Lithosphere - glaciers
1/79
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
Glaciation
This is the process of which the land is covered by glaciers
Glaciers
Large, thick masses of ice that form on land when fallen snow is compressed over many years
Where does ice form?
In cold regions close to the poles or on areas of a high latitude, usually on north-facing slopes
What three processes are glaciers capable of doing?
Deposition
Erosion
Transportation
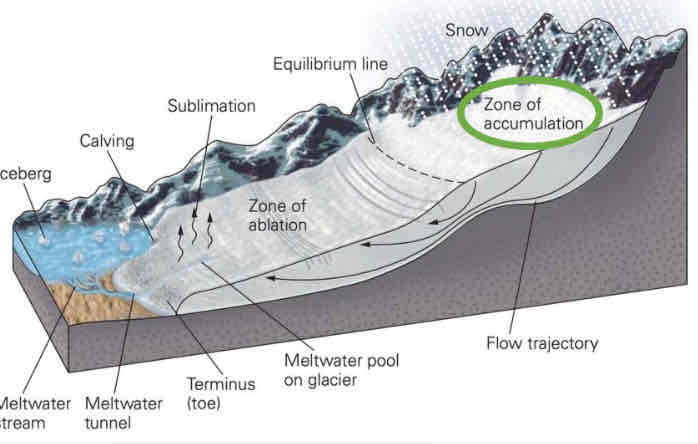
Zone of accumulation
Areas where ice does not melt during summer leads to a build-up of pressure as more snow compacts into ice
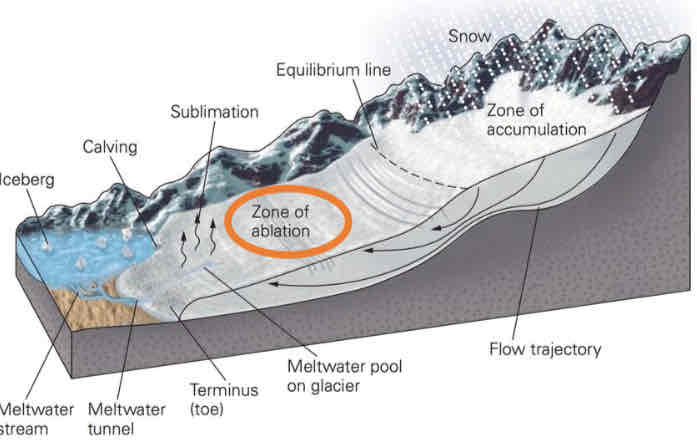
Zone of ablation
As a glacier moves downhill due to gravity it will begin to melt, losing mass, creating meltwater streams that wash away sediment
Where is accumulation the greatest?
In the upper part of the glacier
Where is ablation the greatest?
In the lower part of the glacier
Advance
When temperatures are lower the glacier will move forwards due to the accumulation of ice
Retreat
When there is more ablation than accumulation and the glacier begins to melt
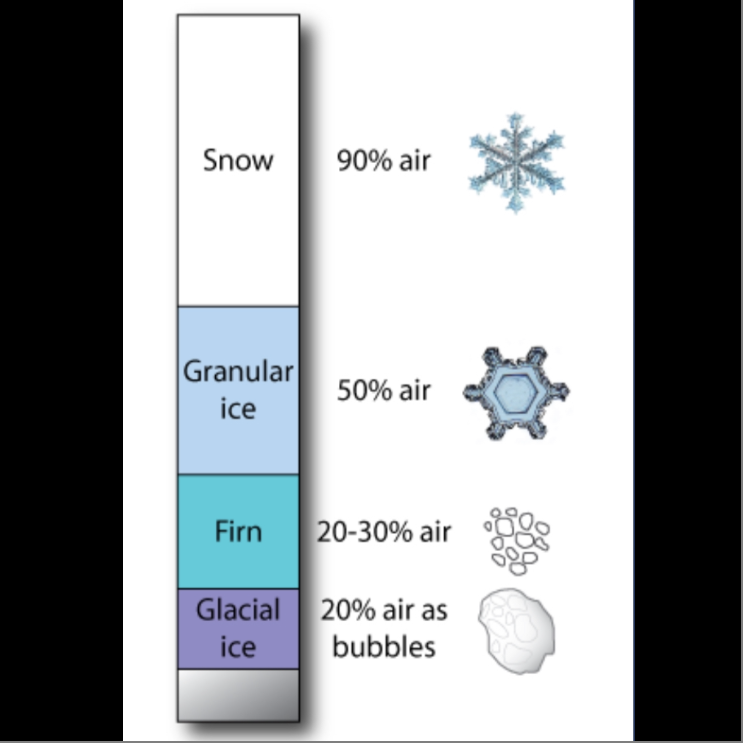
Accumulation of snow
How do glaciers accumulate?
If firn continues to build-up it will become more and more compacted, compressing the air out which forms glacial ice
What are the two process of glacial erosion?
Abrasion and plucking
Plucking
Glacial ice freezes onto rocks, moving it away as it pulls large rock pieces with it
Abrasion
Material carried by glaciers wears away the sides and floor of a valley
Weathering: freeze-thaw
Water repeatedly freezes and puts pressure on rocks that breaks them down
How is the eroded material from plucking further used?
The angular, jagged rock is picked up by the glacier as it moves downhill due to gravity, further eroding more rock
How is the eroded material from abrasion further used?
Large angular rocks widen and deepen a valley as striations are made on the surface
How is the weathered material from freeze-thaw further used?
The expansion of ice explodes open the sides of cliffs, steepening them, and as the scree falls the glacier picks them up
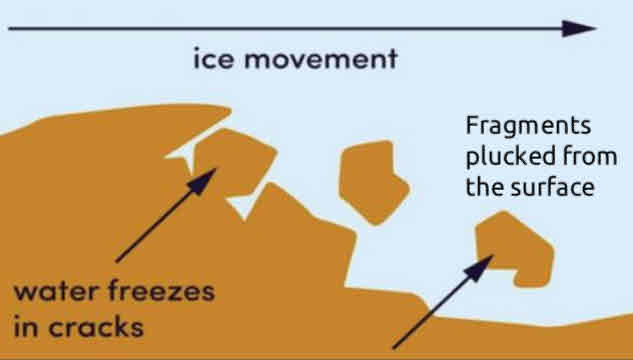
Plucking
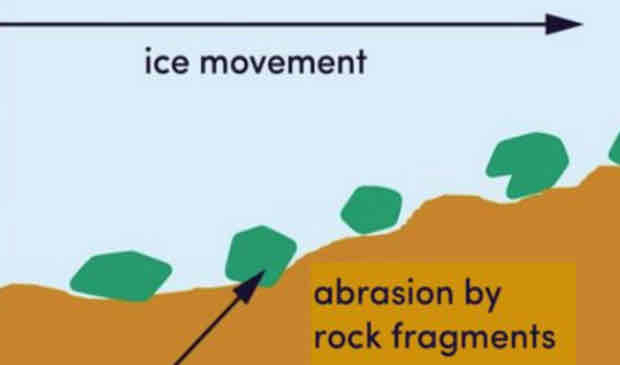
Abrasion

Weathering: freeze-thaw
Corrie
A steep-sided armchair shaped hollow found on the side of a mountain
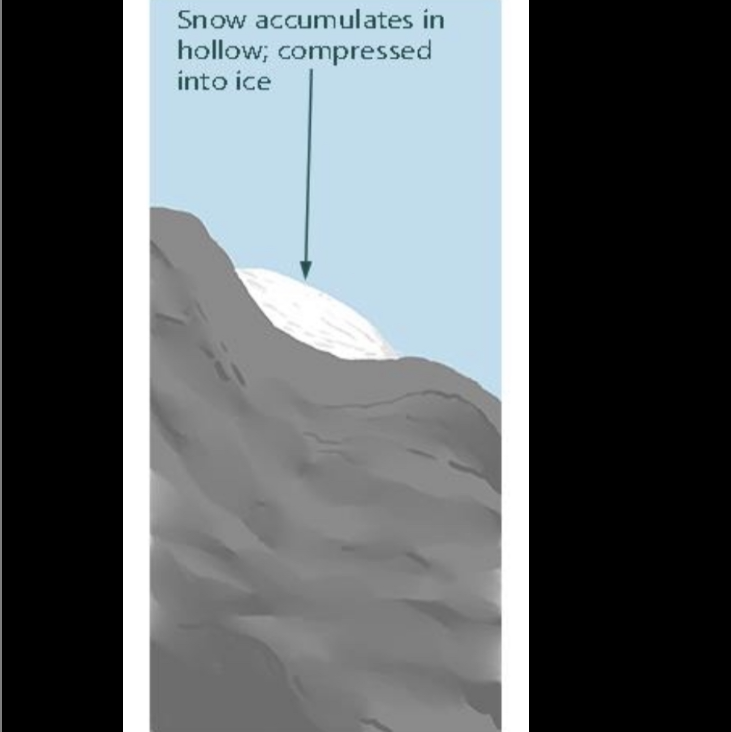
Formation of a corrie before glaciation
Snow accumulates in hollows on north-facing mountains where more snow falls in winter and less melts in summer
North and north-east facing slopes are more shaded, so snow lies longer which compresses into firn and then glacial ice
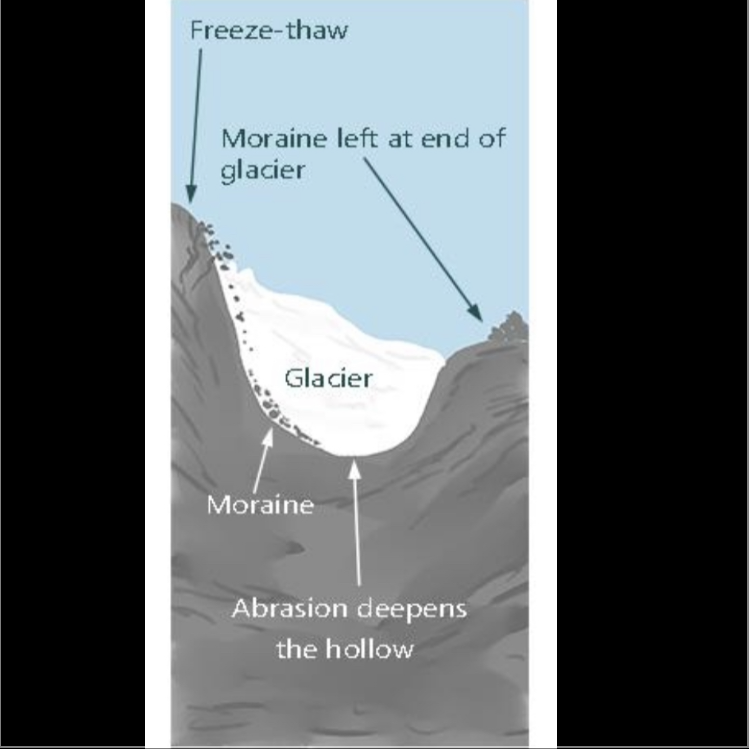
Formation of a corrie during glaciation
The glacier begins to move downhill due to gravity
The weight of the glacier pushes down causing rotational sliding, deepening the hollow
Friction causes the ice to slow down at the front edge of the corrie, allowing a corrie lip to form
A bergschrund crevasse opens at the back of the hollow, allowing meltwater and sediment to get to the base
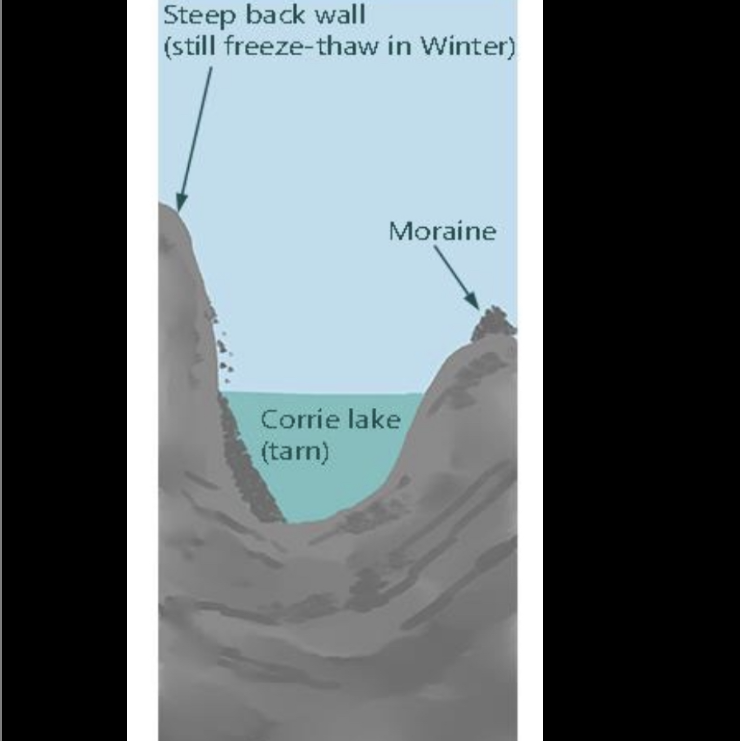
Formation of a corrie after glaciation
After the glacier has melted, a large armchair shaped hollow becomes visible
The corrie lip helps to trap rainwater in the deepens hollow, forming a corrie loch
What are the three processes involved in the formation of a corrie during glaciation?
Abrasion
Plucking
Weathering: freeze-thaw
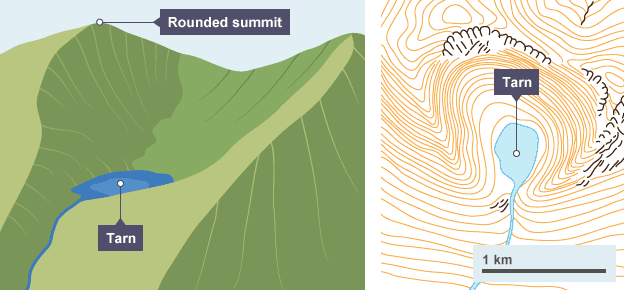
Corrie
Named example: corrie
Corie Lagan, Skye
When explaining the formation of an arête or a pyramid peak what erosional formation much be explained before?
A corrie
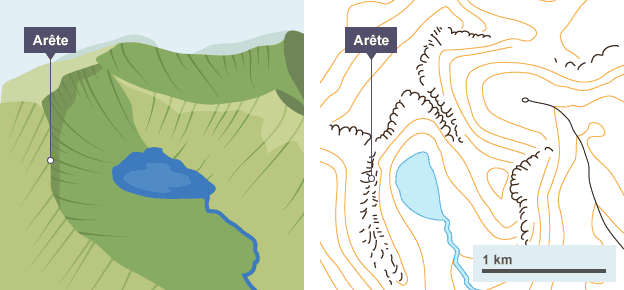
Arête
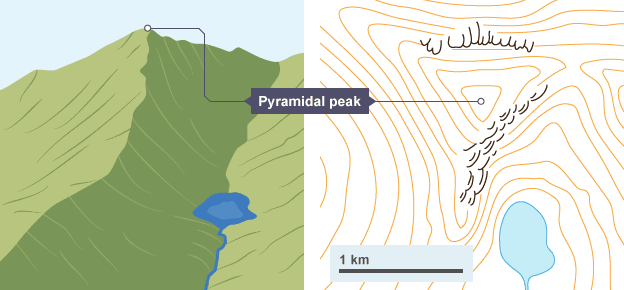
Pyramidal peak
Formation of an arête
When two corries form back-to-back on a mountain, the back walls become steeper which creates a narrow ridge between the two corries
Formation of a pyramidal peak
When three or more corries form back-to-back on a mountain, the back walls become steeper which creates a serious of ridges and a jagged pyramidal peak in the centre
What are the six formations created through glacial erosion?
Arête
Corrie
Hanging valley
Pyramidal peak
Ribbon lake
U-shaped valley
What are the three formations created through glacial deposition?
Drumlin
Esker
Terminal moraine
U-shaped valley
Glaciers abraded and plucked the sides and the valley floor of a v-shaped valley, smoothing it
What are the three processes involved in the formation of an u-shaped valley during glaciation?
Abrasion
Plucking
Weathering: freeze-thaw
Characteristics of an u-shaped valley
Misfit stream that winds along the valley floor
Scree slopes formed from weathered rock fragments
Steep valley sides with exposed rock
Wide and flat valley floor
Characteristics of a corrie
Contains a small lake known as a corrie loch
North-facing hollow
Raised lip at front
Steep back wall
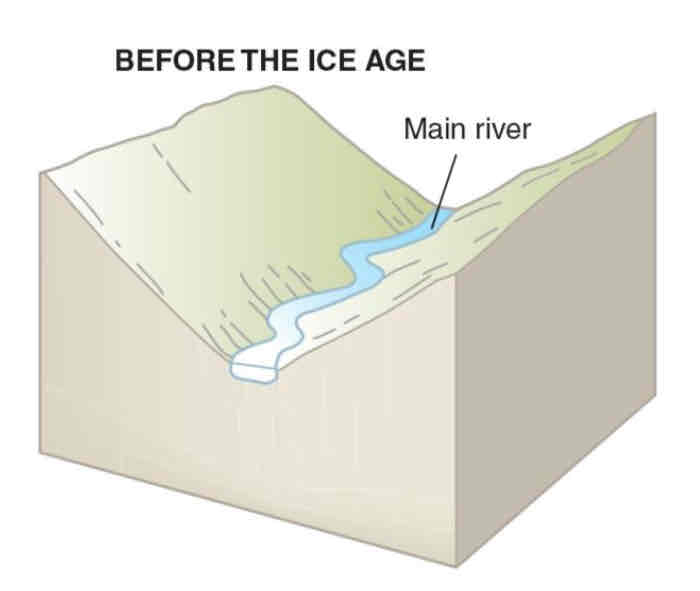
Formation of an u-shaped valley before glaciation
Before glaciation, a river ran through a v-shaped valley
Snow accumulated in north-facing hollows, where more snow falls in winter than melts in summer
The snow is compressed to ice and the glacier moves downhill due to gravity
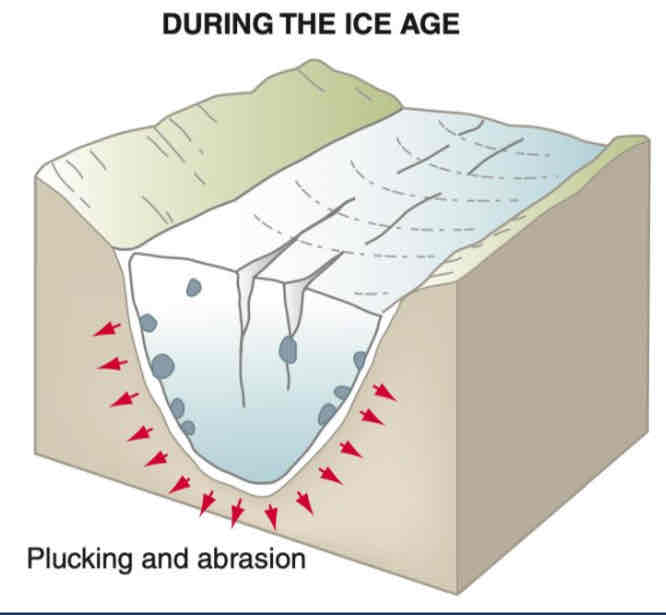
Formation of an u-shaped valley during glaciation
The valley’s floor widens and deepens, turning it from a v-shape to an u-shape
Loose rock fragments fall into the glacier as it moves downhill which will then move to the valley floor as scree
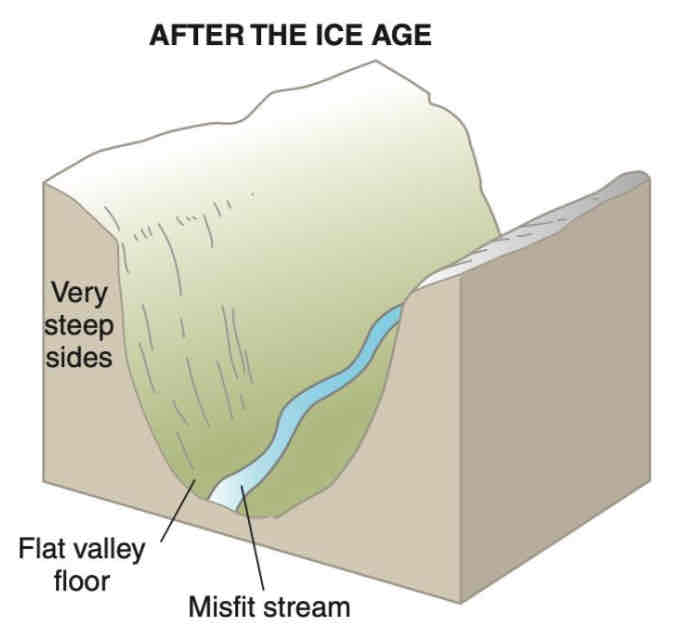
Formation of an u-shaped valley after glaciation
When a period of glaciation is over, a deeper, wider, and straighter valley is left behind
A misfit stream usually forms at the base of the valley floor as the glacier melts
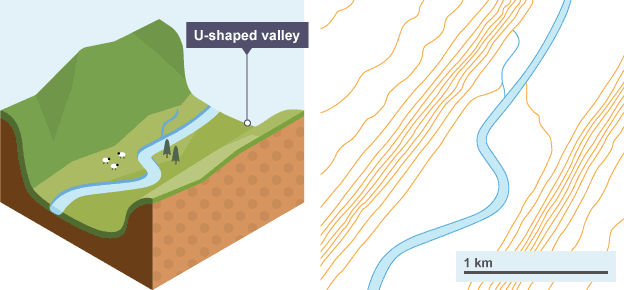
U-shaped valley
Named example: u-shaped valley
Glen Torridon, Highlands
Truncated spur
Ridges of land (spurs) that stick out into the main valley and are then cut by the glacier as it moves through the valley
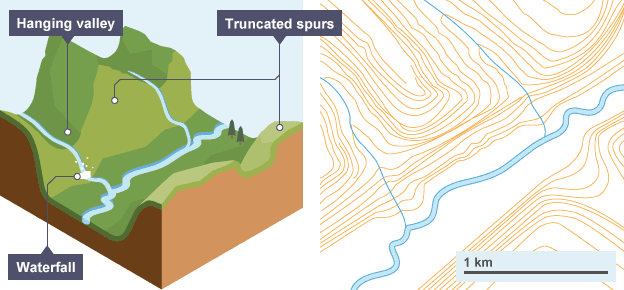
Hanging valley/truncated spur
When explaining the formation of a hanging valley or a ribbon lake what erosional formation much be explained before?
U-shaped valley
Hanging valley
A shallow valley carved out by a small tributary glacier which sits above the main valley
Formation of a hanging valley
A glacier travels through a river tributary into the main valley
The tributary glacier has less erosive power and so it becomes cut off by the glacier in the main valley
A steep drop is found where the tributary valley meets the u-shaped valley
If there is a misfit stream in the tributary valley, it will drop suddenly as a waterfall
Once the ice has melted, it reveals the u-shaped valley with the tributary valley hanging about the main valley
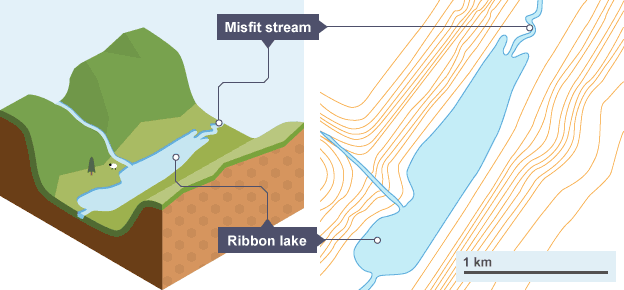
Misfit stream/ribbon lake
Ribbon lake
A long, thin lake which forms on the floor of a u-shaped valley
Formation of a ribbon lake
Harder, more resistant rock is less affected by the glacier
Softer, less resistant rock is eroded more easily by the glacier, leaving a deeper area
Moraine deposited by the glacier may also create a dam, trapping water
When the glacier has retreated, water can collect in deep areas carved out by the glacier
Named example: ribbon lake
Lake Windermere, Lake District
Named example: hanging valley
Little Langdale, Lake District
Named example: pyramidal peak
Matterhorn, Switzerland
Named example: arête
Striding Edge, Lake District
What are the two ways a glacier deposits material?
Fluvio-glacial and till
Till
Unsorted and unstratified material deposited by the ice
Fluvio-glacial
Sorted and stratified material deposited by the meltwater flow
Terminal moraine
The material carried by the glacier as it is scraped from the valleys floor and sides through the three processes of erosion
What are the three types of terminal moraine?
Lateral moraine
Medial moraine
Terminal moraine
Lateral moraine
Found at the sides of an u-shaped valley and are caused by the freeze-thaw of bare rocks above a glacier
Medial moraine
Found in the middle of an u-shaped valley running parallel with the valley sides caused when a tributary glacier joins the main valley
Terminal moraine
Ridges of unsorted material dumped directly by the ice
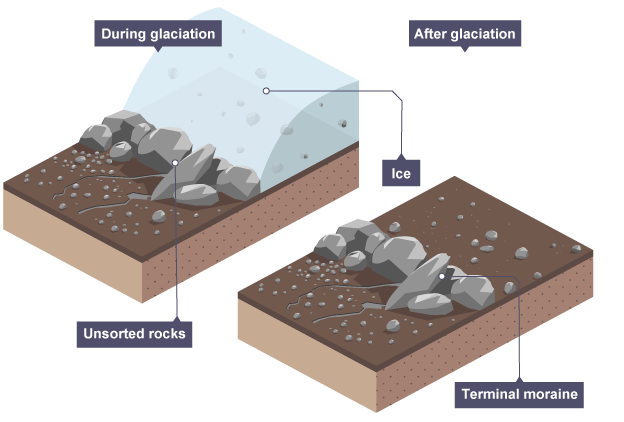
Formation of terminal moraine
The glacier acts like a bulldozer, pushing sediment in front of its snout
As it reaches lower altitudes/when temperatures rise, the glacier melts
When the glacier melts, it loses power and deposits the material it was carrying
Terminal moraine marks the furthest point the glacier reached
The ridge across the valley is made up of till
Once the ice has retreated, the terminal moraine can often form a natural dam creating a ribbon lake
Esker
Meandering ridges of fluvio-glacial deposits along a valley floor, formed by meltwater streams in or underneath a glacier
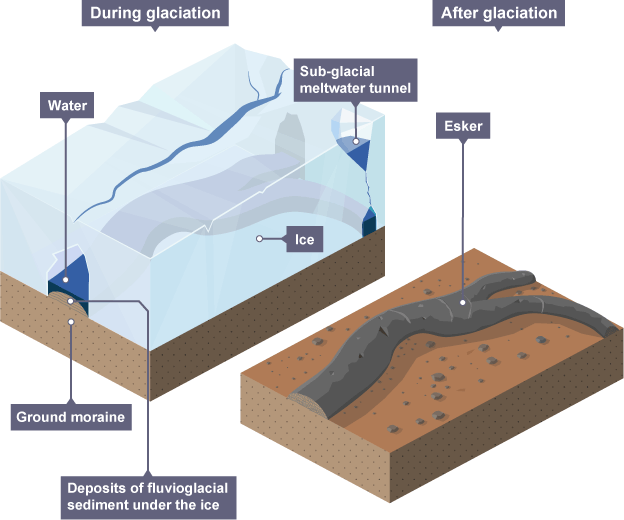
Formation of an esker
In the zone of ablation, the glacier loses mass as it melts
Meltwater streams travel through the glacier and deposit sediment in the channels underneath
Deposits are sorted because heavier stones will be dropped first by the flowing water
When the glacial period is over and the ice has melted, the raised ridges can be seen on the valley floor
Drumlin
Elongated rounded hills made up of till, often found in groups known as ‘baskets of eggs’
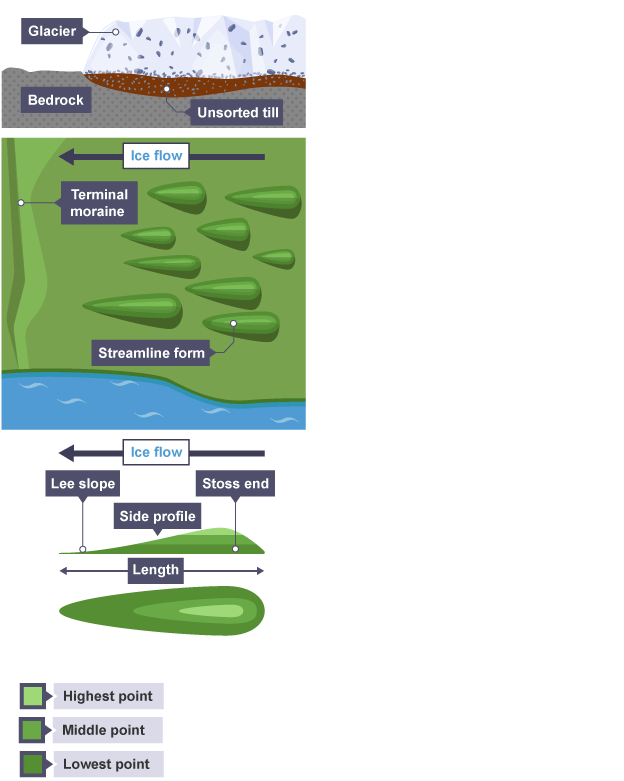
Formation of a drumlin
Formed when the glacier becomes overloaded with sediments and deposits it
As the glacier continues to flow past the sediment, it streamlines it
The steep ‘stoss’ side faces up-valley and the more gently sloping ‘lee’ slope faces down-hill
If there is a small obstacle on the ground, this may act as a trigger point and till can build up around it
Named example: drumlin
Glasgow
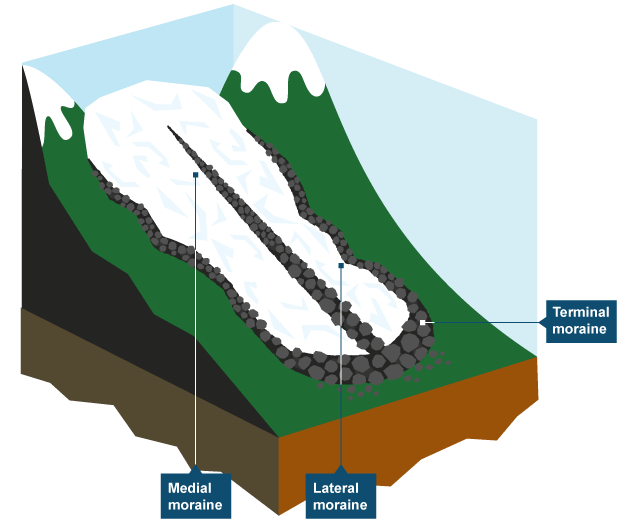
Three types of terminal moraine
Erosion
The wearing away and removal of materials such as rocks and soils
Glacial deposition
This is when glaciers melt and deposit materials
Glacial transportation
This is when glaciers move materials
What is the dominant processes of glacial transportation?
Gravity
What are the three processes involved in the formation of an arete during glaciation?
Abrasion
Plucking
Weathering: freeze-thaw
What are the three processes involved in the formation of a pyramidal peak during glaciation?
Abrasion
Plucking
Weathering: freeze-thaw
What are the three processes involved in the formation of a hanging valley during glaciation?
Abrasion
Plucking
Weathering: freeze-thaw
What are the three processes involved in the formation of a ribbon lake during glaciation?
Abrasion
Plucking
Weathering: freeze-thaw