CAPACITORS TO REMEMBER
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Capacitance
The charge stored per unit potential difference of a capacitor.
Time constant
For discharge of a capacitor C through a fixed resistor R, the time constant is RC. This is the time taken for the voltage/current/charge to reduce to 1/e of its initial value.
Dielectric
An electrically insulating material that can be inserted between the parallel plates of a capacitor, that increases the ability of the capacitor to store charge.
Relative permittivity
For a fixed p.d. across a parallel plate capacitor, the ratio of the charge stored with a dielectric to the charge stored without the dielectric.
Dielectric constant
The dielectric constant of a medium is: permittivity of the medium / permittivity of free space
Explain how the polar molecules cause a change in the capacitance
1. When the polar molecule in a dielectric align with the applied electric field from the plates, 𝒕𝒉𝒆𝒚 𝒑𝒓𝒐𝒅𝒖𝒄𝒆 𝒕𝒉𝒆𝒊𝒓 𝒐𝒘𝒏 𝒆𝒍𝒆𝒄𝒕𝒓𝒊𝒄 𝒇𝒊𝒆𝒍𝒅
2. This electric field opposes
3. The 𝒍𝒂𝒓𝒈𝒆𝒓 𝒕𝒉𝒆 𝒐𝒑𝒑𝒐𝒔𝒊𝒏𝒈 𝒆𝒍𝒆𝒄𝒕𝒓𝒊𝒄 𝒇𝒊𝒆𝒍𝒅 from the polar molecules in the dielectric, the 𝒍𝒂𝒓𝒈𝒆𝒓 𝒕𝒉𝒆 𝒑𝒆𝒓𝒎𝒊𝒕𝒕𝒊𝒗𝒊𝒕𝒚
4. Opposing electric field reduced the overall electric field / Eᵣ = E - Eᵈ
5. ∴ A lower voltage is required to maintain the same charger E ∝ V
6. Therefore capacitance increases C ∝ ¹⁄ᵥ
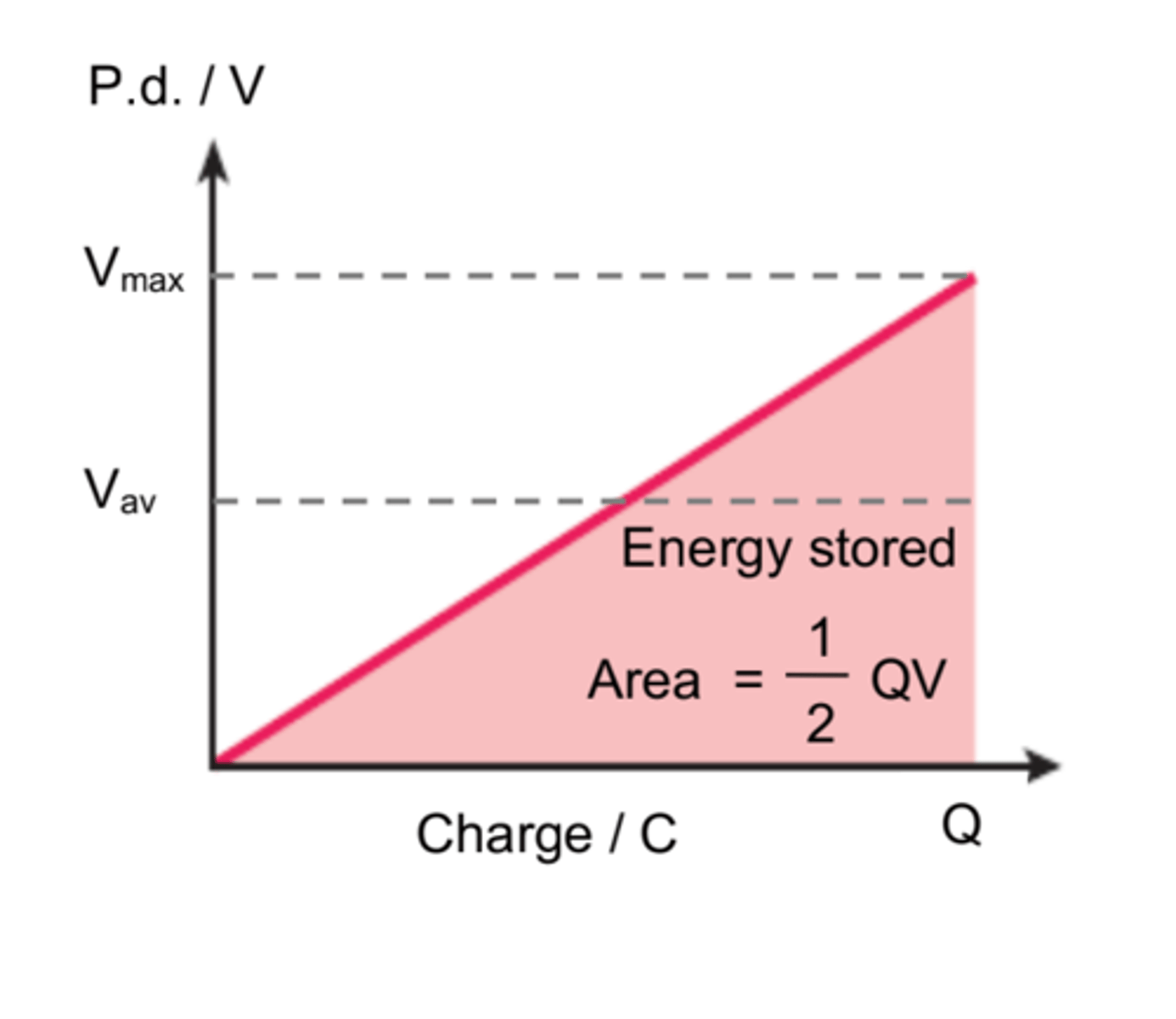
Charge against potential difference
Area under the graph = electrical (potential) energy stored
area = ½bh
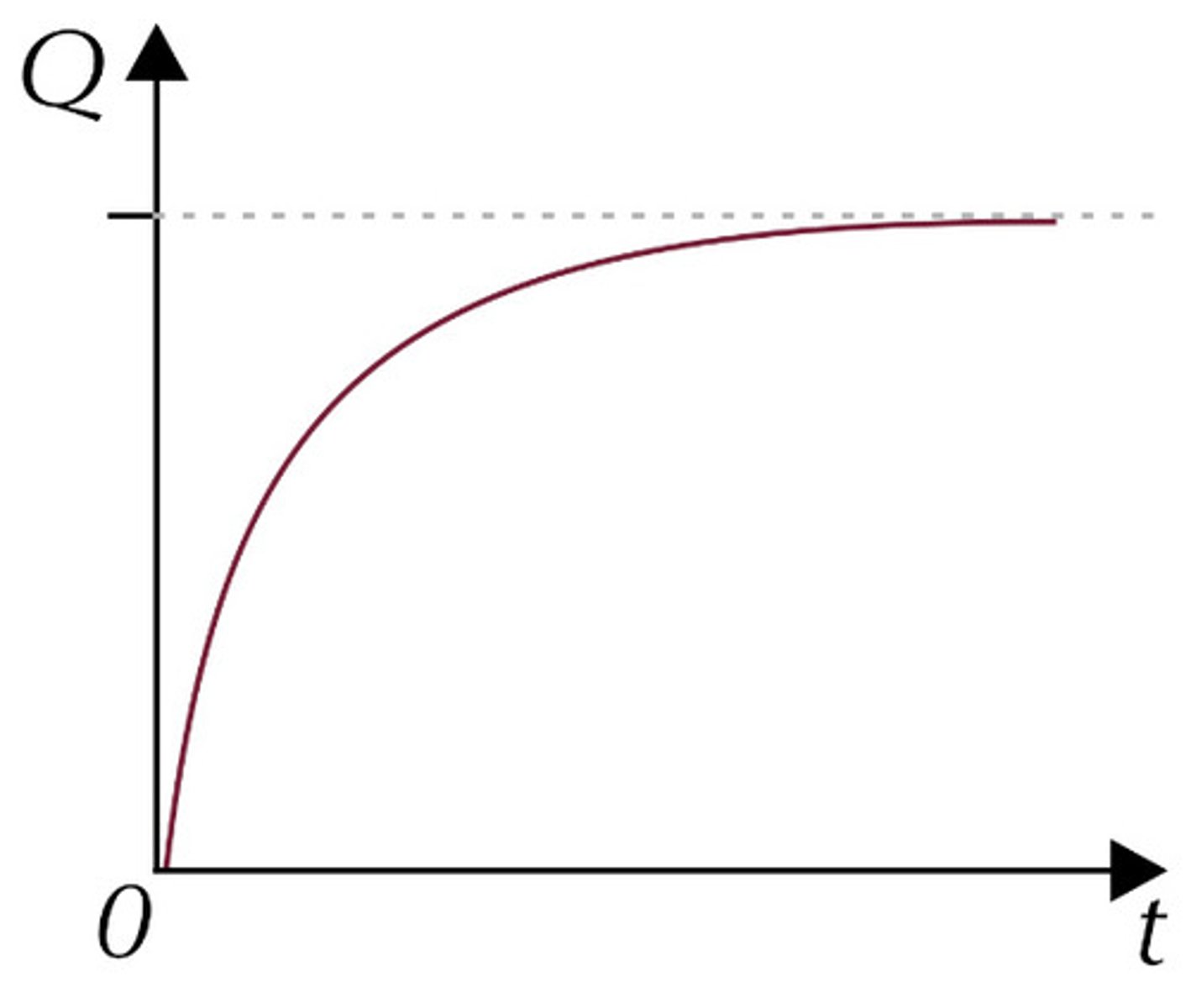
Charging charge against time
Q = Q₀(1-e)⁻ᵗ/ʳᶜ
gradient: current
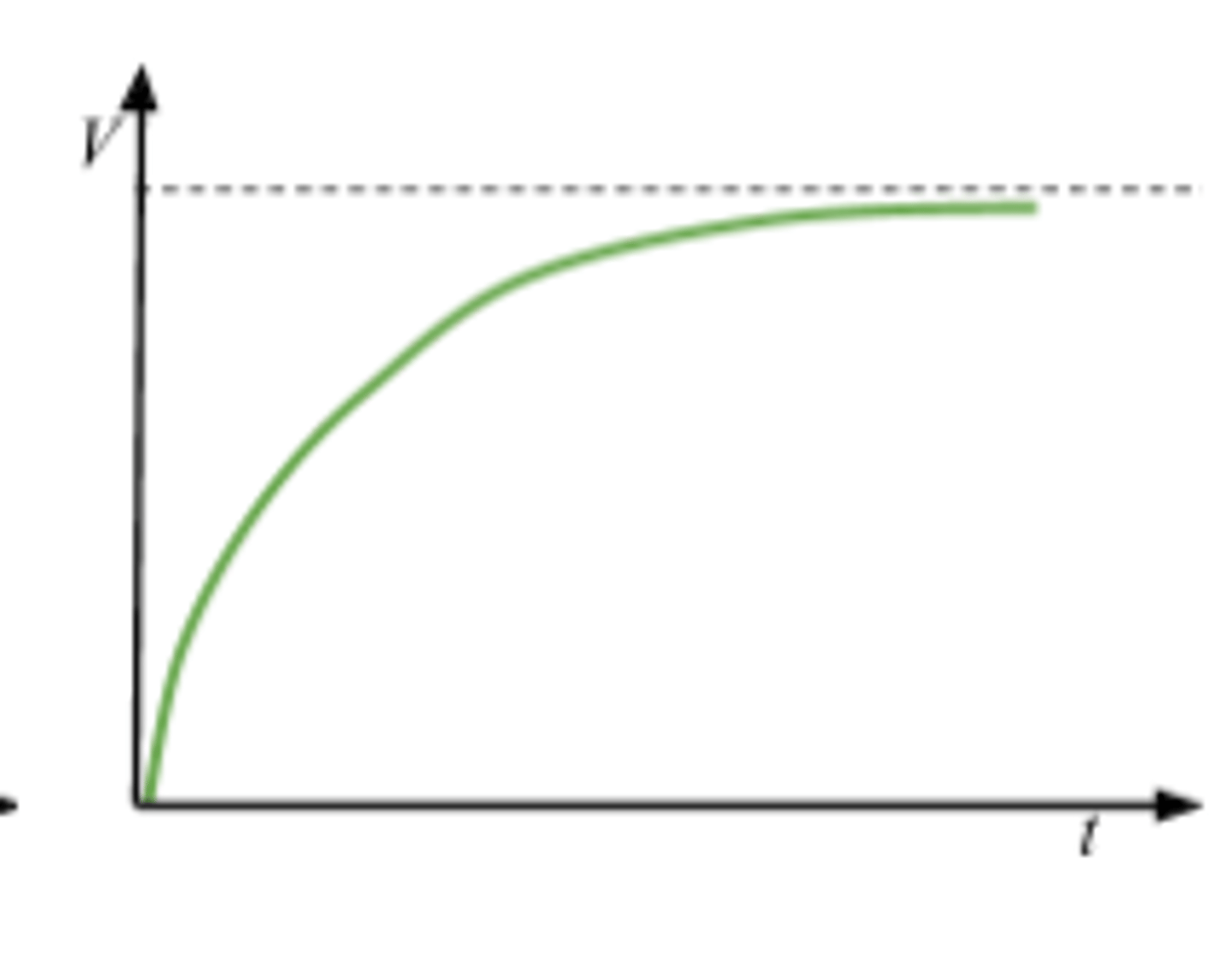
Charging voltage against time
V = V₀(1-e)⁻ᵗ/ʳᶜ
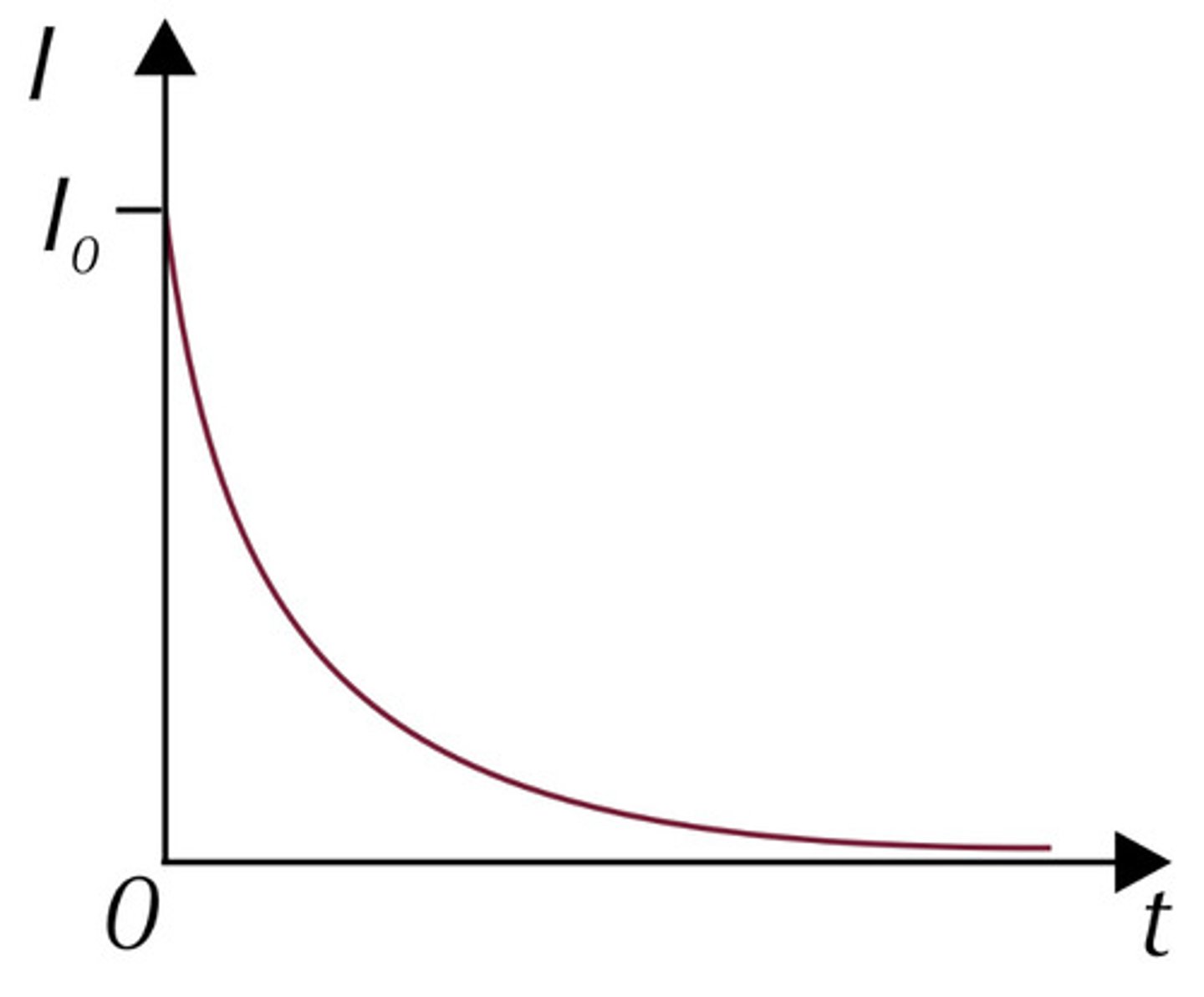
Charging current against time
I = I₀e⁻ᵗ/ʳᶜ
area: charge stored for a certain time interval
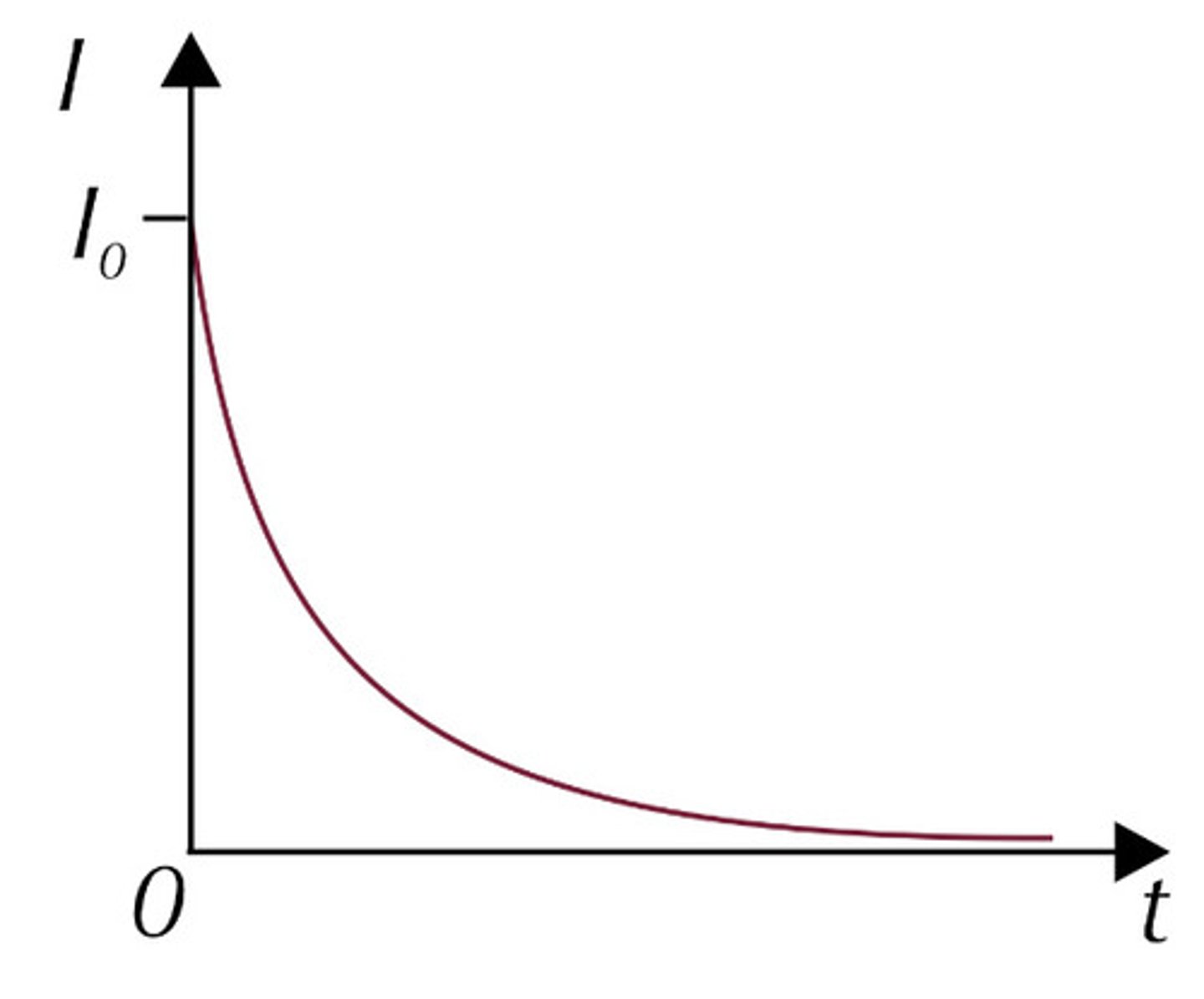
Discharging charge against time
Q = Q₀e⁻ᵗ/ʳᶜ
gradient: current
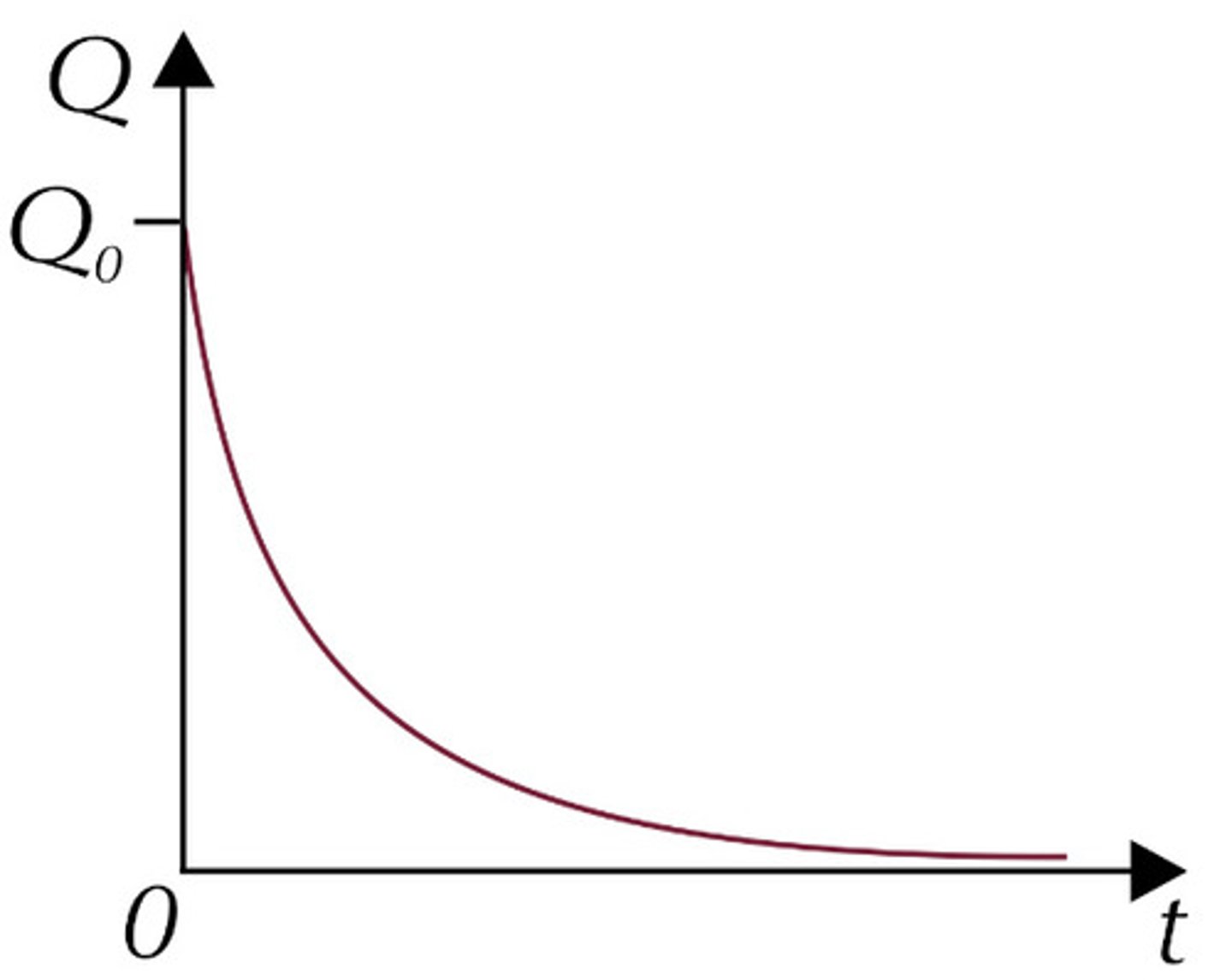
Discharging voltage against time
V = V₀e⁻ᵗ/ʳᶜ
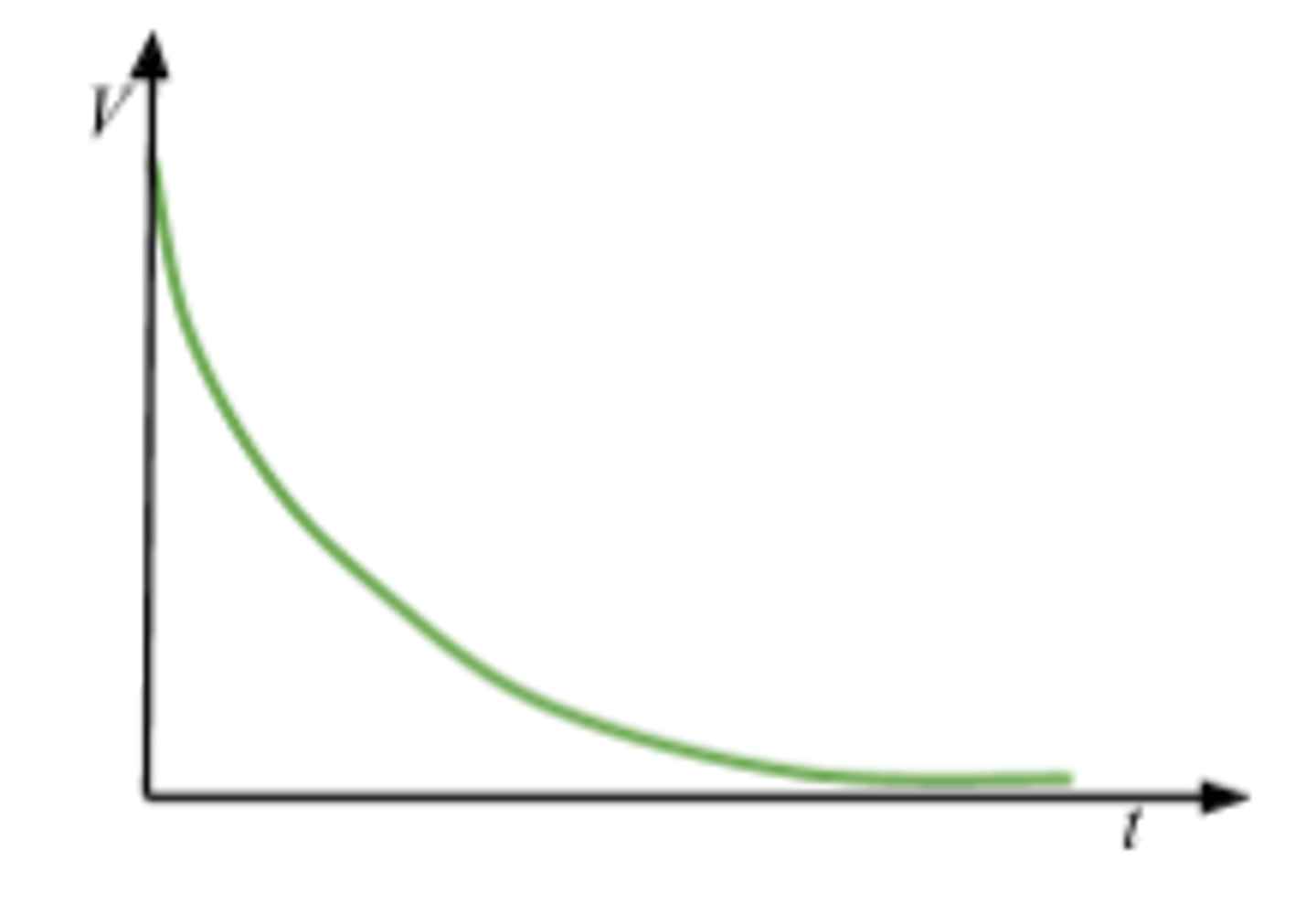
Discharging current against time
I = I₀e⁻ᵗ/ʳᶜ
area: charge stored for a certain time interval
What is time to halve t₁/₂
The time taken for the charge (or pd or current) in a discharging capacitor to decrease to half of its initial value
t₁/₂ = 0.69RC
