PVCC RAD Quiz- Chapter 7 Femur, Patella, & Intercondylar Fossa
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
The largest and strongest bone in the body is the:
femur
The bone part identified in the figure above is the:
medial condyle

The bone part identified in the figure above is the:
lesser trochanter

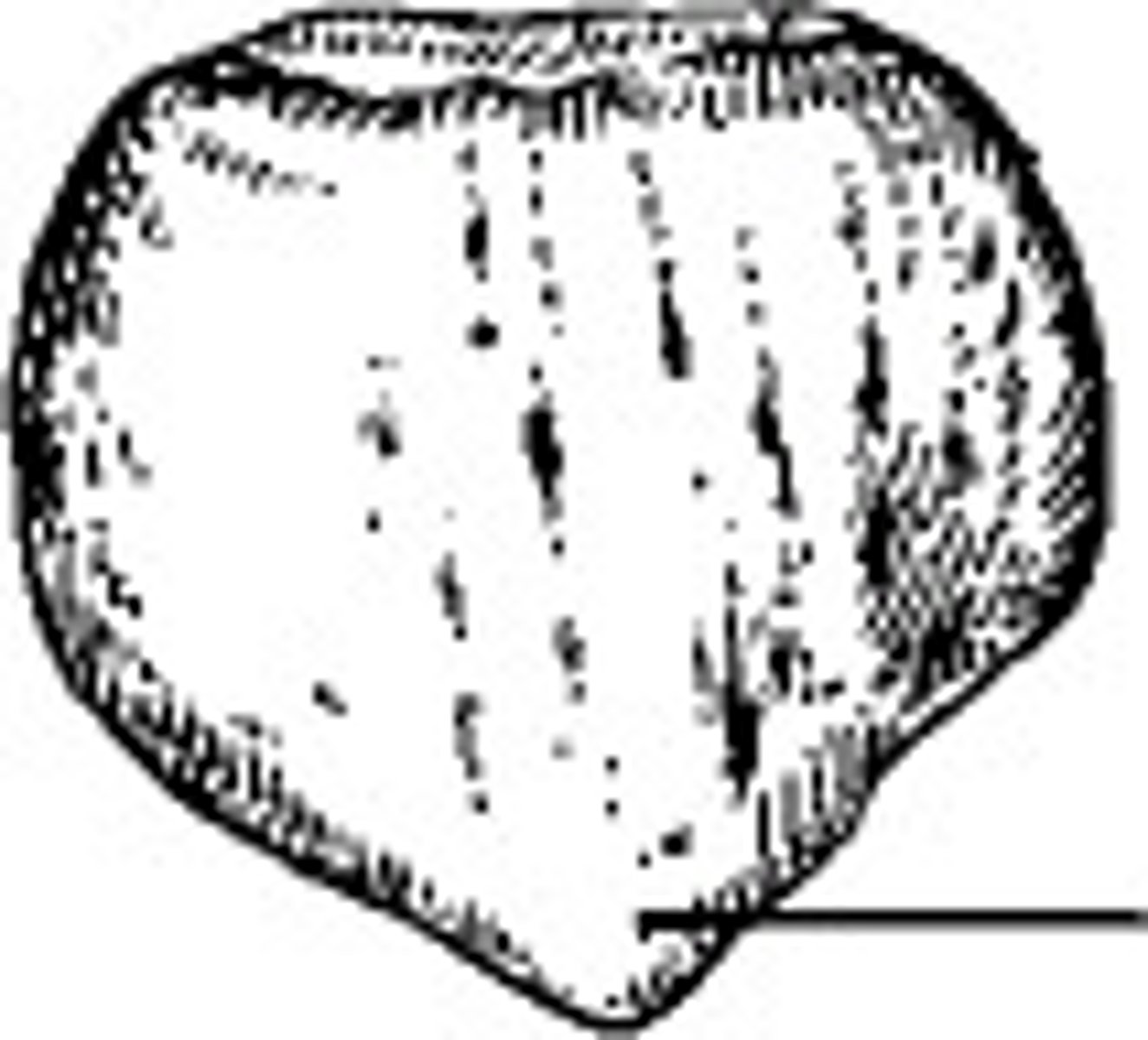
The area identified on the patella in the figure above is the:
apex
Which of the following methods are used to demonstrate the intercondylar fossa?
1) Holmblad (PA axial)
(2) Camp-Coventry (PA axial)
(3) Settegast (tangential)
1 and 2
The patient position and central ray shown in the figure above will demonstrate the:
intercondylar fossa
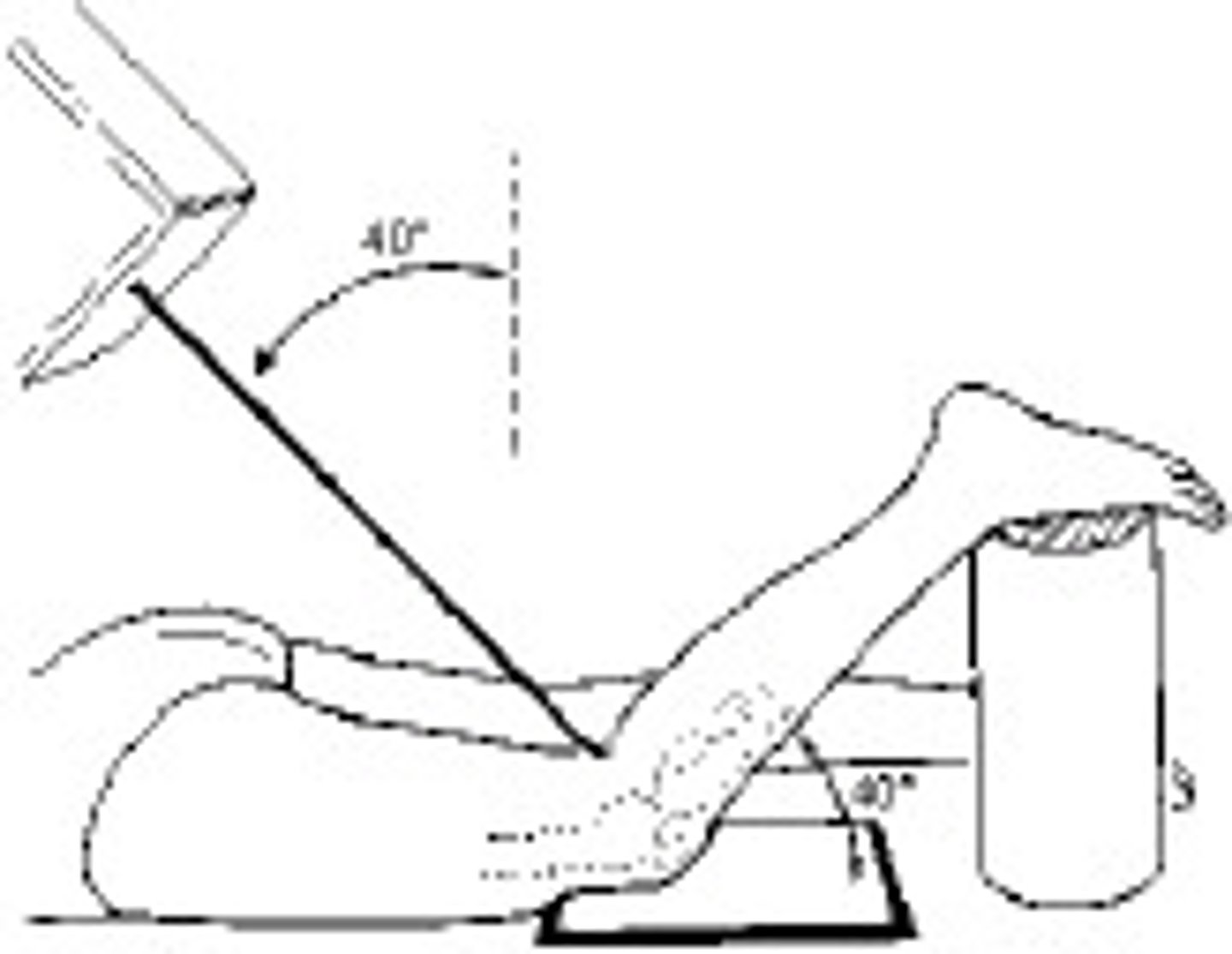
How much is the knee joint flexed for the PA axial projection (Holmblad method) of the intercondylar fossa?
70 degrees
How is the central ray directed for the PA axial projection (Holmblad method) of the intercondylar fossa?
perpendicular to the lower leg
Which of the following positions can be used to demonstrate the intercondylar fossa using the Holmblad method?
(1) standing (horizontal central ray)
(2) kneeling on the table (vertical central ray)
(3) standing with knee on stool (vertical central ray)
1, 2, and 3
The patient position and central-ray method demonstrated in the figure above is the:
Camp-Coventry (intercondylar fossa)
Which position is the patient placed in for a PA projection of the patella?
prone
In order to place the patella parallel with the plane of the IR for a PA projection, the heel must be rotated:
5 to 10 degrees laterally
What is the central-ray angle for a PA projection of the patella?
0 degrees
Where should the central ray be directed for a PA projection of the patella?
midpopliteal area
How much is the knee flexed for a lateral projection of the patella?
5 to 10 degrees
The knee is in the correct position for a lateral projection of the patella if the:
(1) leg is flexed 20 to 30 degrees
(2) epicondyles are superimposed
(3) patella is perpendicular to the IR
2 and 3
What is the central-ray angle for a lateral projection of the patella?
0 degrees
Where does the central ray enter the knee for a lateral projection of the patella?
through the patellofemoral joint space
Which of the following is the essential method of demonstrating the patella in the tangential projection?
Settegast
The projection of the patella demonstrated in the figure above is the:
settegast
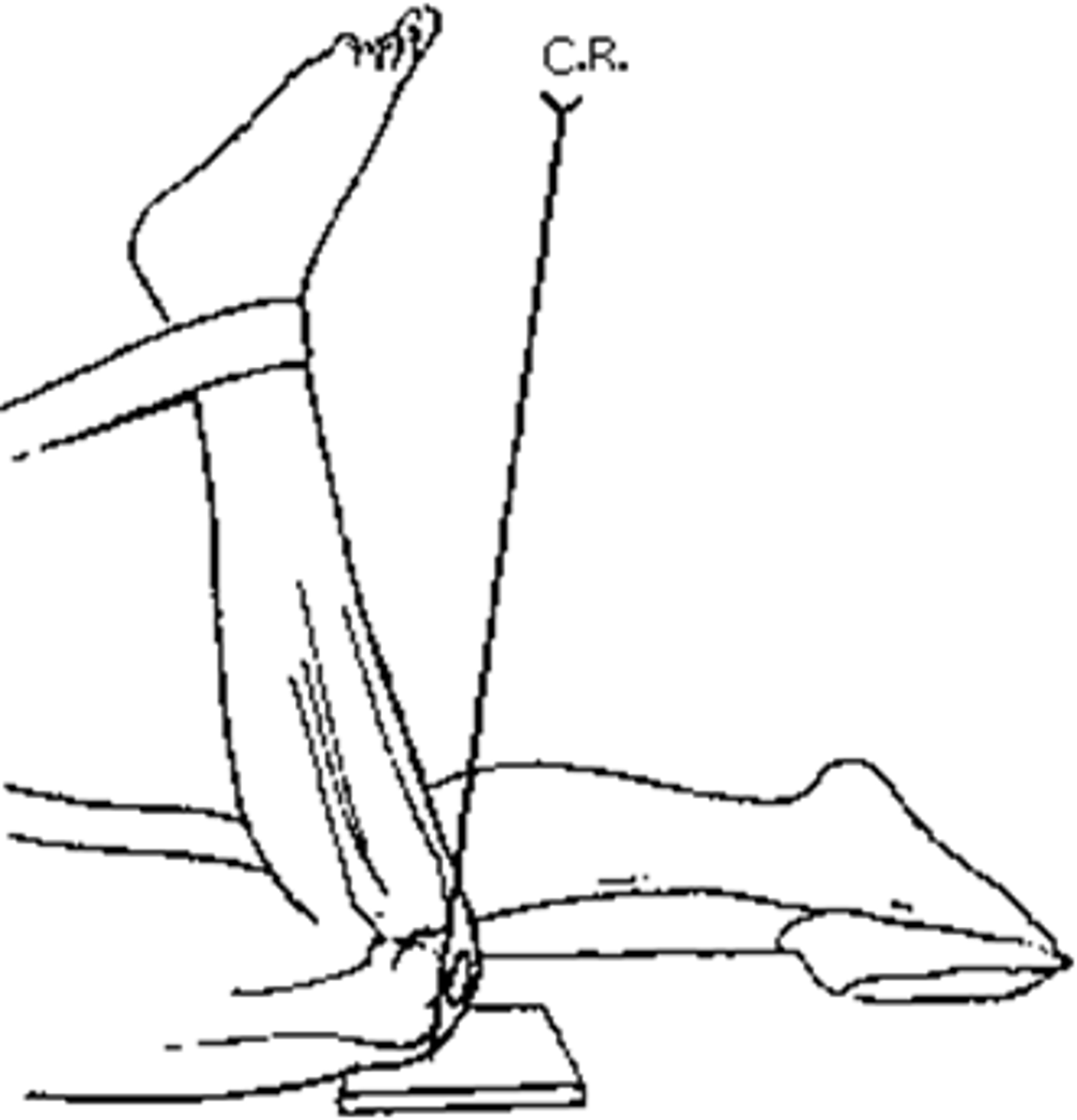
Which of the following positions can be used to perform the tangential projection (Settegast method) of the patella?
(1) seated
(2) supine
(3) prone
1, 2, and 3
The preferred method of positioning the patient for the tangential projection (Settegast method) of the patella is:
prone
How far should the knee be flexed for the tangential projection (Settegast method) of the patella when done in the prone position?
(1) 50 to 60 degrees from the table
(2) as much as possible
(3) until the patella is perpendicular
2 and 3
Where is the central ray directed for the tangential projection (Settegast method) of the patella?
through the patellofemoral joint space
What is the degree of angulation for the tangential projection of the patella (Settegast method)?
variable—depending on the degree of knee flexion
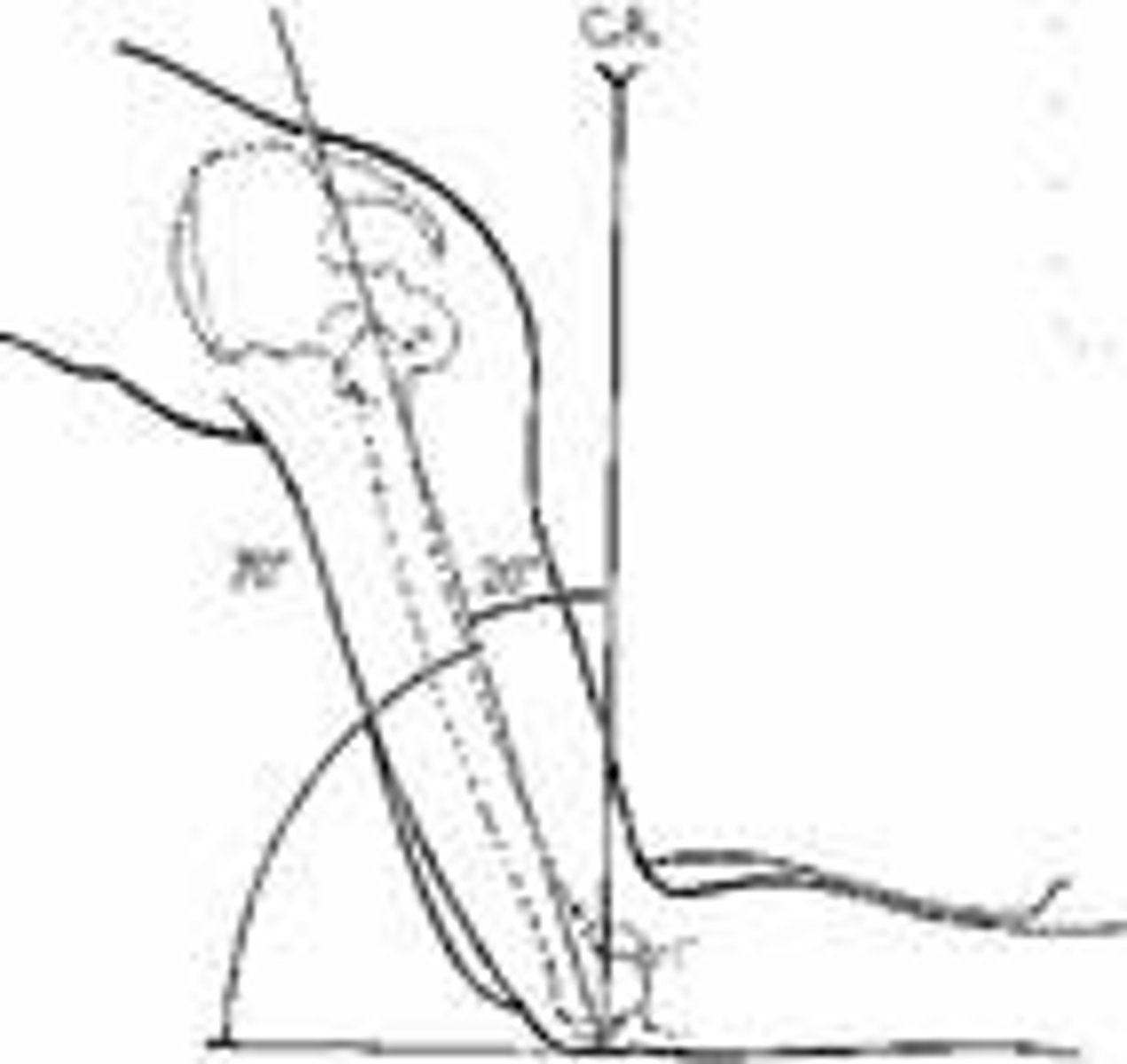
What is the central-ray angle for an AP projection of the femur?
0 degrees
How many degrees should the limb be internally rotated for an AP projection of the proximal femur?
10-15 degrees
How far should the IR/collimated field extend below the knee for a lateral projection of the femur?
2 inches
If a lateral projection of the femur will include the hip joint, where should the top of the IR/collimated field be placed?
anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS)
How far should the patient be rolled posteriorly from the lateral position, for a lateral projection of the hip that will include the proximal femur?
10 to 15 degrees
When the femur is vertical, the medial condyle is lower than the lateral condyle. How many degrees’ difference is there between the two?
5 to 7 degrees
Posteriorly, the femoral condyles are separated by a deep depression called the:
intercondylar fossa
The area identified on the figure above is the:
patella surface
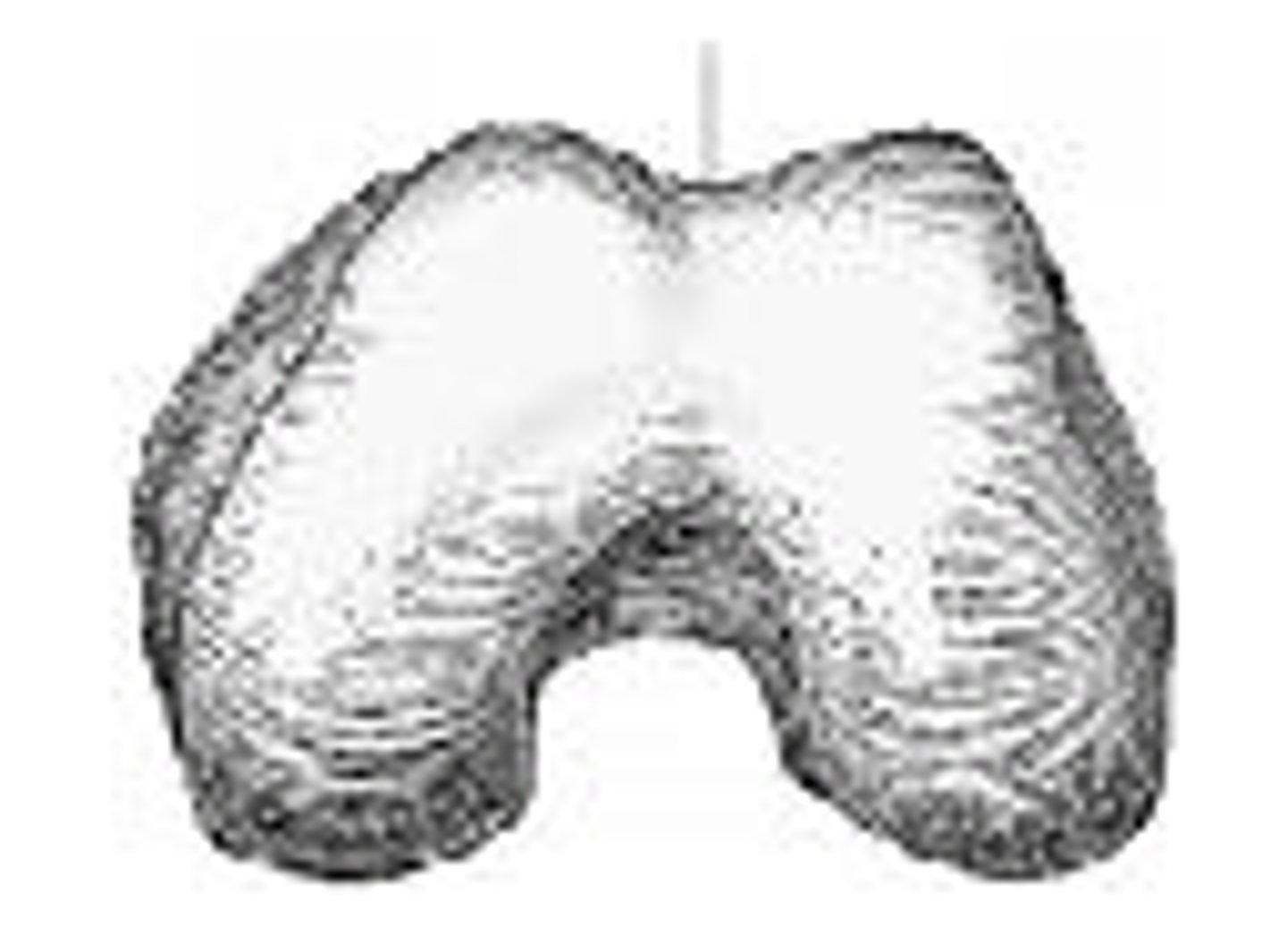
Which anatomical part must be identified on lateral radiographs of the knee in order to identify over-or-under rotation?
adductor tubercle
The circular fibrocartilage disks or pads that lie on the tibial plateaus are called the:
menisci
The PA axial intercondylar fossa (Camp-Coventry) projection requires the knee to be flexed:
1) 30 degrees
2) 40 degrees
3) 50 degrees
2 and 3
If the knee is flexed 40 degrees for the PA axial intercondylar fossa (Camp-Coventry) projection, the central ray will be angled:
40 degrees
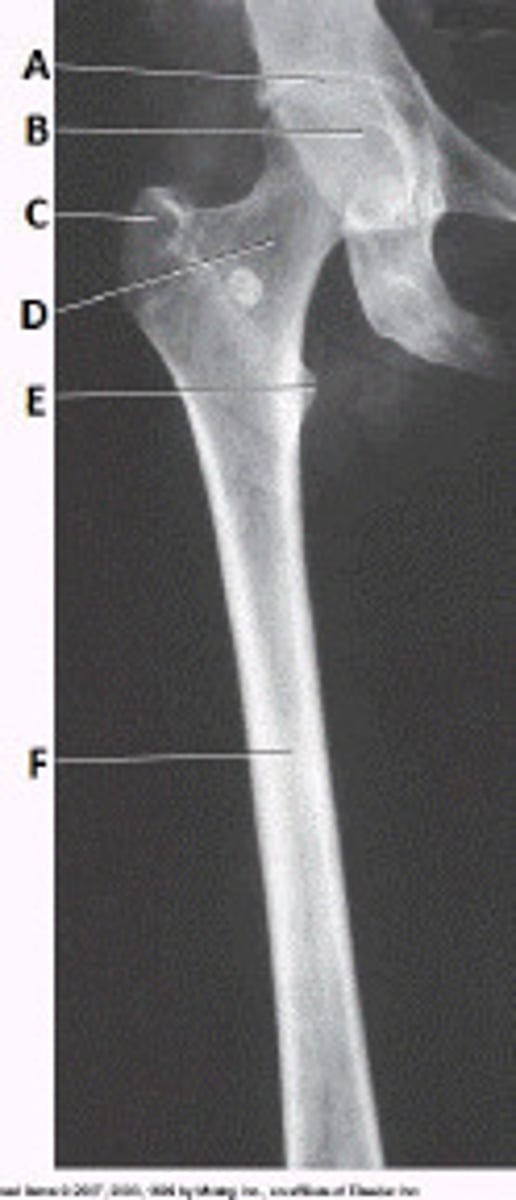
Refer to the image below. What anatomy is labeled with the letter C?
greater trochanter
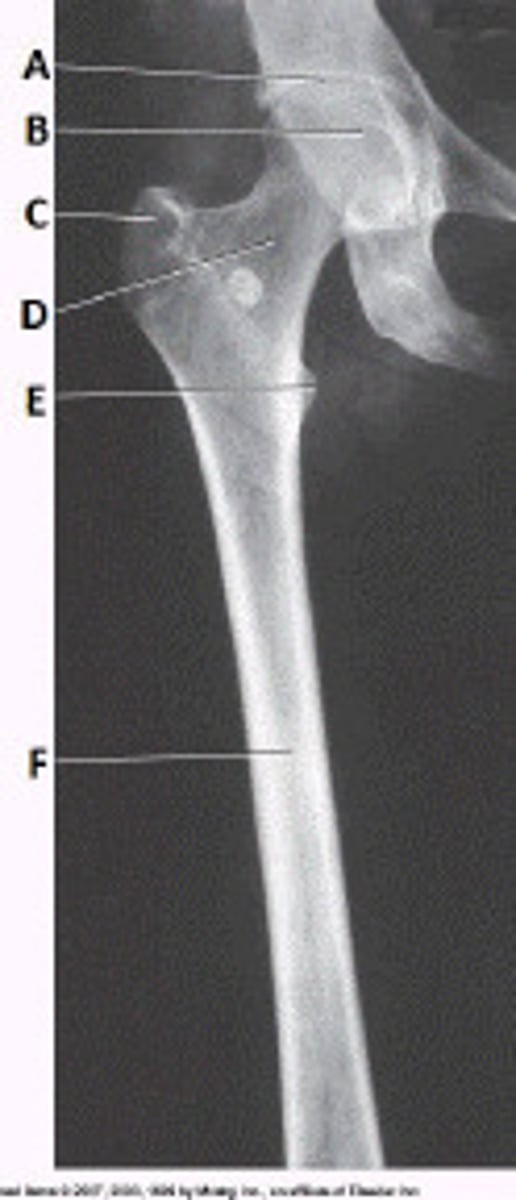
Refer to the image below. Identify the projection and anatomy of interest.
AP proximal femur
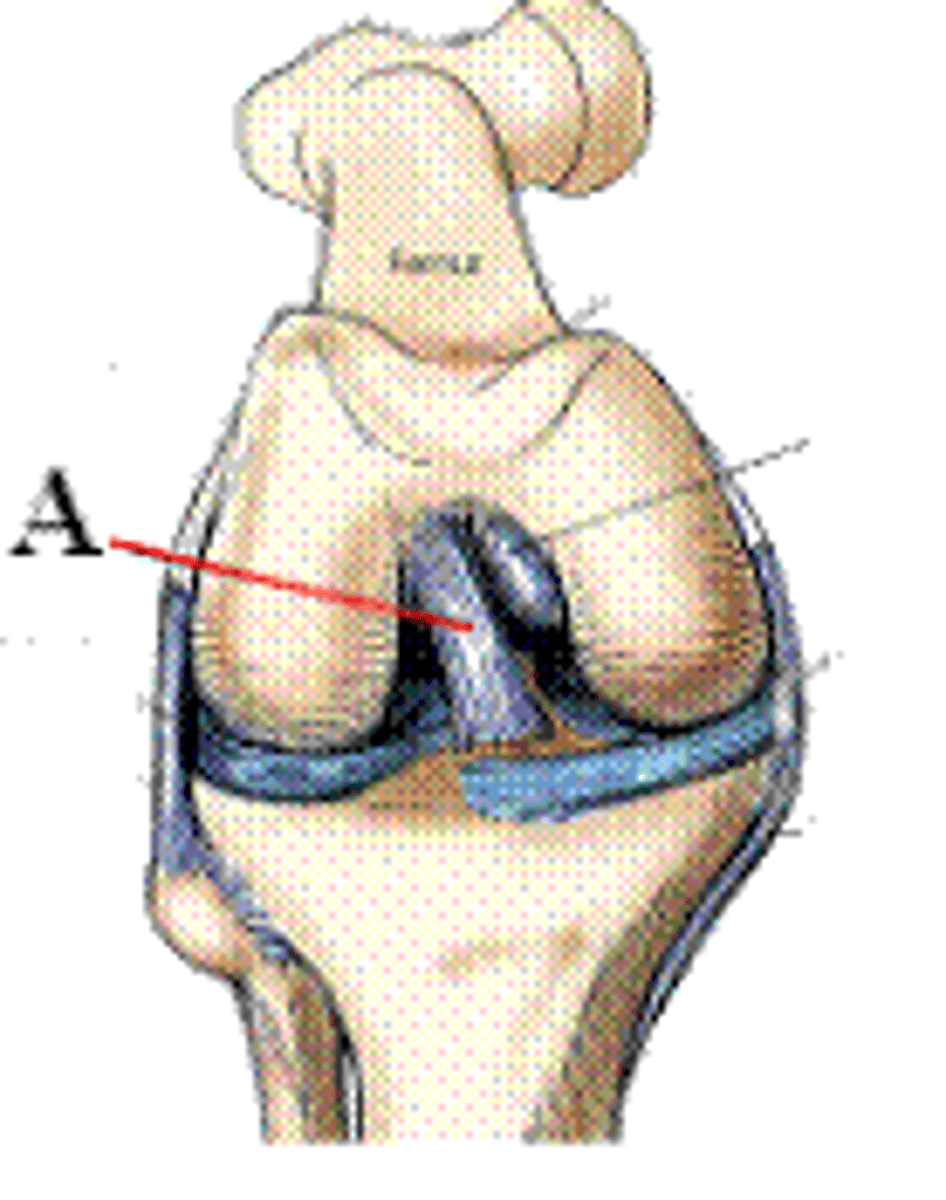
Identify which part of the knee that is labeled A in the figure above.
anterior cruciate ligament