Module 1 - Basic Principles & Thermoregulation
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
List the basic principles of physiology.
All life is…
Aquatic
Compartmentalized
Deals with same fundamental problems
Constrained by the laws of physics & chemistry
Can tolerate only a limited range of conditions
Aquatic
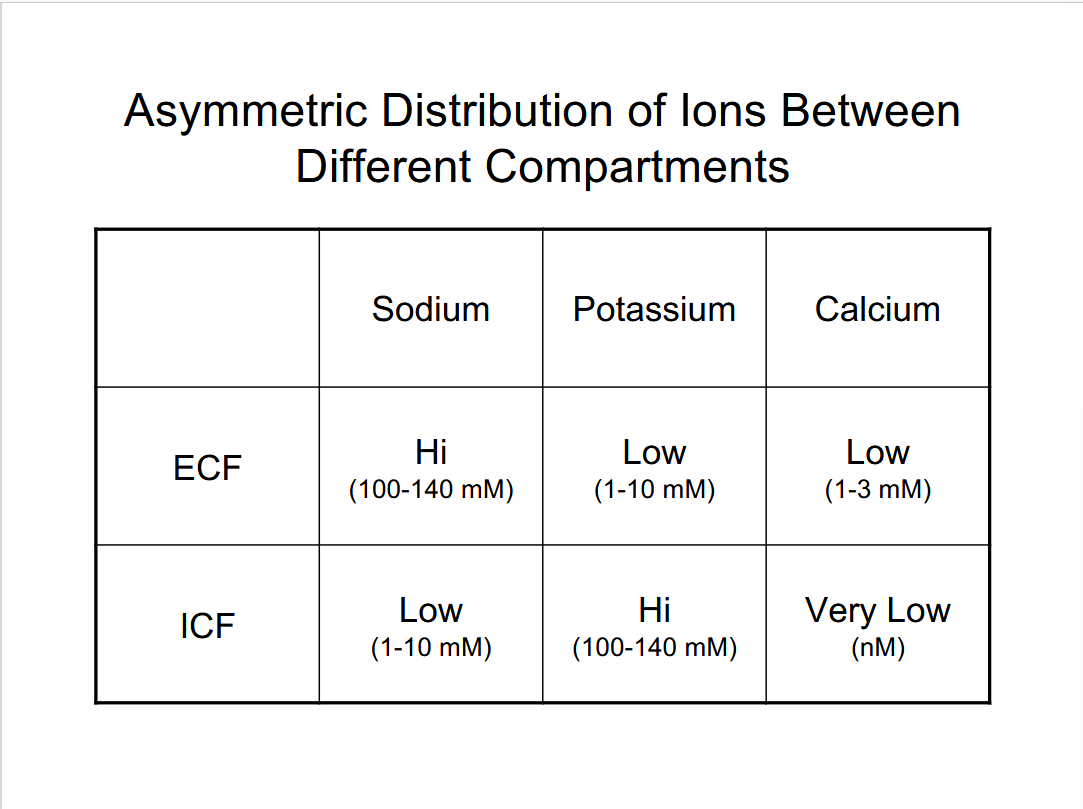
All body fluids of animals have the same general composition of water, salts (Na+, K+, etc), and biochemical substances (proteins, nucleic acids, etc).
Compartmentalized
substances are separated in different compartments like cell (ICF, ECF)
Interstitial fluid, plasma
Explain the asymmetric distribution of ions in an organism.
Maintaining asymmetries between compartments is crucial because it allows the organisms to transport substances selectively between compartments.
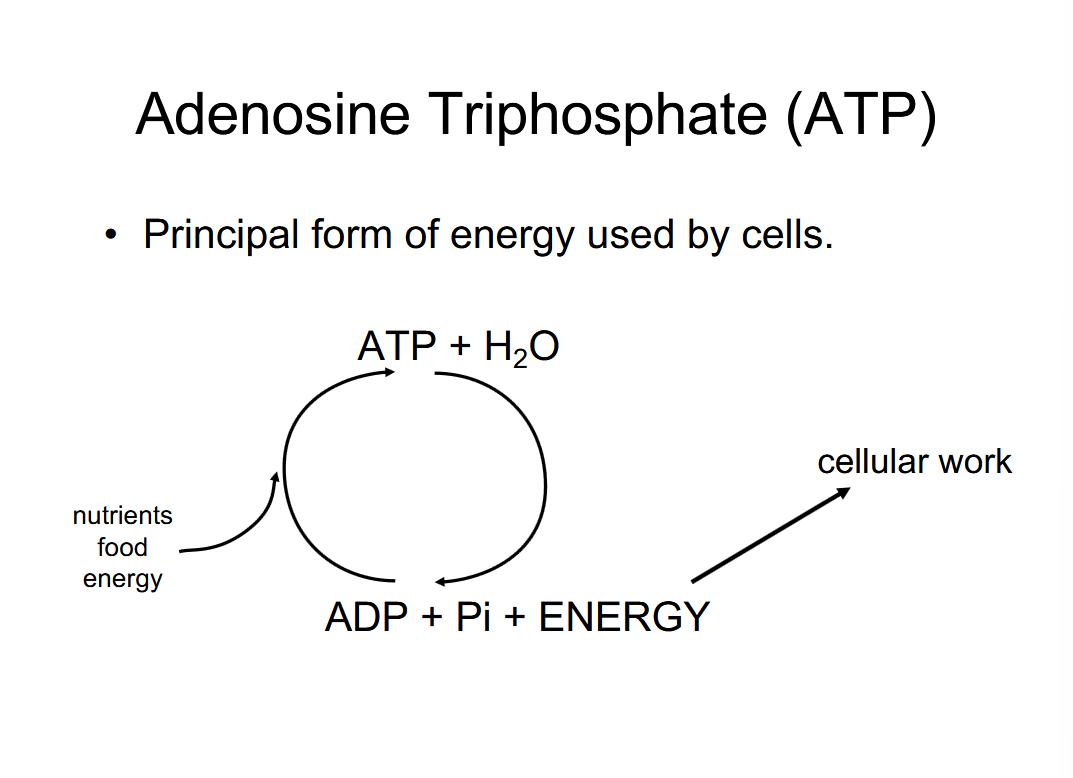
What are two ways life generate energy?
ATP-ADP
Cellular Respiration
How does life generate energy with ATP?
ATP is a high-energy molecule that stores energy in its phosphate bonds.
ATP is produced during cellular respiration and converted into ADP when energy is released.
ADP is regenerated into ATP through oxidative phosphorylation or substrate-level phosphorylation.
The ATP-ADP cycle is a continuous process that ensures a constant supply of energy for cellular activities
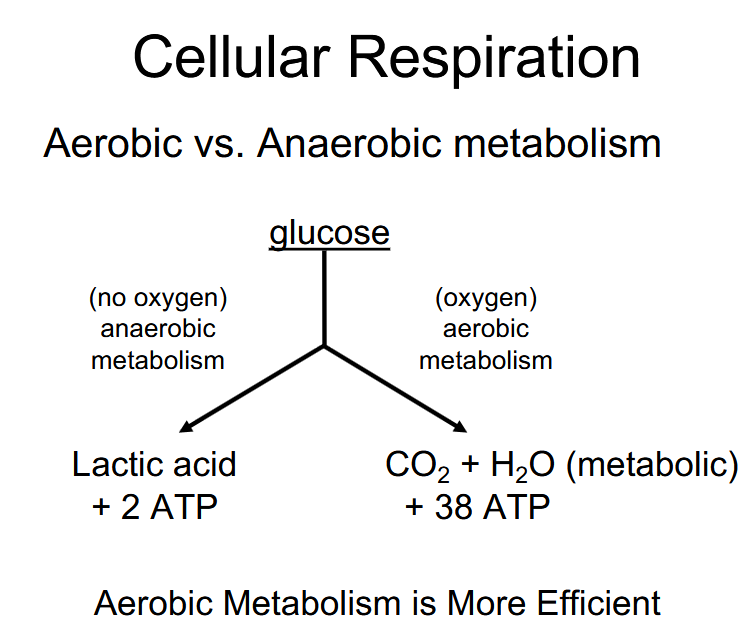
Describe aerobic and anaerobic metabolism from and discuss the
advantages and disadvantages of each.
Metabolic Rate (MR)
The amount of energy an animal uses in a unit amount of time
measured as O2 consumptions in units calories/kilocalories
Sum of all energy-requiring biochemical reactions
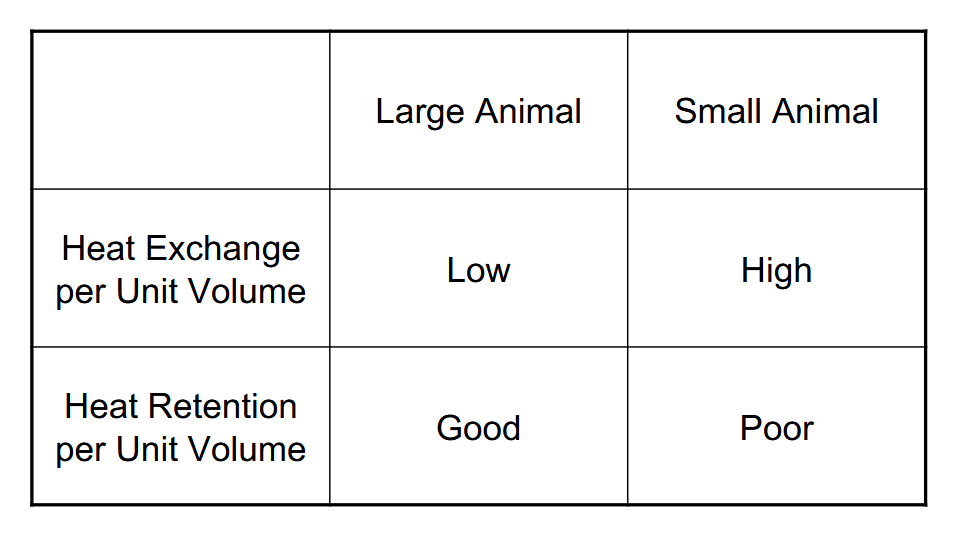
Explain the relationship between surface area (A) and volume(V)
\frac{A}{V}\varpropto\frac{\pi r^2}{\pi r^3}\varpropto\frac{1}{r}
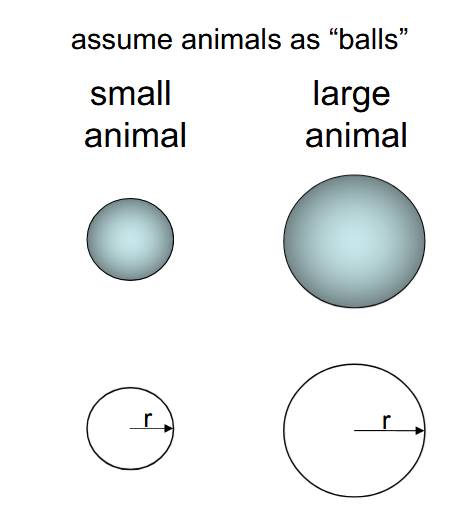
Explain the size principle for organisms and the impact on
thermoregulation.
Homeostasis
Maintenance of a relatively constant internal environment
requires cell-to-cell communication
requires negative feedback
What are the 3 components of feedback system?
Sensor: measures smth going on on the inside (measure the temperature)
Integrator: compares that to reference value (오마이갓 지금 좀 춥네)
Effector: the output of the system (온도 올려어어어ㅓㅓ~~!)
Describe positive and negative feedback processes and their role in
homeostasis.
Negative Feedback: The effector counteracts the initial sensor stimulus
ㅈㄴ 더워져서 온도 낮춤
Positive Feedback: The effector increases the initial sensor stimulus
온도 높아지기 시작했는데 이걸 더 높여버려 쌰갈
Cause rapid changes.
Physiological ecology
how the organism uses basic physics and chemistry laws to meet biological needs / solve basic physiological problems.
Temp. regulation
Water ion balance
What are the 4 major types of heat transfer?
Conduction
Convection
Evaporation
Radiation
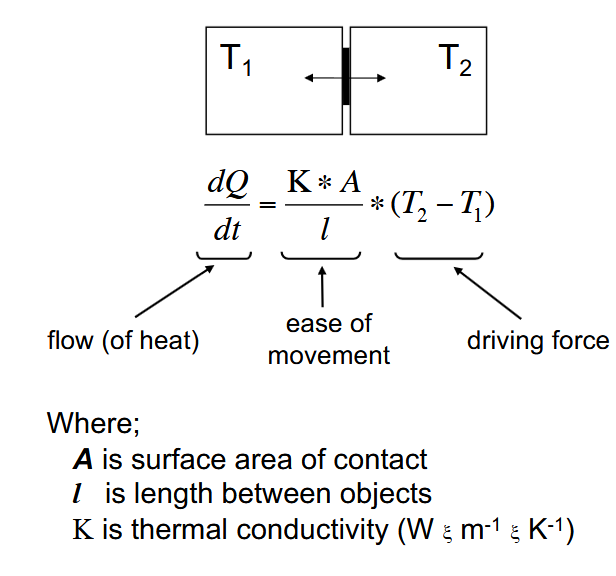
Heat transfer- Conduction
Heat transfer through direct physical contact.
Warm → Cool
Describe the transport equation for heat conduction and explain the
difference between ‘driving force’ and ‘ease of movement’.
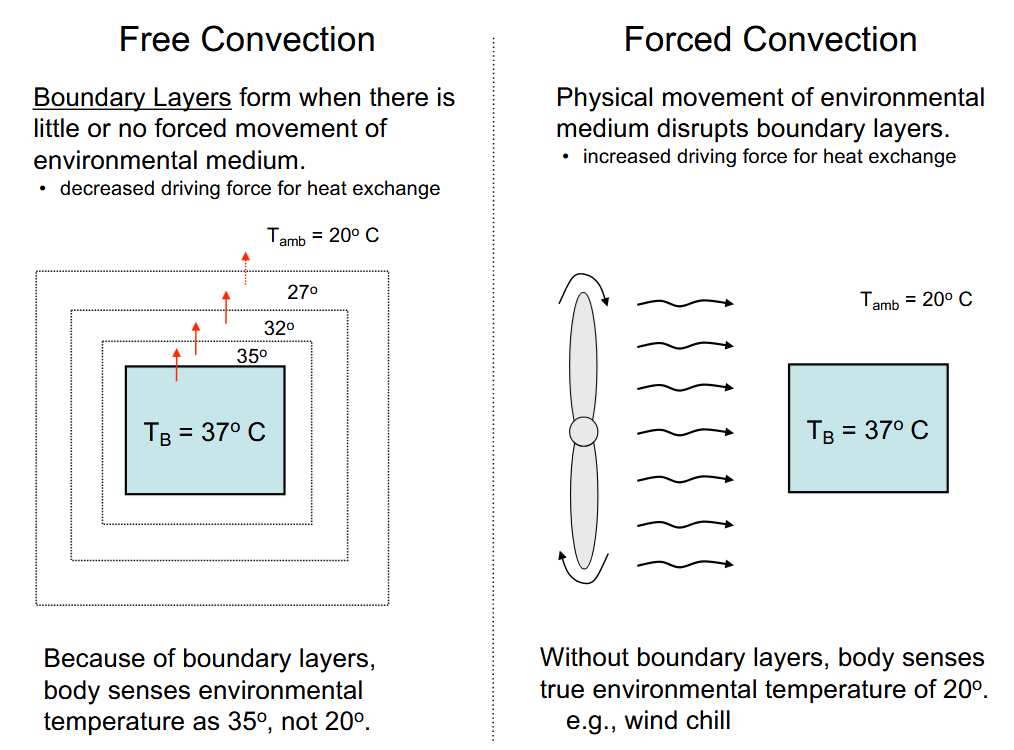
Heat transfer- Convection
Heat transfer through environmental medium (air/water)
Free Convection vs. Forced Convection
Heat transfer- Evaporation
Transformation of water from liquid to vapor (gas)
Evaporating cooling: 기화하면서 표면의 열(에너지)을 흡수
Heat transfer- Radiation
the process of energy moving as electromagnetic waves, primarily infrared radiation, from a warmer object to a cooler one without needing a medium.