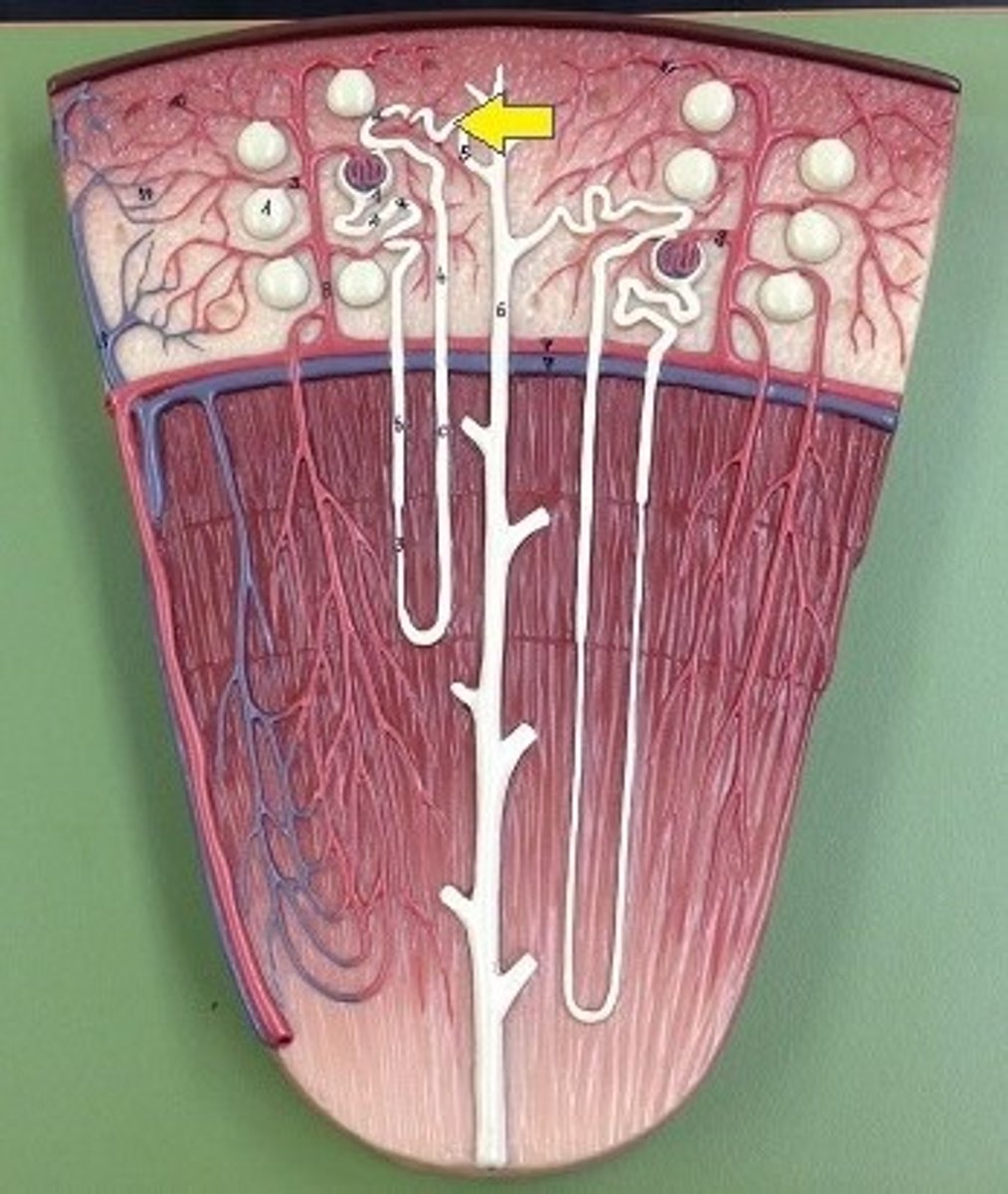
collecting duct
carries urine down through the medullary pyramid and terminate at a renal papilla. The cells will reabsorb water from the urine as necessary.
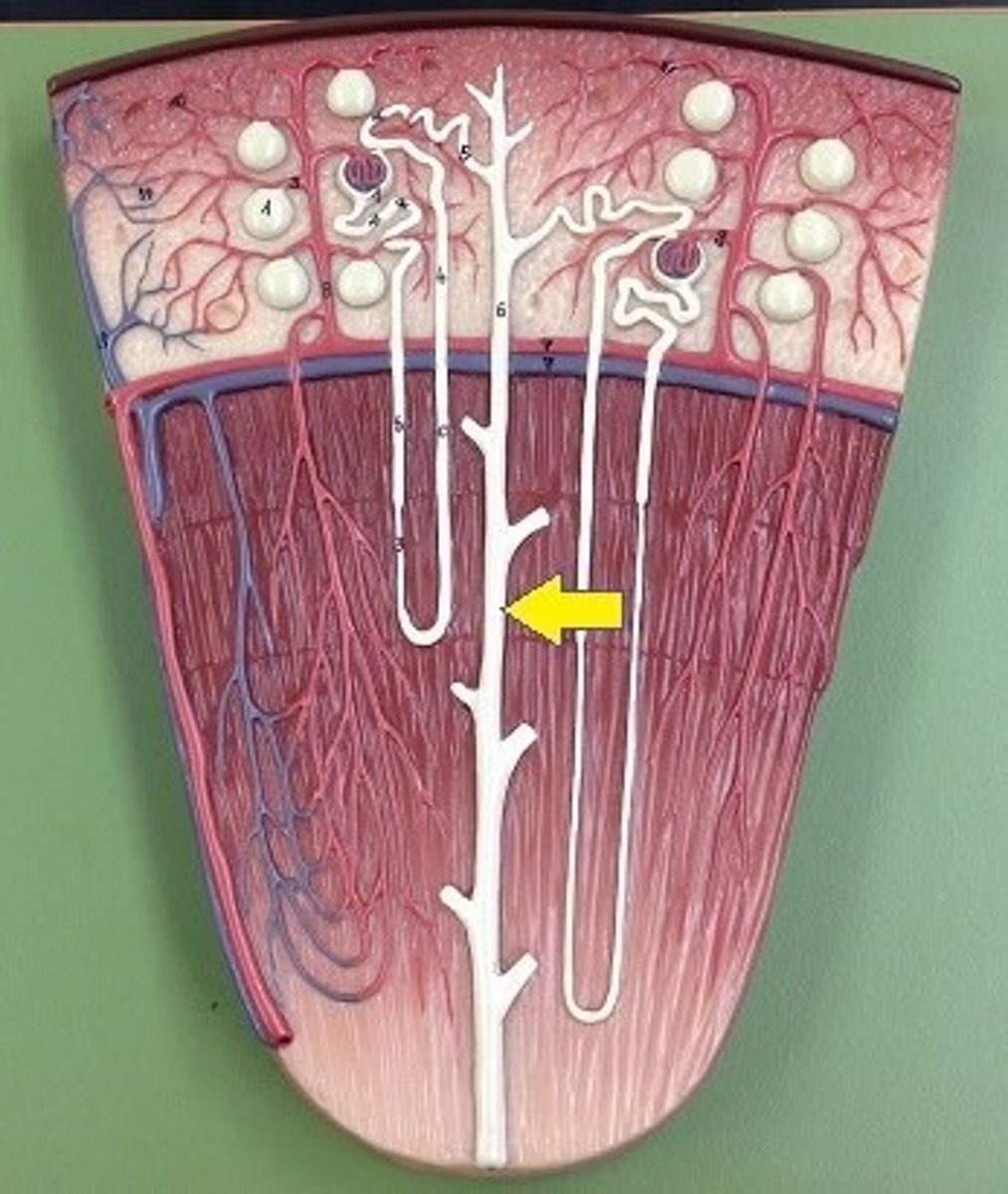
nephron
A set of tubes that carry filtrate to the collecting duct.
How many nephrons are contained in the kidney?
one million nephrons and it is due to their collective effort that blood is filtered and urine is produced.
Why is the PCT epithelium so heavily endowed with microvilli?
They provide the necessary surface area for the enormous amount of reabsorption that occurs.
Many desert-dwelling animals exhibit extremely long loops of Henle. Suggest a reason why.
It allows them to super-concentrate their urine, which helps retain water a necessary skill in arid environment.
What structures allow urination to be discontinuous even through urine production is continuous?
Urinary bladder and urethral sphincters
How could damage to podocytes affect the protein content of urine?
It would decrease their filtering ability and larger molecules such as proteins could start appearing in the urine.