Econ chapter 1-6
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Optimal choice:
maximizes benefit minus cost
What happens when MB > MC:
What happens when MB = MC:
MB > MC: consumption increases
MB = MC: allocative efficiency
Allocative efficiency means that ________ cannot be produced without giving up ________ that provides ________
Allocative efficiency means that more of one good cannot be produced without giving up some other good that provides greater benefit
When demand is elastic and price increases, what happens to revenue?
revenue decreases
When demand is inelastic and price increases, what happens to revenue?
revenue increases
When demand is unit elastic and price increases, what happens to revenue?
revenue stays the same
The cross (price) elasticity of demand of good A relative to good B is the percentage change in:
Formula:
The cross (price) elasticity of demand of good A relative to good B is the percentage change in quantity demanded for good A per unit of percentage change in the price of good B
Formula:
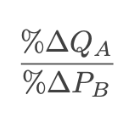
The price elasticity of supply is the percentage change in:
Formula:
The price elasticity of supply is the percentage change in quantity demanded per unit of percentage change in price along the supply curve
Formula:
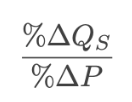
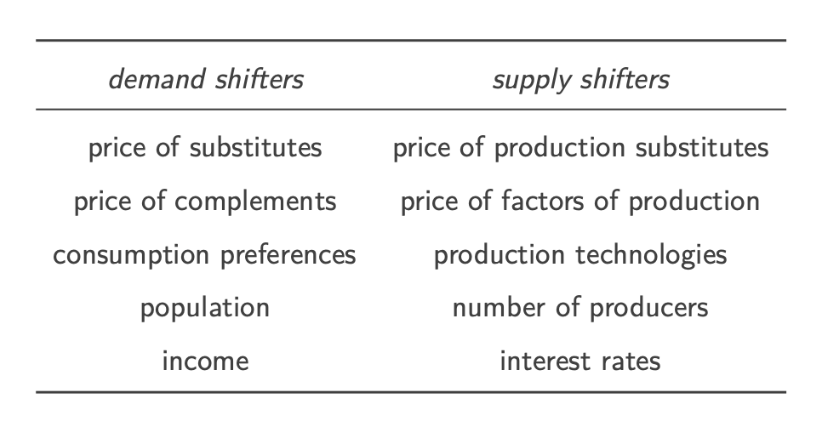
What are the main demand and supply shifters?