Joints (types of joints, word parts, and disorders)
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Articulations (joints)
A place where bones meet. There are 3 types of joints:
Synovial
Fibrous
Cartilaginous
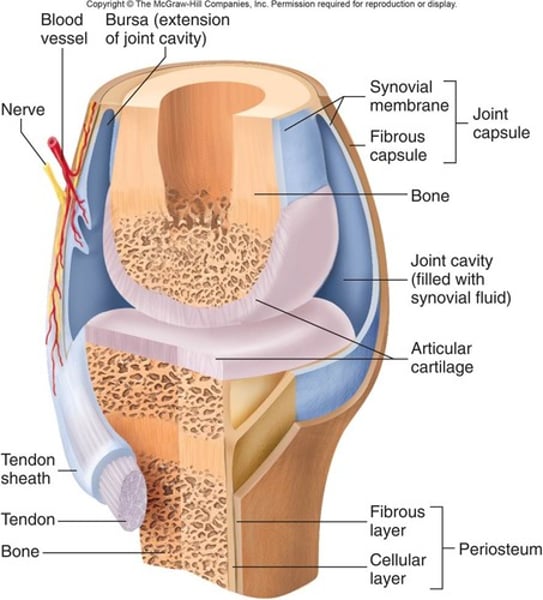
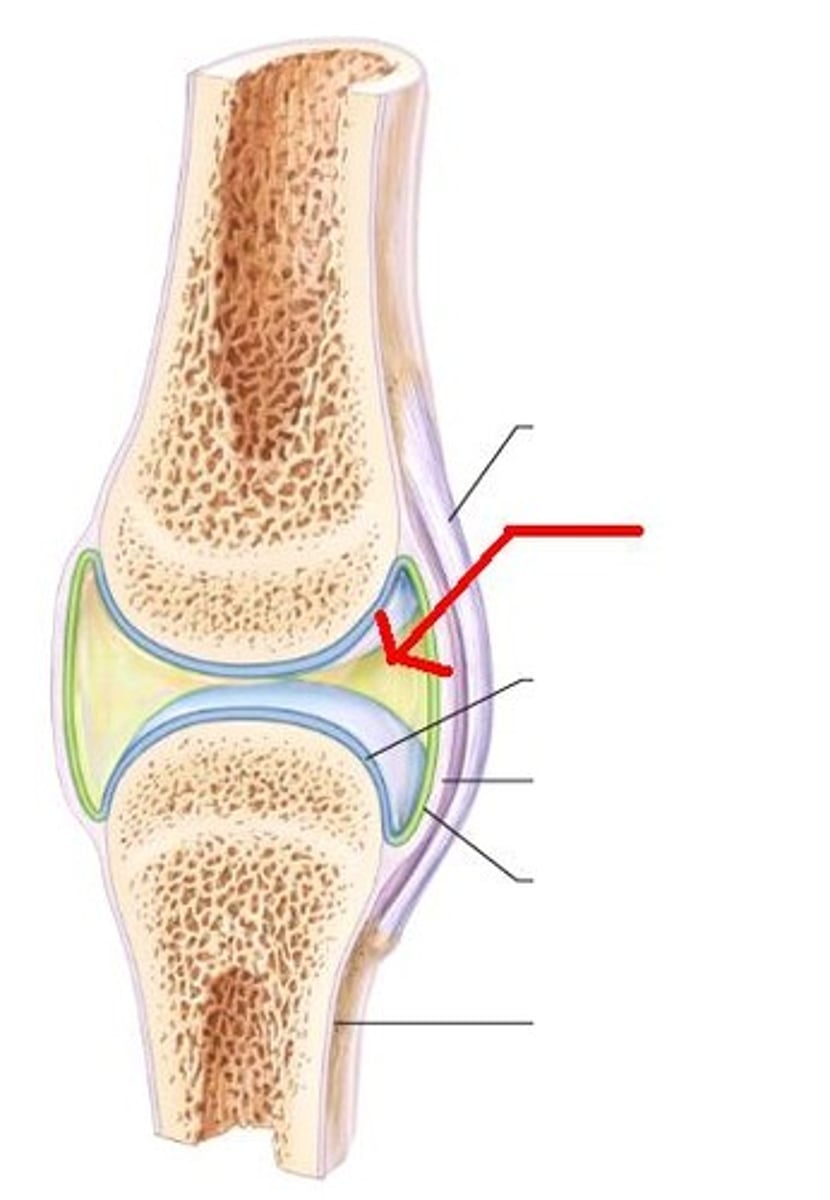
Synovial joint
Moving joints. Separated by the synovial cavity. Freely moveable. All joints are in the limbs.
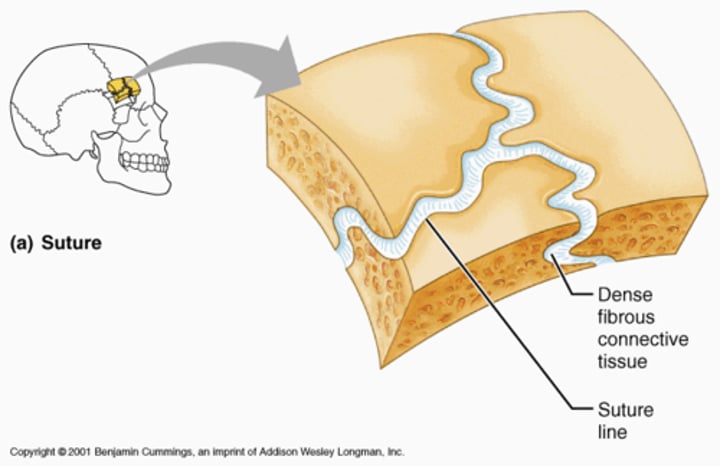
Fibrous joint
Bones held together by fibrous connective tissue. No movement occurs. E.g sutures in the skull
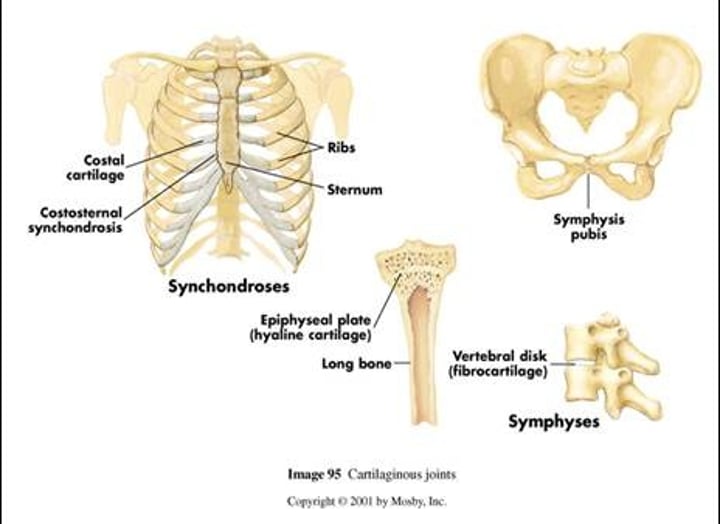
Cartilaginous joint
Bones are connected by cartilage. Slight movement. E.g. Public symphysis, joints between the vertebrae, joint between first rib and sternum
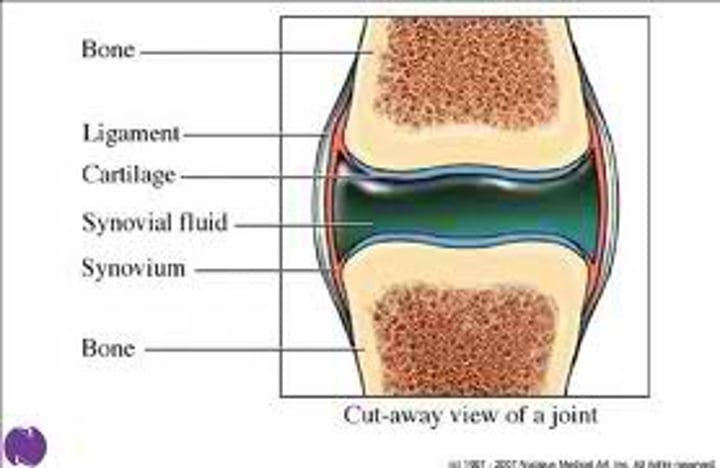
Synovial fluid
The synovial cavity contains synovial fluid which is secreted by the synovial membrane - a connective tissue membrane.
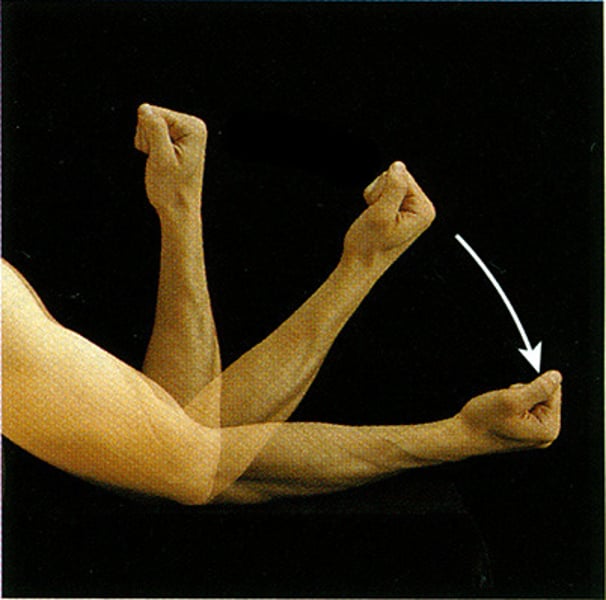
Flexion
Decrease the angle between bones
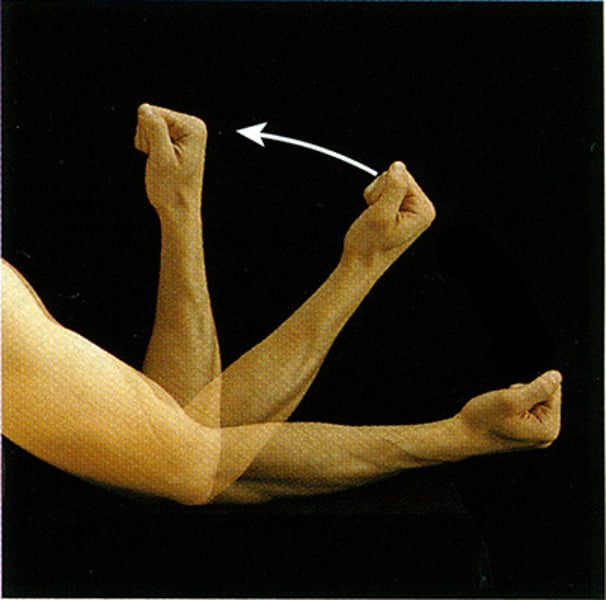
Extension
Increase the angle between the bones
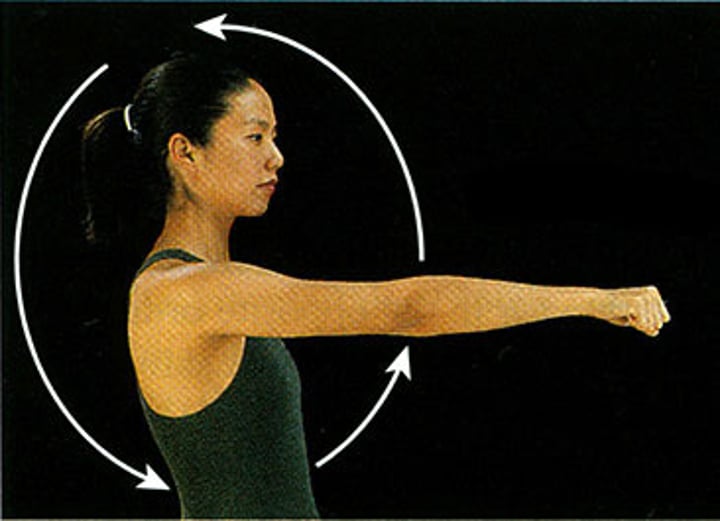
Circumduction
Circular movement at a joint
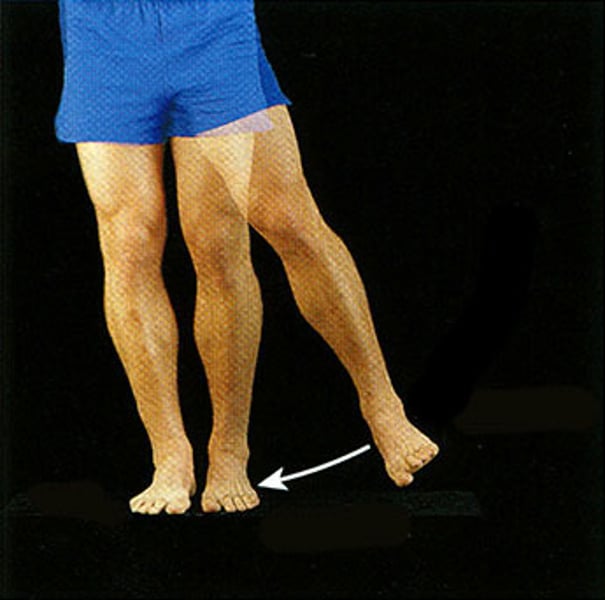
Adduction
Movement.towards the midline
Abduction
Movement away from the midline
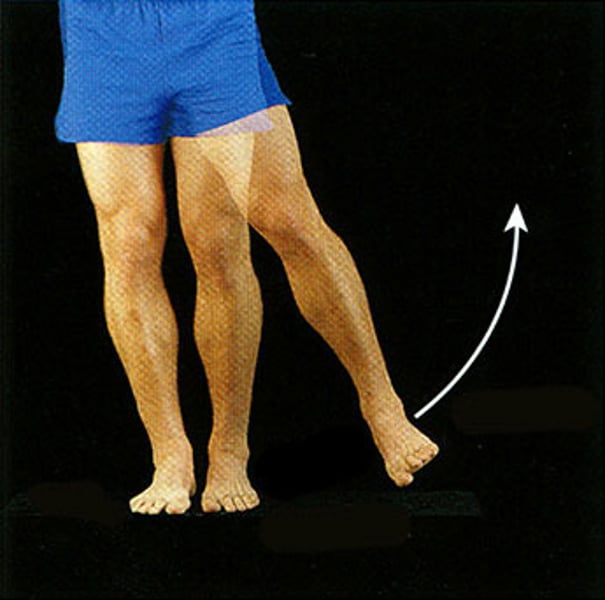
Rotation
Turning a bone on its axis
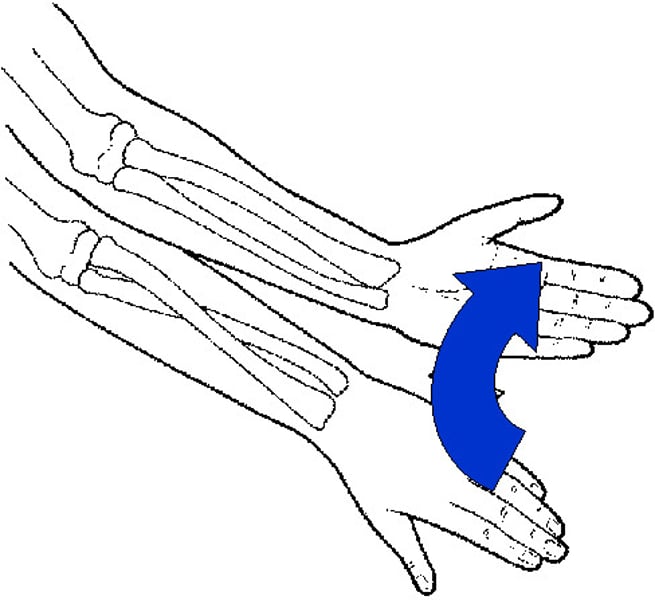
Supination
Turning the hand up or forward
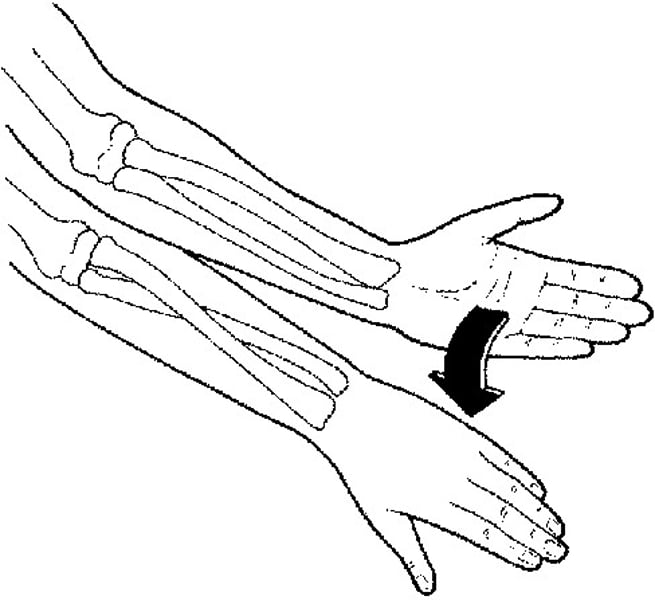
Pronation
Turning the.hand backwards or down
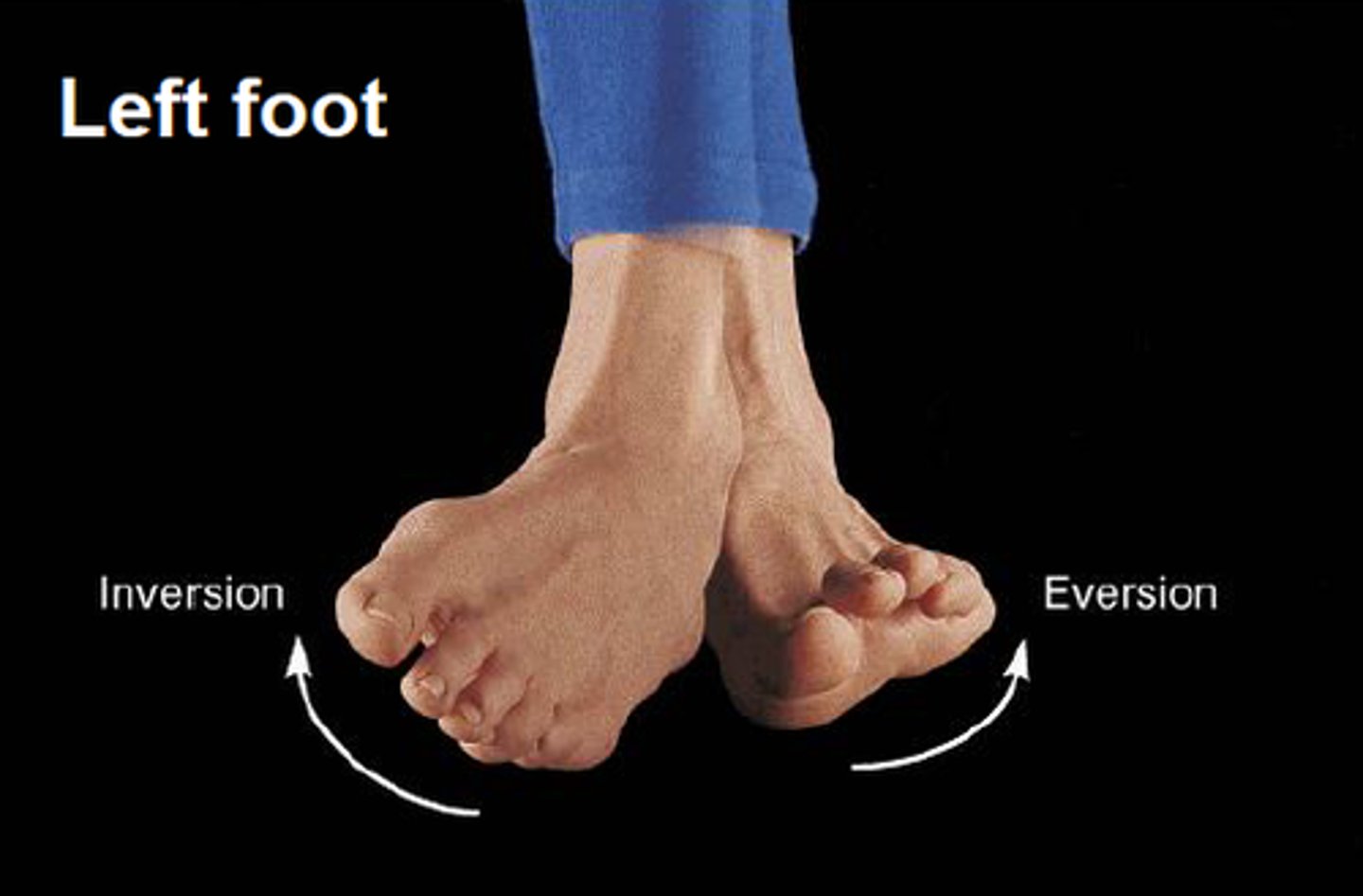
Inversion
Turning the sole of the foot inwards
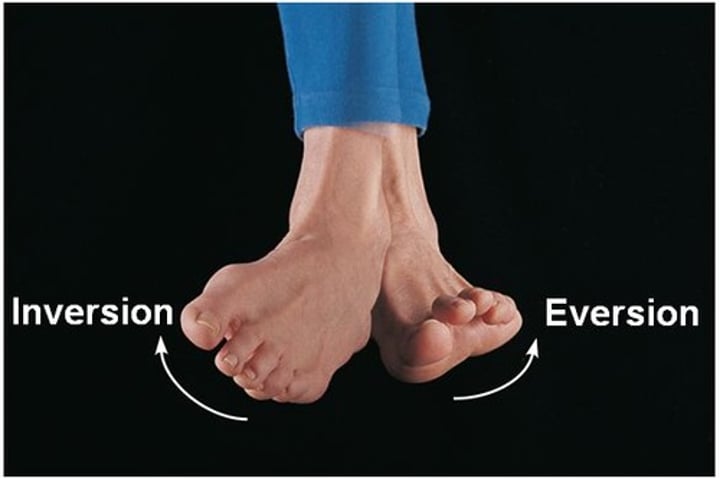
Eversion
Turning the sole of the foot outwards
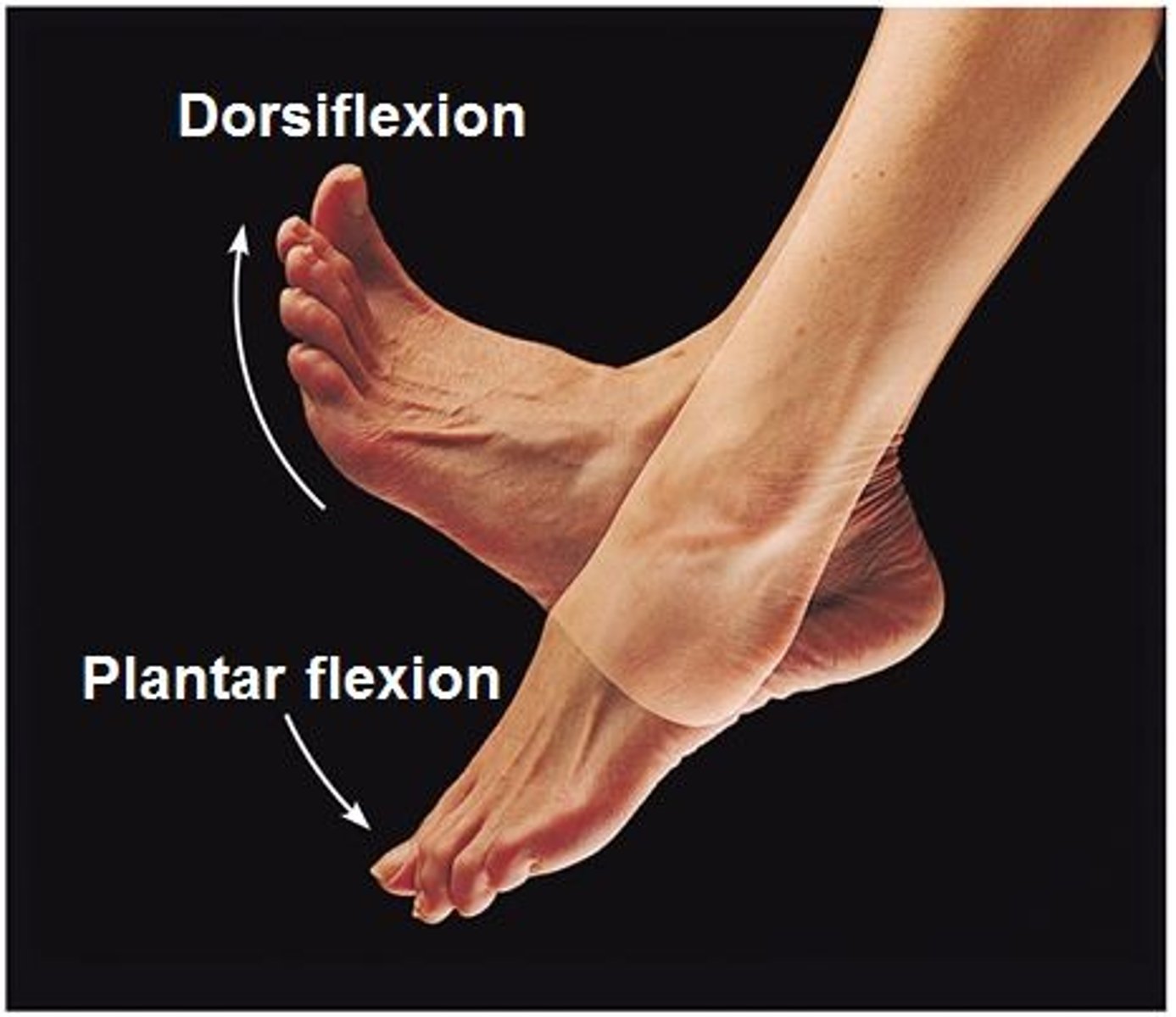
Dorsiflexion
Bending the foot towards the leg e.g. painting the toenails
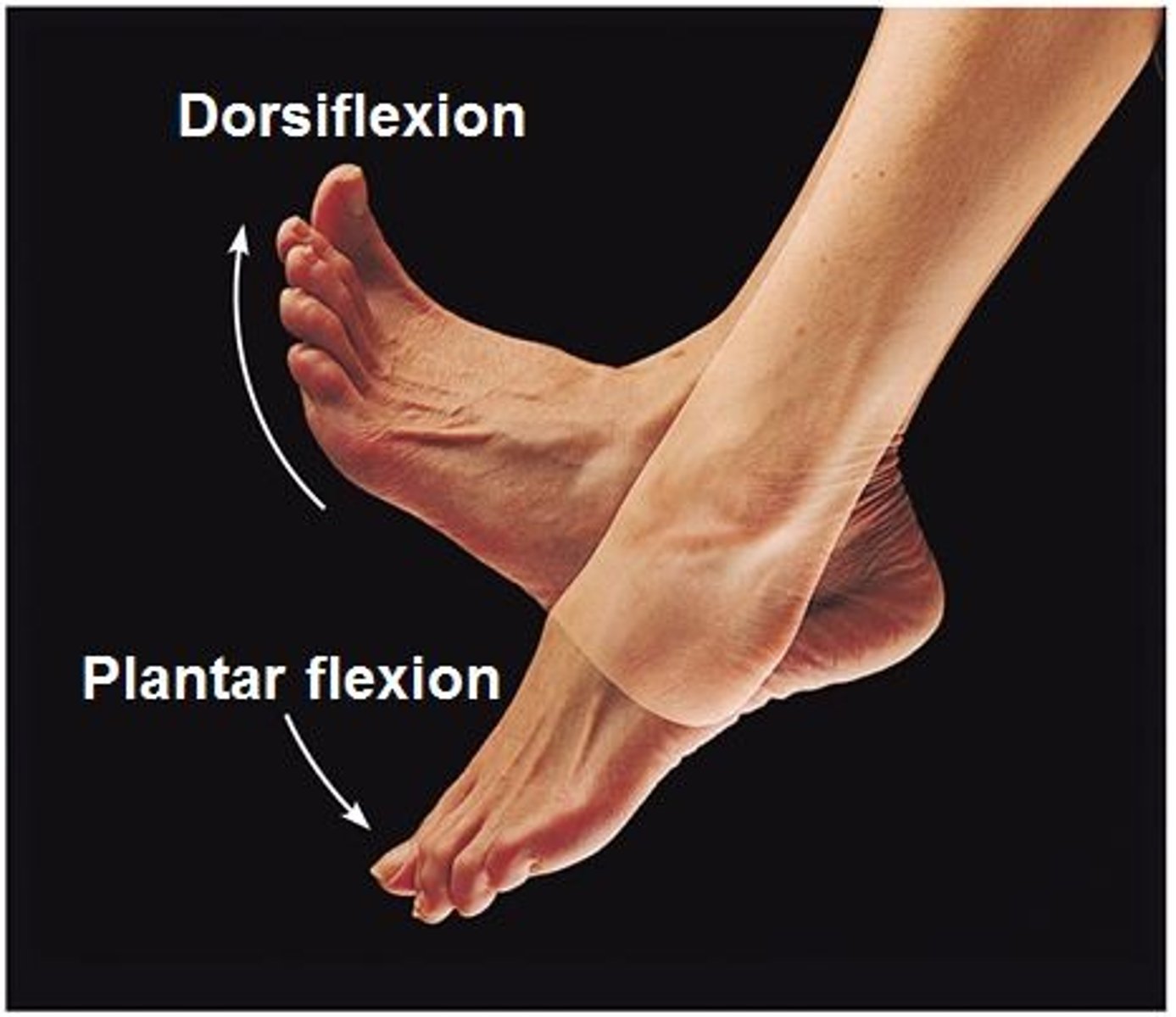
Plantar flexion
Pointing the tow downwards e.g. tip toes
Types of synovial joints
Plane joint
Hinge joint
Pivot joint
Condyloid joint
Saddle joint
Ball and socket joint
Plane joint
Flat articular surfaces. Short slipping or gliding movements. Intercarpal and Intertarsal joints e.g. wrist
Hinge joint
Movement in one plane only ). E.g. Elbow and interphalangeal joints
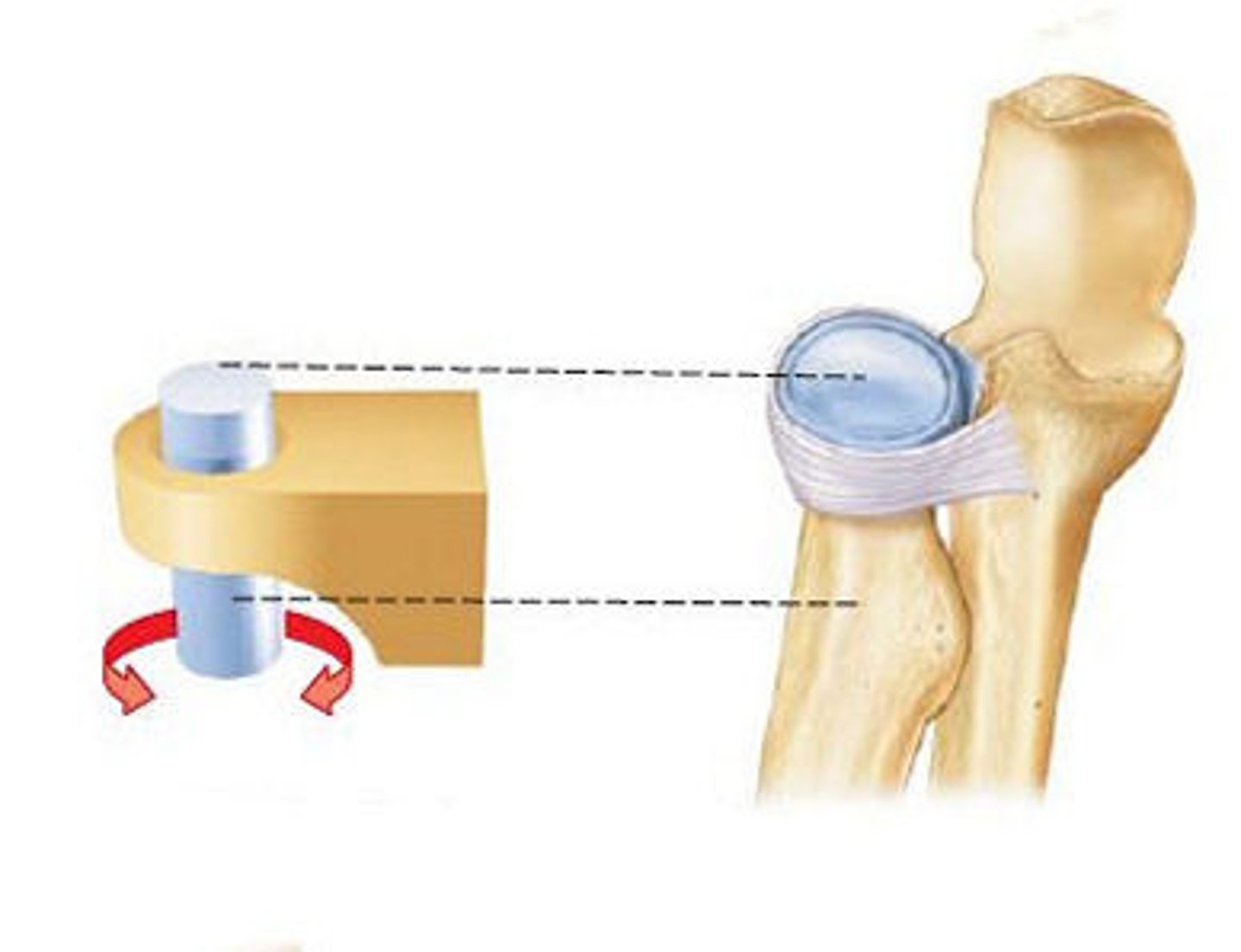
Pivot joint
Rounded end of one bone sits in a sleeve made from ligaments. Rotation around axis. Axis amd atlas, proximal radioulnar joint
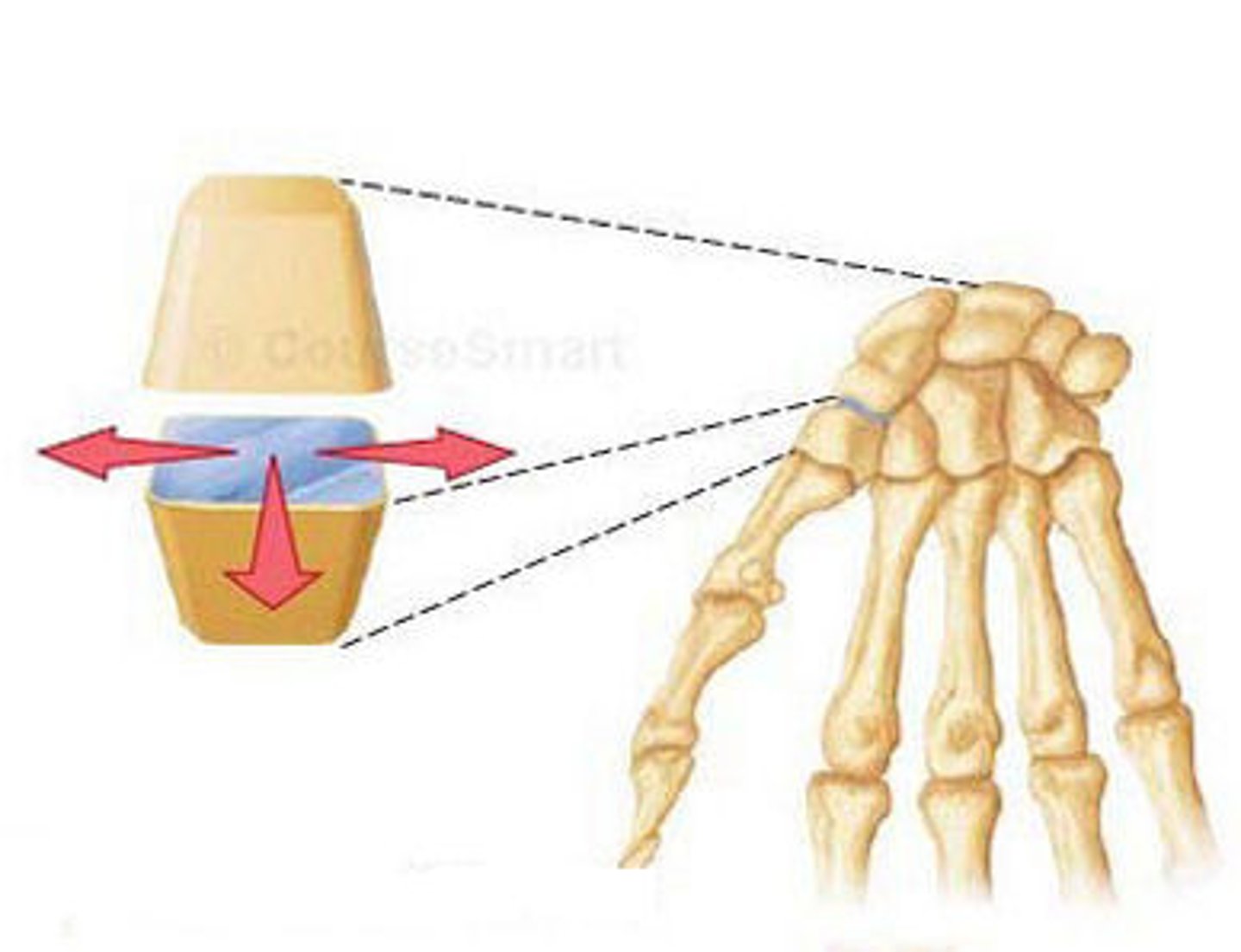
Condyloid joint
Overall surface of one bone sits in a shallow bowl. Movement around 2 axis. E.g. Knuckle joints amd wrist (radiocarpal)
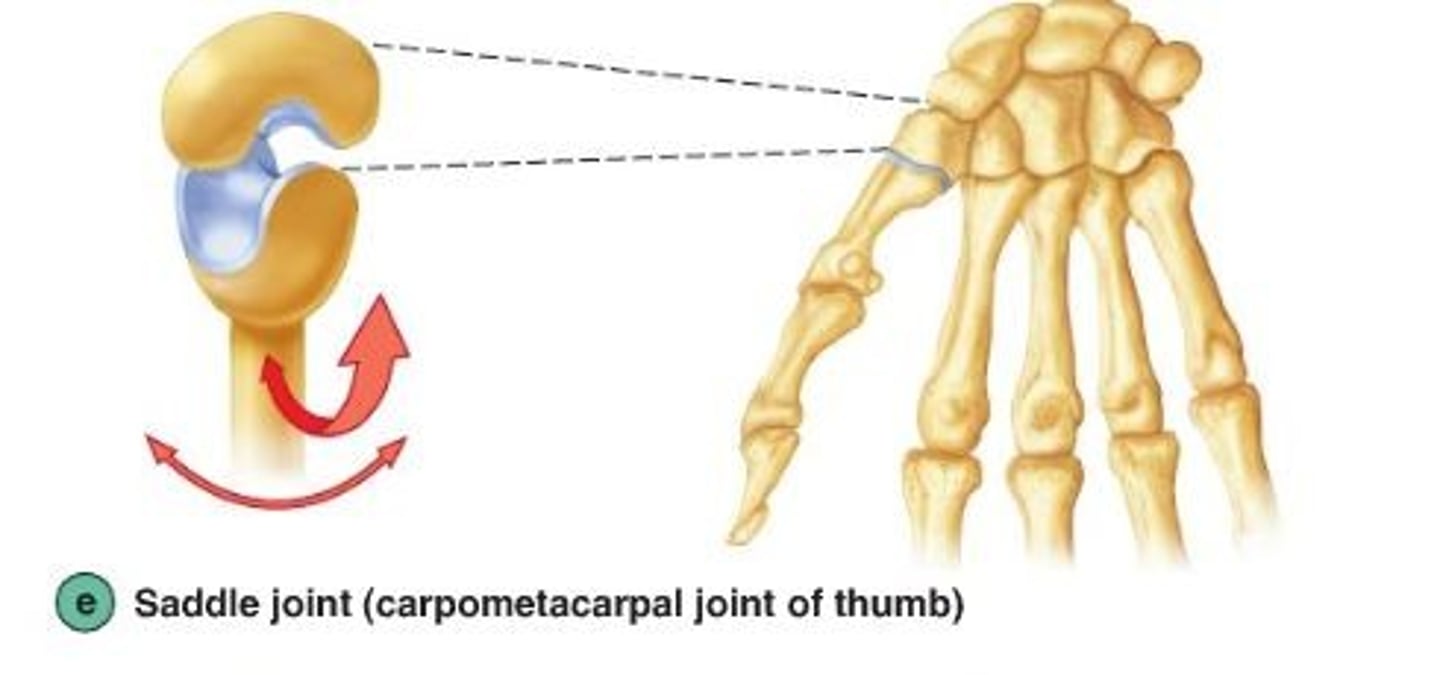
Saddle joint
Surface is saddle shaped. Greater freedom of movement than a condyloid joiny. E.g. Carpometacarpal thumb joint
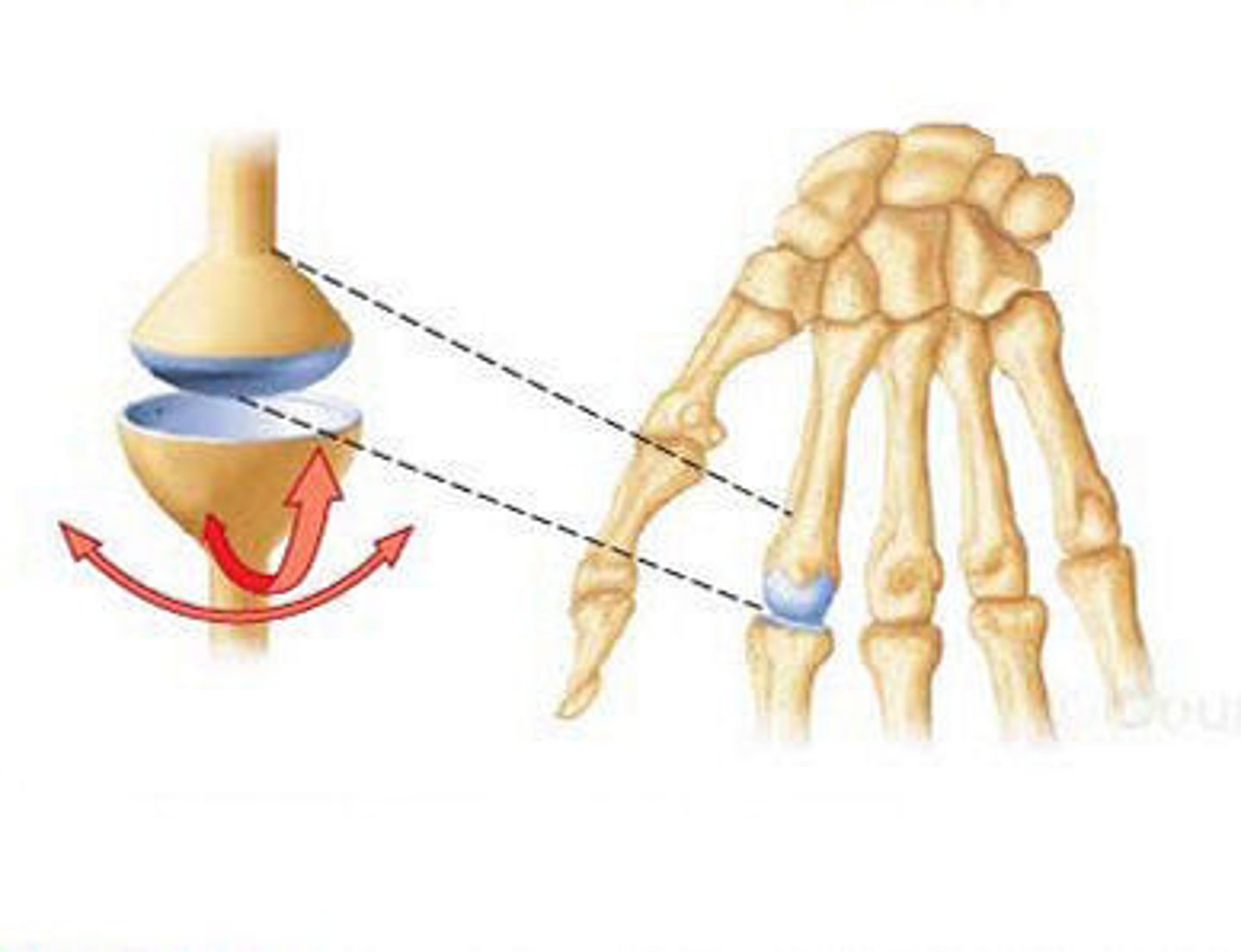
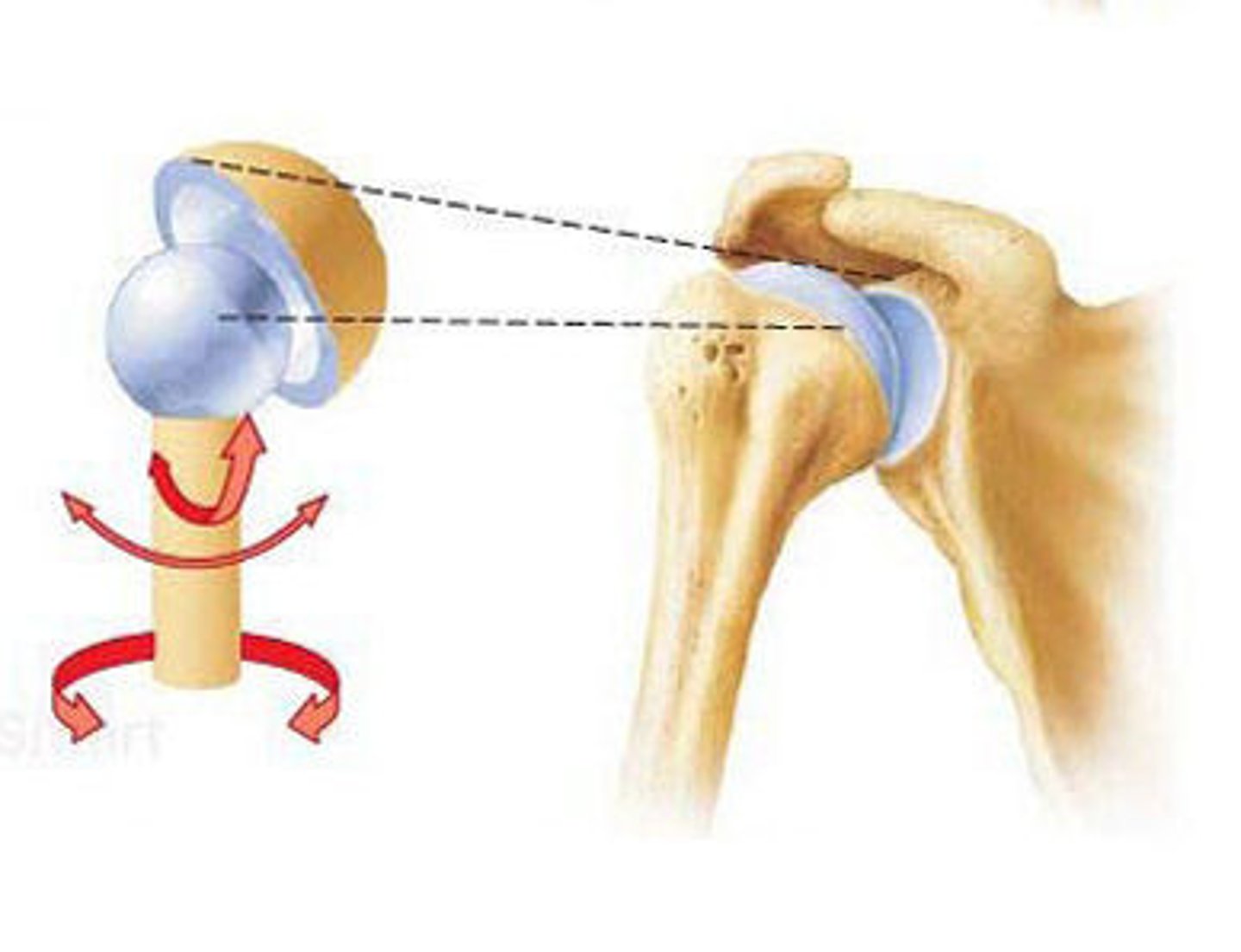
Ball and socket joint
Ball of one bone fits into the cup of another bone. Universal movement. E.g. Hip and shoulder
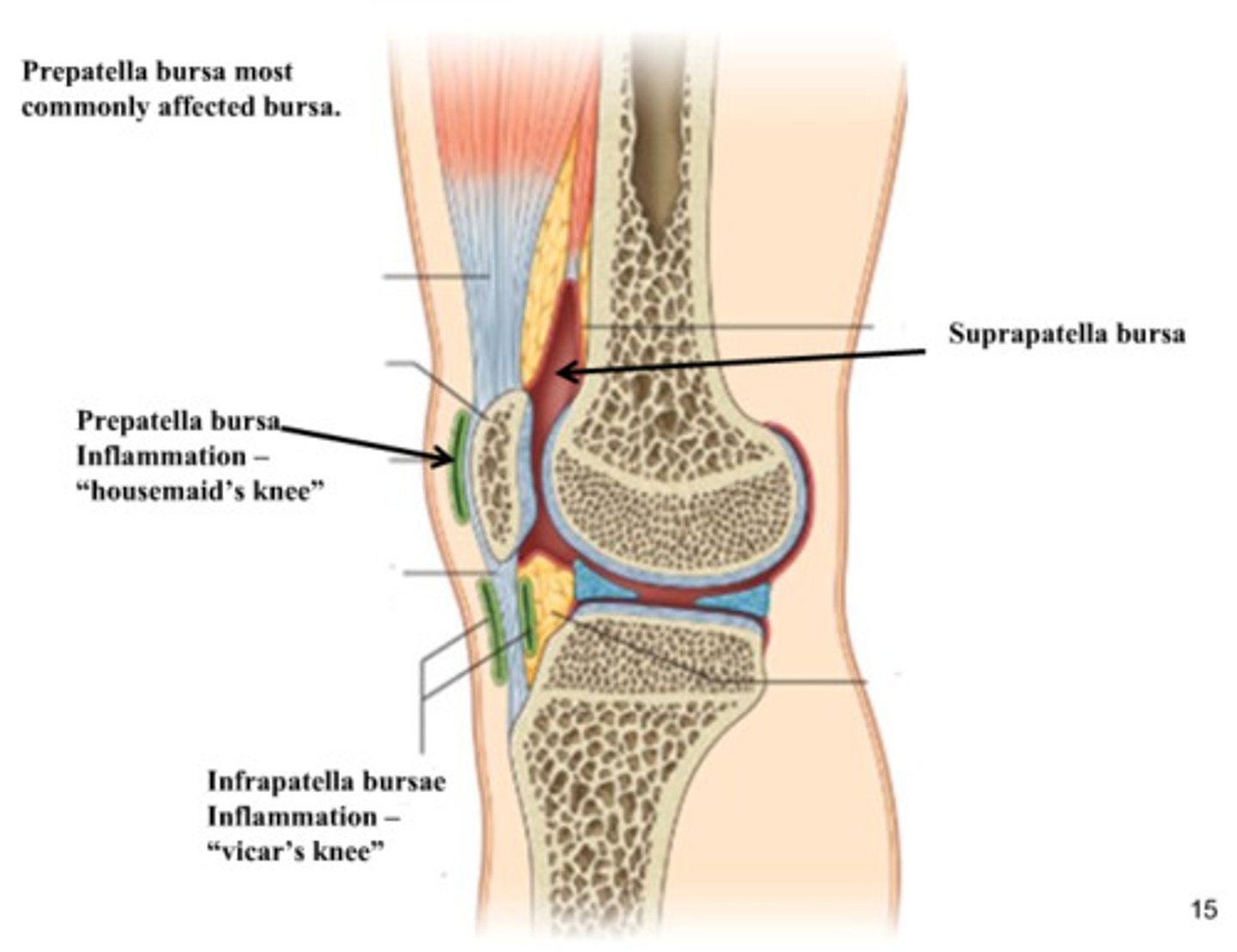
Bursae
A small sac filled with synovial fluid. Found in areas subject to stress. Helps ease movement.
synarthrosis
immovable
amphiarthrosis
slightly movable
Diarthrosis
freely movable
revision surgery
replacement of a worn or failed implant
arthroscopic surgery
a minimally invasive procedure for the treatment of the interior of a joint
ankyl/o
crooked, bent, stiff
-osis, -esis
abnormal condition
-algia
pain, painful condition
-sclerosis (suffix)
abnormal hardening
burs/o
bursa, sac of fluid near joint
-oma
tumor
-malacia
abnormal softening
hem/o
blood, relating to the blood
oste/o
bone
hallux
big toe
valgus
bent outward
-pasty
surgical repair
synov/o
synovial membrane, synovial fluid
Ankylosis
the loss, or absence, of mobility in a joint due to disease, injury, or a surgical procedure
arthralgia
pain in a joint or joints
arthrosclerosis
stiffness of the joints, especially in the elderly
chronrdroma
slow-growing benign tumor derived from cartilage cells
chondramalacia
abnormal softening of cartilage
hallux valgus (bunion)
abnormal enlargement of the joint at the base of the great toe
hemarthrosis
blood within a joint
synovitis
inflammation of synovial membrane
dislocation (luxation)
the total displacement of a bone from its joint
subluxation
partial dislocation of a joint
arthritis
inflammation of a joint
osteoarthritis (OA)
normal wear and tear of the joints
rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
crippling, autoimmune disorder , attack the synovial membrane they become inflamed and thickened so that the joints are increasingly swollen and immobile
gouty arthritis (gout)
disease where uric acid accumulates in the blood and is deposited as needle sharp like crystal in the soft tissues of the joint
movement of fibrous joints
synarthroses (immovable)
movement of cartilaginous joints
amphiarthroses (slightly movable)
movement of synovial joints
diarthroses (freely moveable)